Healing & Repair
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Regeneration can be seen in what 3 renewing tissues
Epidermis
GI tract epithelium
Haematopoietic system
Regeneration can be seen in what 2 stable tissues
Liver & kidneys
What are the 3 cell types based on regenerative capacity/cell cycle
1) Continuously dividing / Labile cells
2) Stable or quiescent cells
3) Permanent (non-dividing ) cells
Describe & give examples of Labile cells
Constantly replacing dying cells
E.g. Epithelia: skin, oral cavity, exocrine ducts, GI tract & gynecological surfaces and Haematopoietic cells
Describe & give examples of Stable/Quiescent cells (what cell cycle stage are they in)
Usually in G0 but driven into G1 → rapid proliferation
E.g. parenchyma of glands: Liver, kidney & pancreas, and endothelium, fibroblast & smooth muscle connective tissue.
Describe & give examples of Permanent (non-dividing ) cells (what cell cycle stage are they in)
Permanently removed from cell cycle
Irreversible injury leads only to scar
E.g. Nerve cells, myocardium (heart)
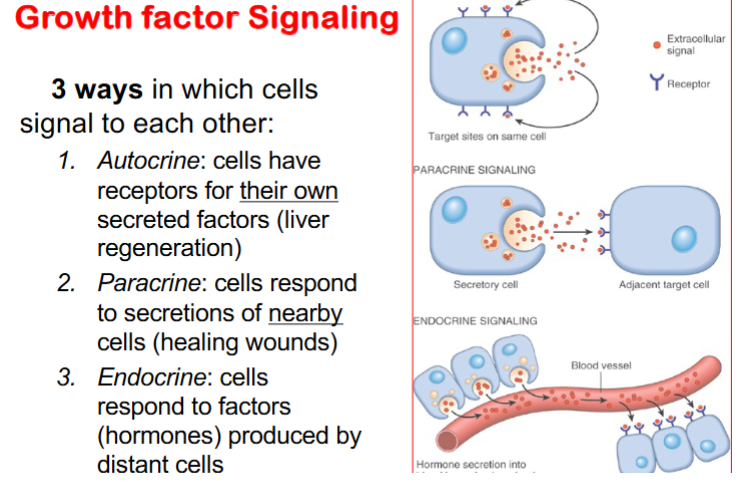
Describe the 3 ways in which cells signal to each other
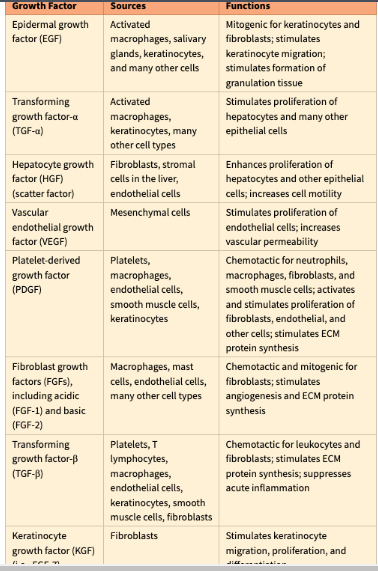
Give 5 examples of growth factors
• Epidermal growth factor (EGF)
• Fibroblast growth factors
• Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
• Transforming growth factor (TGF)
• Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Which growth factor is involved in monocyte chemotaxis
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Which growth factor is involved in epithelial cells & fibroblasts
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)
Which growth factor is involved in fibrogenesis
Transforming growth factor (TGF)
Which growth factor is involved in Migration and proliferation of fibroblasts
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Which growth factor is involved in smooth muscle
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)

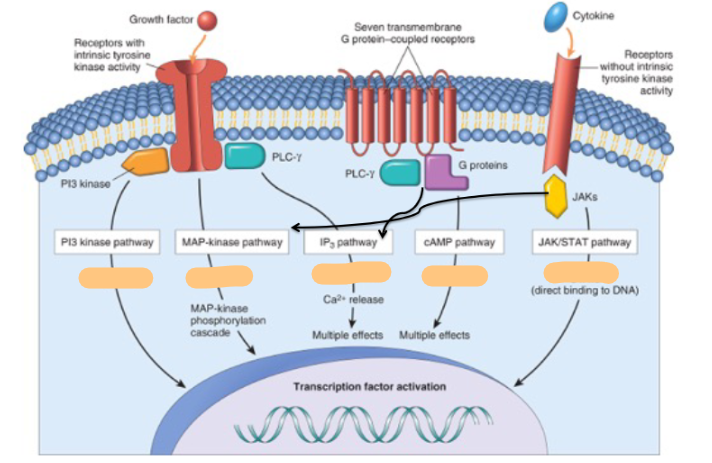
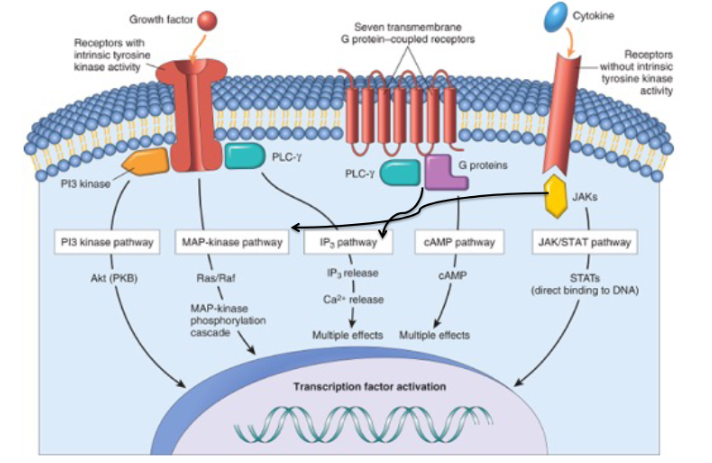
Steroid hormone receptors are ______ activated
ligand
True/False some eicosanoids signal through steroid receptors
True
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) function
ECM provides turgor, rigidity, support, adhesion substrate, reservoir for factors
ECM must remain intact for ______ healing
parenchymal healing
What are the 2 basic forms of ECM
Interstitial matrix & basement membrane
What 4 components make up Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Collagens
Adhesive glycoproteins/Cell adhesion Molecules
Proteoglycans
Elastin
Role of Collagens in ECM
fibrous structural proteins
Which of these types of collagen are (i) interstitial/fibrillar or (ii) non-fibrillar mesh-like in basement membranes:
I-V & XI
III, V, XI: interstitial/fibrillar
IV: non-fibrillar mesh-like in basement membranes
Which form of collagen is more abundant: interstitial/fibrillar or non-fibrillar mesh-like
interstitial/fibrillar
What is the role of of Adhesive glycoproteins/Cell adhesion Molecules in the ECM
Bind ECM components to each other, and to other cells
Give some examples of Adhesive glycoproteins/Cell adhesion Molecules in the ECM
Laminin, fibronectin, thrombospondin, integrins
What are proteoglycans in ECM & what’s their role
sugars linked to proteins; form highly hydrated compressible gels (cartilage in joints)
Role of elastin in ECM
Elastic fibres allows tissue to recoil and return to normal after physical stress
Structure of elastin in ECM
Central core of elastin protein surrounded by meshlike fibrillin (glycoprotein)
What steps of Repair by Connective Tissue (Scar Formation) occur in the first 24 hrs
Formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis)
Fibroblast migration and proliferation (lay down collagen)
What steps of Repair by Connective Tissue (Scar Formation) occur in days 3-5
Deposition of loose ECM- “Granulation tissue”: pink, soft, granular gross appearance
What steps of Repair by Connective Tissue (Scar Formation) occur after 5 days
Maturation and organization (remodeling) of fibrous tissue
In Angiogenesis, what are vessels derived from
budding of pre-existing vessels
Describe the 5 steps of Angiogenesis
– Proteolytic degradation of parent vessel BM
– Endothelial migration
– Endothelial proliferation
– Cell recruitment (pericytes and smooth muscle) to stabilise the new endothelial tube
– Endothelial maturation
What growth factors are involved in angiogenesis
VEGF
FGF
ANgiopoietins
PDGF
TGF- β
Role of VEGF in angiogenesis
Promotes migration and proliferation of endothelial cells.
Stimulates vasodilation by increasing NO.
Role of FGF in angiogenesis
Induces proliferation of fibroblasts/endothelial cells and migration of macrophages and fibroblasts
Role of angiopoietins in angiogenesis (which angiopoietins)
Ang1 & 2 → maturation of the new vessels by recruitment of pericytes and smooth muscle cells
Role of PDGF in angiogenesis
Recruits SM cells
Role of TGF- β in angiogenesis
suppresses endothelial proliferation
enhances production of ECM protein
Role of ECM proteins in angiogenesis
Interact with integrins on endothelial cells and provide scaffold for endothelial growth. Matrix metalloproteinases degrade ECM to permit remodelling and extension of the new tube
Fibrosis (Fibroplasia) occurs where? Within what framework?
Occurs within the granulation tissue framework (new blood vessels and loose ECM)
2 steps of Fibrosis (Fibroplasia)
1) Migration and proliferation of fibroblasts into the site of injury
2) Deposition of ECM produced by these cells
In step 1 of Fibrosis, what 2 things help this stage out
– Growth factors (TGF-b, PDGF, FGF)
– Cytokines (IL-1, TNF-a)
What is the purpose of the remodelling phase of tissue repair
To strengthen the repaired tissue by reorganising and modifying the extracellular matrix after initial healing
Which enzymes are responsible for extracellular matrix breakdown during remodeling
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
Name the main types of metalloproteinases involved in tissue remodeling
Interstitial collagenases
Gelatinases
Stromelysins
Which cells produce metalloproteinases during remodeling
Macrophages, neutrophils, and fibroblasts
In what form are metalloproteinases initially produced
As inactive precursors (proenzymes)
What regulates the activity of metalloproteinases
Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs).
What happens to cellular debris during the remodeling phase
It is removed by phagocytes in a process called debridement
What happens in the 1st 1-2 days of 1st intention wound healing
epithelial basal cells grow along cut dermis
What happens @ day 3 of 1st intention wound healing
neutrophils gone, macrophages enter, granulation tissue forms
What happens @ day 5 of 1st intention wound healing
space filled with granulation tissue and collagen fibrils bridge line of closure, epidermis at pre-incision thickness
What happens @ week 2 of 1st intention wound healing
accumulation of collagen, fibroblasts, and “blanching” begins (edema inflammation vascularity reduced)
What happens @ month1 of 1st intention wound healing
connective tissue devoid of inflammation; epidermis intact
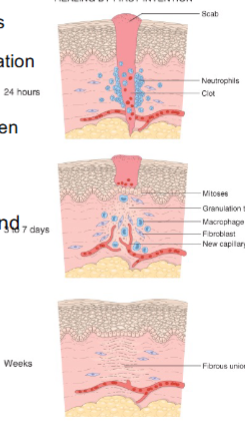
Tensile strength increases to ____% of unwounded skin in 3 months
70 - 80%
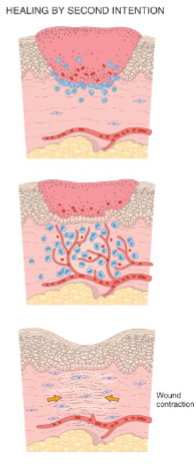
What differentiates 1st intention & 2nd intention wound healing
2nd intention is for a Large tissue defect with more intense inflammation, granulation (leads to scar) & wound contraction
For 2nd intention, regeneration of parenchymal cells alone cannot restore the tissue
5 local factors that influence repair
" Infection
" Mechanical factors
" Foreign bodies
" Size
" Location
5 general factors that influence repair
" Nutrition
" Diabetes mellitus
" Circulatory status (atherosclerosis)
" Steroid treatment
" Hydrogen Peroxide treatment
Name 2 things that can arise from deficient repair
Wound dehiscence (rupture)
Ulceration
Give example of when Wound dehiscence (rupture) could happen
often after abdominal surgery
Give example of how ulceration could happen
Poor vascularization or neuropathy (e.g.,diabetic foot)
Name 4 things that could arise from excessive repair
• Hypertrophic scars – raised, confined to injury site
• Keloids – raised scars extending beyond wound
• Exuberant granulation (proud flesh) – blocks epithelialization; needs removal
• Desmoids (aggressive fibromatoses) – rare, fibroblast proliferation with recurrence
Which of the 4 excessive repair scars can you be genetically predisposed to
Keloids
What type of injury could lead to exaggerated contraction
After severe burns