Unit 2: Networks of Exchange
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
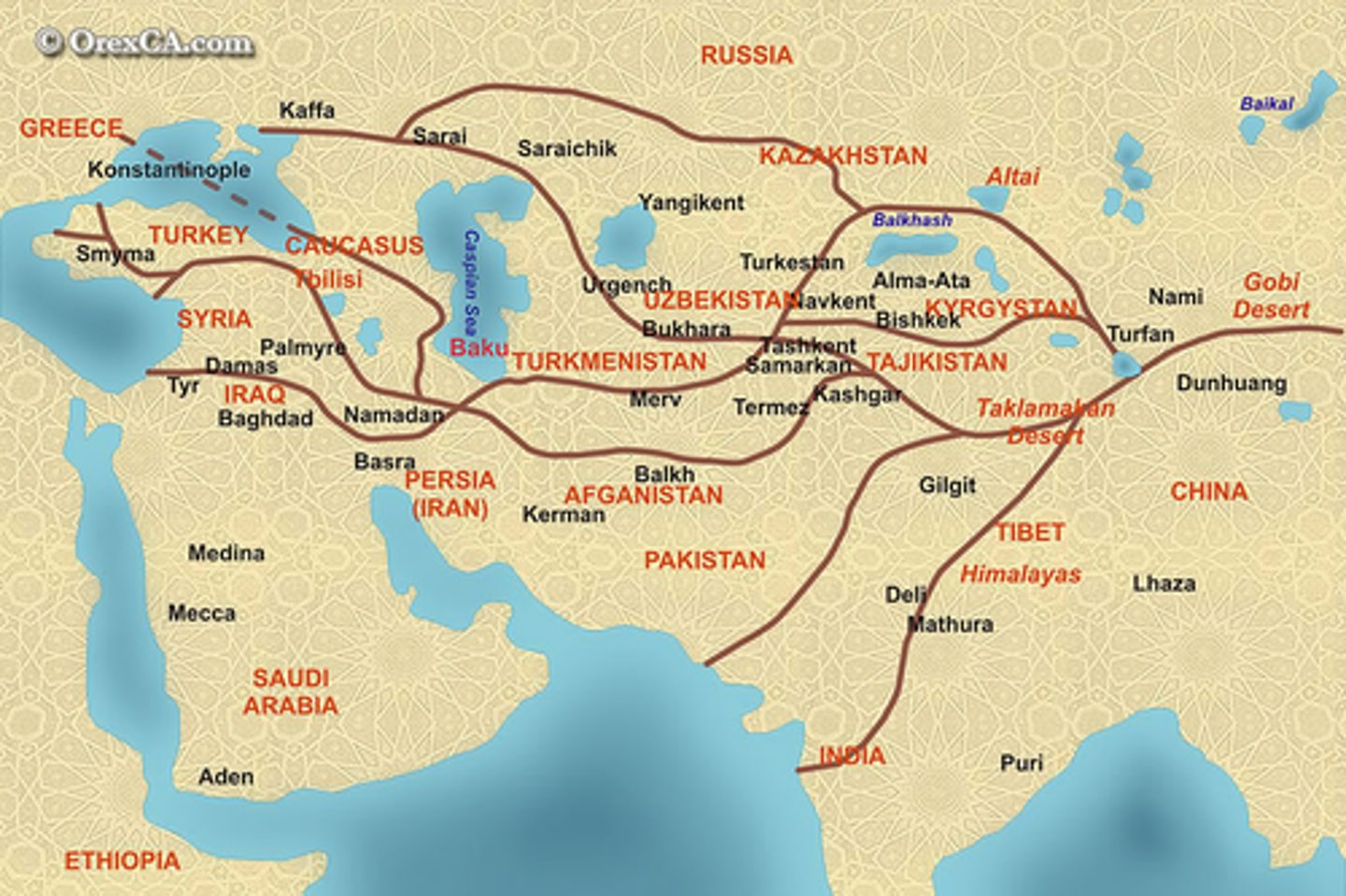
Silk Roads
A system of ancient caravan routes across Central Asia, along which traders carried silk and other trade goods; known for spreading religions such as Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam as well as technological transfers and diseases like the Bubonic plague
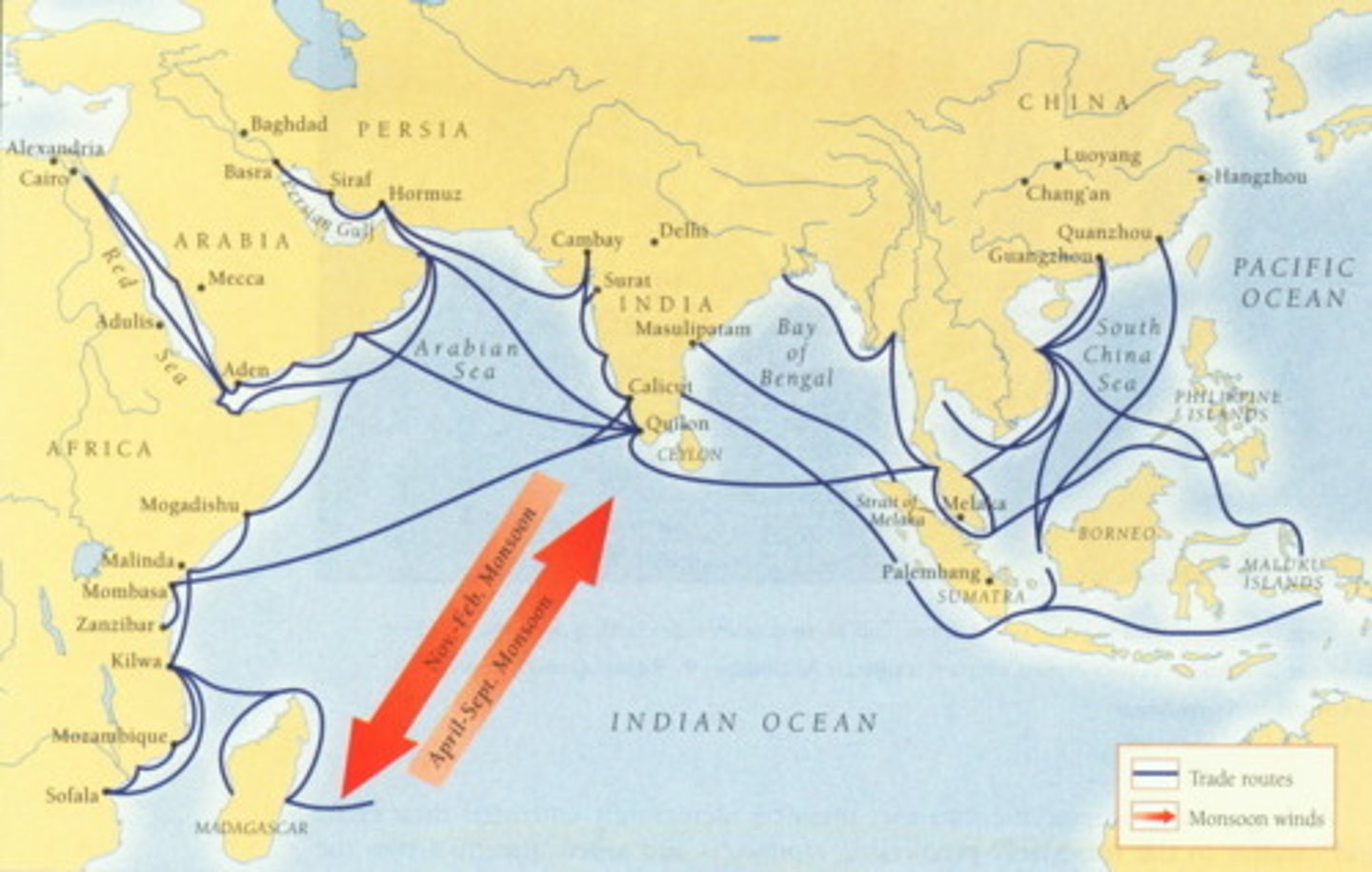
Indian Ocean Trade
connected to Europe, Africa, South Asia, and China.; worlds richest maritime trading network and an area of rapid Muslim expansion, spread of goods, ideas
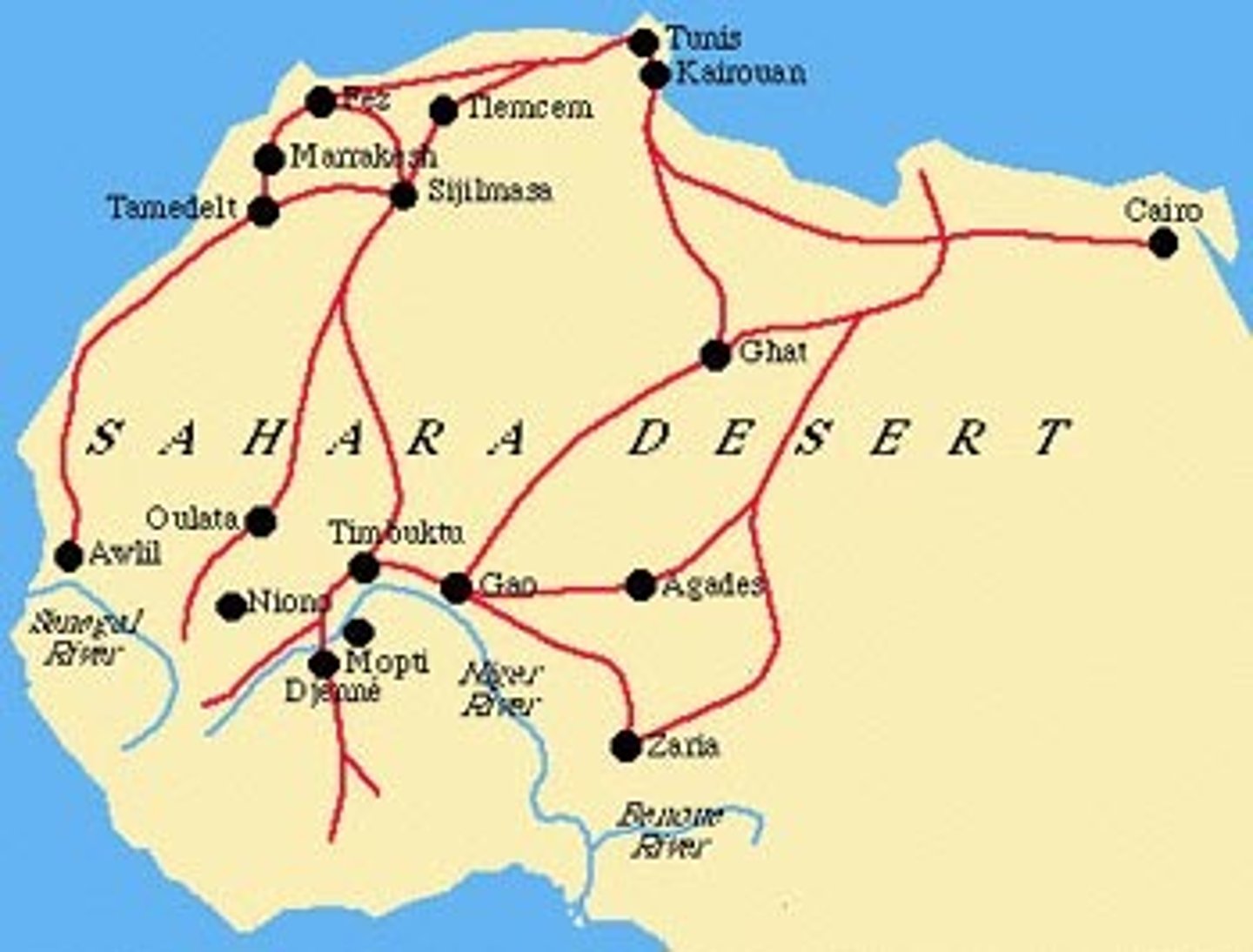
Trans-Saharan Trade
route across the Sahara Desert; traded for gold and salt, created caravan routes, economic benefit for controlling dessert, camels and camel saddles were crucial in the development of these trade networks; facilitated the spread of Islam
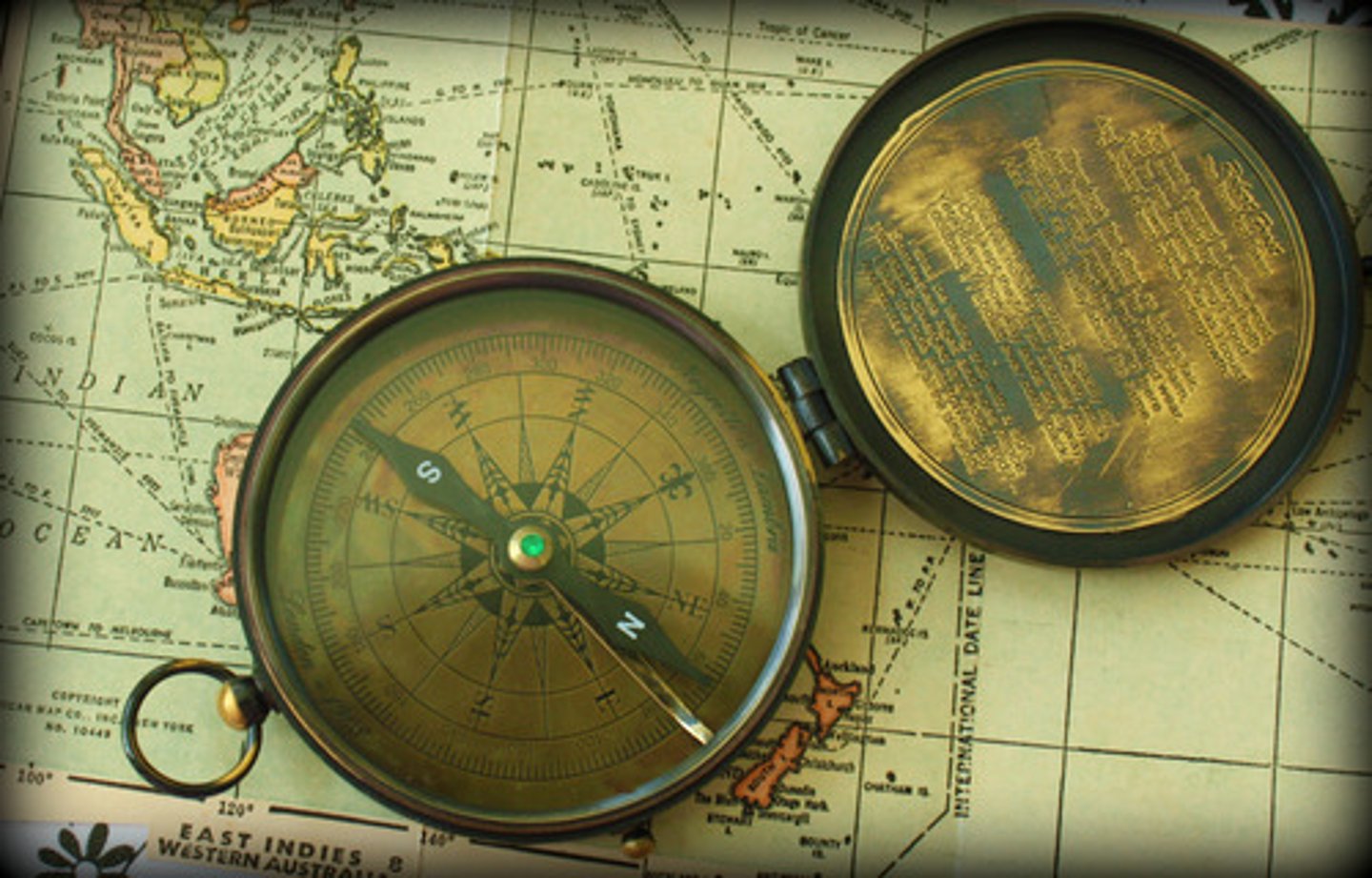
magnetic compass
Chinese invention that aided navigation by showing which direction was north

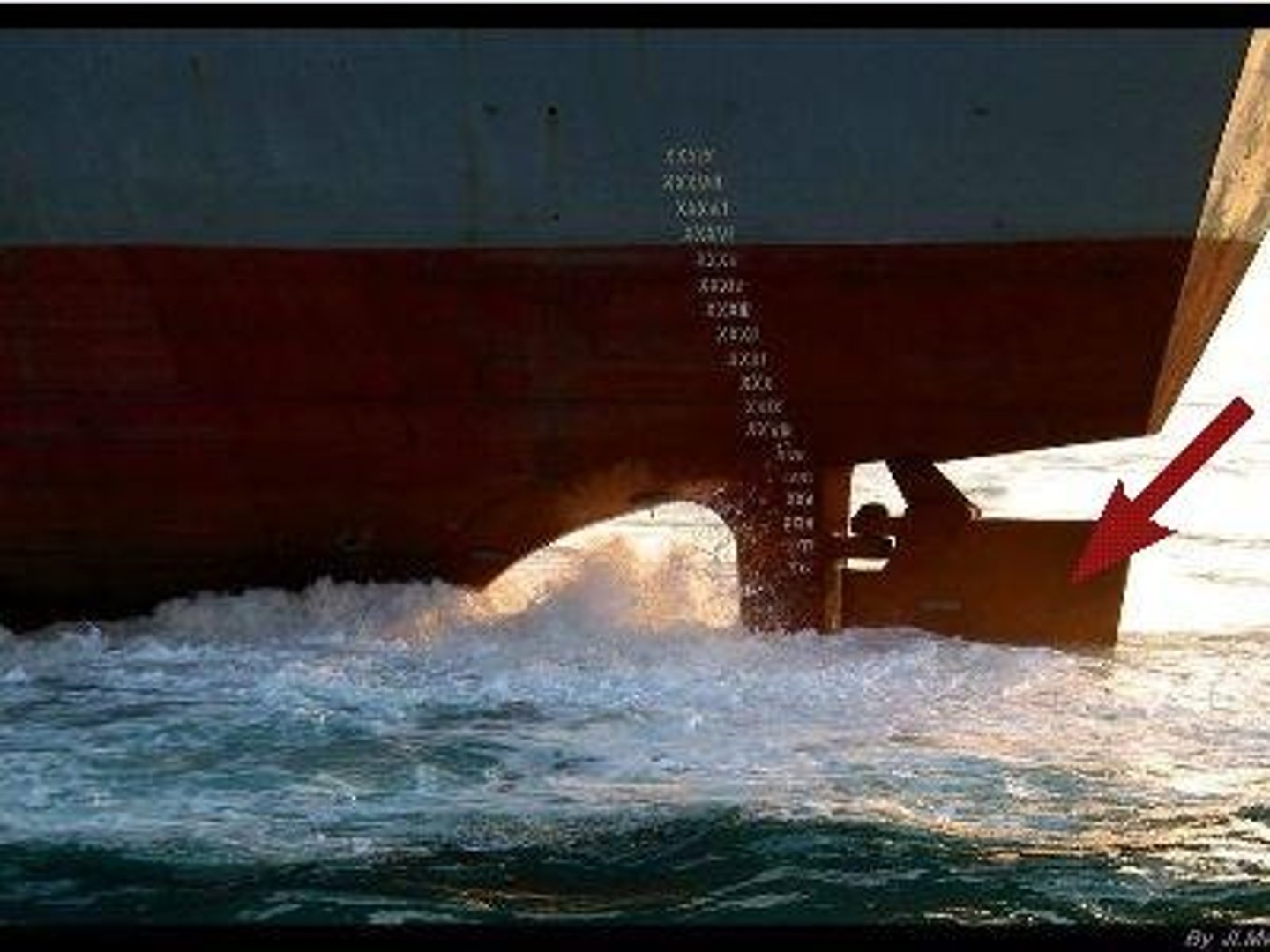
rudder
Steering device, usually a vertical blade attached to a post at, or near, the stern of the boat; improved sea trade

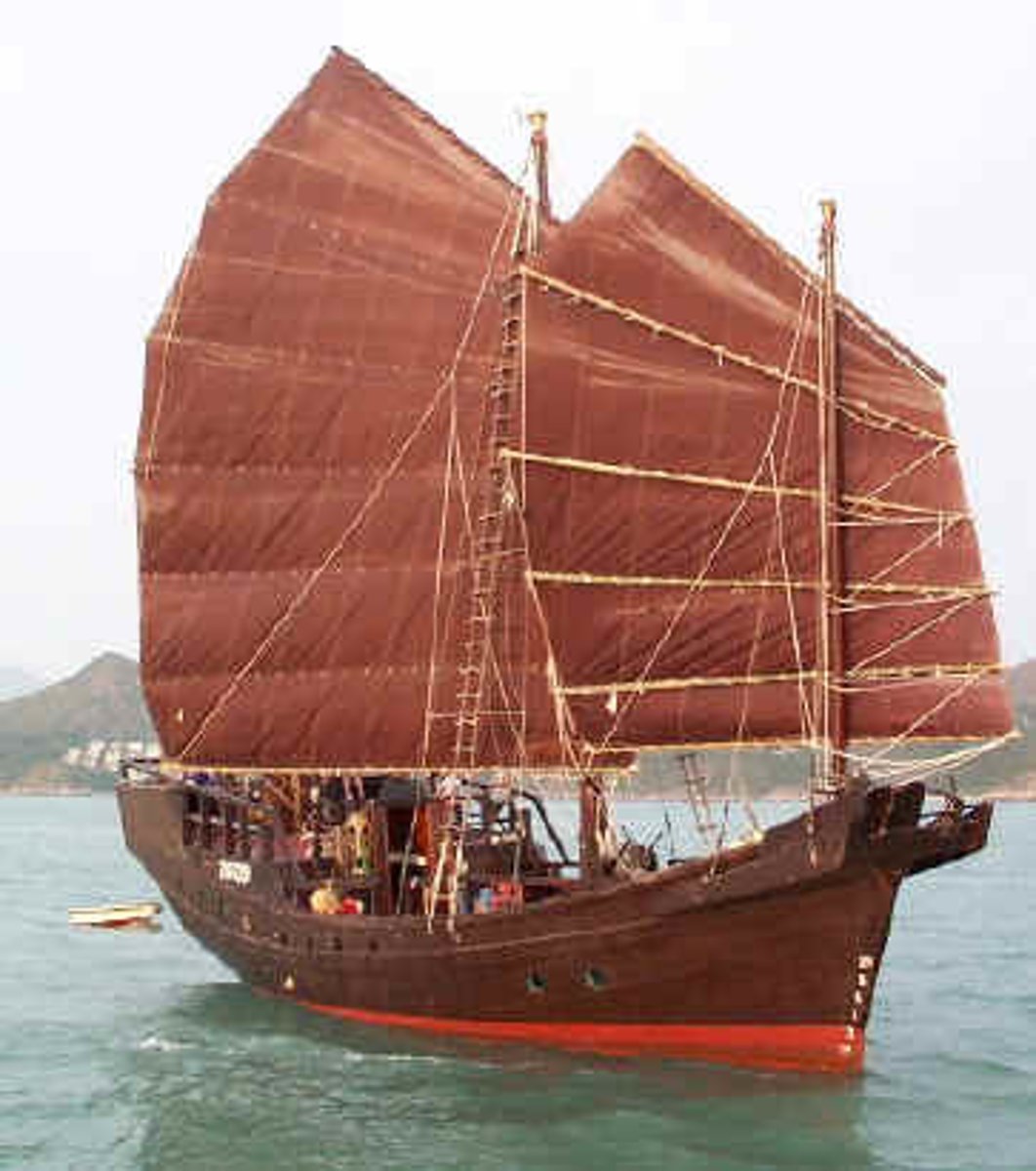
junk ship
A very large flat-bottom sailing ship produced in the Tang and Song Empires, specially designed for long-distance commercial travel and participation in the tribute system

Kashgar
Also known as Kashi, a central trading point at which the western and the eastern Silk Road met; It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with modern day Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, and Tajikistan.
Samarkand
During the rule of Timur Lane was the most influential capital city, a wealthy trading center known for decorated mosques and tombs; a key trading city along the Silk Roads
paper money
legal currency issued on paper; it developed in China as a convenient alternative to metal coins; facilitated trade

Caravanserai
an inn with a central courtyard for travelers in the desert regions of Asia or North Africa; allowed caravans and their camels to rest in a protected environment, encouraging trade

Hanseatic League
an organization of north German and Scandinavian cities for the purpose of establishing a commercial alliance; facilitated trade and commercial growth in the 1200-1450 time period
porcelain
a thin, beautiful pottery invented in China

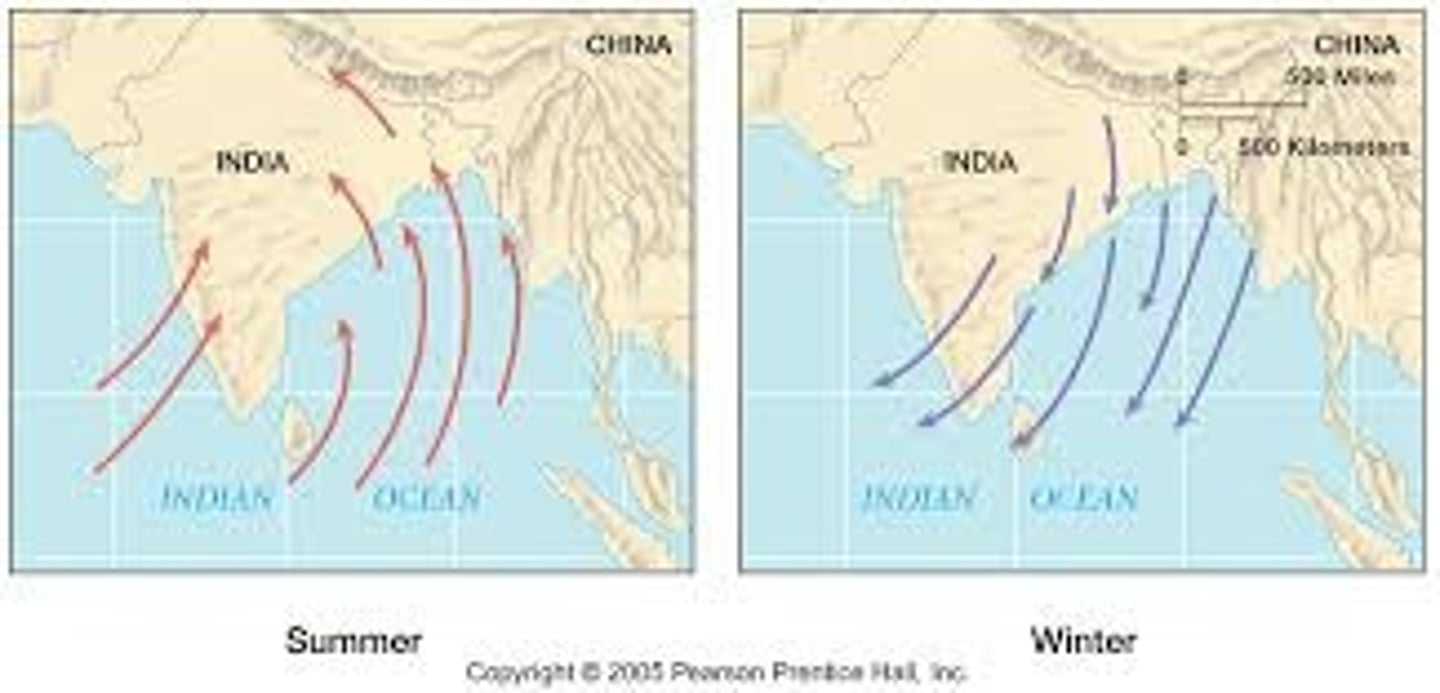
monsoon winds
seasonal wind in India, the winter monsoon brings hot, dry weather and the summer monsoon brings rain
Spice Islands
Europeans' name for the Moluccas, islands rich in cloves and nutmeg - highly valued spices often traded in the Indian Ocean trade network
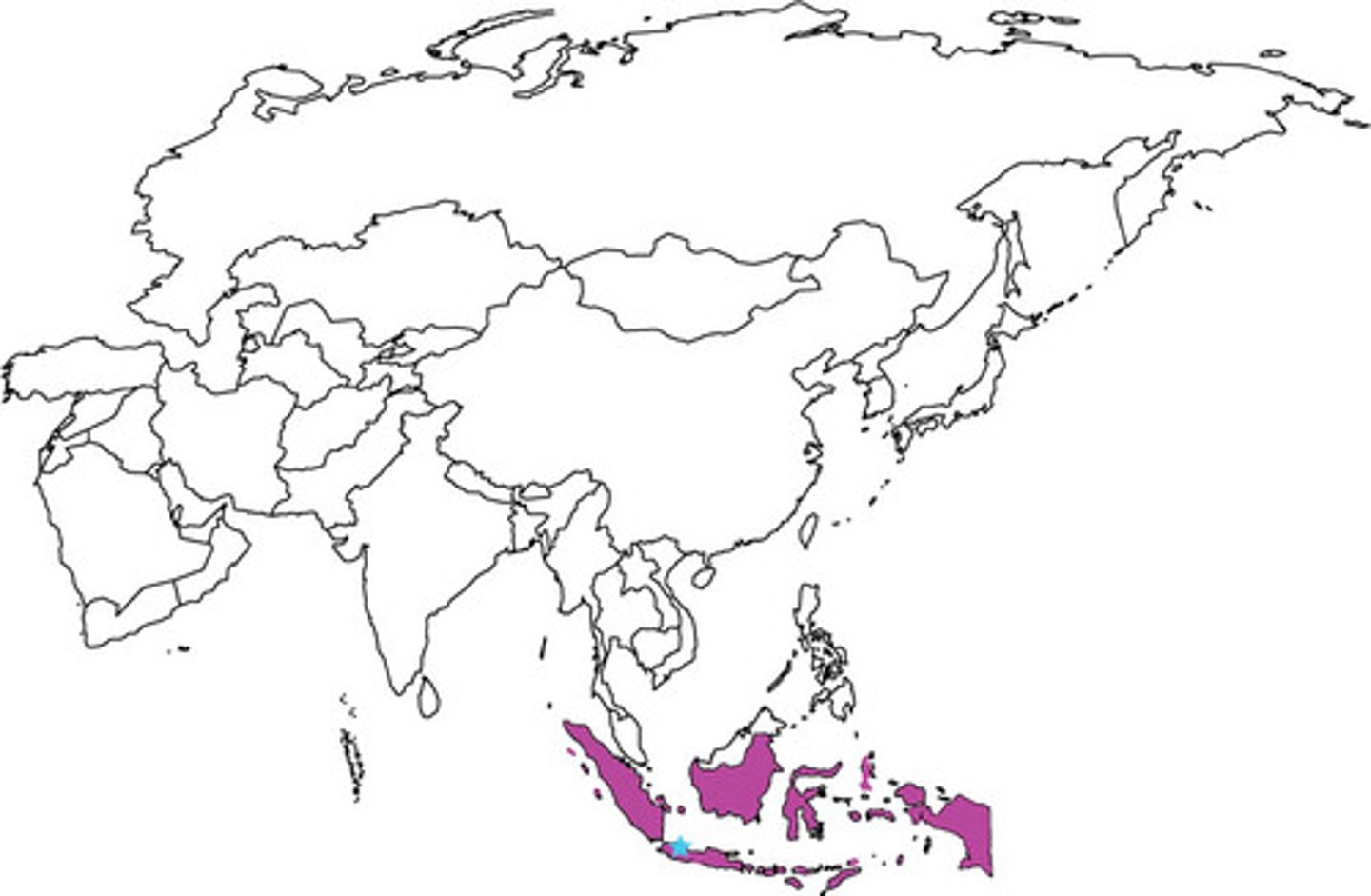
Diasporic communities
A dispersion of people from their homeland. For example, merchant communities of Muslims spread Islam throughout Southeast Asia, China, India & the east coast of Africa.
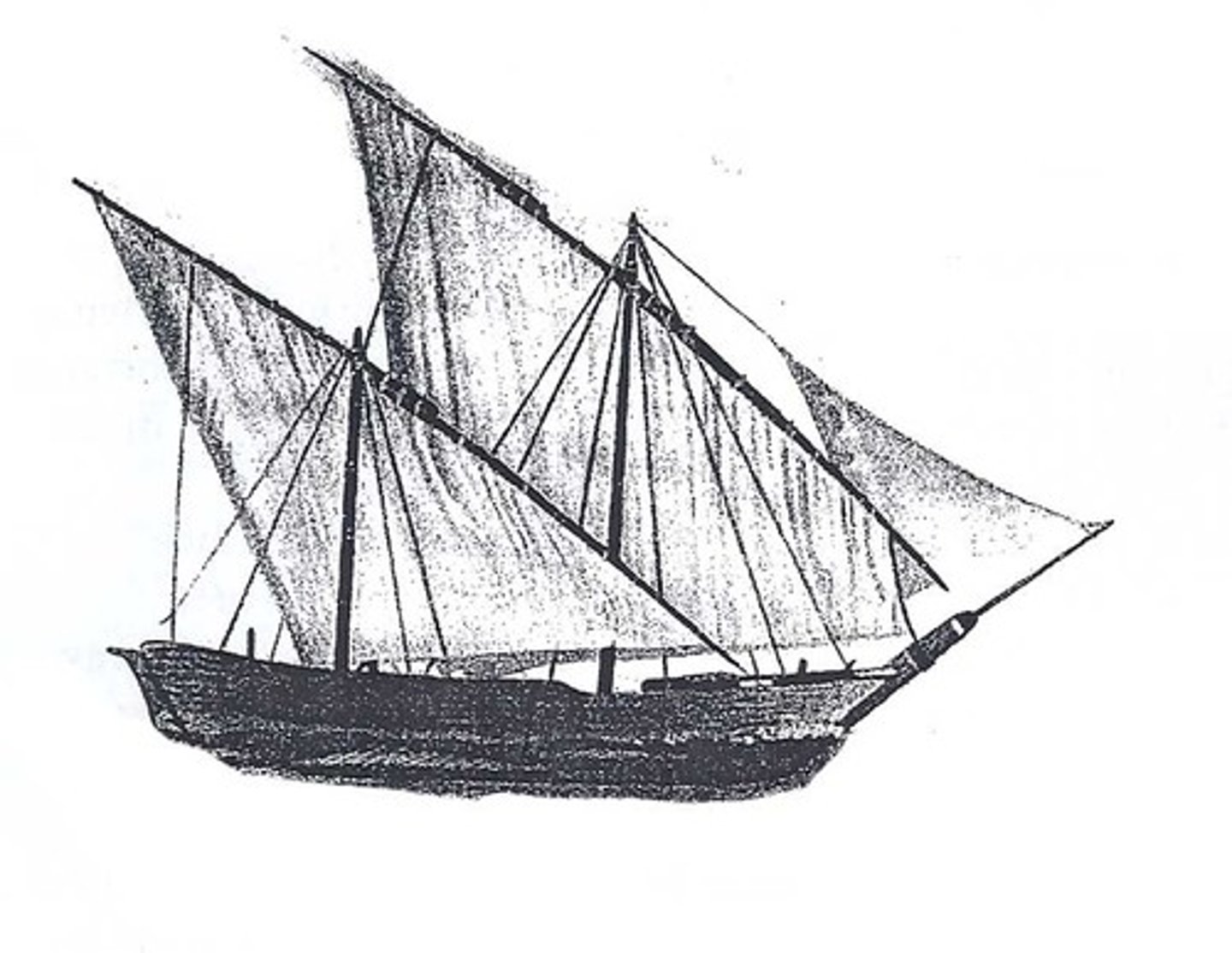
Dhow Ships
Arab sailing vessels with triangular or lateen sails; strongly influenced European ship design; facilitated trade in the Indian Ocean networks
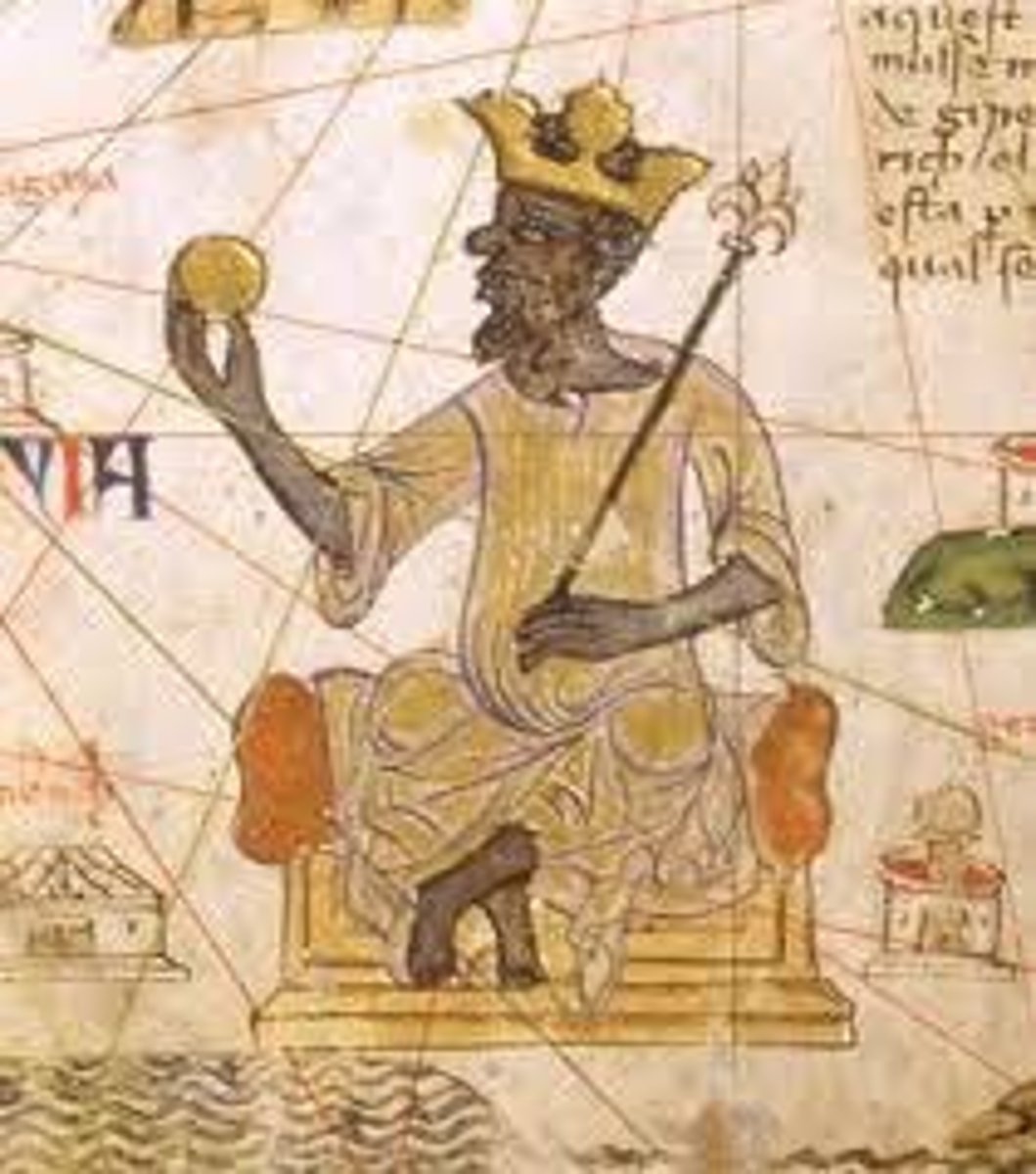
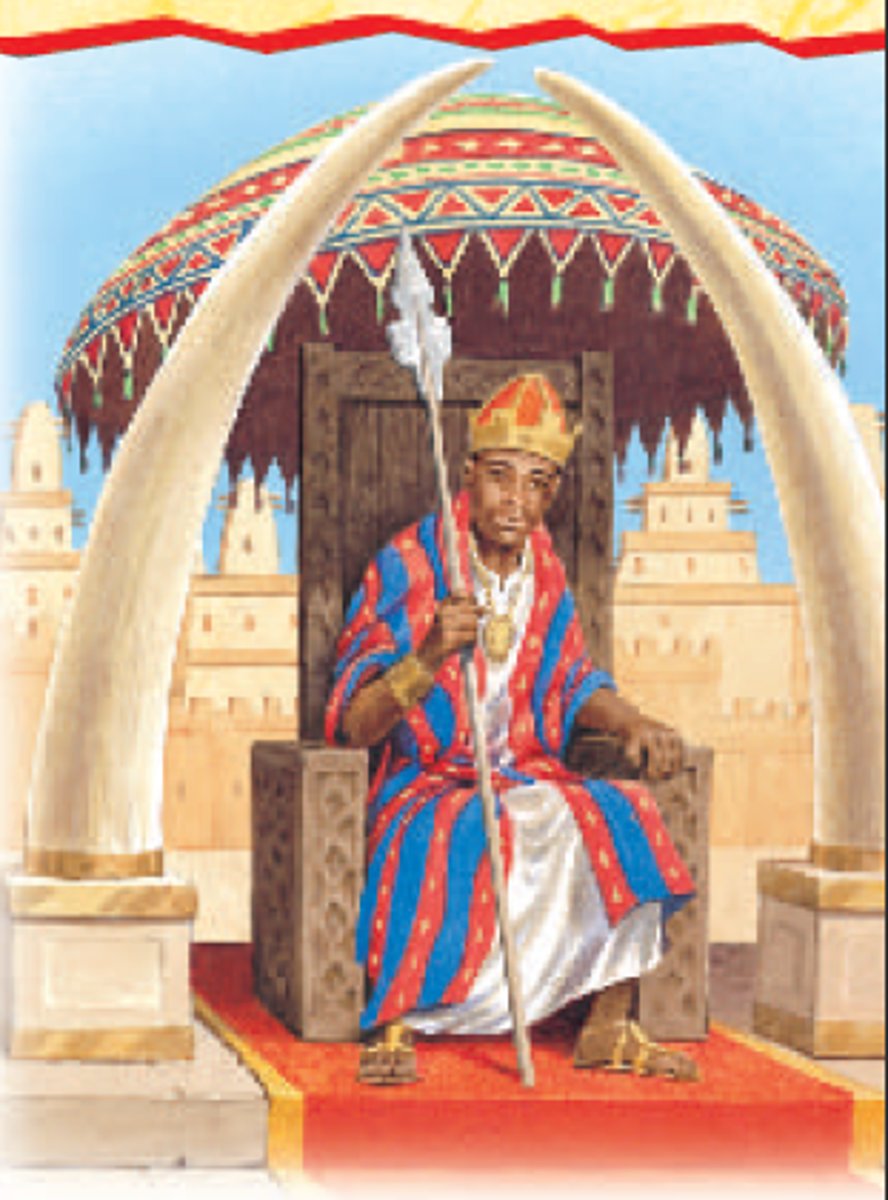
Mansa Musa
Ruler of Mali (r. 1312-1337). His extravagant pilgrimage through Egypt to Mecca in 1324-1325 established the empire's reputation for wealth in the Mediterranean world.

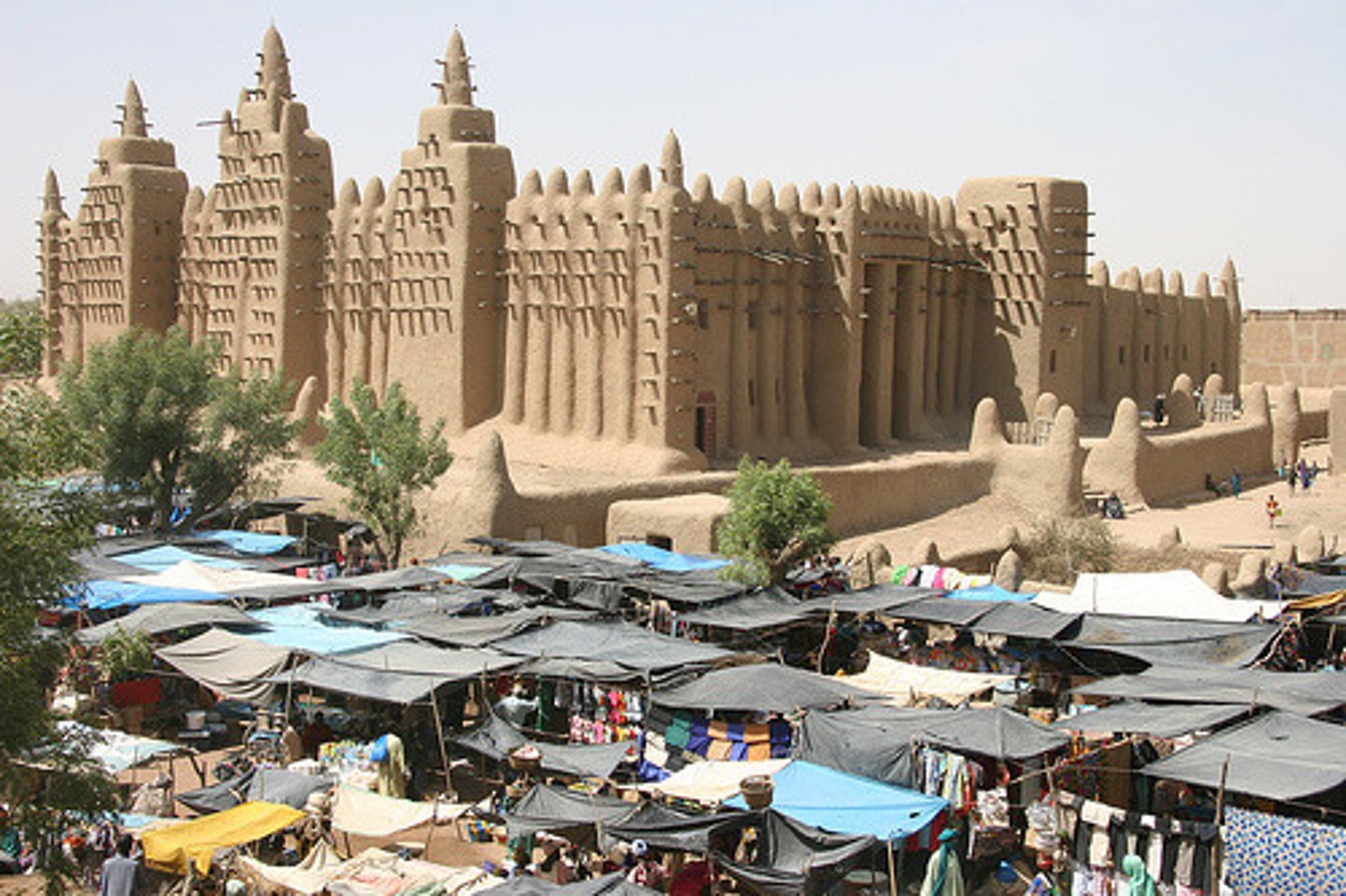
Timbuktu
Mali trading city that became a center of wealth and learning thanks to its location in the trans-Saharan trade networks; universities, mosques, and libraries

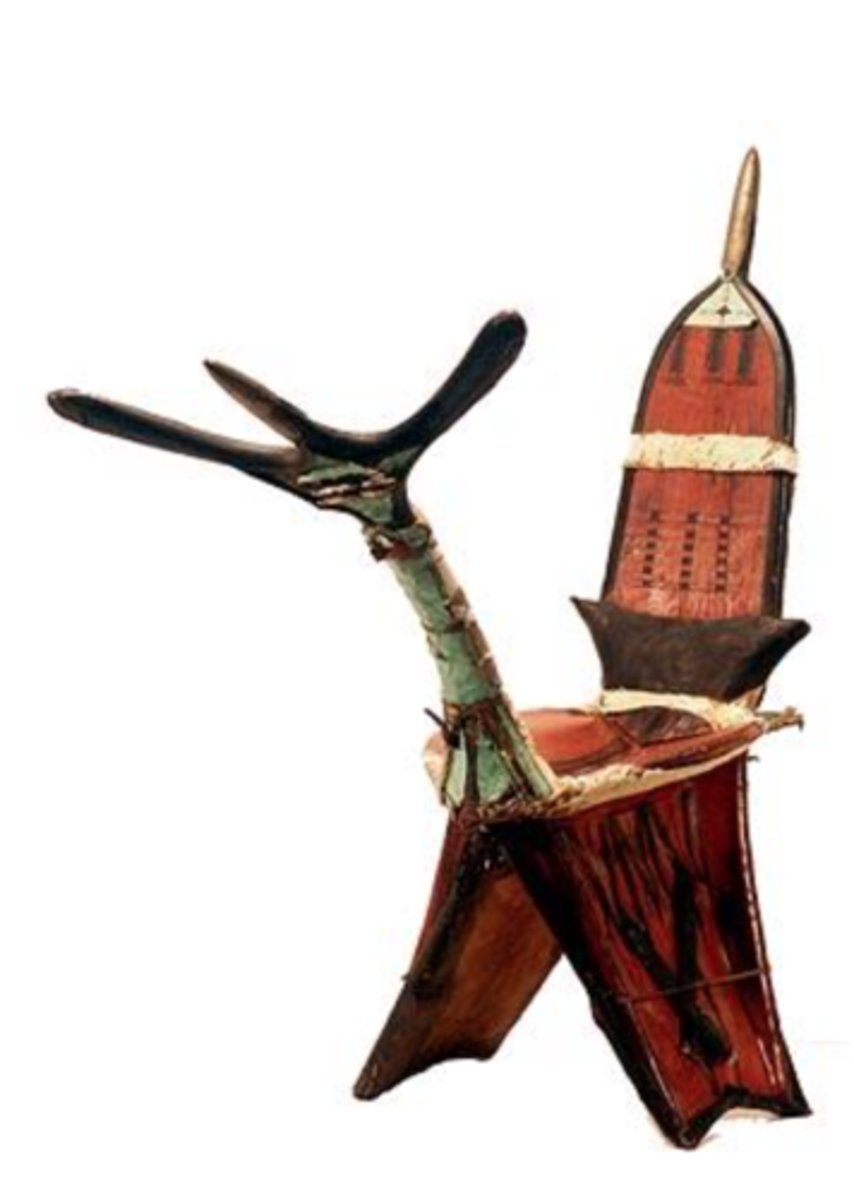
Camel Saddle
An invention which gives camel riders more stability on the animal and its invention and basic idea traveled along the Trans-Saharan Caravan Trade Route. Invented somewhere between 500 and 100 BCE by Bedouin tribes.

caravan
group of traveling merchants and animals

Sundiata
the founder of Mali empire. He crushed his enemies and won control of the gold trade routes along the trans-Saharan trade networks

Khan
Name for a Mongol ruler
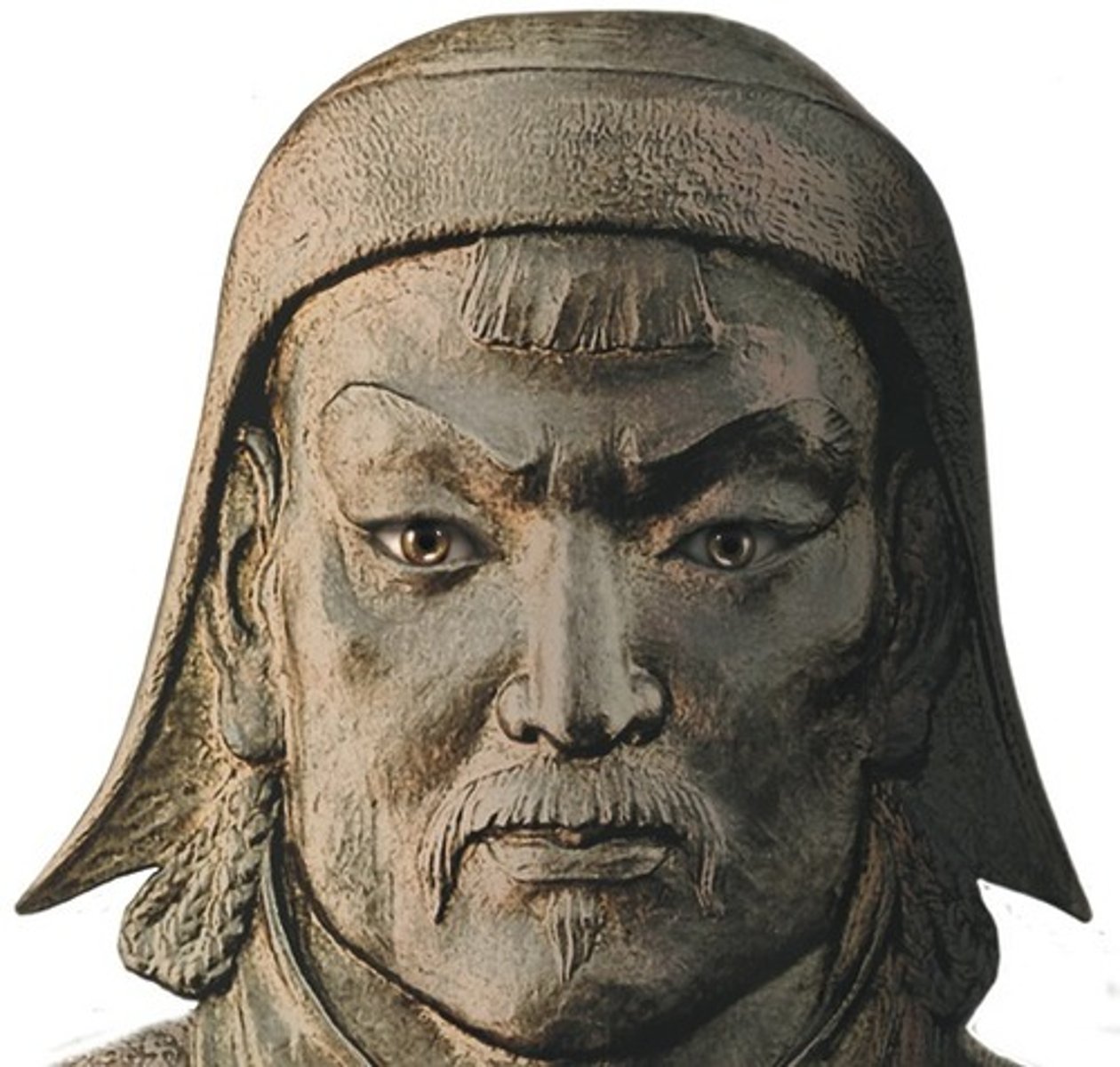

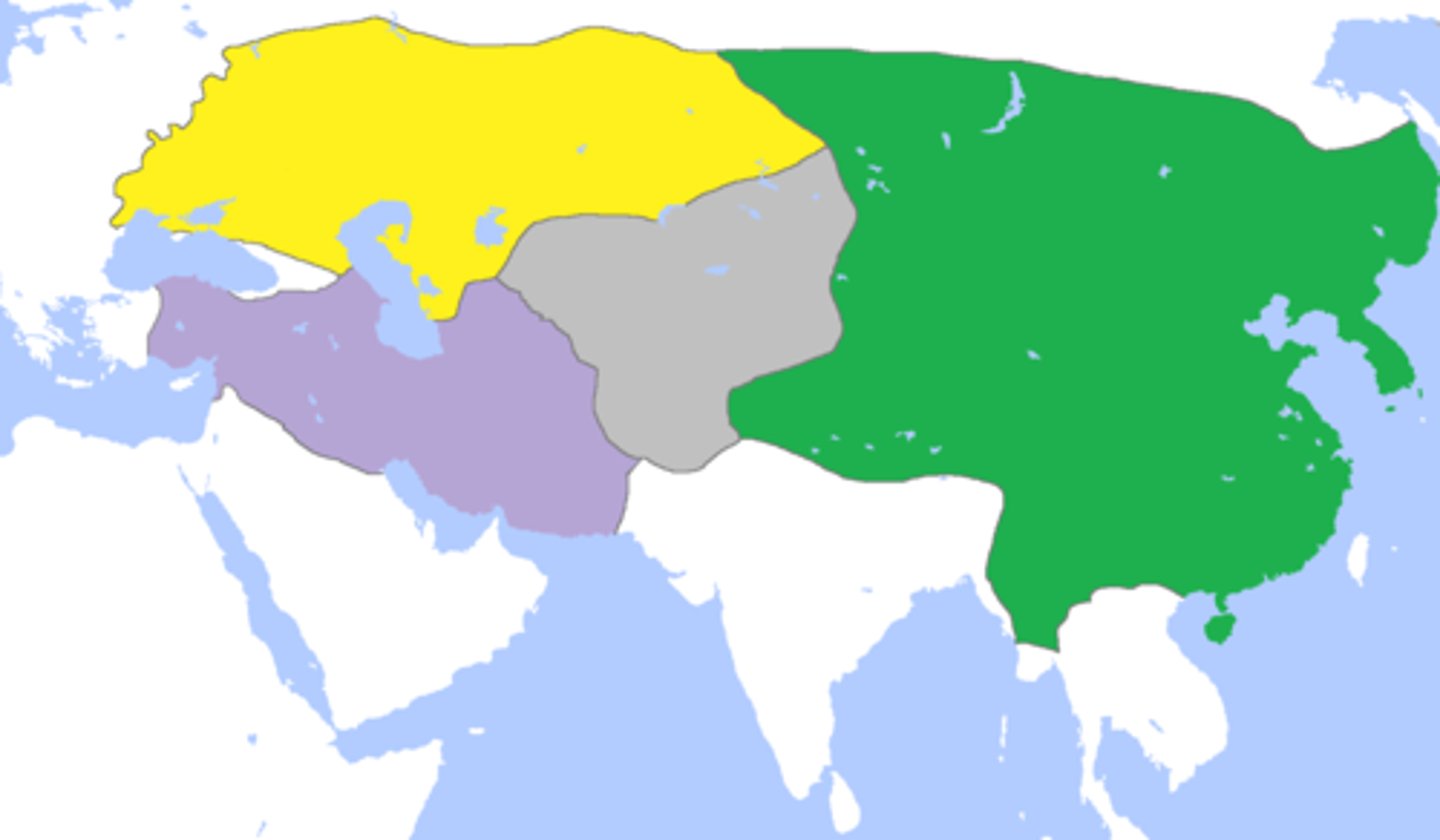
Khanates
Four regional Mongol kingdoms that arose following the death of Ghengis Khan.
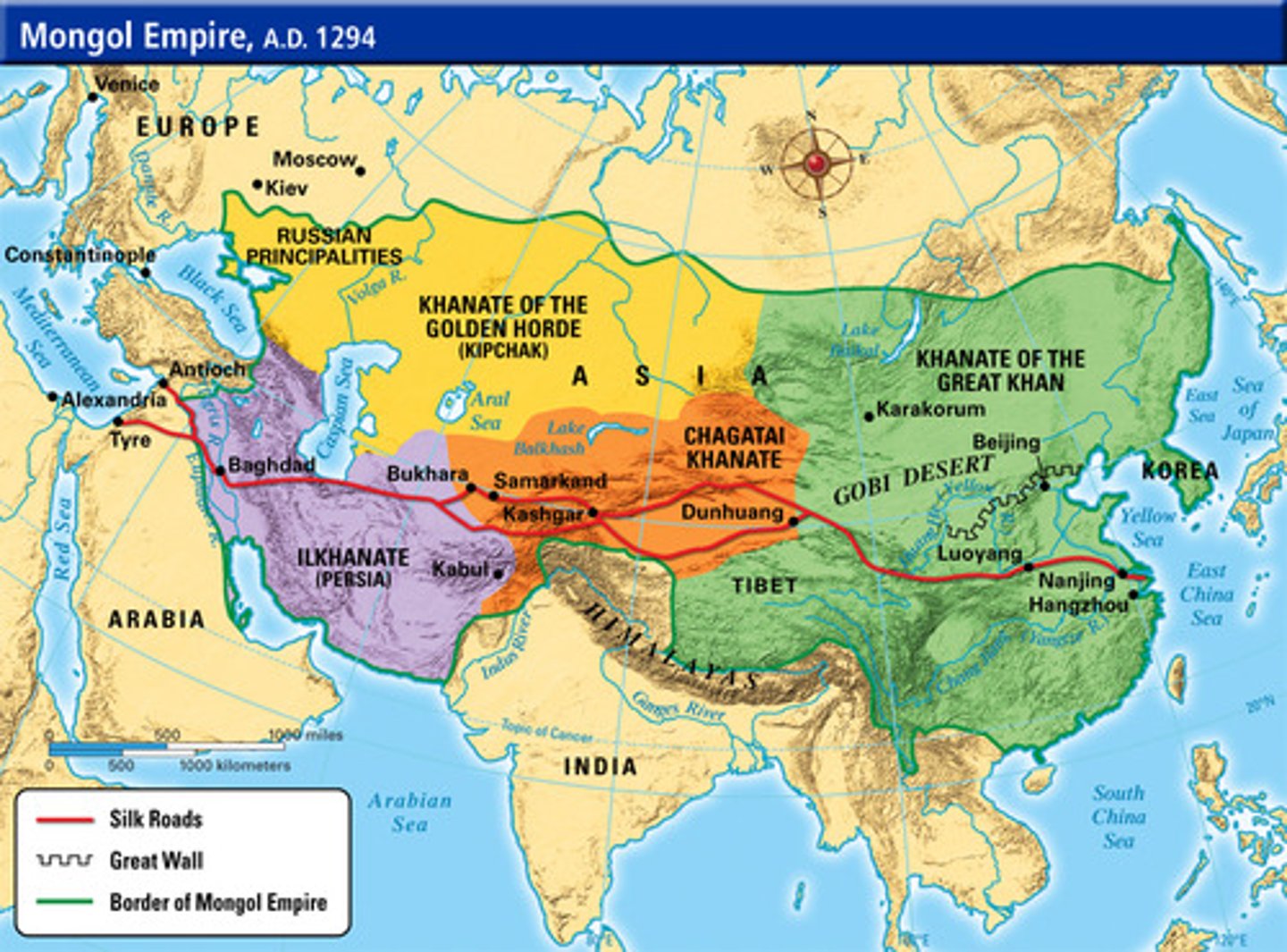
Pax Mongolica
The period of approximately 150 years of relative peace and stability created by the Mongol Empire.
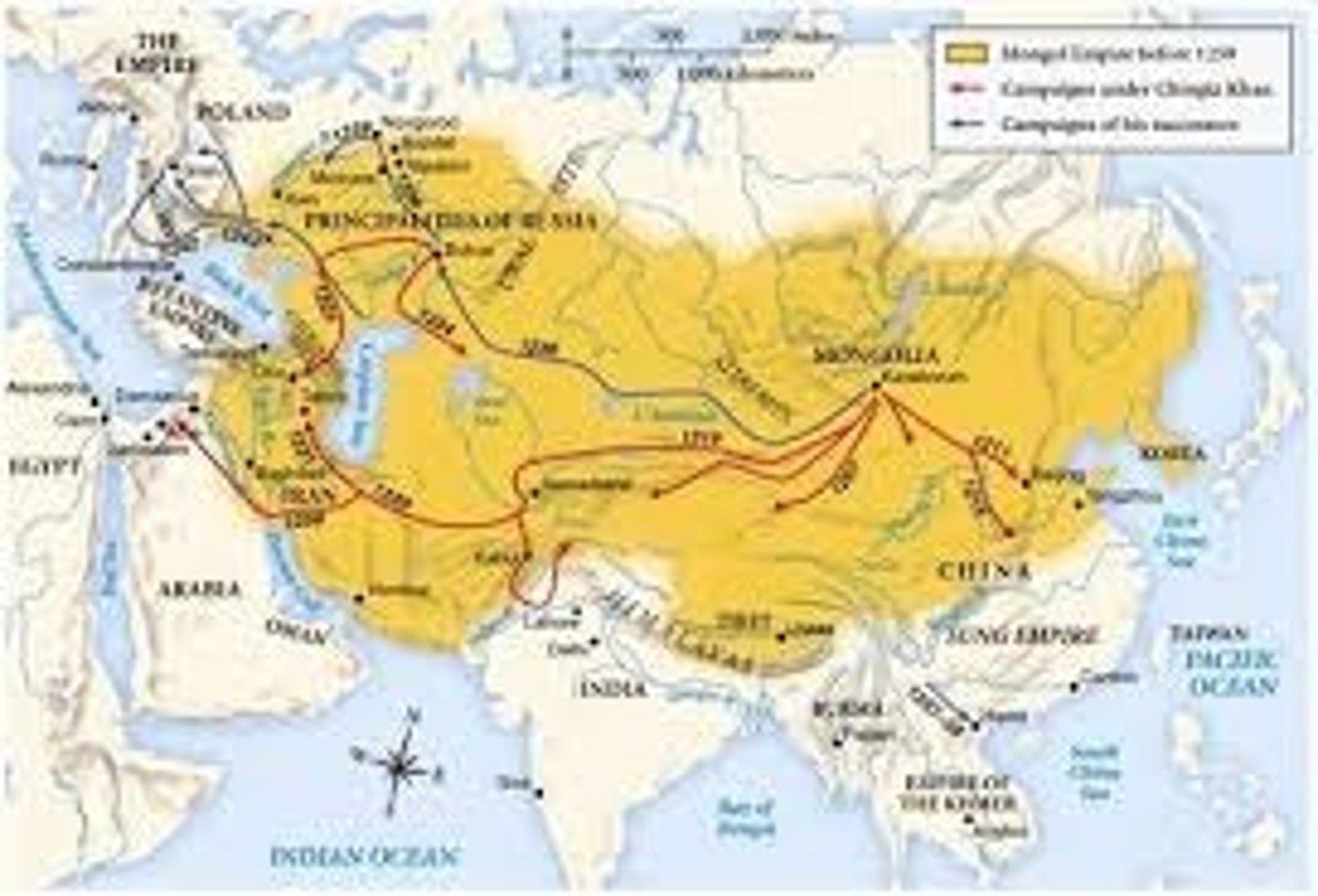
Golden Horde
Mongol khanate founded by Genghis Khan's. It was based in southern Russia and quickly adopted both the Turkic language and Islam.
Il-Khanate
Mongol empire that ruled over Iran (Persia) & the Middle East
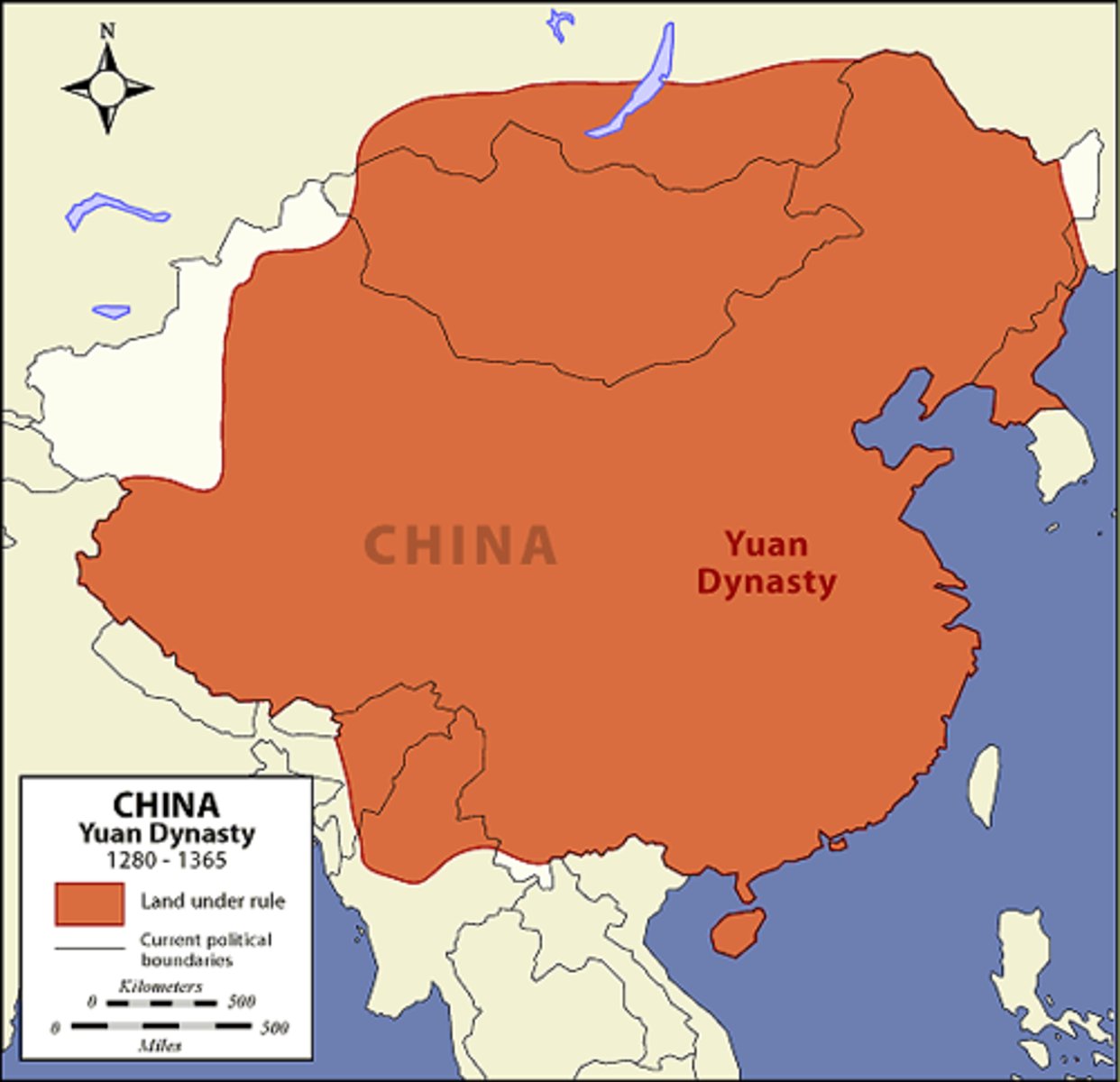
Yuan Dynasty
(1279-1368 CE) The dynasty with Mongol rule in China; centralized with bureaucracy but structure is different: Mongols on top->Persian bureaucrats->Chinese bureaucrats; did not emphasize Confucianism and the civil service exams
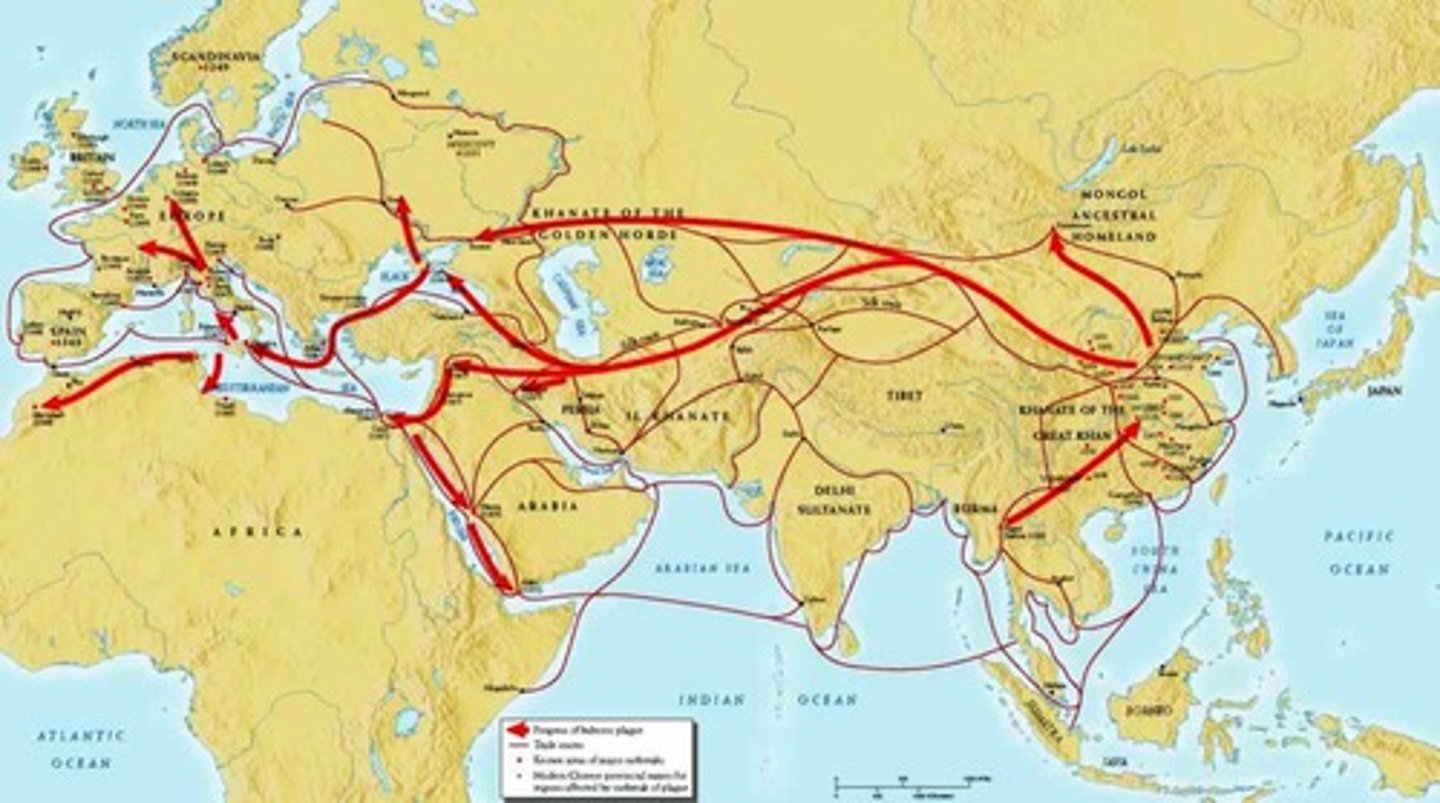
Bubonic Plague
Also called the Black Death; the deadly disease that spread through Asia and Europe and killed more than a third of the population in some areas; hit Europe (peak 1347-1351) especially hard due to unsanitary living conditions and overcrowded cities; spread thanks to increased trade along the Silk Roads
Gunpowder
Invented within China during the 9th century, this substance was became the dominate military technology used to expand European and Asian empires by the 15th century; spread from East to West via trade networks like the Silk Roads and help from the Pax Mongolica

Ibn Battuta
(1304-1369) Moroccan Muslim scholar, the most widely traveled individual of his time. He wrote a detailed account of his visits to Islamic lands from China to Spain and the western Sudan. His writings gave a glimpse into the world of that time period.

Marco Polo
(1254-1324) Italian explorer and author. He made numerous trips to China and returned to Europe to write of his journeys. He is responsible for much of the knowledge exchanged between Europe and China during this time period.
Margery Kempe
Wrote the Book of Margery Kempe - considered the 1st autobiography in the English language. Chronicles her pilgrimages to holy sites in Europe and Asia. Claimed to have vision that called her to leave the vanities of the world
Swahili city-states
City coasts that actively participated in Indian Ocean trade along the East coast of the African continent
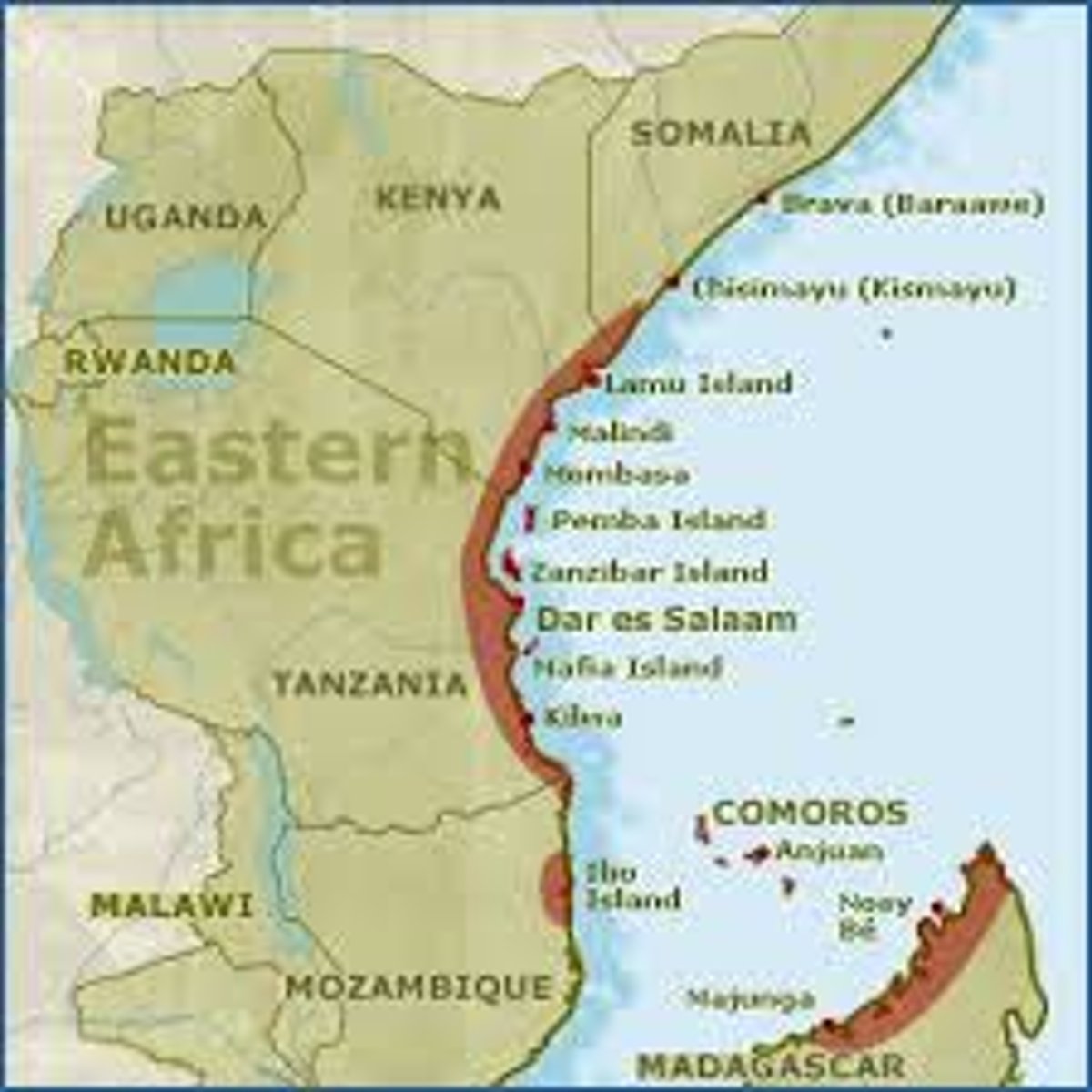
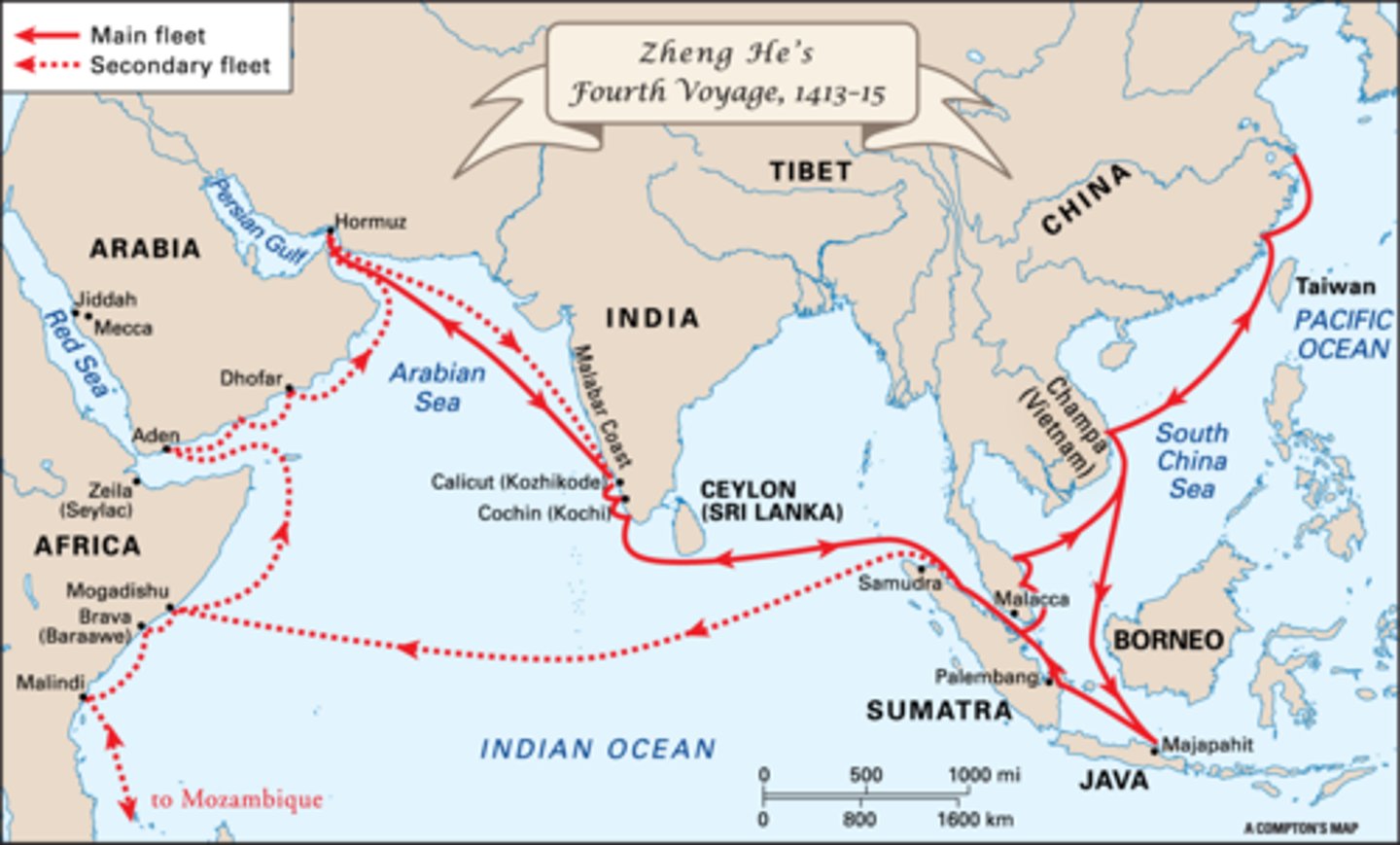
Zheng He
(1371-1433?) Chinese Ming Dynasty naval explorer who sailed along most of the coast of Asia, Japan, and half way down the east coast of Africa before his death; facilitated China's role in the tribute system in the Indian Ocean trade network
Commercial Practices
Any activities (like banking practices, trade, customs, taxes, money systems, etc.) related to merchants and business practices along the major trade networks.
Interregional
The connection or movements across two or more regions
silk
a soft, light, highly valued fabric from China

Bills of Exchange
A written order to a person requiring the person to make a specified payment to the signatory or to a named payee; a promissory note. First used by Chinese merchants along the Silk Road & later adopted by the Song Dynasty.

Banking Houses
Handled the financial transactions of a variety of merchants. Specialized in money changing, loans, and investments. Banking was introduced to encourage the exchange of money and goods over a large distance. First used on the Silk Roads.

money economies
Aa system or stage of economic life in which money replaces barter in the exchange of goods.

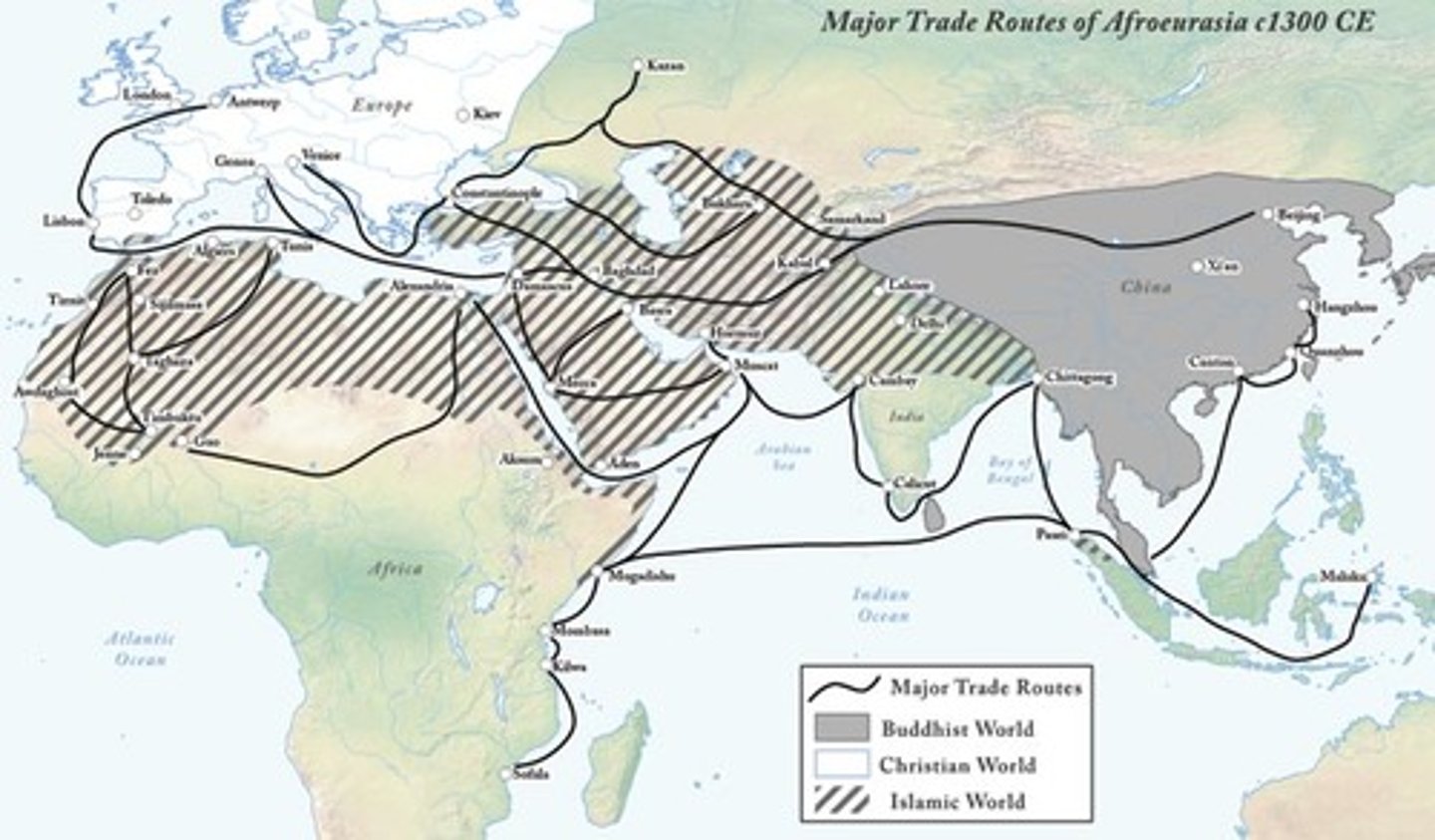
Afro-Eurasia
Africa, Europe, and Asia
Artisans
skilled workers who make goods by hand

Merchants
people who buy and sell goods

Textiles
cloth items like silk, wool, cotten, etc.

export
send (goods or services) to another country for sale.
Chagatai Khanate
Mongol Khanate in Central Asia between the Il-khanate in Persia & the Yuan Dynasty in China
Uyghur script
Genghis Khan's effort to unify his empire including directing a scribe captured in 1204 to adapt the Uyghur alphabet to represent mongols- effort to establish one system throughout the empire but failed- alphabet still used today in Mongolia

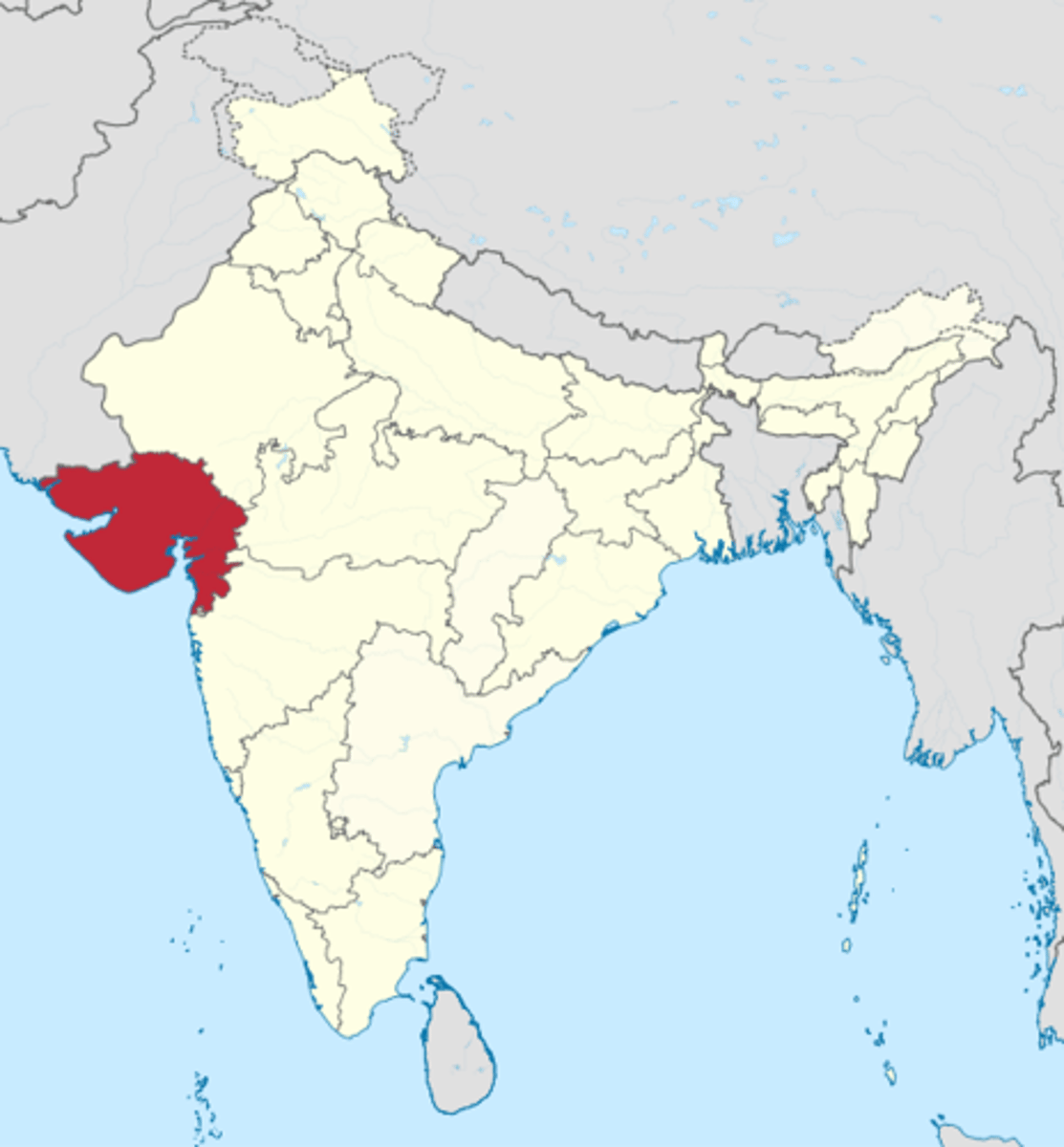
Gujarat
Region of western India famous for trade and manufacturing of textiles. Played a major role in Indian Ocean Trade from 1200-1450.
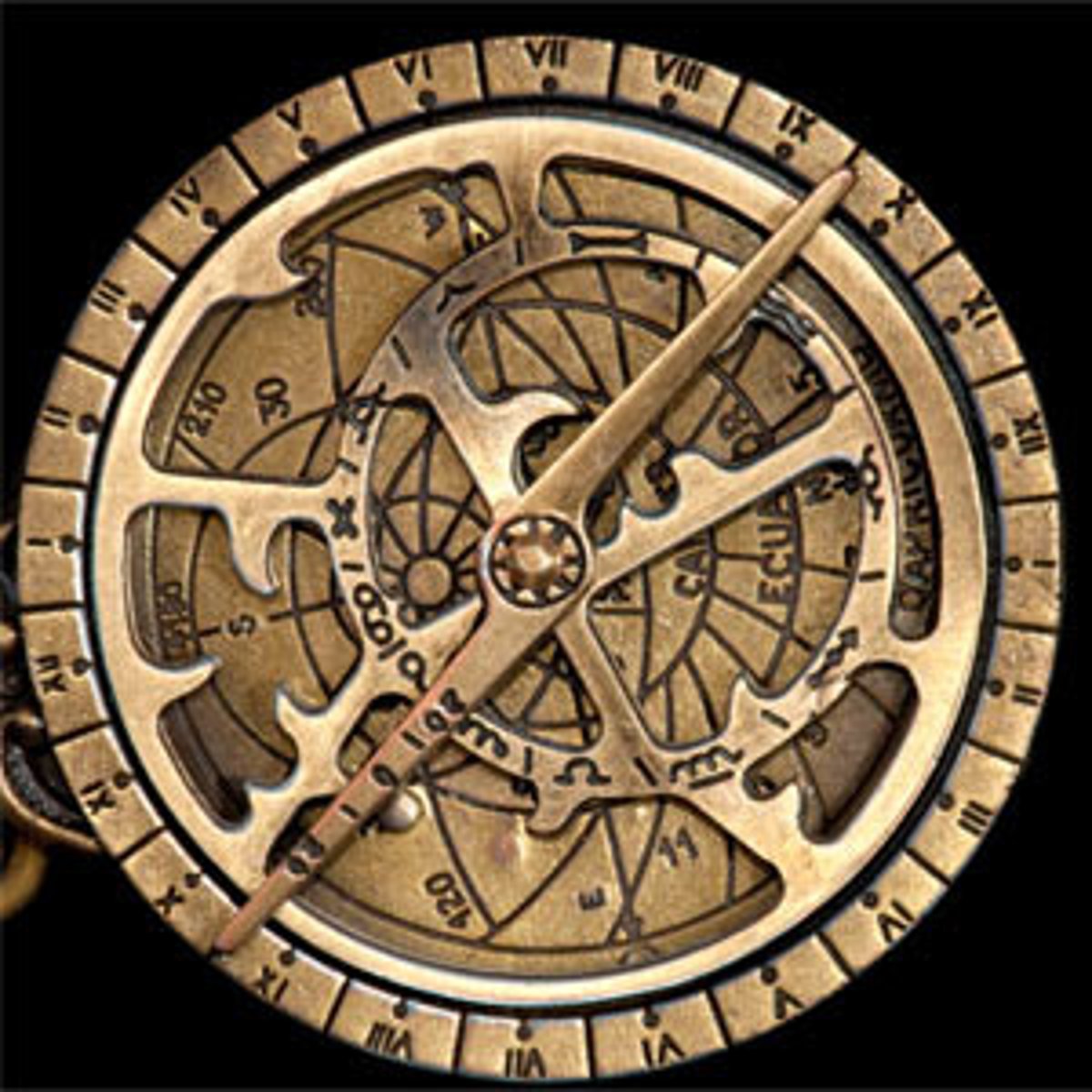
Astrolabe
An instrument used by sailors to determine their location (latitude) by observing the position of the stars and planets

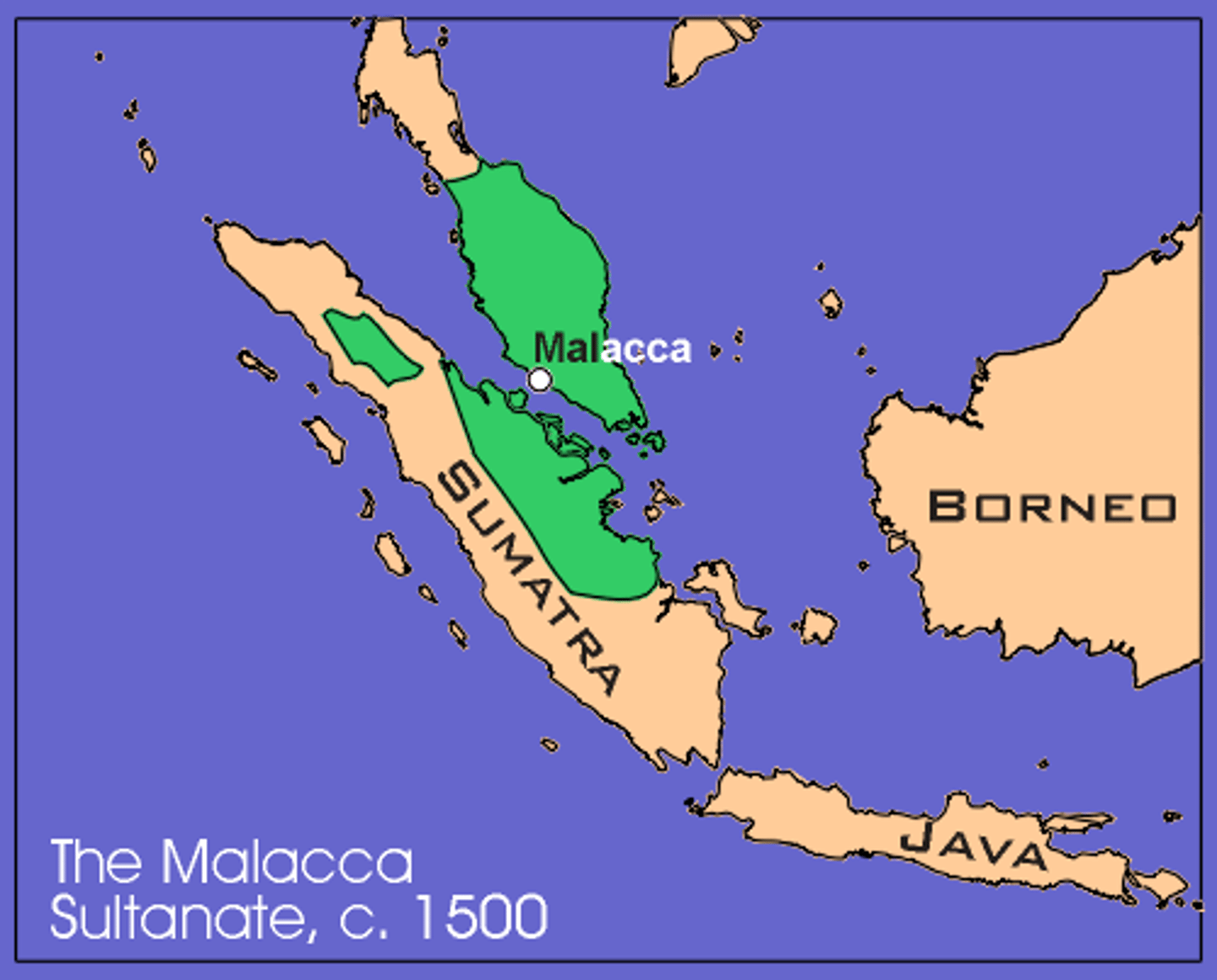
Sultanate of Malacca
Islamic sultanate in modern day Indonesia/Malay Peninsula from c. 1403-1511. Would have controlled the Strait of Malacca and practiced state-building through its taxation.
Maritime Activity
refers to trade conducted in major bodies of water, like Indian Ocean or Mediterranean trade routes.
Trans-Saharan Trade
route across the sahara desert. Major trade route that traded for gold and salt, created caravan routes, economic benefit for controlling desert, camels played a huge role in the trading
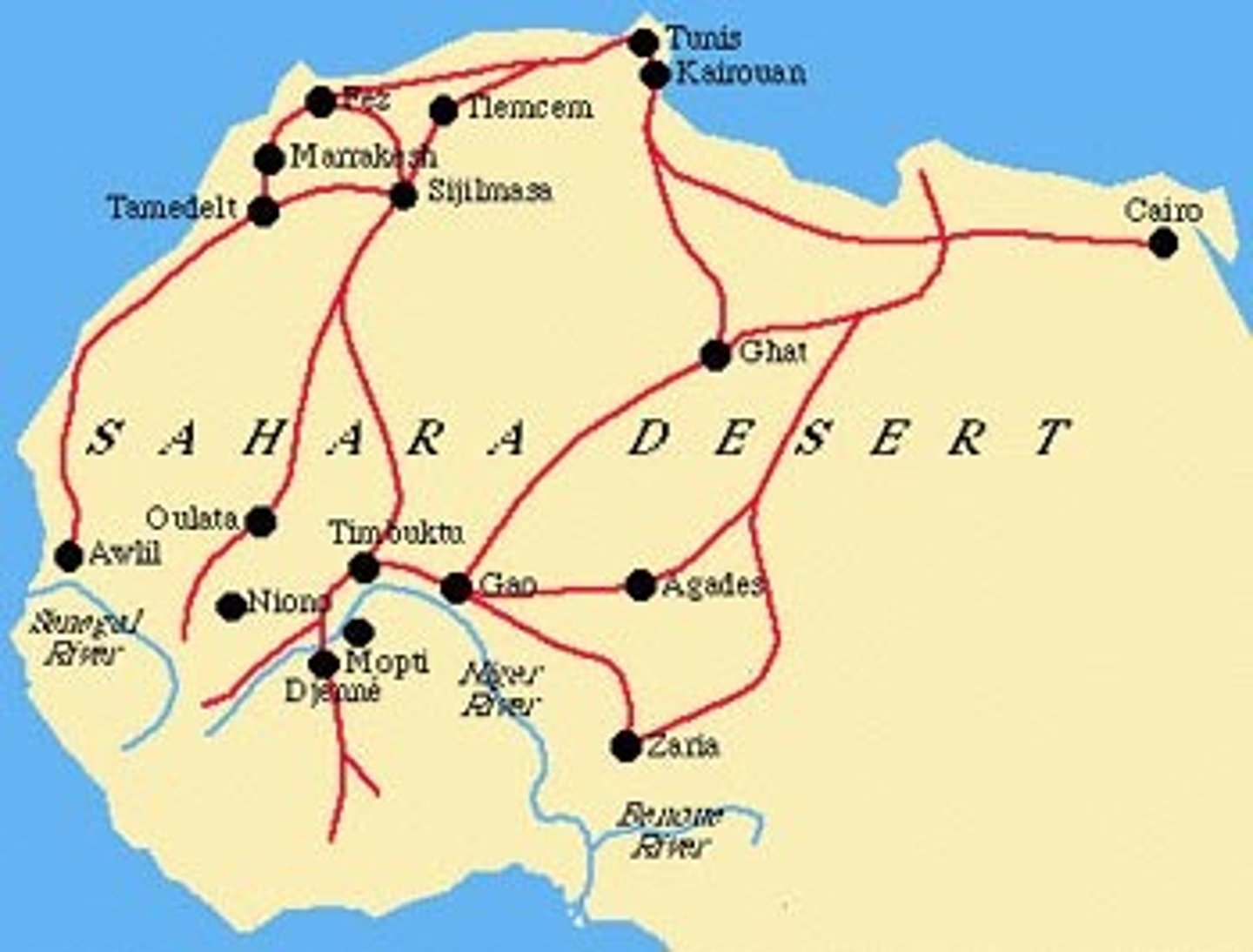
Kingdom of Mali
a huge territorial empire that flourished in west Africa during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries. Its capital was Timbuktu, which became a center of Islamic learning (see Islam). The empire controlled trade routes that stretched from the edge of the Sahara in the north to forests in the south and that carried gold and other luxuries

facilitated
made easy; helped bring about, assisted
Diffusion
to move or spread
Urbanization
Growth of cities. Was an effect of increased trade from 1200 to 1450. As foods such as rice, bananas & citrus fruits spread to new locations, local inhabitants saw improvements in diets and thus population increased. More mobility also led to emergence of diasporic communities in centers of trade resulting into the growth and creation of new cities/towns.
stirrup
device for securing a horseman's feet, enabling him to wield weapons more effectively. First evidence of the use of stirrups was among the Kushan people of northern Afghanistan in approximately the first century C.E. The Mongols used and facilitated the spread of this innovation to new locations.

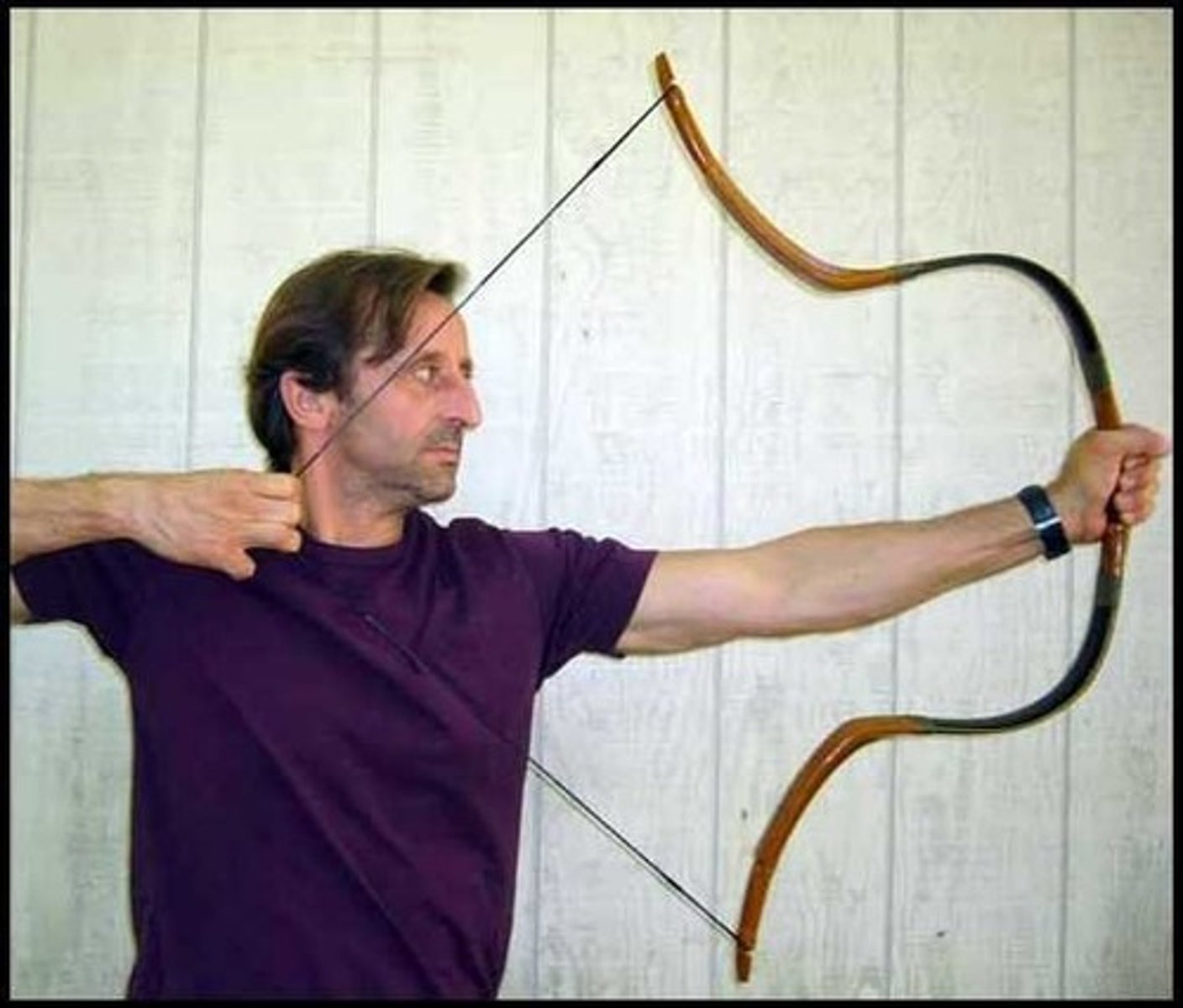
Composite Bow
A special bow used by the Mongols, which could pierce armor and fire faster than any other bow.

Kublai Khan
(1215-1294) Grandson of Genghis Khan and founder of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty in China.
Pathogen
A disease causing agent
Epidemic Diseases
A disease that spreads rapidly and extensively by infections and affecting many individuals at the same time (ex: the Bubonic Plague)