06.3D U6P1 (PART D) Contraction of Skeletal Muscle as a Whole
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
All or None Law of Muscle Contraction
The principle that that states if the stimulus exceeds the threshold potential, the nerve or muscle fiber will give a complete response otherwise, there is no response.
Graded Responses of Muscle Contraction
Different degrees of shortening can be produced by changing the:
- Frequency of muscle stimulation
- Number of muscle cells being stimulated
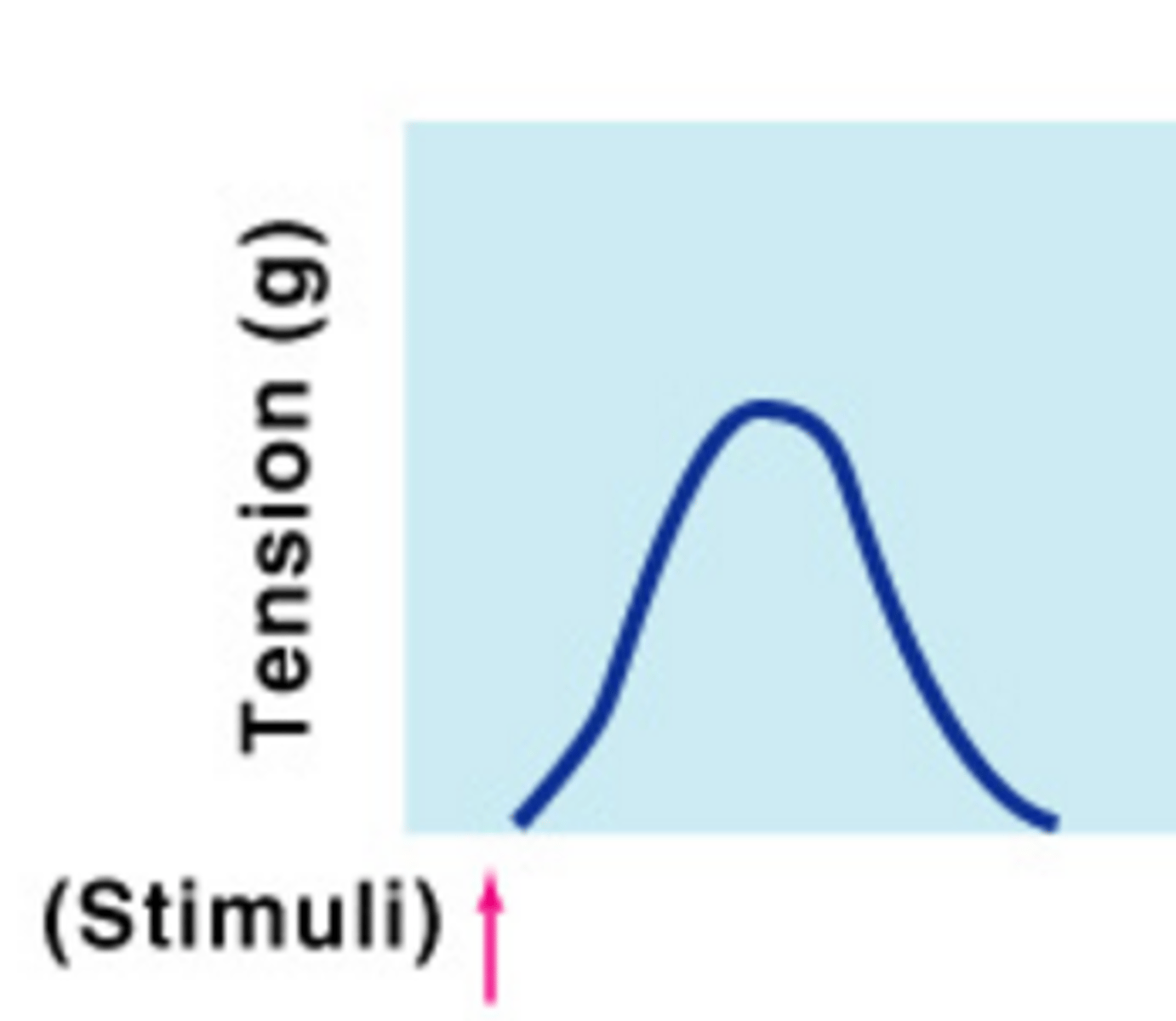
Twitch
A single stimulus that causes muscle to quickly contract and then relax
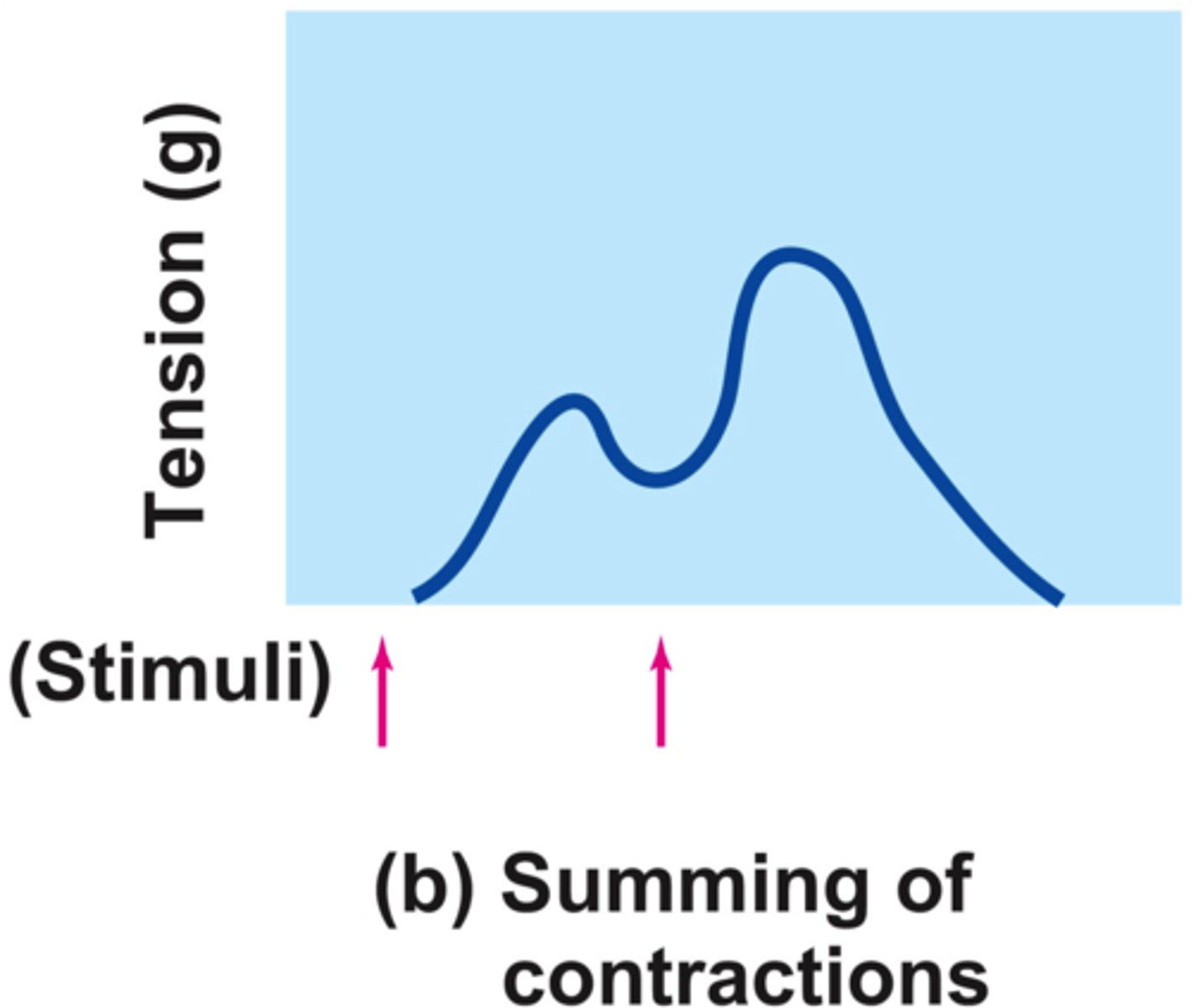
Tetanus (Summing of contractions)
Also known as summing of contractions; occurs when one contraction is immediately followed by another and the muscle does not completely return to a resting state; the effects are added
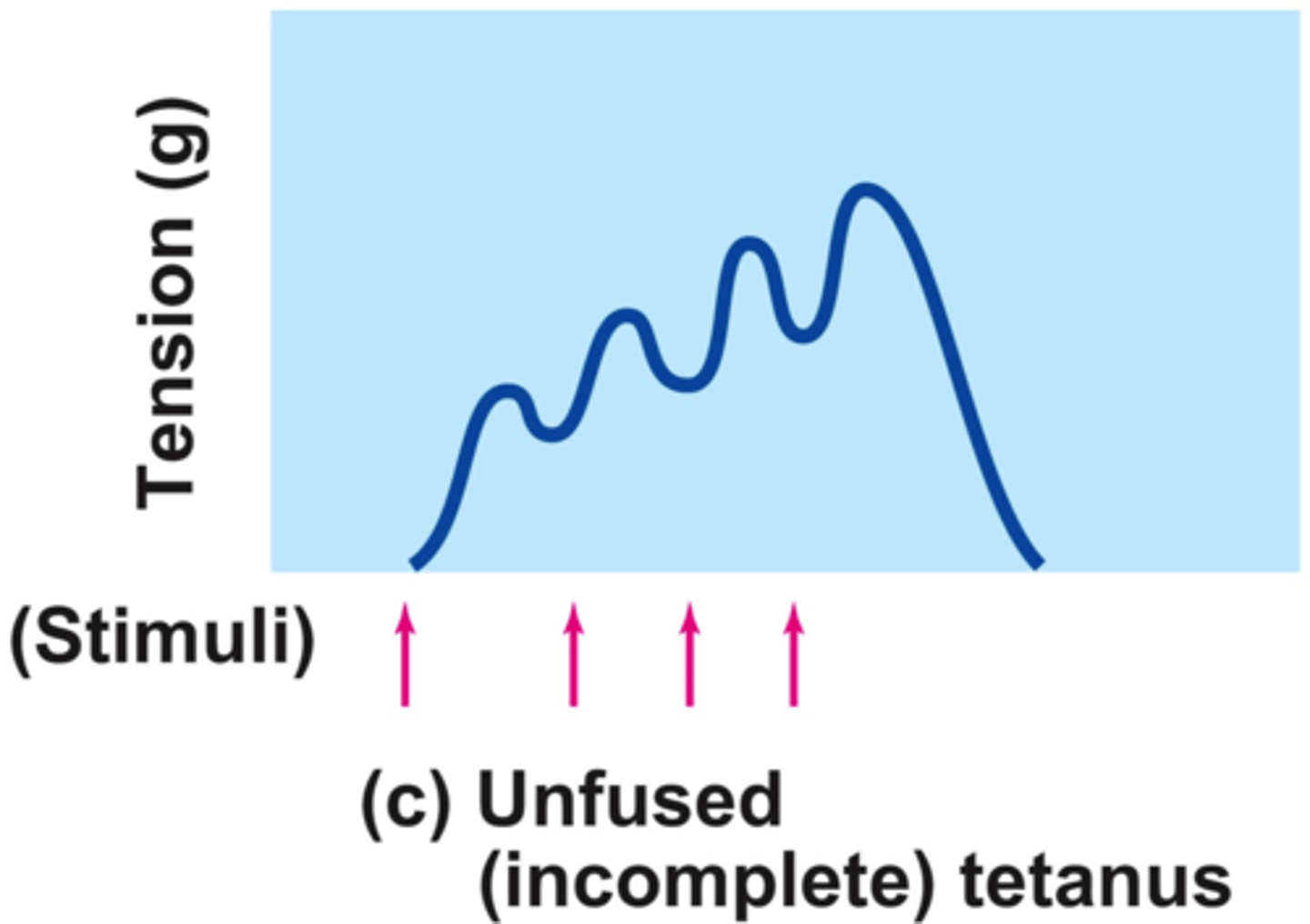
Unfused or Incomplete Tetanus
Occurs when some relaxation occurs between contractions; the results are summed
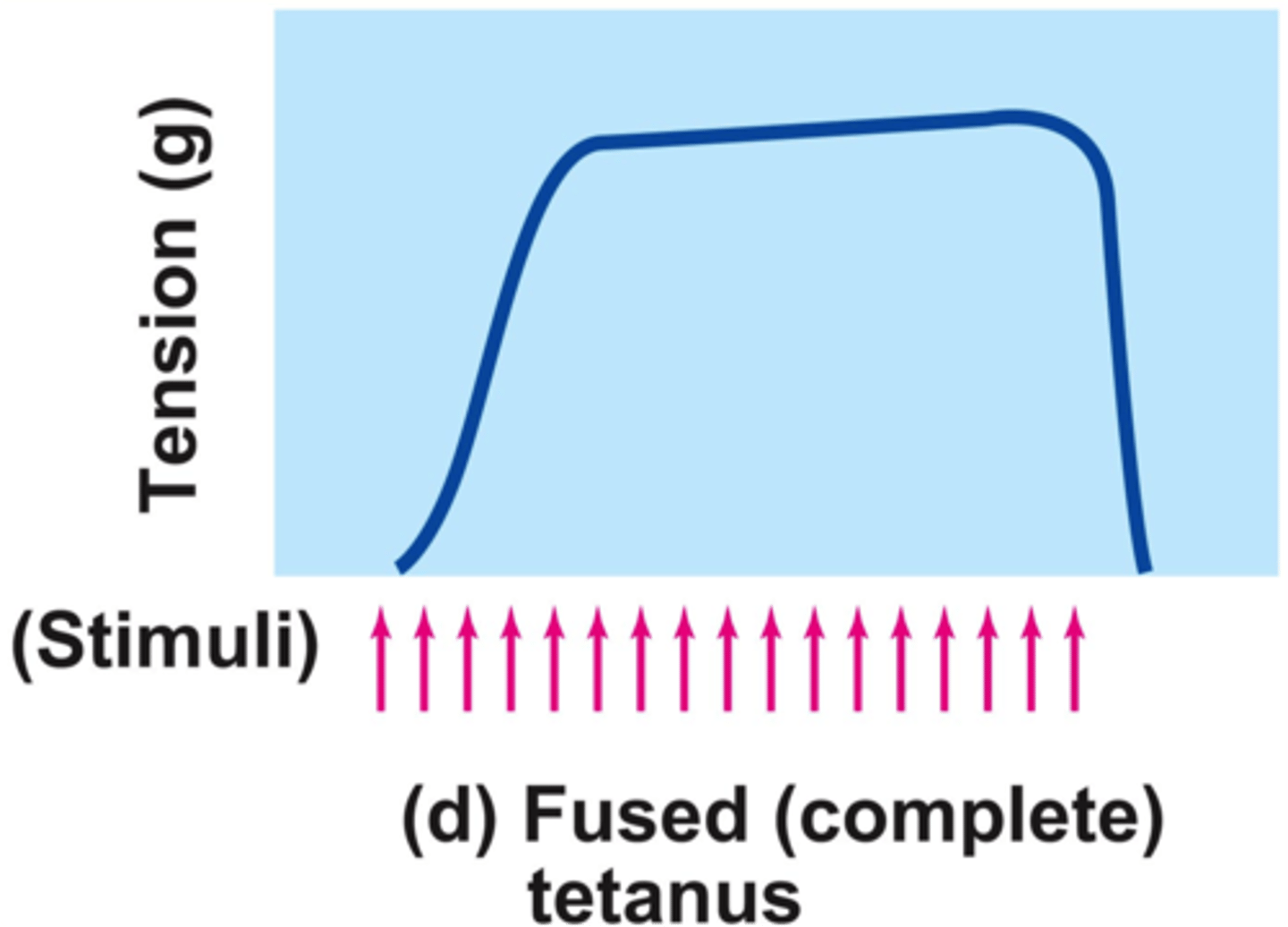
Fused or Complete Tetanus
Occurs when there is no evidence of relaxation before the following contractions
The result is a sustained muscle contraction
Graded response (Types)
Twitch
Incomplete tetanus
Complete tetanus
Muscle force
Depends upon the number of fibers stimulated
Muscle tension
Results when more fibers contract
Muscle response to strong stimuli
Muscle force depends upon the number of fibers stimulated; more fibers contracting results in greater muscle tension; muscles can continue to contract unless they run out of energy
ATP stored in muscle
High energy molecule found in muscles; provides 4-6 seconds of muscle contraction
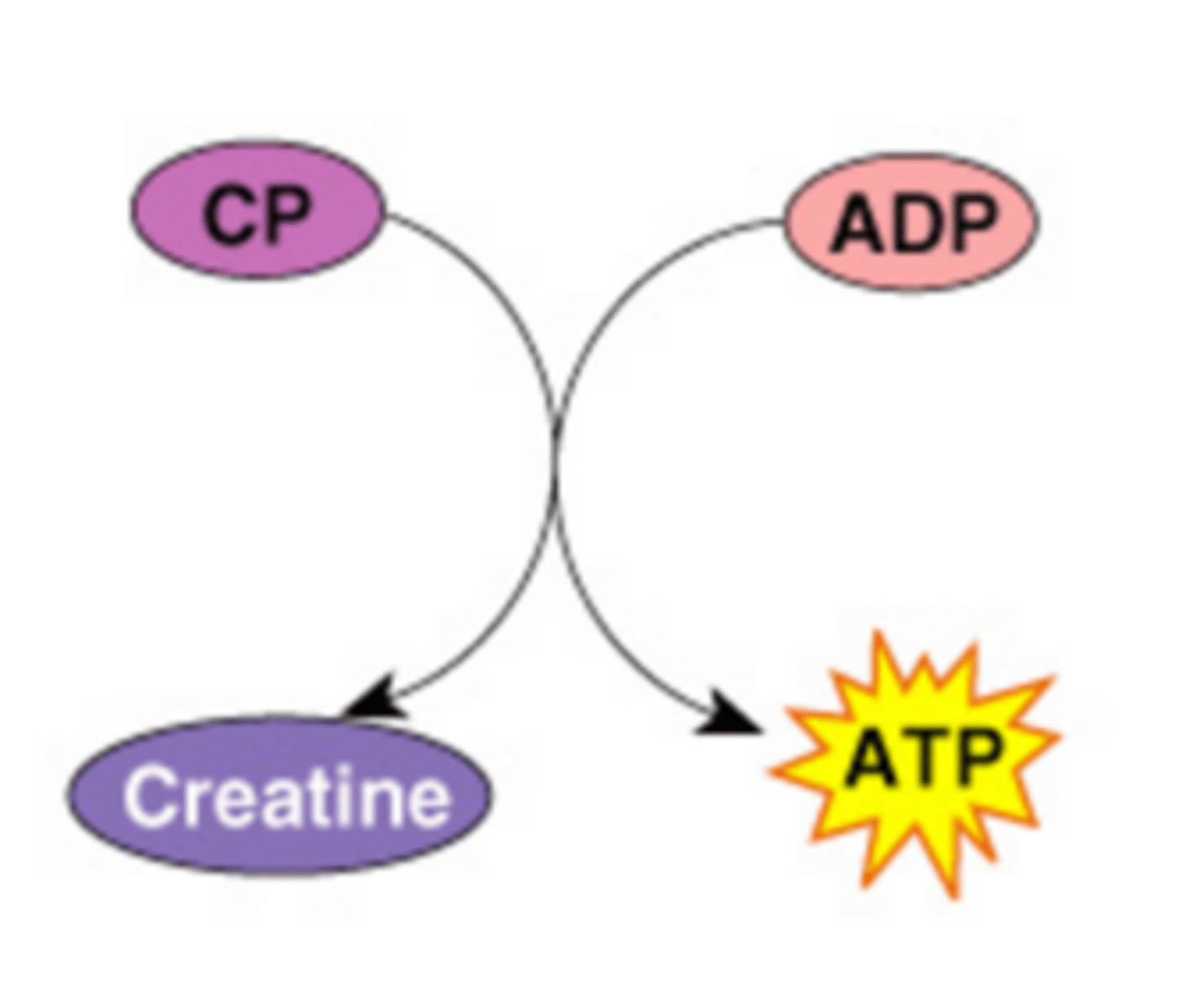
Creatine phosphate
A high energy molecule found in muscles that transfers energy to ADP, to regenerate ATP when ATP stores have been used up; no oxygen required; provides about 15 seconds of energy
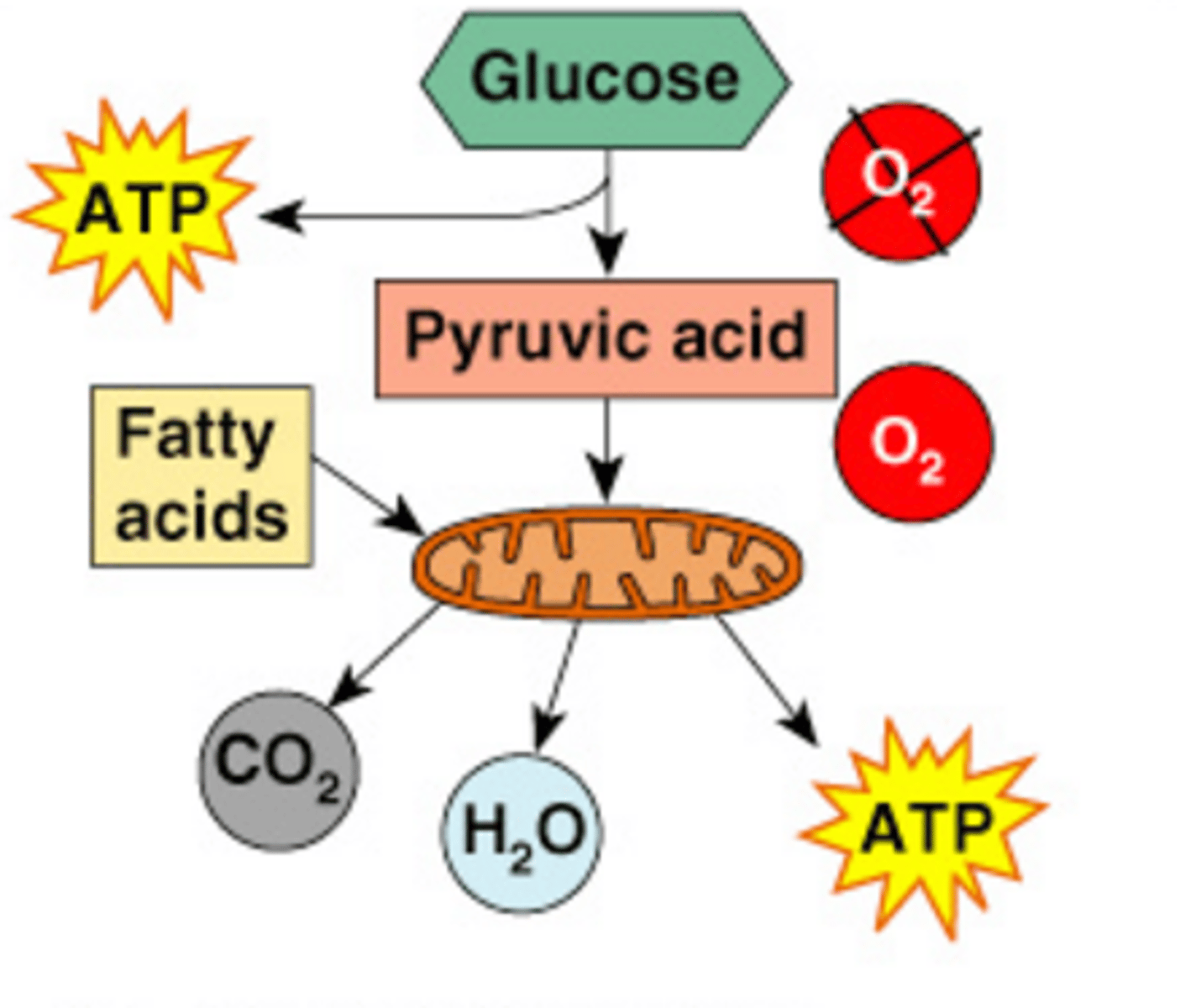
Aerobic respiration
A series of metabolic pathways that occur in the mitochondria; in the presence of oxygen glucose is broken down into to carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy in the form of 36 ATP; provides hours of energy
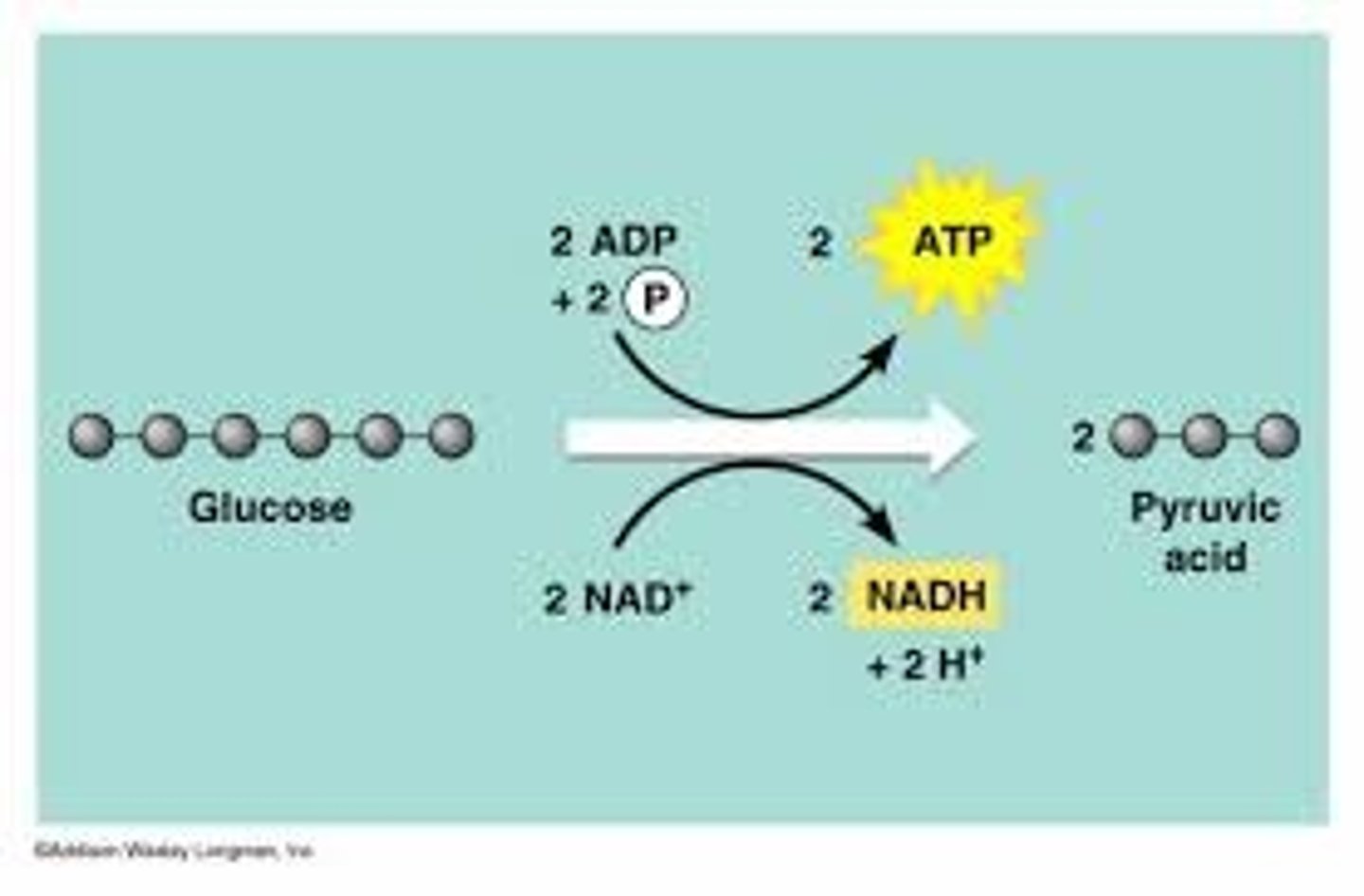
Glycolysis
A reaction that breaks down glucose into to pyruvic acid in the absence of oxygen to produce 2 ATP; provides 30-60 seconds of energy
Lactic acid fermentation
In the absence of oxygen pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid to ensure that glycolysis can continue
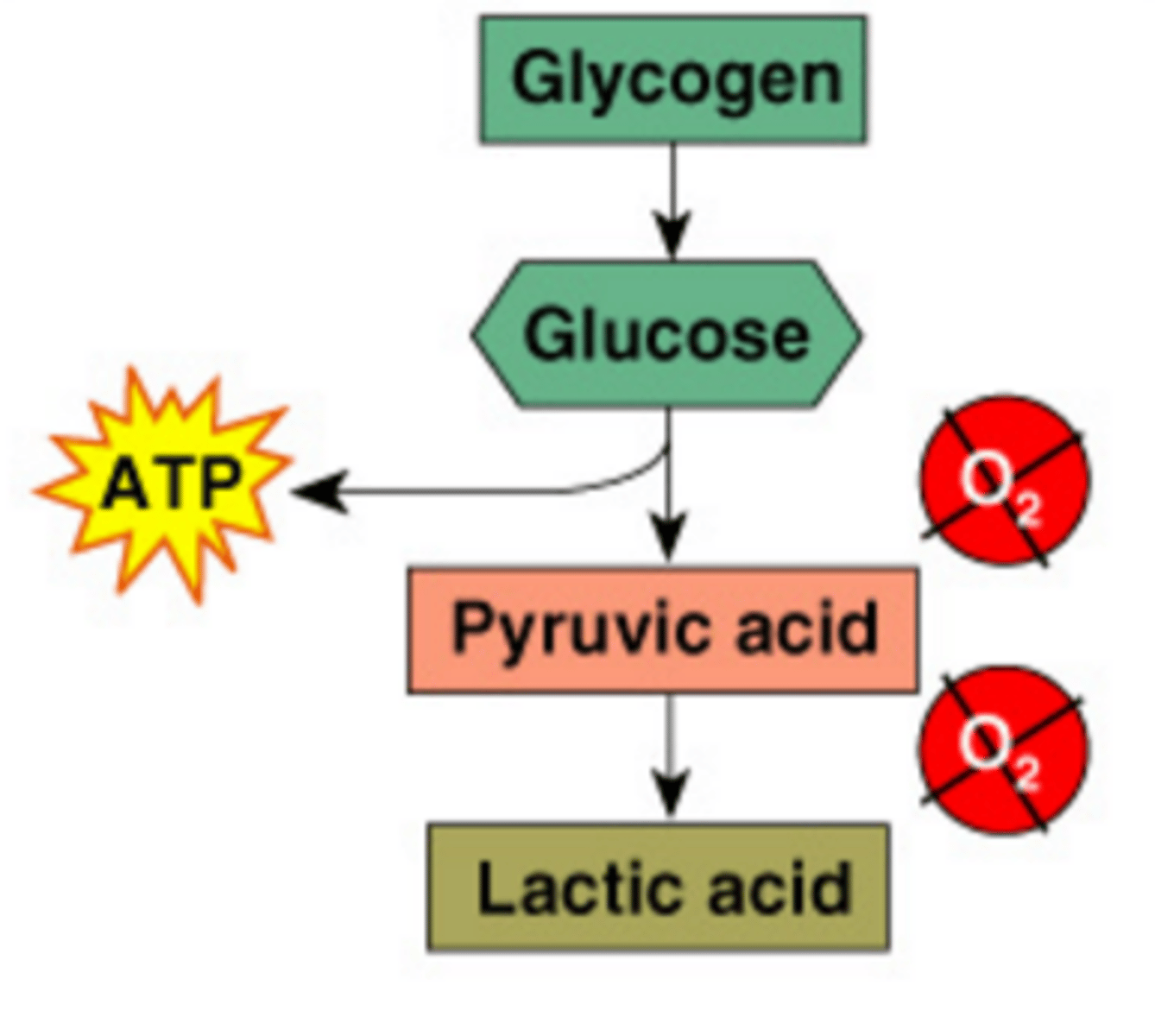
Anaerobic respiration
The process of releasing energy from food without the use of oxygen; includes glycolysis and lactic acid fermentation

Lactic acid
A chemical produced in the muscles when glucose is broken down during strenuous muscular activity; accumulation of this chemical creates the soreness in muscles after prolonged heavy exercise

Muscle fatigue
A condition in which the muscle is no longer able to contract; usually caused by a lack of energy due to overexertion and build up of lactic acid
Muscle contraction (Types)
Isometric muscle contraction
Isotonic muscle contraction
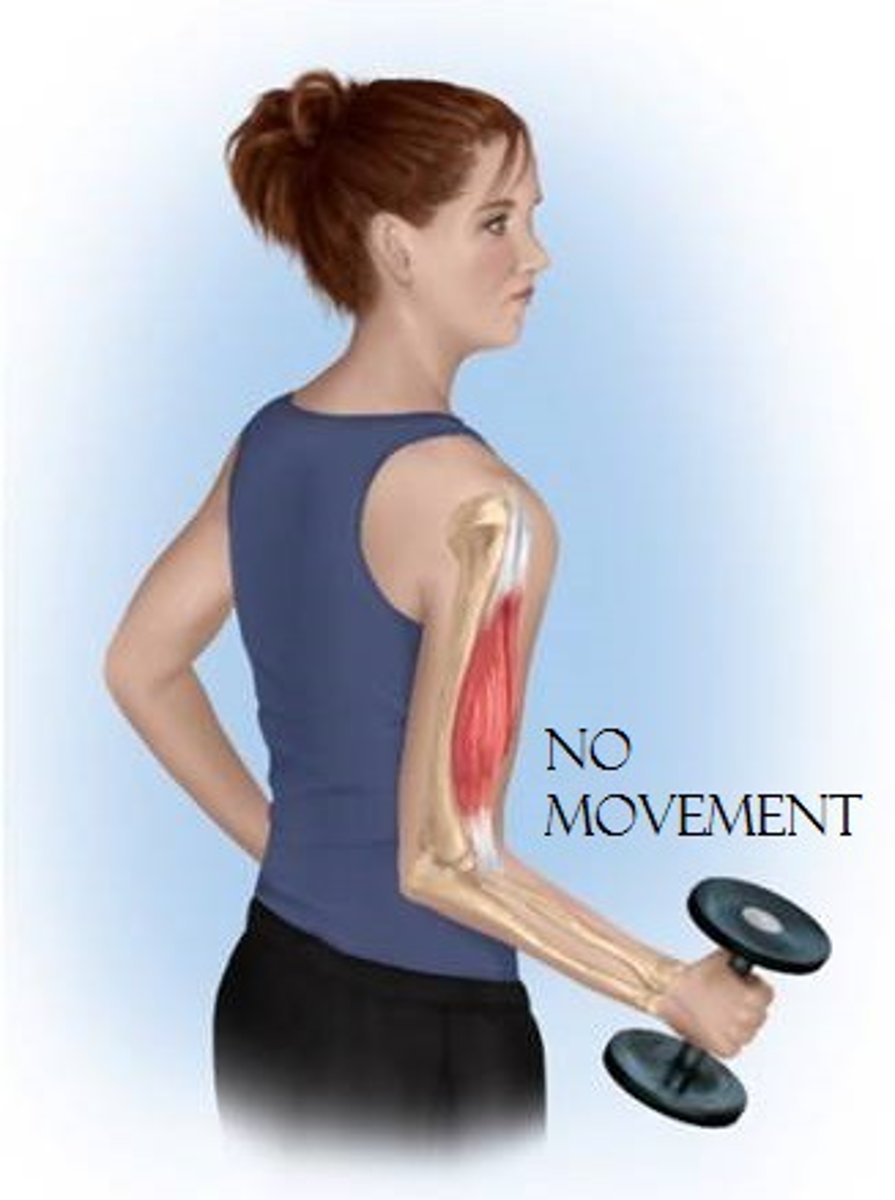
Isometric muscle contraction (Description)
A static contraction in which muscle tension is generated but the myofilaments are NOT able to slide past one another; as a result the body does not move
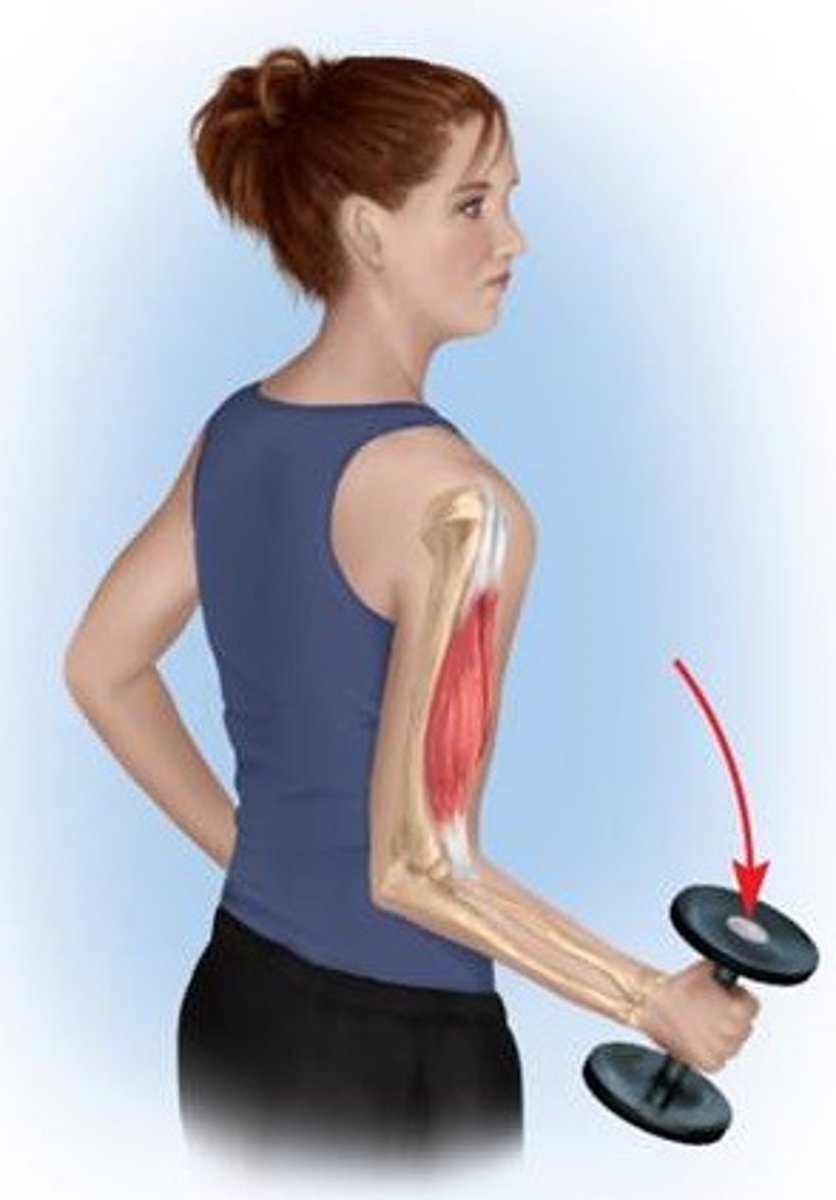
Isotonic muscle contraction (Description)
Myofilaments are able to slide past each other during contraction and the muscle shortens
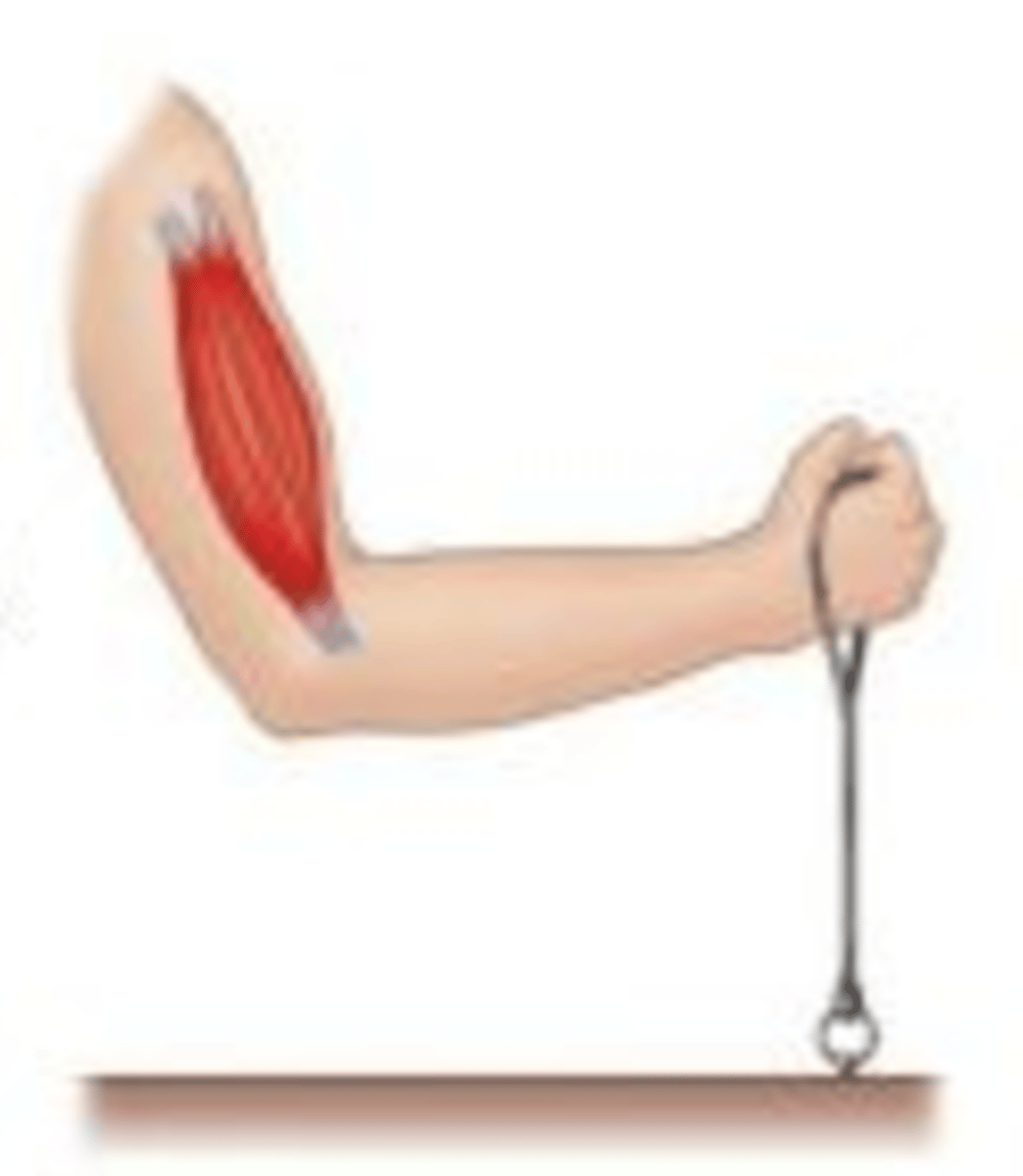
Isometric muscle contraction (Example)
Pushing against a wall or trying to lift a weight that is too heavy
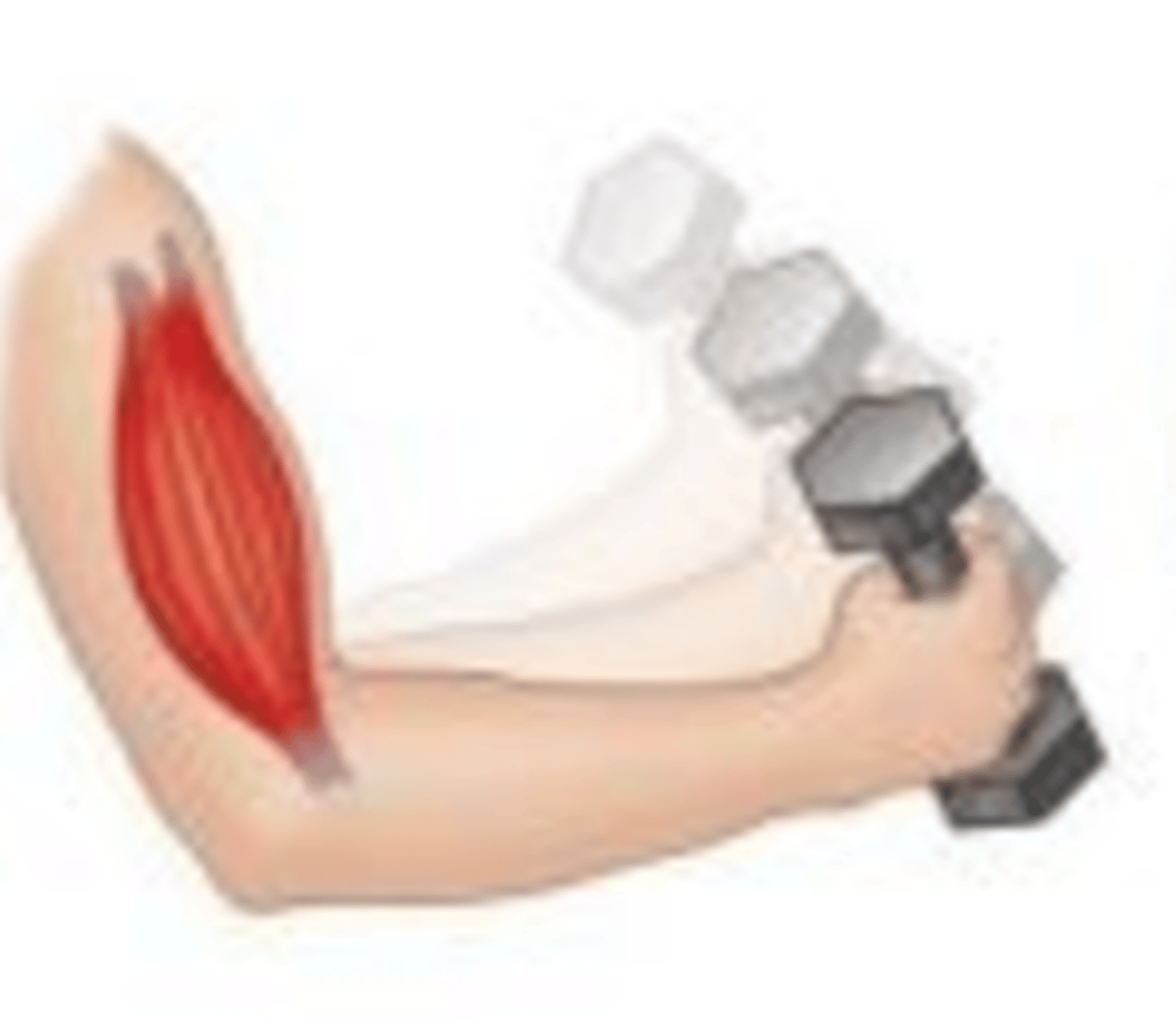
Isotonic contraction (Example)
Lifting a weight
Muscle tone
The condition in which some fibers are contracted even in a relaxed muscle; different fibers contract at different times; under involuntary control
Effects of exercise on muscle
Results in the increase in muscle size, muscle strength muscle efficiency and more fatigue resistance