Mulliken Symbols & Degrees of Freedom (9/15)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is commuting?
Two operations where the order in which they happen does not matter.
What commutes with a rotation?
a rotation about the same axes
an inversion
a reflection in a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis
What commutes with a reflection?
another reflection on a perpendicular plane
an inversion
a rotation in a plane if the rotation is perpendicular to the rotation axis
What is a character table?
irreducible representation of a point group
In a character table, are the columns carried out first or the rows?
columns
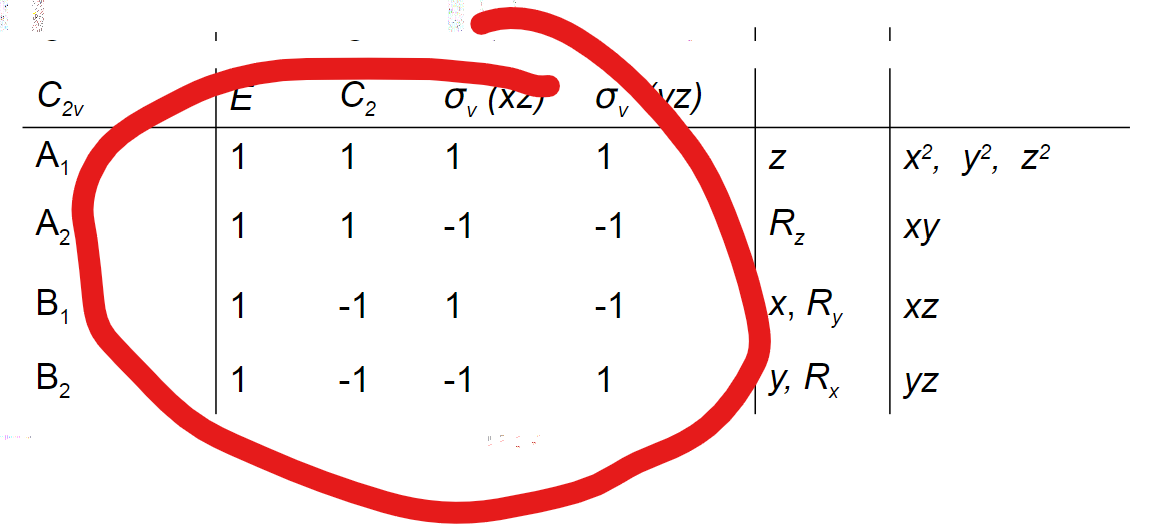
What is in the upper left hand corner of a character table?
Schoenflies notation for the point group (ex. C2v)
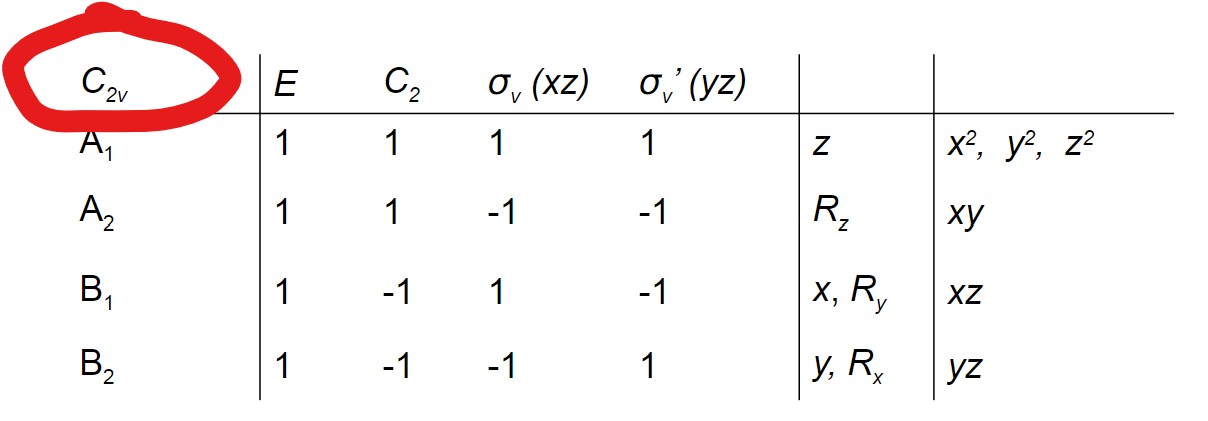
What is in the lower left hand section of a character table?
Mulliken symbols of representations

What is in the upper middle-left section of a character table?
The operations of the point group for the point group described in upper left

What is in the lower middle-left section of a character table?
The representations of a group, entry = character
What is in the lower middle-right section of a character table?
Symbols for coordinates (xyz) and rotations (Rx Ry Rz)
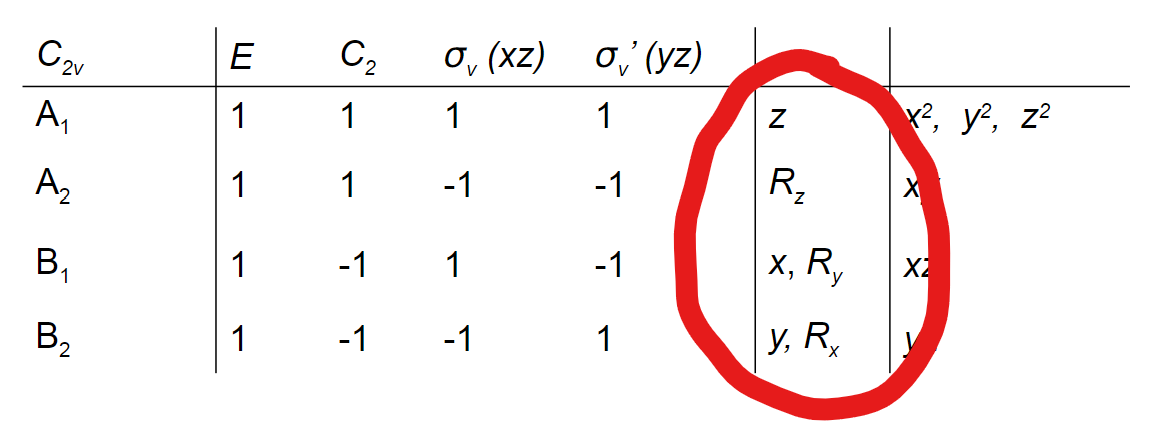
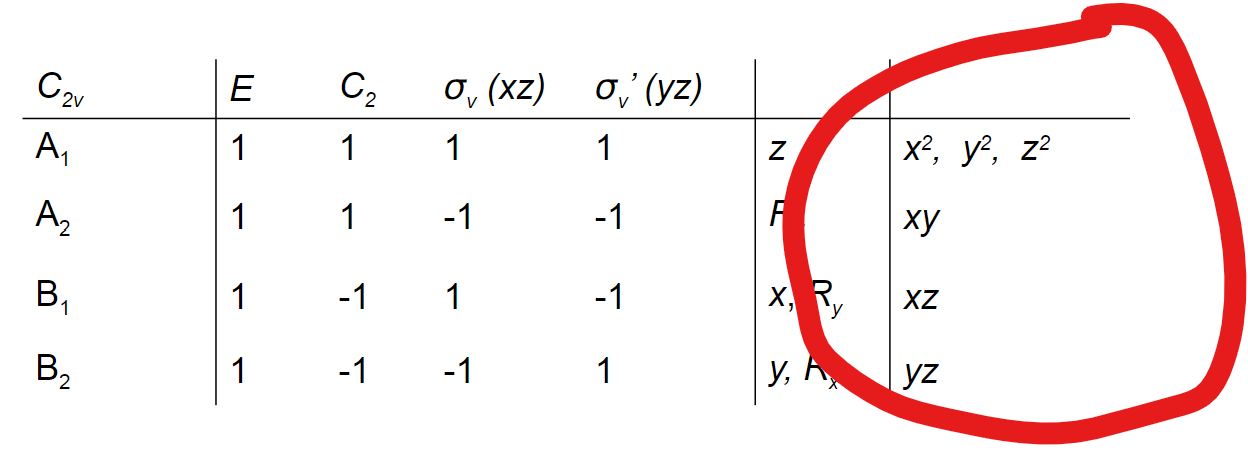
What is in the lower right section of a character table?
The squares or binary products of coordinates
What does 1 and -1 mean in entries?
1 means symmetry, -1 means asymmetry
What’s always in the first row of a character table? What is this called?
All 1s - called totally symmetric
What type of atomic orbitals relate to the right column of a character tables?
d-orbitals
Describe the different d-orbitals.
The clover with leaves that don’t align with the axes are the dxy, dxz, and dyz orbitals. The clover with leaves that do align is the dx^2-y^2 orbital.
The one that looks like a p-orbital with the ring is z2.
If the Mulliken Symbol is A, what does this mean?
1 under E, 1 under Cn
If the Mulliken Symbol is B, what does this mean?
1 under E, -1 under Cn
If the Mulliken Symbol is E, what does this mean?
2 under E
If the Mulliken Symbol is T, what does this mean?
3 under E
What does the subscript of 1 mean under A or B in Mulliken Symbols?
1 under C2
What does the subscript of 2 mean under A or B in Mulliken Symbols?
-1 under C2
What does prime mean in Mulliken Symbols?
symmetric to mirror plane
What does double prime mean in Mulliken Symbols?
antisymmetric to mirror plane
How many reducible representations do molecules have?
infinite
What is the range of IR spectroscopy in mu meters?
2.5-1000
In v = (1/2pi*c) * (k/M)^1/2, what does the v stand for and what units is it in?
vibrational frequency 1/cm
In v = (1/2pi*c) * (k/M)^1/2, what does the c stand for and what units is it in?
speed of light; 299,000,000 m/s meters/second
In v = (1/2pi*c) * (k/M)^1/2, what does the k stand for and what units is it in?
Force constant
dxne/cm dxne = 1 g*cm / s^2 → dxne is the change in energy vs nuclear distance; measuring curvature of that well
In v = (1/2pi*c) * (k/M)^1/2, what does the M stand for?
reduced mass (product of masses / sum of masses).
What is the requirement for a molecule to be IR-active?
dipole moment change
What is the requirement for a molecule to be Raman-active?
polarizability change
What type of symmetry does IR have?
u
What type of symmetry does Raman have?
g
What are the two main vibrational modes?
stretching and bending
What is scattering? What are the three main types?
Scattering is going from ground to virtual energy states in photons.
rayleigh
stokes raman
antistokes raman
Which type of scattering is elastic?
Rayleigh
Describe the scattering that is inelastic (loss of energy).
Stokes Raman.
Describe the scattering that is inelastic (gain of energy). What special condition does this require?
Antistokes Raman Scattering. Requires an already excited photon.
What degrees of freedom do all molecules have?
three translational: x, y, and z axes
What degrees of freedom do non-linear molecules have?
3n-6
What degrees of freedom do linear molecules have?
3n-5
What is the equation for degrees of freedom?
3n, n=number of atoms
What type of vibrational mode won’t be IR active?
symmetric stretch (no dipole moment change)