tropes & schemes
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
a trope is to speak figuratively and a scheme is pertaining to syntax
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
anaphora
the repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of successive clauses or sentences.

anastrophe
changing the normal word order for emphasis. Ex. “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.”

antithesis
a rhetorical device that contrasts opposing ideas in a balanced structure, often to highlight differences. Ex. "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times."
apostrophe
a figure of speech in which a speaker addresses an absent person, an abstract idea, or a thing. Ex. "O Death, where is thy sting?"

epistrophe
(OPPOSITE OF ANAPHORA) the repetition of a word or phrase at the end of successive clauses or sentences. Ex. "Where now? Who now? When now?"

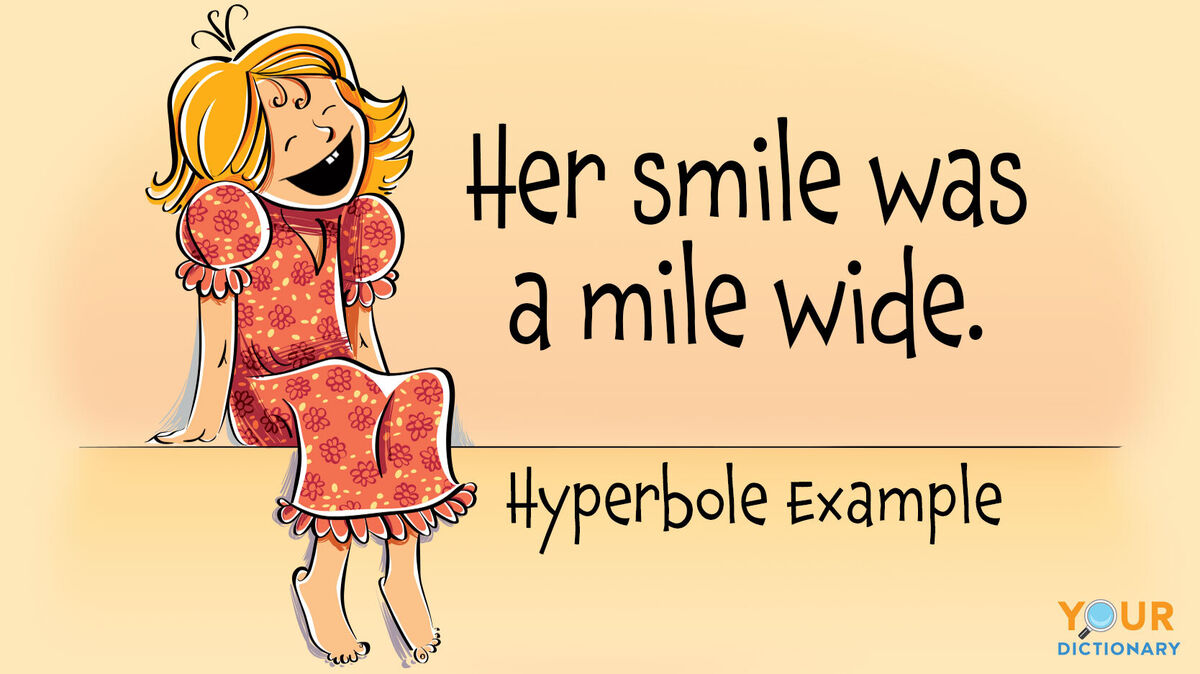
hyperbole
an exaggerated statement not meant to be taken literally, used for emphasis or effect. Ex. "I’m so hungry I could eat a horse."
irony
the expression of one's meaning by using language that normally signifies the opposite, often for humorous or emphatic effect. Ex. A fire station burns down.

litotes
a figure of speech that employs an understatement by using double negatives or, in other words, a positive statement expressed by negating its opposite. Ex. "Not bad" to mean "good."

metaphor
a figure of speech that makes a direct comparison between two unlike things by stating one is the other, often used to illustrate a point or create imagery. Ex. "Time is a thief."

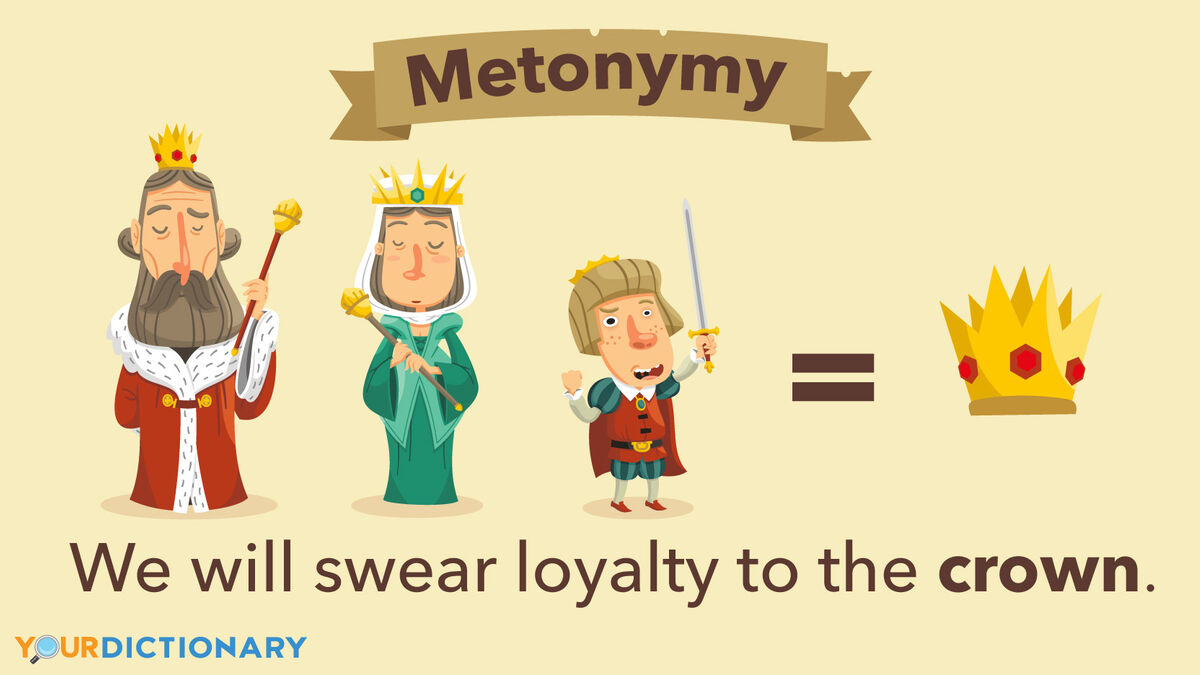
metonymy
a figure of speech in which a thing or concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with it. Ex. "The White House announced a new policy." instead of presidential building
oxymoron
a figure of speech in which contradictory terms appear in conjunction. Ex. "deafening silence."

periphrasis
substituting a descriptive word or phrase for a proper noun. Ex. “The big man upstairs hears your prayers.”

personification
attributing human qualities to non-human entities or objects. Ex. "The wind whispered through the trees."

pun
a form of word play that exploits multiple meanings of a term or similar-sounding words for humorous effect. Ex. "Time flies like an arrow; fruit flies like a banana."

rhetorical question
a question posed for effect, not requiring an answer. Ex. "Isn't it a bit too late to apologize?"

similie
a comparison using like or as

syneedoche
a part stands for the whole. Ex. “Tom just bought a fancy new set of wheels”.

zeugma
one verb governs several words, each in a different sense. Ex. He stiffened his drink and his spine.
