Mitosis One pager
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the basis of cell divsion
organisms are able to reproduce
Cell divison overall idea and process
when one cell becomes two
DNA is replicated in the orginal cell and each new cell recieves one copy of the DNA
Unicellular organisms reproduction and examples
Produce a whoel new organism that is genetically identical
Yeast, Bacteria, Protists
Asexual reprodution idea and examples
Only one organism is needed to Produce a genetically identical offspring
Starfish, plants
3 reasons why cells need to divde
Growth and devleopment
Replace damaged cells
Produce gametes for sexual reporduction
2 types of cell divison
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis goal
Make a genetically identical copy of a cell
DNA of orgainl cell msut be copied
What is a parent cell
Orginal cell
What is daughter cell
The resulting two cells durign mitosis
Define chromosomes
DNA divded into indiviudual segments
Define Histones
Protein complexes that DNA is wrapped around. Helps compact DNA into chromosomes
What does a chromosomes look like
An X

How many chromosomes does each cell in a human have
23 pairs (22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosomes)
Define diploid organism
Organisms that have 2 copies of each chromosome in the cell
Define centromere
how duplicated chromosomes stay attached to the orginal
where sister chromatids connect
Define sister chromatids
The duplicates —> Will soon be split up into two new cells
What is replicated during mitosis
Chromosomes
Pitchure of replicating chromosome
2 chromatids (each half of the chromosome) are duplicated to form 2 chromosomes
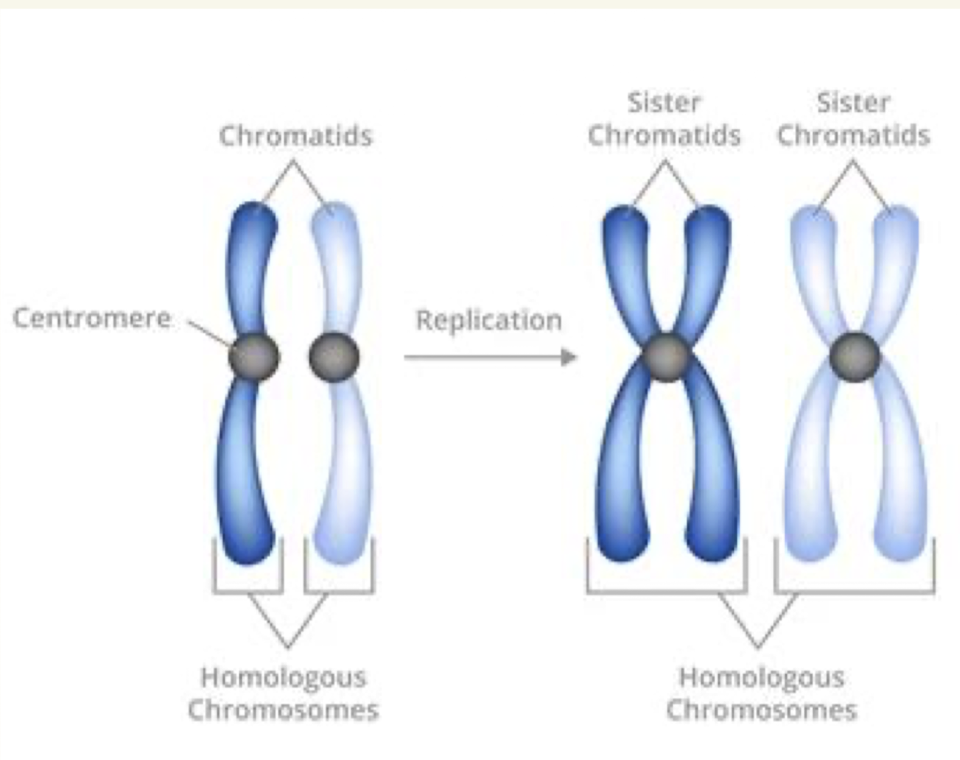
Where do we get two copies of chromosomes
one from each of our parents
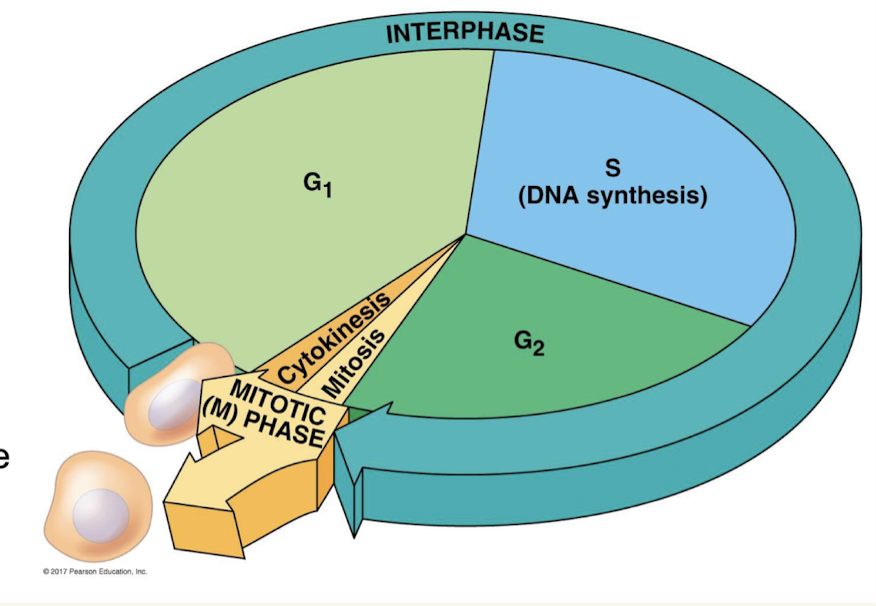
4 stages of Mitosis cycle
G1
S
G2
M
what does interphase include
G1, S, G2
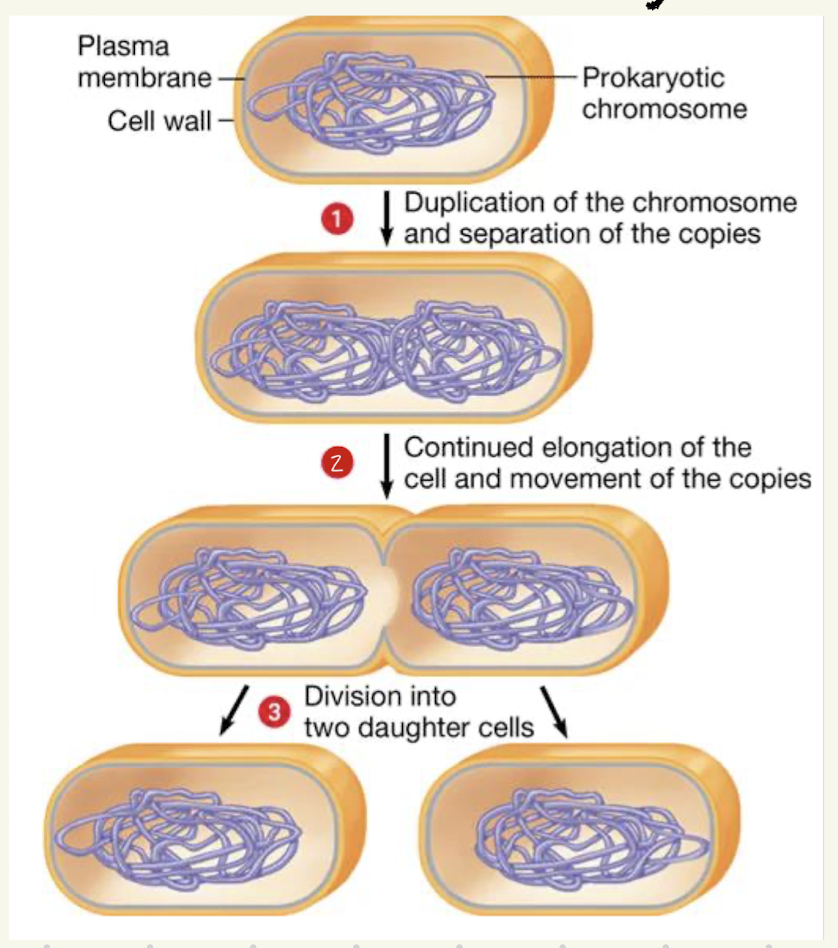
How do prokaryotes reproduce
Chromosomes are duplicated
Copies are separated
Cell elongates
Cells are divided into two daughter cells
G1 basic idea
Growth phase 1 that gets the cell ready for divsion
S basic idea
Synthesis phase refers to the duplcaiting of DNA
G2 basic idea
S phase uses alot of energy so growth pahse 2 gives the cell a chance to rebuild its energy supply
M basic idea
Mitotic phase, the actual division of the cell
G1 phase explained
We want the daughter cells to be the same size as the parent cell. The cell must grow in size for this to happen
Enzymes and proteins for cell divison are also made here
Synthesis Phase expalined
DNA replication that uses alot of ATP
G2 phase explained
Cells must rebuild their energy supply before proceeding to M phase
Also checks to make sure all DNA was replicated
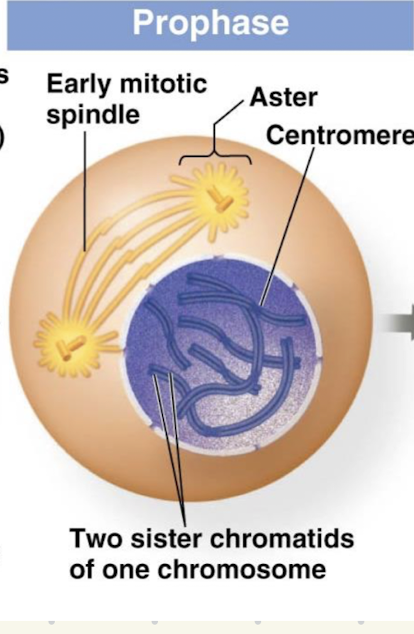
Microtubules
Orginate from centrosomes as they migrate to opposite sides of the cell
These attach to the sister chromatids
Kinetochore protiens
Connects both the sister chromatids and microtubules originating from the centrosomes
Six steps of Mitosis
Prophase
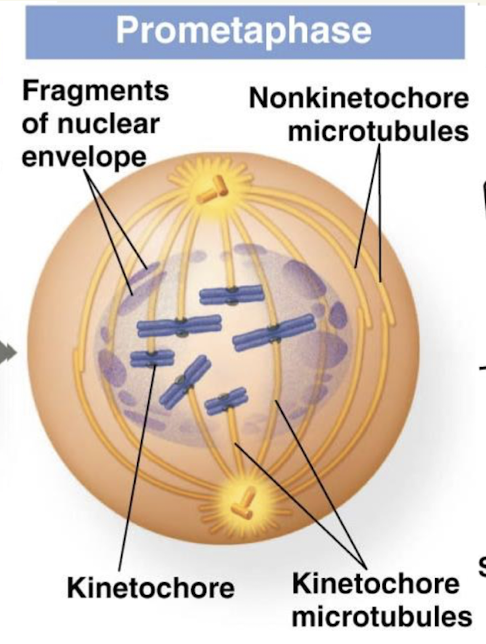
Prometaphase
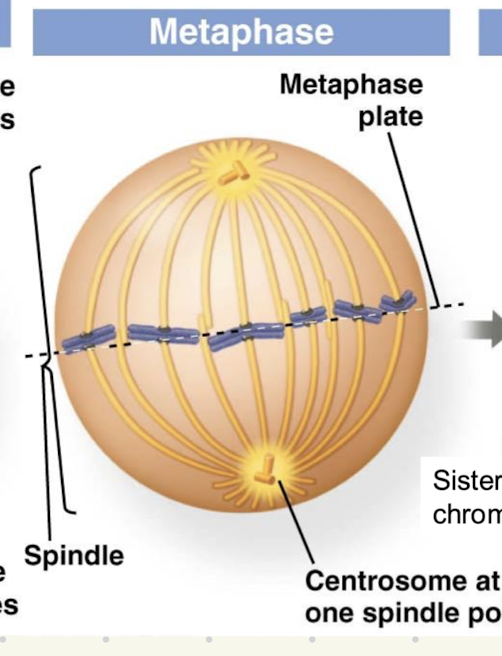
Metaphase
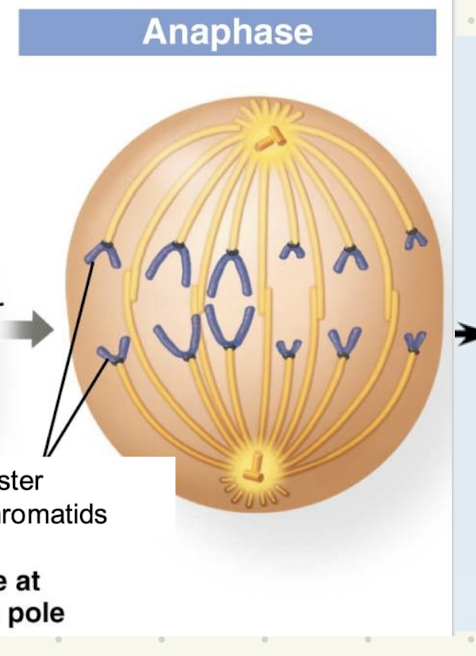
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Polly Pocket Met A Toy Cat
Metaphase plate
Line of chromosomes in metaphase plate
Mitosis
Where one cell becomes two
6 stages
Prophase
DNA is condensed
Centrosomes start to migrate
Prometaphase
Nuclear envelope completely breaks down
Chromosomes are exposed in the cytoplasm
Centrosomes are now on exact opposite sides of the cell
Metaphase
All duplicated chromosomes are arranged in the middle of the cell by the action of the mitotic spindle and microtubules
Each sister chromoatid of duplcaited chromosomes faces one of the centrosomes
Anaphase
Sister chromatids are pulled apart and carried to the centrosomes on opposite sides of the cell
Telophase
Separated sister chromatids and sequestered at opposite sides of the cell.
New nuclei begin to envelope the chromosomes
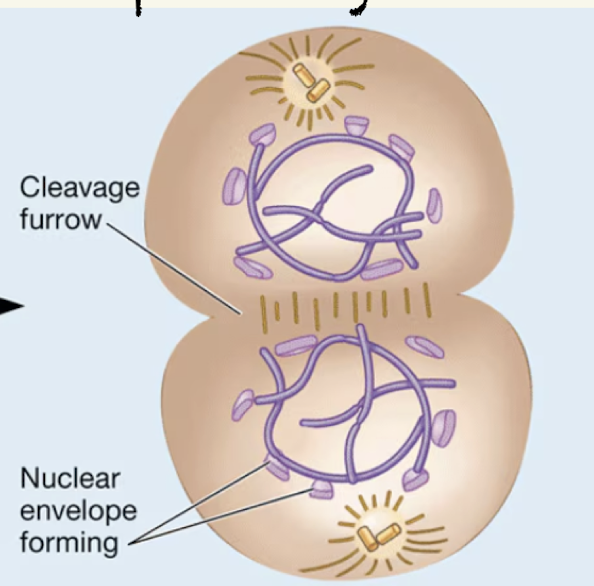
Cytokensis
Splitting of the cell
Diffrent in plants and animals
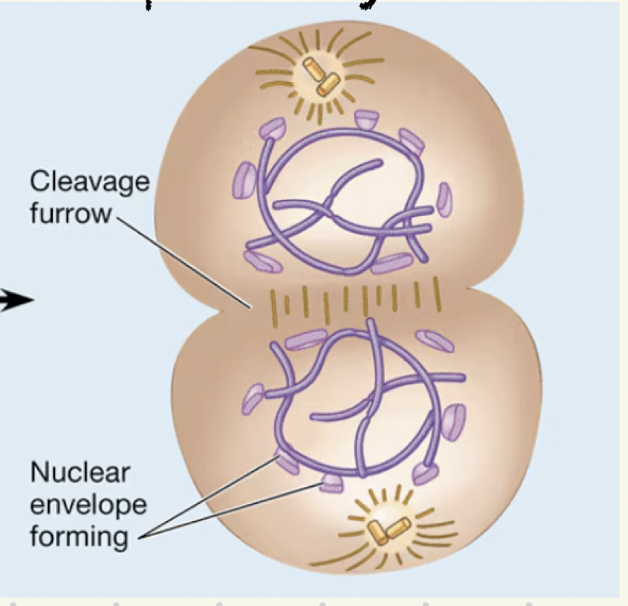
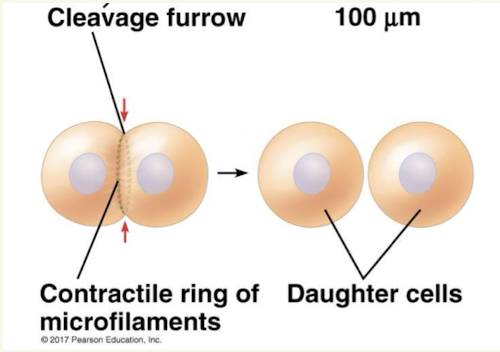
Cytokensis in animal cells
Cleavage furrow that pinches the new cells apart
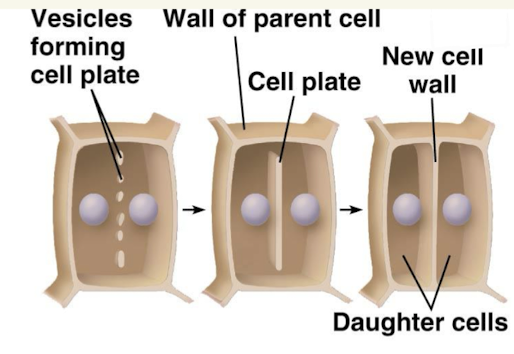
Cytokenesis in plants
A new plant wall is built using vesicles
Mitotic cell cycle checkpoints
G1 checkpoint
G2 checkpoint
Metaphase checkpoint
G1 checkpoint
Waiting for all clear to divide
Checks for:
Nutrients
Growth factors
DNA damage
IF problems are found the cell will be sent to G0
located at end of G1
G2 checkpoint
Checks for Cell size and if the DNA replcaited
Located at end of G2
Metaphase checkpoint
Within mitoic phase
Checks for chromosome spindle attamenent
What could happen if the G1 checkpoint was messed up
Damaged DNA could be replicated and produce daughter cells with damaged DNA
What could happen if the G2 checkpoint was messed up
If DNA is not fully replicated than one of the daughter cells will be missing DNA that will most likly kill the cell
What could happen if the Metaphase checkpoint was messed up
if chromosomes are not attached to the spindle properly then each daughter cell could inherit diffrent number of chromsomes
Cell reproduction life cycle picture
G1 is the longest