Lecture 20 CH 27 - Species Interactions
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
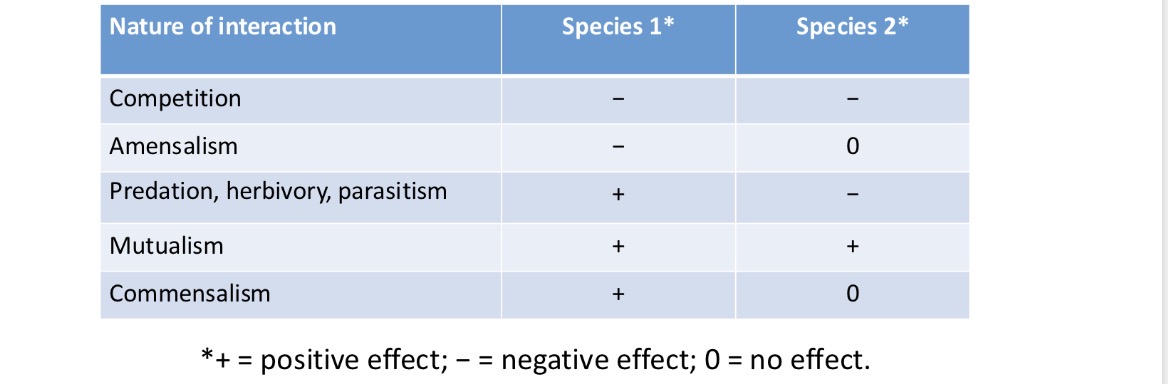
Species interactions
The various ways in which a species can interact with other species, such as predation, competition, parasitism, mutualism ,and commensalism
Competition
An interaction that affects two or more species negatively as they compete over food or other resources
Amensalism
One-sided competition between species, in which the interaction is detrimental to one but not the other
Predation
An interaction in which the action of a predator results in the death of its prey
Herbivory
A form of species interaction in which herbivores feed on plants
Parasitism
A symbiotic association in which one organism feeds off another but does not normally kill it
Pathogen
An agent, such as a virus, bacterium, or parasite which causes disease symptoms in humans or other species
Mutualism
An interaction where both species benefit
Commensalism
Benefits one species and leaves the other unaffected
Summary of types of species interactions
Intraspecific
Between individual of the same species
Interspecific
Between individual of different species
Exploitation competition
Organisms compete indirectly through consumption of a limited resource
Interferenece competition
Individuals interact directly with one another by physical force or intimidation
Allelopathy
The suppression of growth of one species due to the release of toxic chemicals by another species
Niche
The unique set of habitat resources a species requires as well as its effect on the ecosystem
Species with the same requirements cannot live together in the same place with the same resources - They ____ occupy the same niche
Cannot (Gause study on paramecium species
Competitive exclusion principle
The idea that two species with the same resource requirement cannot occupy the same niche
Resource partitioning
Differentiation of niches, both in space and time, that enables similar species to coexist in a community
Morphological difference may allow
Co existence
Sympathetic
Same geographic area
Allopathic
Different geographic area
Size differences did not occur in ___ species
Allopatric
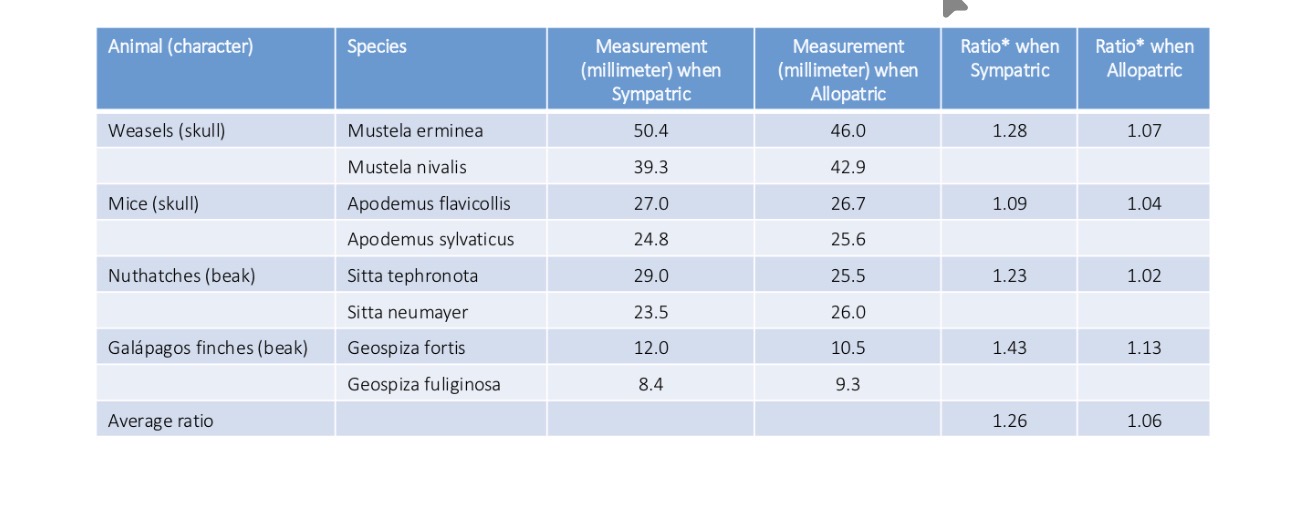
Character displacement
Tendency for two species to diverge in morphology and resources use due to competition
-example: Galapagos finches
Comparison of feeding characters of sympathetic and allopatric species
Fundamental niche
Most species perform best over a physiologically optimal range of conditions
Realized niche
The actual range of an organism in nature
Predation, Herbivory and parasitism
Are interactions that have a positive effect for one species and a negative effect for the other.
-categories of predation can be classified by
-how lethal they are
-length of association between consumer and prey
Antipredator strategies
Chemical defense, aposematic coloration and camouflage
Chemical defense
-example bombardier beetle ejects hot spray
Aposematic coloration
Warning coloration which advertises an organisms unplatatable taste
Example - many lethal tropical fogs have bring coloration
Camouflage
Cryptic coloration
Catalepsis - maintenance of a fixed body position
-example- stick insects, sea horses
Mimicry
Resemblance of mimic to another organism
Mullerian mimicry
Noxious species converge to reinforce warning
-black and yellow stripes on bees and wasps
Batesian mimicry
Palatable mimic resembles unpalatable model
Example - scarlet king snake and coral snake
Herbivory
-involves the consumption of plant material or the material of similar life-forms such as algae
-can be lethal to plants
-often nonlethal because many plant species, particularly larger ones can regrow
Mechanical defense - plant defenses
-thorns and spines
-tough fibers
-silica in grasses and palms
Secondary metabolites
Molecules that are produced by secondary metabolism
Host plant resistance
The ability of plants to prevent Herbivory via either chemical or mechanical defenses
Herbivores can overcome plant resistance by
Detoxify - two pathways, oxidation and conjugation
Oxidation
catalysis of secondary metabolite to corresponding alcohol by mixed-function oxidases
Conjugation
Unites results of oxidation with another molecule to create inactive and readily excreted product
Invertebrates herbivores like insects have a ____ effect on plants populations than vertebrate herbivores such as mammals, at least in terrestrial systems
Stronger
Parasite
An organism that feeds on another organism, called the host, for a relatively long time, but does not normally kill it outright
Host
Prey
Predatory organism
is termed a parasite