Math 8 Midterm 2
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vectors
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Distance Between Three Points
𝑑=√(𝑥2−𝑥1)2+(𝑦2−𝑦1)2+(𝑧2−𝑧1)
Equation of a Sphere
(x - h)² + (y - k)² + (z - l)² = r².
The zero vector
Is a vector in which all components are zero, represented as (0, 0, 0) in three-dimensional space.
The Dot Product
Is an operation that takes two equal-length sequences of numbers (usually coordinate vectors) and returns a single number, calculated as the sum of the products of their corresponding components.
Large Dot Product
Indicates that the two vectors being multiplied are pointing in similar directions. A larger dot product reflects a greater degree of alignment between the vectors.
Orthogonal Vectors
Are vectors that are perpendicular, indicating that their dot product is zero.
Law of Cosines
relates the magnitudes of two vectors 𝐮 and 𝐯 to the magnitude of their difference vector, where theta is the angle between the vectors when placed tail-to-tail.
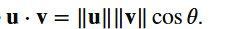
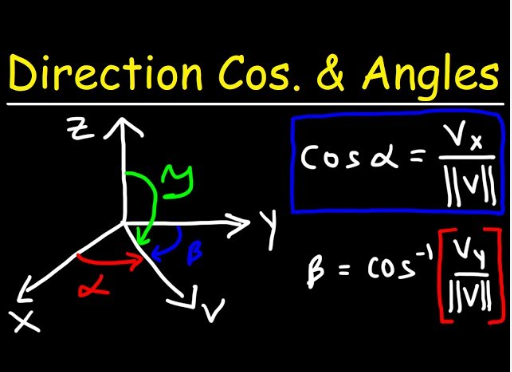
Direction Angles
Direction angles are the angles a vector makes with the positive x, y, and z axes in a 3D Cartesian system, denoted as alpha, beta, and gamma (\(\gamma \)), respectively; The sum of the squares of all the direction cosines is going to be 1
Scalar Projection
The definition of scalar projection is the length of the vector projection. When the scalar projection is positive, it means that the angle between the two vectors is less than 90 Degrees. When the scalar projection is negative, it means that the two vectors are heading in opposite directions.
Vector Projection
calculates how much of one vector extends in the direction of another
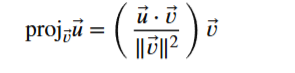
Parallel Vectors
Magnitude of Cross Product
Direction of Cross Product
Triple Scalar Product