Veterinary Parasitology CH3 - Introduction to Nematodes
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study material for Chapter 3 of Diagnostic Parasitology for Veterinary Technicians. For class BIO225 at MWCC.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
The common name of Nematodes is...
Roundworms
Nematodes are...
Multicellular and unsegmented, long, round on both ends
Size range of Nematodes is...
2mm - 1m long, 35um - 1.2cm wide
Nematodes shapes are...
Spherical or Whiplike
Cuticle
Secreted from the hypodermis
Cervical alae
Flattened extensions around the anterior end
Caudal alae/Copulatory bursa/Bursa rays
Lateral flattened extensions of posterior end of male nematodes — holds female during mating
Contains "chitinous spicules" (penis)
The somatic muscular layer is essential for what?
Locomotion
The muscles of the body cavity (pseudoceolom) are essential for what?
Movements of feeding and reproduction
What are the two most important organs?
Reproductive and digestive
The 2-8 lips around the mouth or in some worms, papillae, are called what?
Leaf crown
True or false: Males have a rectum like the females
False; the male has a cloaca
Nematodes are dioecious, this means...
They have separate male and female sexes
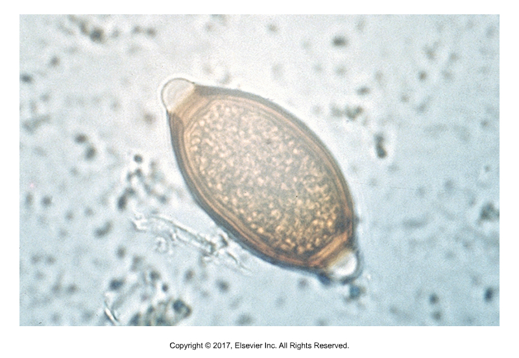
Ascaroid egg
Single cell within egg shell, oviporous
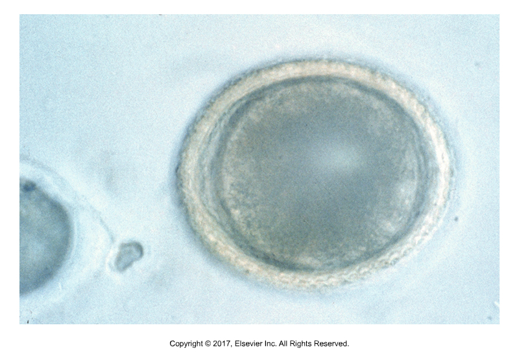
Strongyle egg
Morula (multicellular), oviporous
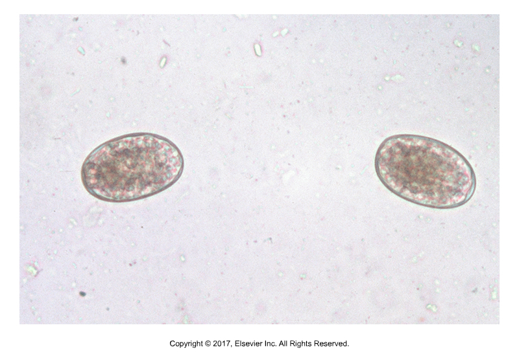
Spiruroid egg
First stage larva within egg shell, ovoviviparous
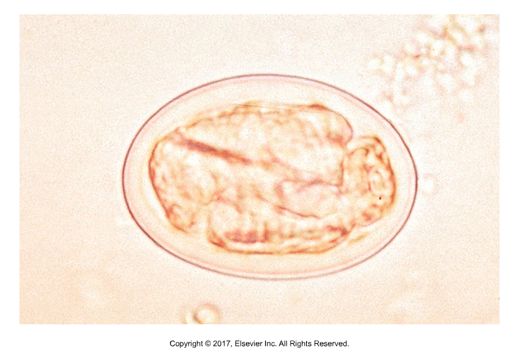
Trichuroid/Trichinelloid egg
Single-cell stage within egg shell, oviparous
Oviparous
Eggs contain single cell or multi-cell (morula) stage inside shell
Ovoviviparous
Eggs contain first stage larva inside shell
Larviparous
Female retains eggs in uterus, gives birth to live larvae
Life cycle of nematodes
Female produces single cell egg
Cell divides (morulates) into tadpole
Develops into first stage larva
Hatches from egg and molts (sheds cuticle) into second stage larva — in environment or intermediate host
Molts again into infective third stage larva — infects definitive host
Molts into fourth then fifth stage larva — immature adult
Migrates to preferred organ and develops into sexually mature adult
Direct life cycle
Does not go through intermediate host
Indirect life cycle
Goes through intermediate host