Geography paper 1 section B
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
what is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a natural system made up of biotic (living e.g. plants) and abiotic (non-living, e.g. sunlight) components.
Example of a small scale ecosystem?
A pond is an example of a small scale UK ecosystem. Different components perform different functions in an ecosystem.
3 components which perfom different functions in an ecosystem?
Producers , consumers, decomposers
What do producers do?
They receive their energy from the sun and convert this into biomass (e.g. plants)
What do comsumers do?
They receive energy by eating producers or other consumers (e.g. fish)
What do decomposers do?
They recycle nutrients by breaking down dead plants and animals and returning nutrients to the soil (e.g. fungi and bacteria)
What does food chains and food webs show?
The biotic and abiotic components interect. Food chains and more complex food webs show how energy moves through different trophic levels in an ecosystem.
What happens when one component in an ecosystem changes?
Changing one component in an ecosystem has knock on effects on all components. If frogs were removed, mayflies could thrive, affecting other parts of the ecosystem.
distribution and characteristics of tropical rainforeests?
Roughly 1-10o north and south of the Equator. Hot and wet climate. Lush and diverse vegetation
distribution and characteristics of hot deserts
Roughly 15-35o north and south of the equator. Hot and dry climate. Sparse vegetation like cacti.
distribution and characteristics of Temperate grassland
Roughly 25-40o north and south of the equator. Hot summers and cold winters with wet and dry seasons. Mostly grasses.
distribution and characteristics of temperate deciduous forest?
roughly 30-60o north of the equator. Mild and wet climates with four seasons. Broadleaf trees that lose their leaves in winter, like oaks.
distribution and characteristics of tropical grassland (savanna)
Roughly 10-20o north and south of the Equator. Hot climate with wet and dry seasons. grasses with occasional trees.
distribution and characteristics of coniferous forests?
Roughly 50-60o north of the equator. cold and dry winters and mild summers. Evergreen trees like pines and firs.
distribution and characteristics of Tundra
Roughly 60-75o north of the equator. cool summers and cold winters. Low-lying vegetation like mosses and lichens.
Characteristics of a tropical rainforest
The climate in a tropical rainforest is hot all year round. Average temperatures are 27oC. Rainfall is high but it is very high for 6 months of the year. Rainforests also create their own climate through the water cycle. Heavy rainfall is rapidly returned to the atmsphere through evaporation and transpiration. This then condenses into clouds, leading to more rainfall.
The hot and wet climate provides ideal conditions for plant and animal species to thrive. Tropical rainforests have more biodiversity than any other ecosystem, containing half of the Earth’s land-based plant and animal species.
The soil in the rainforest have few nutrients because nutrients are leached (washed out) by the heavy rain. However, rapid nutrient recycling means nutrients are stored in the biomass (plants) rather than the soil.
Rainforest nutrient cycle
Leaves fall to the ground (rainfall washes some nutrients away and adds some nutrients.)
leaves rapidly decompose
nutrients added to the soil (some nutrients washed away and some nutrients added from weathered rocks)
nutrients taken up by plants
Most nutrients are stored in the biomass (plants)
Rainforest structure
Forest floor
shrub layer
under canopy
canopy
emergents
What is the forest floor
a thick layer of dead leaves, branches and roots
How big is the shrub layer?
There are few shrubs because there is little light
What is the under capnoy layer?
Younger trees fill in gaps in the canopy
What does the canopy layer do?
a continuous layer blocking the light
What are emergents
these are the trees which break through the canopy
Animal adaptations for living in a rainforest
Mnay animals like the leaf-tailed gecko, are camouflaged agaianst predators.
Spider monkeys have long limbs and prehensile (gripping) tails to help move through the trees.
Plant adaptations for living in rainforests
Lianas are vines that reach the light by wrapping around trees
Some plants have waxy drip tip leaves so rainwater runs of easily.
Deforestation of the amazon rainforest?
The amazon is the world’s largest rainforest, 60% of which is in Brazil. Deforestation has been rapid since the 1970’s, with an average of 6000 football pitches cut down every day. Deforestation peaked in 2004, but after a decade of decline has recently been increasing again. The main reason for deforestation is economic development. Many people in Brazil want to explout the Amazon’s resources in oder to develop.
Causes of deforestation
Logging, road building, subsistence farming, mineral extraction, commercial farming, energy development and settlement and population growth.
How does logging cause deforestation?
Logging accounts for about 2% of deforestation. Much of it is illegal. Valuable hardwood trees like mahogany are cut down and exported for furniture.
How does Road building cause deforestation?
Road building only accounts for a small amount of deforestation but is significant because it opens up the rainforest to subsistence farming, logging, and other activities.
How does subsistence farming cause deforestation?
Subsistence farming accounts for about 25% of deforestation. This is when local brazilians move into the Amazon to grow food for themselves and their families.
How does Mineral extraction cause deforestation?
Mineral extraction like golf and copper mines produce exports for the global market. The iron ore mine at Carajas is the world’s largest mine, employing 3000 people.
How does Energy development cause deforestation?
Energy development is when generated hydroelectric power floods huge areas of land.
How does settlement and population growth cause deforestation?
Towns like Manaus near Carajas grow through migration as people move from other parts of Brazil in search of work
How does Commercial farming cause deforestation?
It accounts for about 70% of deforestation, mostly due to cattle ranching. Trees are cut down to provide land to rear cattle to supply the beef and leather industries. There are also large commercial farms growing crops like soy.
how does local climate change impact deforestation in the Amazon
Rainsorest trees create a local water cycle by releasing moisture through evapotranspiration.
Rainforests generate 75% of their own rain this way
Removing trees leads to a drier and hotter environment
Summer temperatures in the Amazon have increased by 3.2oC since 1980.
This causes more frequent drought and forest fires, destroying more trees.
How does global climate change impact deforestation in the Amazon
The Amazon absorbs 25% of global CO2
The amount it absorbs has reduced 30% since 1990.
The Amazon also stores 150 billion tonnes of carbon
Deforestation releases stored carbon, contributing to the enhanced greenhouse effect
Brazil’s CO2 emissions rose by 9.5% in 2020, largely due to deforestation.
How does increased soil erosion impact deforestation in the Amazon
Trees bind the soil together and protect it from heavy rainfall
Deforestation means the soil is washed away
Nutrients in the soil are also washed (leached) out.
Most rainforest nutrients are stored in the vegetation, so the soil quickly becomes infertile
This means more trees need to be cut down for grazing cattle and growing crops
How does economic growth impact deforestation in the Amazon
Activities like logging and mining have created wealth for many people in Brazil
8% of Brazil’s GDP comes from the Amazon
This means money can be spent on health, education, and building infrastructure
but deforestation has negative impacts on local global climates
The estimated cost of global reduced crop yields caused by Amazon deforestation is US$3.6 trillion over the next 30 years.
The value of tropical rainforests
Rainforests worldwide are important to the people and the environment
They absorb and store CO2, reducing the enhanced greenhouse effect
They regulate local and regional water cycles, reducing drought
They are home to half the world’s plant and animal species
25% of the world’s medicines come from rainforest plants
They provide many resources like fruit, rubber, and hardwood
Indigenous tribes live in the rainforest.
Strategies to sustainably manage tropical rainforests
Selective logging, replanting, Conservation, education, ecotourism, international tropical hardwood agreements and debt reduction
What is selective logging with an example
What is it?
Instead of clearing big sections of forest, only specific trees are felled. These are removed by helicopters or dragged out by animals like elephants
Example: heli-logging is used in Malaysia.
One advantage and disadvantage of selective logging
Advantage
The cycle of destruction is managed and the forest can regenerate.
Disadvantage
The amount of timber obtained is reduced.
What is Replanting and give an example?
What it is?
Forest seeds grown in nurseries are planted to recreate the original forest
E.g. Conservation international is planting 73 million trees in the Amazon.
One advantage and disadvantage of Replanting
Advantage
Some success, especially if done soon after deforestation.
Disadvantages
Impossible to recreate the ecosystem
What are conservations. give one example
What it is
National parks and nature reserve are established to stop deforestation
E.g. Corcovada National Park in Costa Rica
One advantage and disadvantage of Conservations
Advantage
Effective at preserving the forest
Disadvantage
economic development opportunities are reduced
What is education with an example
What it is?
Local people are taught more sustainable ways to make money from the rainforest. People in HICs are encouraged to stop buying products that damage the rainforest.
E.g. The rainforest Alliance work with farmers in Peru to promote sustainable coffee production
One advantage and disadvantage of education
Advantages
Money is earned in a more sustainable way
Disadvantages
Relies on goodwill rather than legal agreements
What is ecotourism and give an example
What it is?
Small-scale tourism where tourists stay in ecolodges and are educated about the rainforest by local guides
E.g. Monteverde Cloud Forest in Costa Rica
One advantage and disadvantage of ecotourism
Advantages
Local people earn money through conserving the environment
Disadvantages
too small scale to have a large economic benefit
What is international tropical hardwood agreements and give an example
What it is
The 2006 International Tropical Timber Agreement ITTA promotes the sale of timber from sustainable sources (e.g., selective logging) by registering each tree felled.
E.g. ITTA
One advantage and disadvantage of international tropical hardwood agreements
Advantages
Covers 80% of tropical rainforests
Disadvantages
Illegal trade in hardwood is difficult to stop
What is debt reduction and give one example
What it is
Cancelling part of a country’s debt in exchange for conservation of the rainforest. This reduces the economic need for deforestation and has become known as ‘debt for nature swapping’
E.g. The USA paid $21 million to Brazil in 2010 in return for rainforest conservation
One advantage and disadvantage of debt reduction
Advantages
Makes conserving the rainforest economically beneficial
Disadvantages
Has a minimal impact with less than 1% of debt typically affected.
where are polar and tundra environments located
Polar ecosystems are found in the Arctic and Antartic. Tundra is found just south of the Arctic at 60o to 70o north.
describe the climate in polar environments
winter temperatures fall below -50oC
Low precipitation
describe the soil in polar environments
Land is covered in ice so no soil is exposed
describe the plants in polar environments
Little vegetation
mosses and lichens on rocks
Describe the animals in polar environments
very low biodiversity
too cold for most animals
few insects
polar bears, penguins, whales, and seals live in the ocean and on the fringes of the ice
Describe the people in polar environments
some indigenous people
no permanent residents in Antarctica- only scientists
Climate, soils, plants, animals, and people in Tundra environments
Winter temperatures fall to -20oC
Warmer summers
Some precipitation, especially in coastal areas
Describe the soil in tundra environments
Soils frozen (permafrost) but top layer (active layer) melts in the summer
can become waterlogged
infertile and acidic
Describe the plants in tundra environments
Low-growing plants and mosses
Low bushes and small trees in warmer regions
Describe the animals in tundra environemnts
Low biodiversity
more food options for animals
Reindeer, foxes, hares and birds like ptarmigans
Insects like midges and mosquitoes, especially in the summer
Describe the people in tundra environments
Indigenous people and settlements built around mineral (coal/oil) extraction
Issues related to biodiversity
The cold climate and harsh conditions mean that cold environments have low biodiversity. When the ecosystem is damaged, it takes a long time to recover because the growing seasons are short. Global warming is melting sea ice and threatening many species like polar bears, walruses, and seals.
Interdependence in cold environments
All parts of an ecosystem are linked
Describe a cold environment ecosystem: soil, plants, people, animals
Soils
permanently frozen (permafrost).
Few nutrients
Plants
the climate allows little diversity. Slow decomposition when plants die
People
too cold for most humans.
No agriculture and few food sources.
Difficult to build in frozen ground
Animals
the climate and limited food allos low diveristy.
Herbivores live off plants and carnivores live of herbivores.
Animal adaptations to cold environments
thick fur to keep warm
white fur to camouflage
insulating fat
wide feet and large claws to grip on ice
black nose to absorb sunshine
strong sense of smell to find food
Types of Animals: Polar bear, arctic foxes, hares
Plant adaptations to cold environments
Flowers very quickly in the short growing season
low growing to protect it from wind
A cushion-like texture to retain heat
Shallow root systems in frozen ground
Hairy stems to retain heat
Thick and waxy leaves to reduce water loss.
What is a landscape
A landscape is an area whose character has been shaped by the interaction of physical and human processes.
How is the UK’s landscape divided?
The UK’s landscapes are broadly divided by the Tee-Exe lines running from the mouth of the River Tees in north-east England to the mouth of the River-Exe in south-west England.
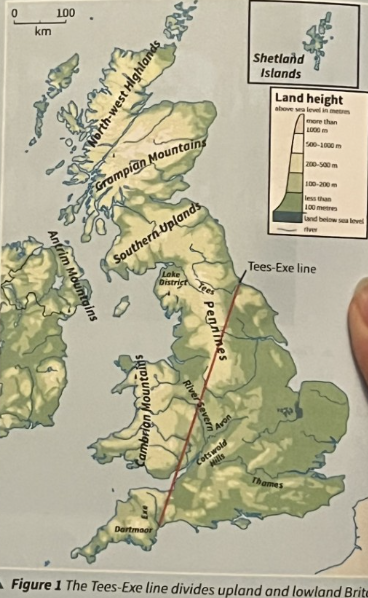
What is the Upland and lowland landscapes in the UK and how is it created?
North of this line are upland landscapes, south of this line are lowland landscapes. These landscapes are created by physical processes and human activity.
Upland Landscapes examples and features
scotland, north and west England, Wales and Northern ireland.
Hard, resistnt rocks like granite and slate
In the north, Wales, and in Northern Ireland, glacial features like aretes, pyramidal peaks and U-shaped valleys.
Lowland Landscapes examples and features
south and east of England
Less resustant rocks like clays and chalk
Rolling hills and flat fens
Describe the UK’s river systems
The UK has an extensive system of interconnected rivers. The longest river is the River severn, which starts the Cambrian Mountains in wales, flows into England where it is joined by the River Avon, and then flows into the Bristol Channel.
Why do Cold Environments need to be protected
Indigenous people like the inuit live there, depending on the fragile ecosystem for their way of life
Untouched wilderness environments are important for scientific study
Mnay plant and animal species only live in cold environments, so need protecting
Thie white snow and ice reflect the Sun’s energy back to space. If the snow and ice melts, global warming will quicken
Permafrost is a big store of methane. If melting gets quicker, then lots of methane will be released, adding to the enhanced greenhouse effect.
Strategies to balance economic development with conservation
Use of technology
international agreements
Role of governments
Conservation groups

How does the use of technology help balance economic development with conservation?
The Trans-Alaska pipeline allows the oil in the Arctic to be transported without using ships. It is raised above the ground to prevent the hot oil melting the permafrost and to allow caribou to move underneath it when they migrate
How does international agreements help balance economic development with conservation?
The 1959 Antarctic Treaty prevents economic development and controls tourism in Antarctica. The Arctic Council is an international organisation of eight countries who collaborate to manage the Arctic in a sustainable way.
How does the role of the government help balance economic development with conservation
Governments can create laws to protect the environment. The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge in Alaska was established in 1960 and protects 19 million acres from economic development.
How do conservation groups help balance economic development with conservation
Greenpeace campaigns for a ban on oil drilling and large-scale fishing in the Acrtic. The World Wildelife Fund helps protect Arctic environments.
Name a case study for challenges and opportunities in cold environments?
Svalbard islands
Challenges of development in svalbards
Extreme temperatures, provisions of buildings and infrastructure, inaccessibility.
How is extreme temperature a challenge in the development of svalbard?
Daily temperatures can be as low as -30oC. This makes it difficult fot people to work outside and for machinery to operate.

How is provision of buildings and infrastrucutre a challenge in developent in svalbard?
Building on permafrost means buildings need to be raised above ground level so the heat they give off does not melt the land underneath (figure 2). Buildings sink (suffer from subsidence) and topple over if the permafrost melts. Roads are built on gravel to stop the permafrost melting and heated water pipes are also kept off the ground.
How is inaccessibility a challenge in development in svalbard?
Svalbard is very remote with only one main airport. There are few roads outside of Longyearbyen and most people use snowmobiles or 4×4s.
Opportunities for development in svalbard?
Mineral extraction, fishing, tourism, energy?
How does mineral extraction create opportunities for development in svalbard?
Coal mining was once the most important economic activity and still employs around 300 people.
How does fishing create opportunities for development in svalbard?
Fish stocks are plentiful in the Barents Sea off svalbard. Cod and herring are popular and fishing is controlled jointly by Norway and Russia.
How does tourism create opportunities for development in svalbard?
In 1990 there was virtually no tourism in svalbard but it is now the biggest employer. 2018 saw 85,000 visitors and a further 45,000 on cruise ships coming for attractions like the Northern lights, dog sled trips, and ice cave visits. Large visitor numbers can damage fragile ecosystems.
How does energy create opportunities for development in svalbard?
Burning coal is controversial because of climate change. All of Svalbard’s energy is providd by the coal-fired power station at Longyearbyen, solar energy in the summer months (when there is 24 hours of sunlight a day) or geothermal energy might provide greener alternatives in the future.