Chapter 10: An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Ecology
study of the interactions between organisms and the environment
Ecologists work at levels ranging from _______ to _______
individuals to planet
Organismal ecology
studies how an organism’s structure, physiology, and (for animals) behavior meet environmental challenges
population
is a group of individuals of the same species living in an area
Population ecology
focuses on factors affecting how many individuals of a species live in an area
community
is a group of populations of different species in an area
Community ecology
deals with the whole array of interacting species in a community
ecosystem
is the community of organisms in an area and the physical factors with which they interact
Ecosystem ecology
emphasizes energy flow and chemical cycling among the various biotic and abiotic components
landscape
is a mosaic of connected ecosystems
Landscape ecology
deals with arrays of ecosystems and how they are arranged in a geographic region
biosphere
is the global ecosystem, the sum of all the planet’s ecosystems
Global ecology
examines the influence of energy and materials on organisms across the biosphere
how did they study the effect of climate change?
They make 3 area, one is completely dry, one is completely wet, and one is in between the two, then observe the ecological impacts.
what did they notice with the effect of climate change with the dogwood?
They found flowering dogwoods would be more sensitive to extended periods of drought than other species of hardwoods
when linking ecology and evolutionary biology what is a good example
Darwin finches is an example. After a long period of drought, 180 out of the 1200 medium ground finches survived. The average beak size in the next generation was larger
who is Rachel Carson?
warned that the widespread use of pesticides such as DDT was having an effect the eagle
what was Rachel Carson book called and when was it made?
Silent Spring in 1962
what was the name of the pesticide that Rachel Carson looked into?
DDT
Ecologists recognize two kinds of factors that
determine distribution
biotic and abiotic
abiotic
nonliving factors
biotic
living factors
Dispersal
is movement of individuals away from centers of high population density or from their area of origin
can dispersal be limited by barriers?
Yes
Natural Range Expansions
the process where a species extends its geographic distribution into areas where it wasn't previously present
name an example of Natural Range Expansions
Cattle egret migrated from Africa, to is current range and the bird who followed the cattle for the flies they attract
Species transplants
include organisms that are intentionally or accidentally relocated from their original distribution
Why is it bad to do species transplant?
can disrupt the communities or ecosystems to which they have been introduced
name an example of a species transplant
Bullfrog
Habitat selection
the rules used by organisms to choose among patches or habitats that differ in one or more variables, such as food availability or predation risk, that influence its fitness
name an example of habitat selection
pine snakes
Biotic factors that affect the distribution of organisms may include:
Interactions with other species
Predation
Competition
Abiotic factors affecting distribution of organisms include:
Temperature
Water
Sunlight
Wind
Rocks and soil
climate
temperature, water, sunlight, and wind
Macroclimate
consists of patterns on the global, regional, and local level
Microclimate
consists of very fine patterns, such as those encountered by the community of organisms underneath a fallen log
More heat and light per unit of surface area reach the ______ than the high latitudes
tropics
Seasonal variations of light and temperature increase steadily toward the poles because of
the tilt of the Earth's axis and its orbit around the sun.
Global air circulation and precipitation patterns play major roles in determining
climate patterns
What does air flow close to Earth’s surface create?
predictable global wind patterns
Cooling trade winds blow from east to west in the tropics; prevailing westerlies blow from
west to east in the temperate zones
The Gulf Stream carries
warm water from the equator to the North Atlantic
Mountains have a significant effect on
The amount of sunlight reaching an area
Local temperature
Rainfall
rain shadow
Rising air releases moisture on the windward side of a peak
Biomes
are the major ecological associations that occupy broad geographic regions of land or water
turnover
Many lakes undergo a semiannual mixing of their waters
thermocline
In oceans and most lakes, a temperature boundary; separates the warm upper layer from the cold deeper water
disturbance
Biome patterns can be modified; such as a storm, fire, or human activity
climograph
a plot of the temperature and precipitation in a region
ecotone
Terrestrial biomes usually grade into each other, without sharp boundaries
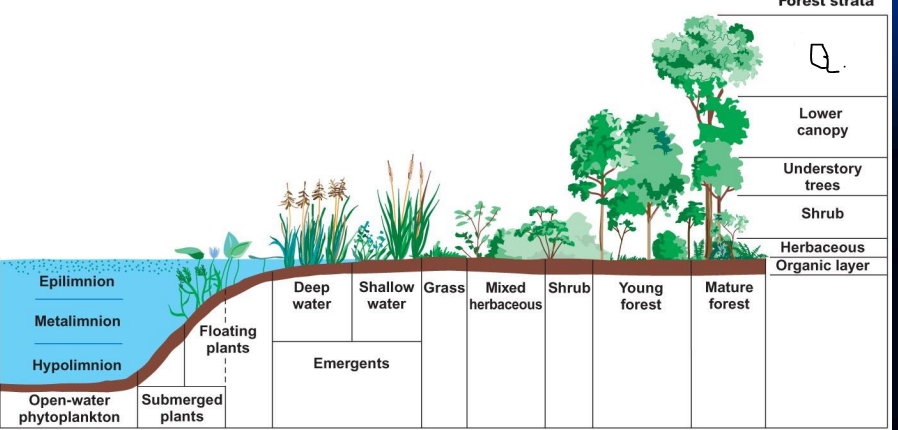
what is a?
Canopy
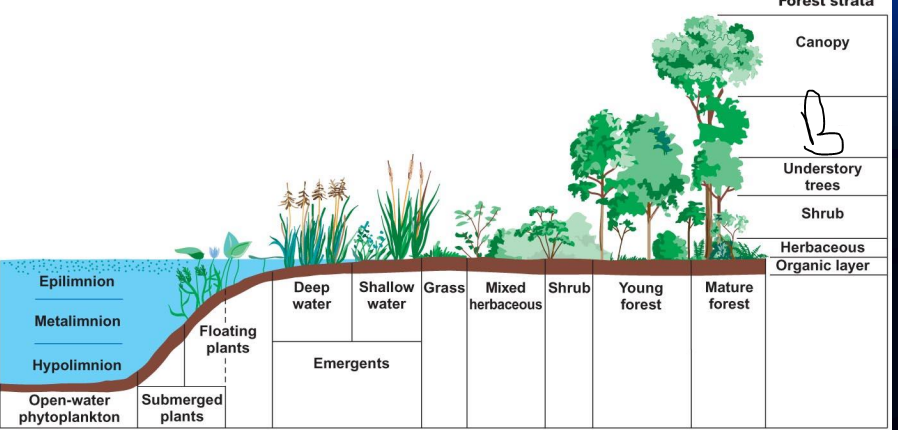
what is B?
lower canopy
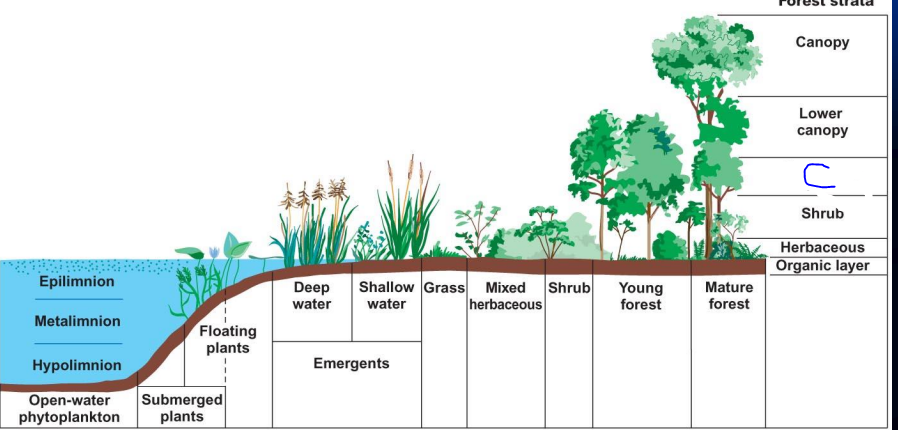
what is c?
understory trees
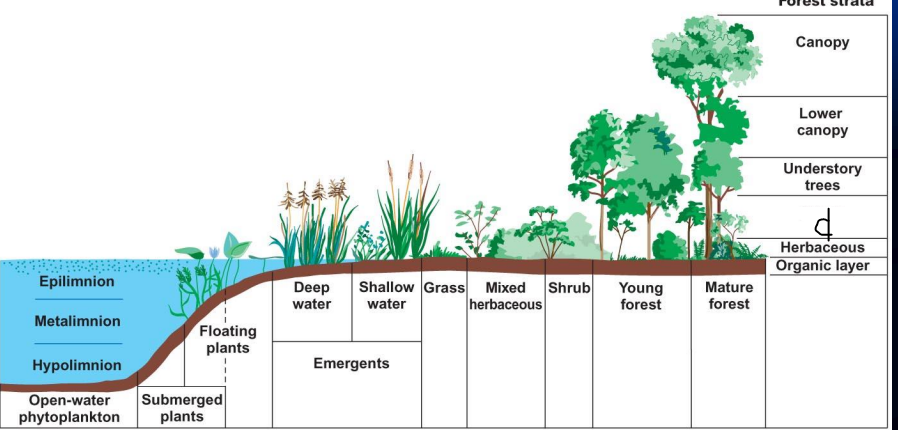
what is d?
Shrub
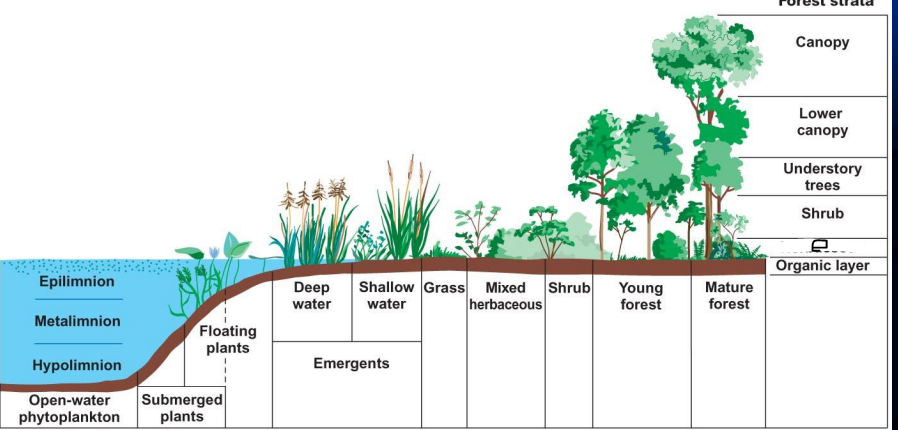
what is e?
Herbaceous
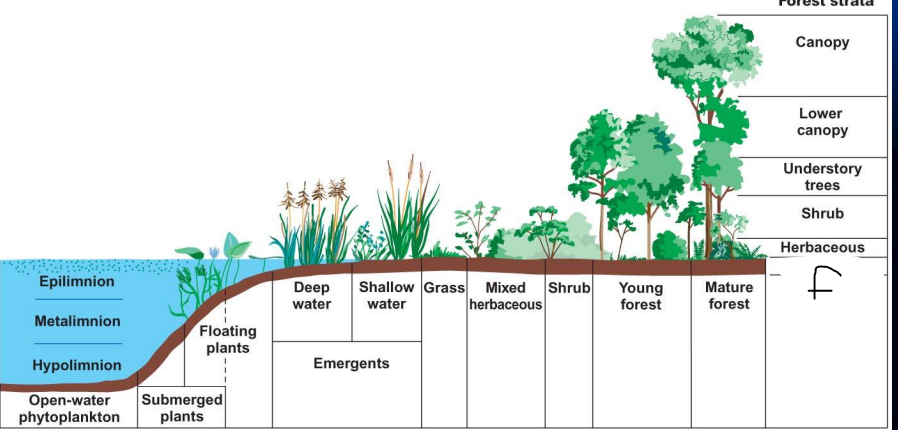
what is f?
organic layer
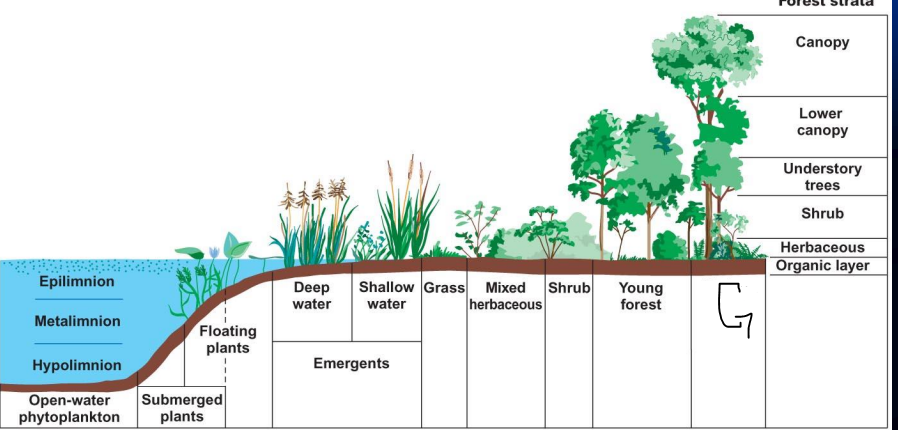
what is g?
Mature forest
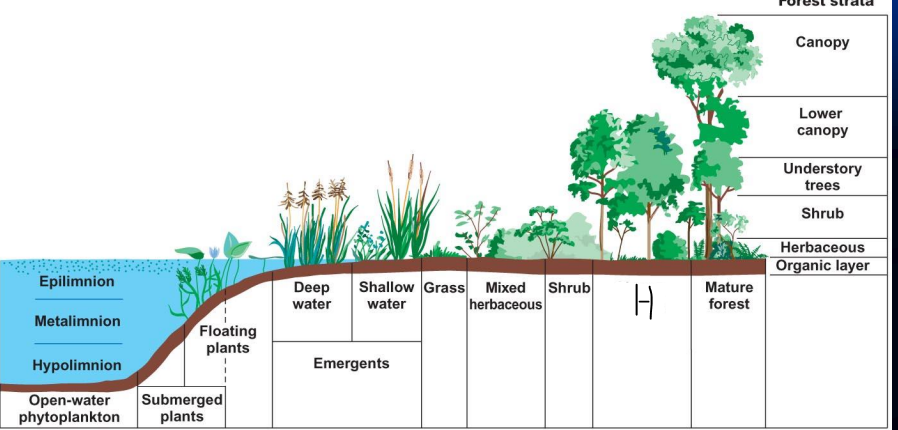
what is h?
young forest
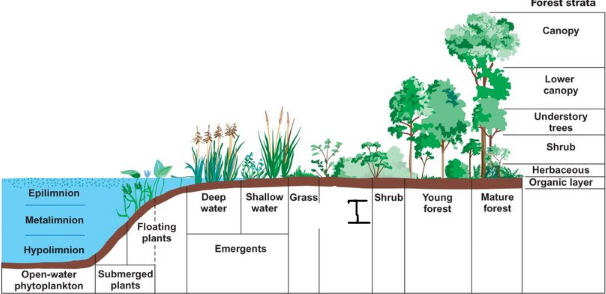
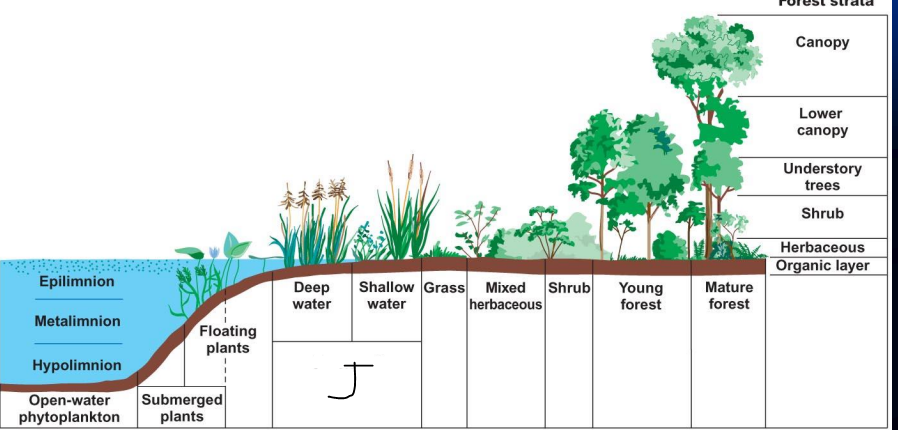
what is i?
mixed herbaceous
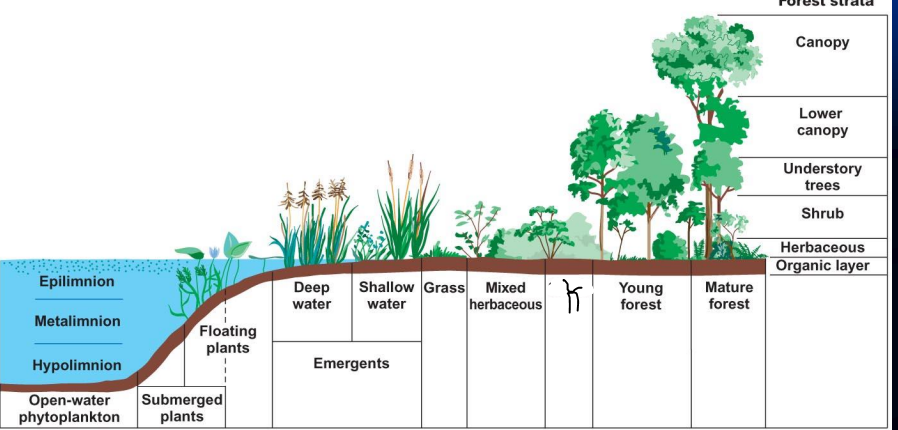
what is J?
Emergent
what is k?
shrub
what is L?
deep water
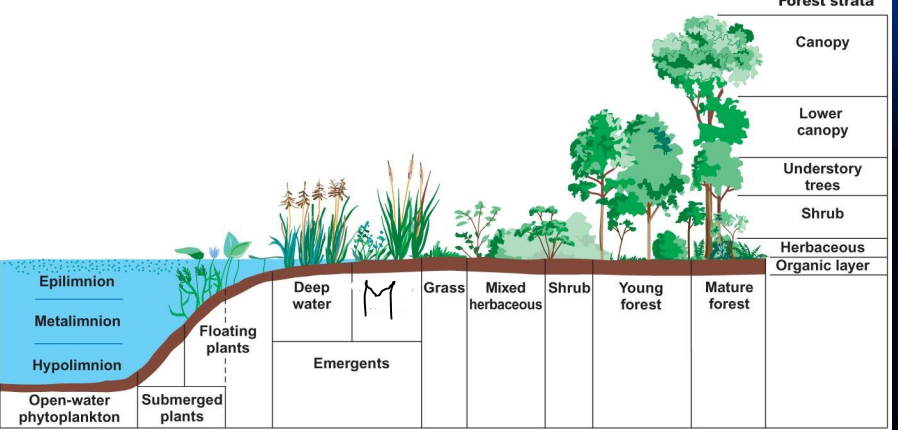
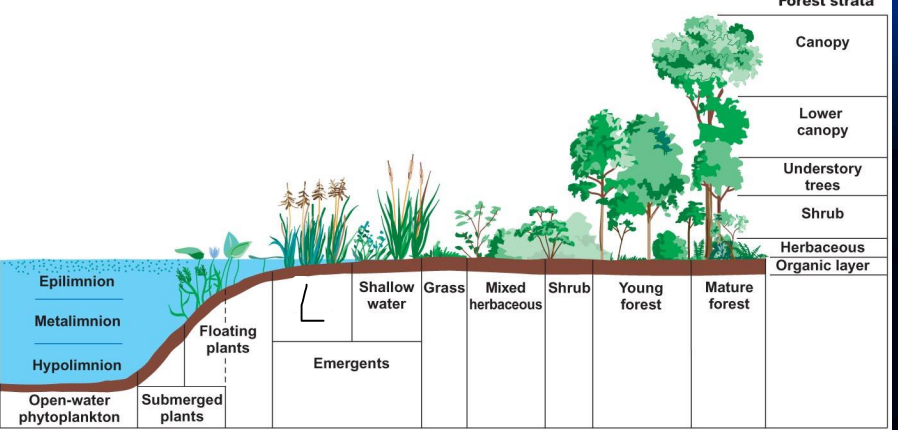
what is m?
shallow water
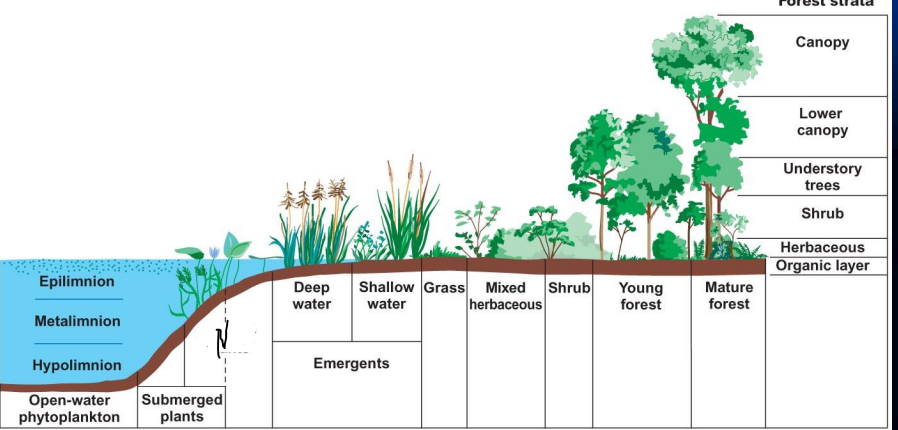
what is N?
Floating plants
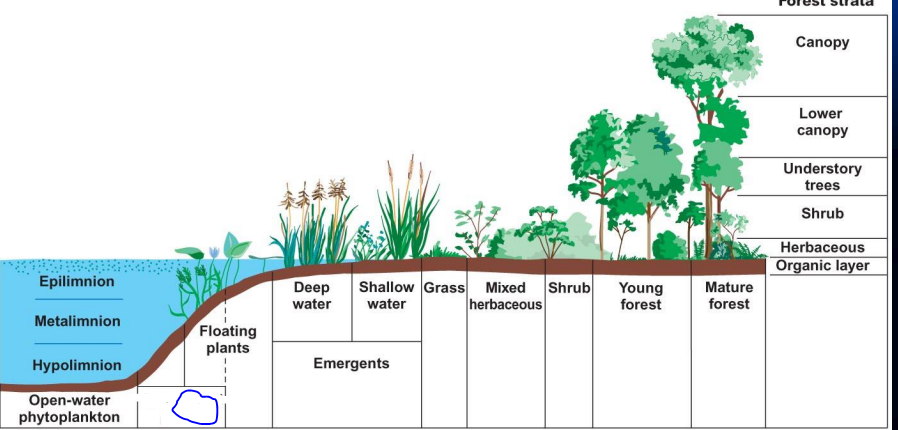
what is o?
submerged plants
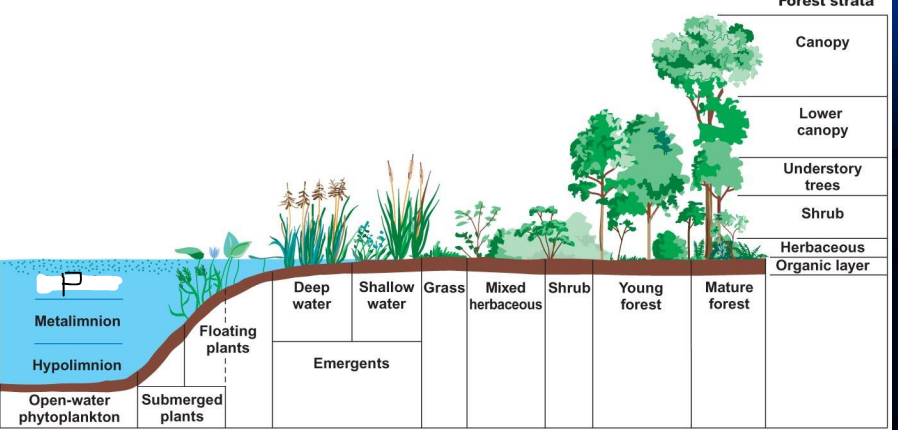
What is p?
Epilimnion
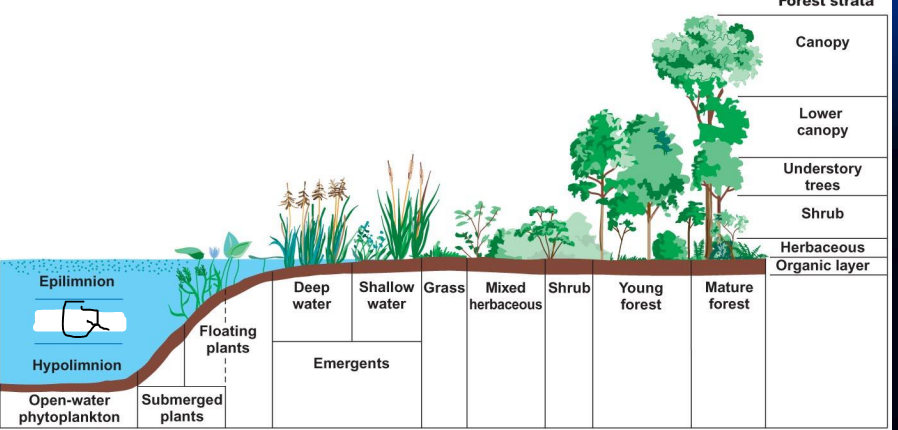
what is Q?
metalimnion
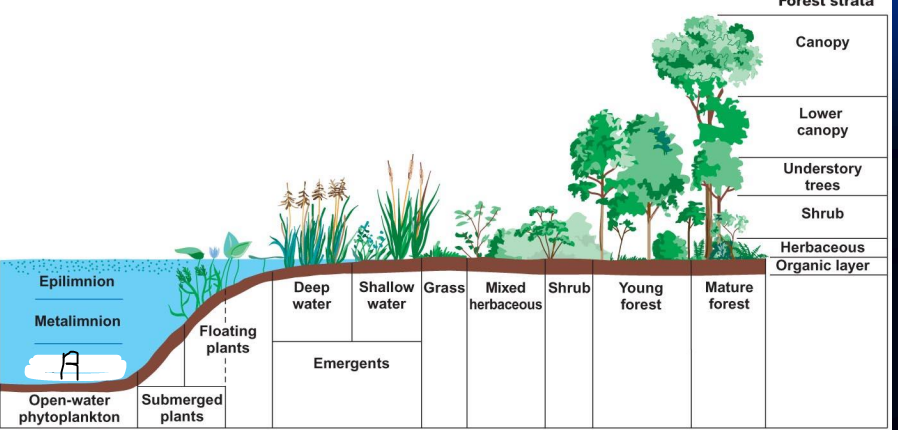
what is R?
hypolimnion
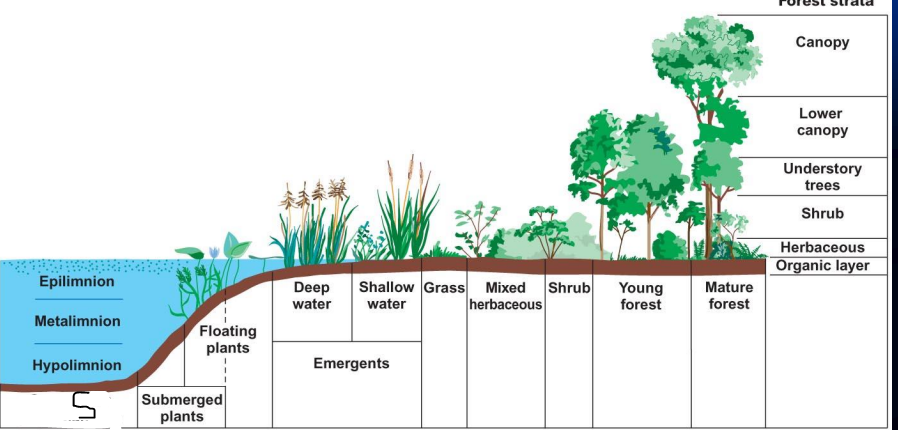
what is s?
open-water phytoplankton
Aquatic biomes account for the_____ _____ of the biosphere in terms of area
largest part
Oceans cover about ____ of Earth’s surface and have an enormous impact on the biosphere
75%
littoral zone
the down-sloping shelf of a pond or lake
limnetic zone
the open water area where light does not generally penetrate all the way to the bottom
The pelagic zone consists of the water column
• Photic receives light
• Aphotic does not
benthic zone
the lowest ecological zone in a water body
Many aquatic biomes are stratified into zones or layers defined by
light penetration, temperature, and depth
neritic zone
shallow marine environment extending from mean low water down to 200-metre (660-foot) depths, generally corresponding to the continental shelf
abyssal zone or abyssopelagic zone
This zone remains in perpetual darkness and covers 83% of the total area of the ocean and 60% of Earth's surface.