HPNU 3050: Lecture 11 Part 1: Skull bones, Nervous System, and Grey/White Matter
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
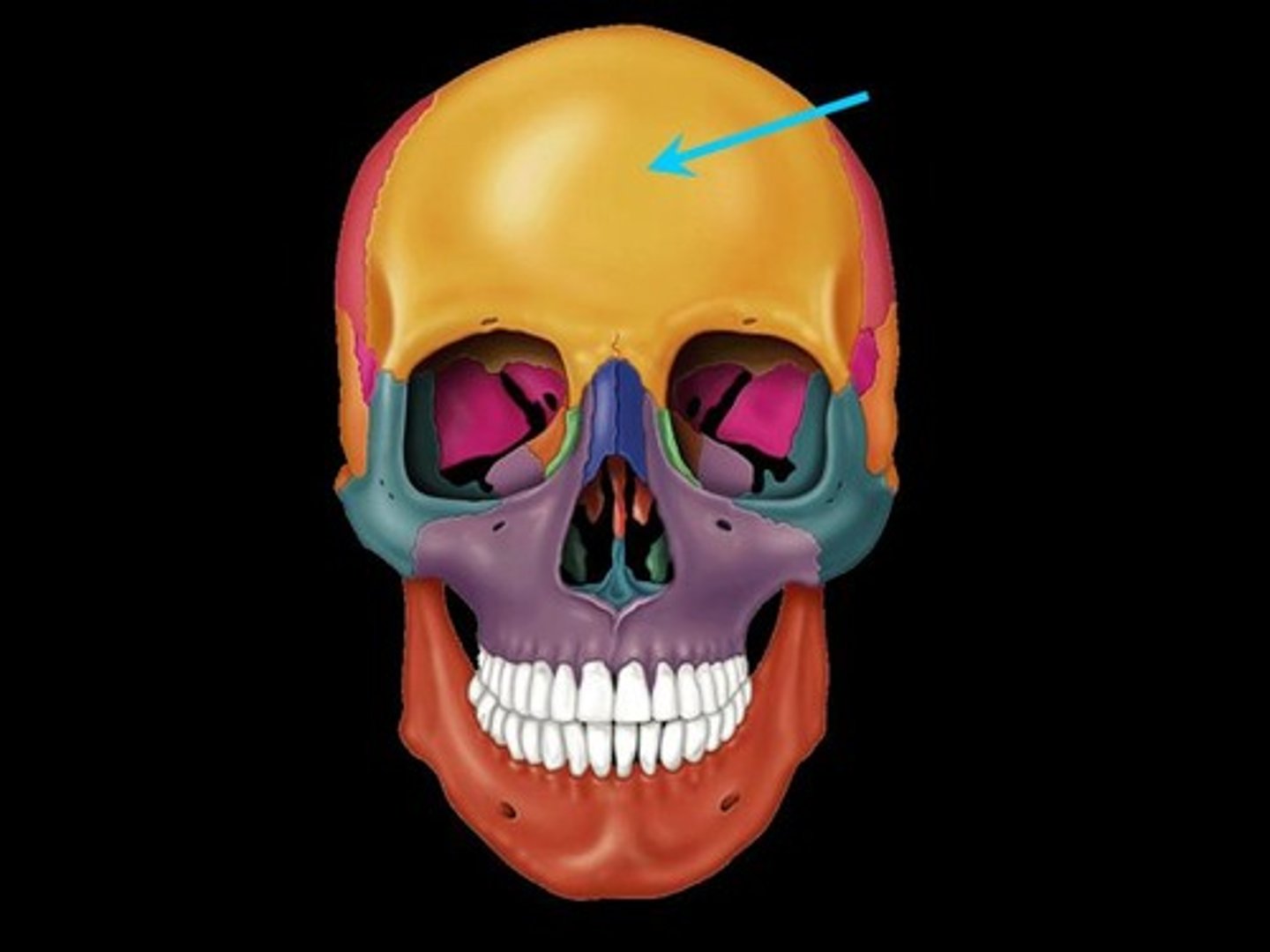
Where is the frontal bone?
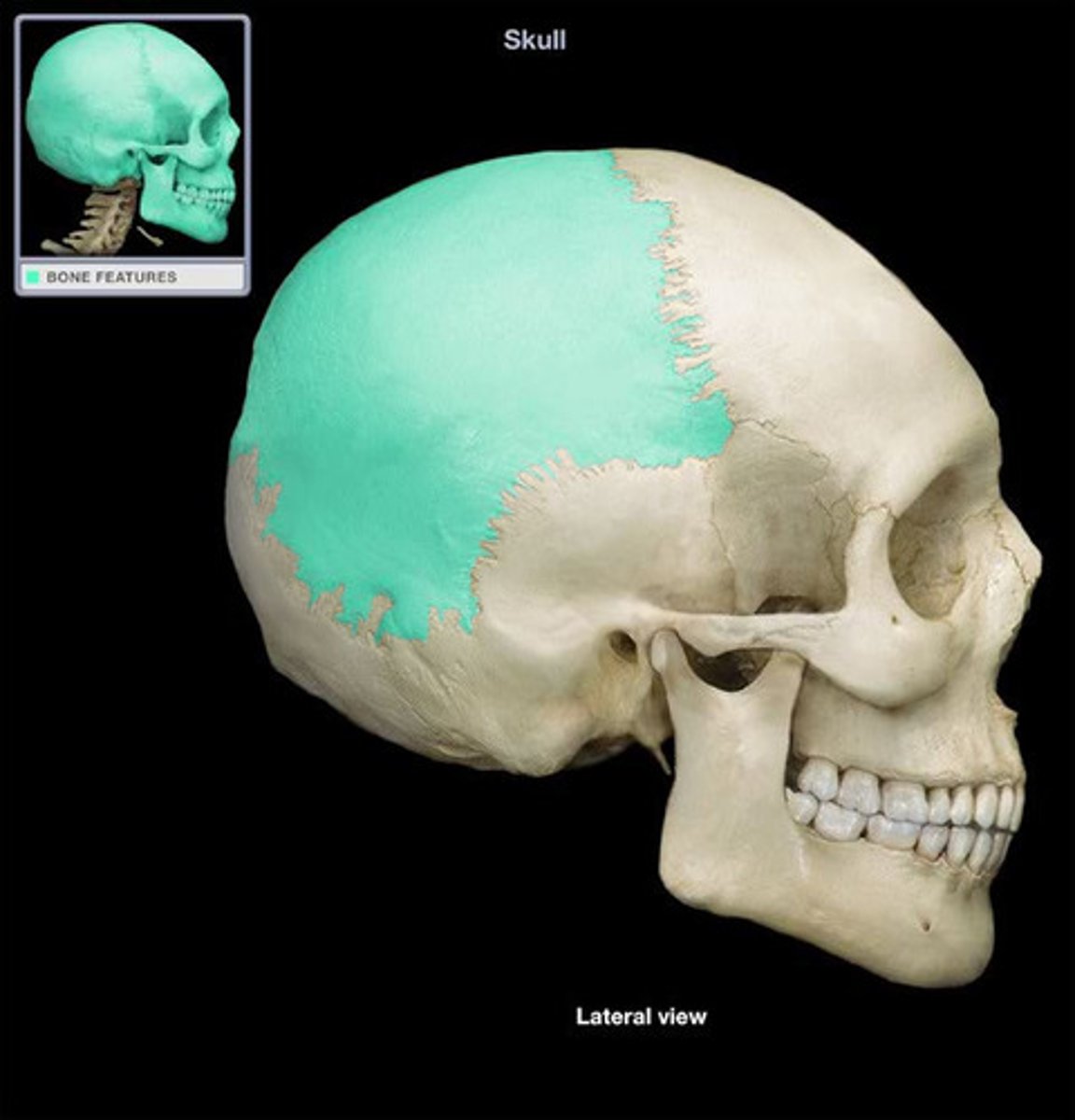
Where is the parietal bone?
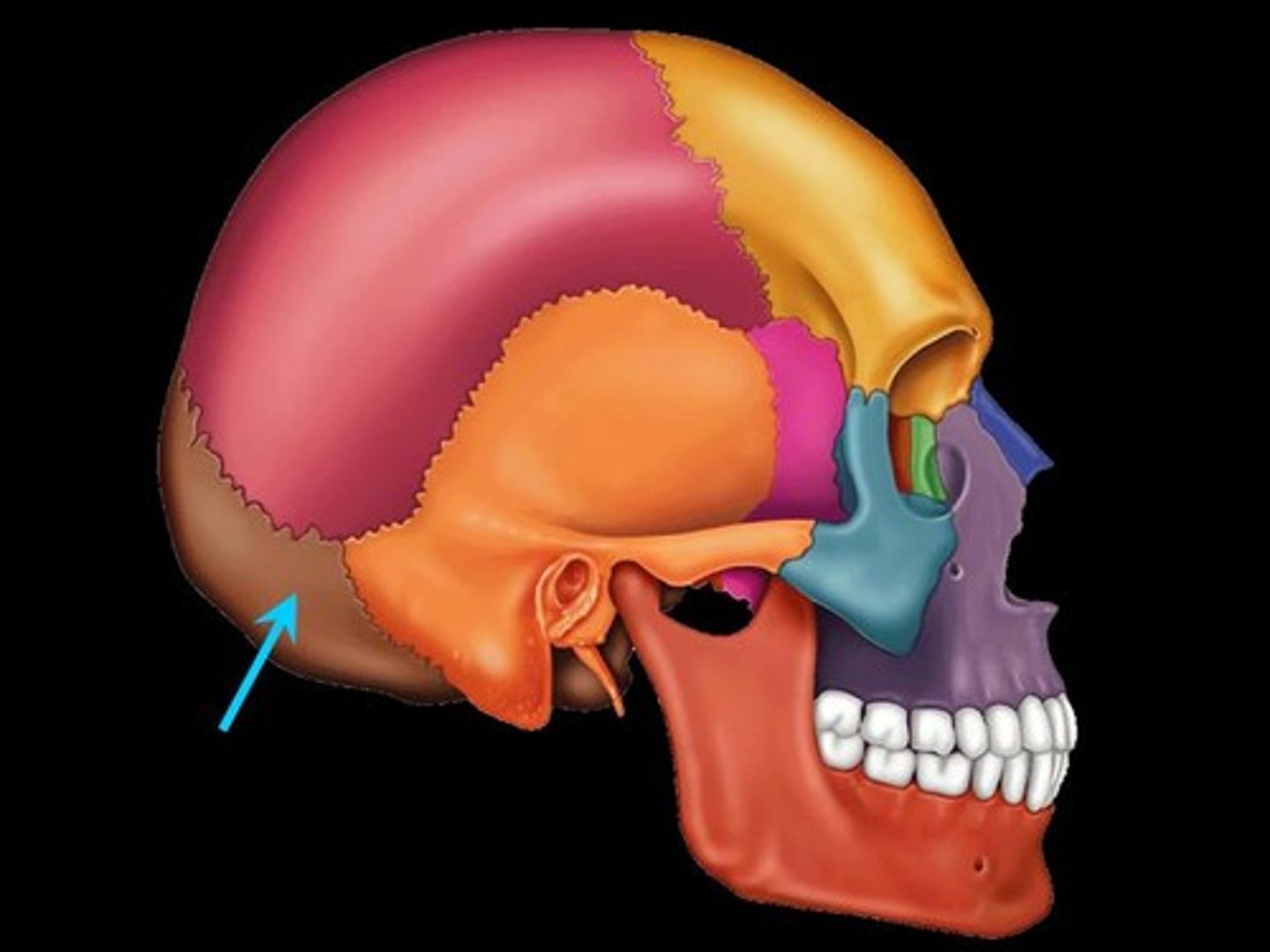
Where is the occipital bone?
Where is the temporal bone?
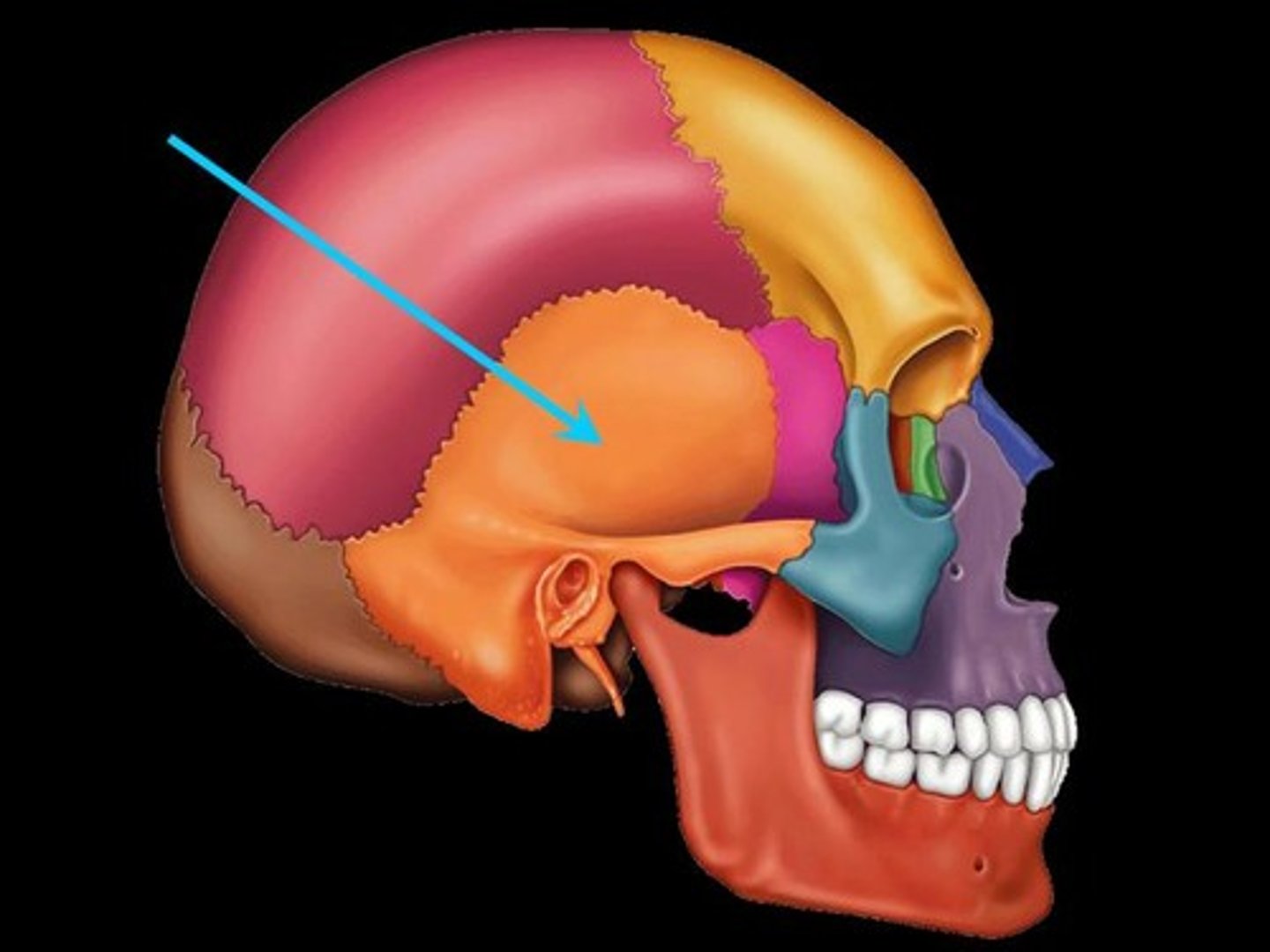
Where is the sphenoid bone?
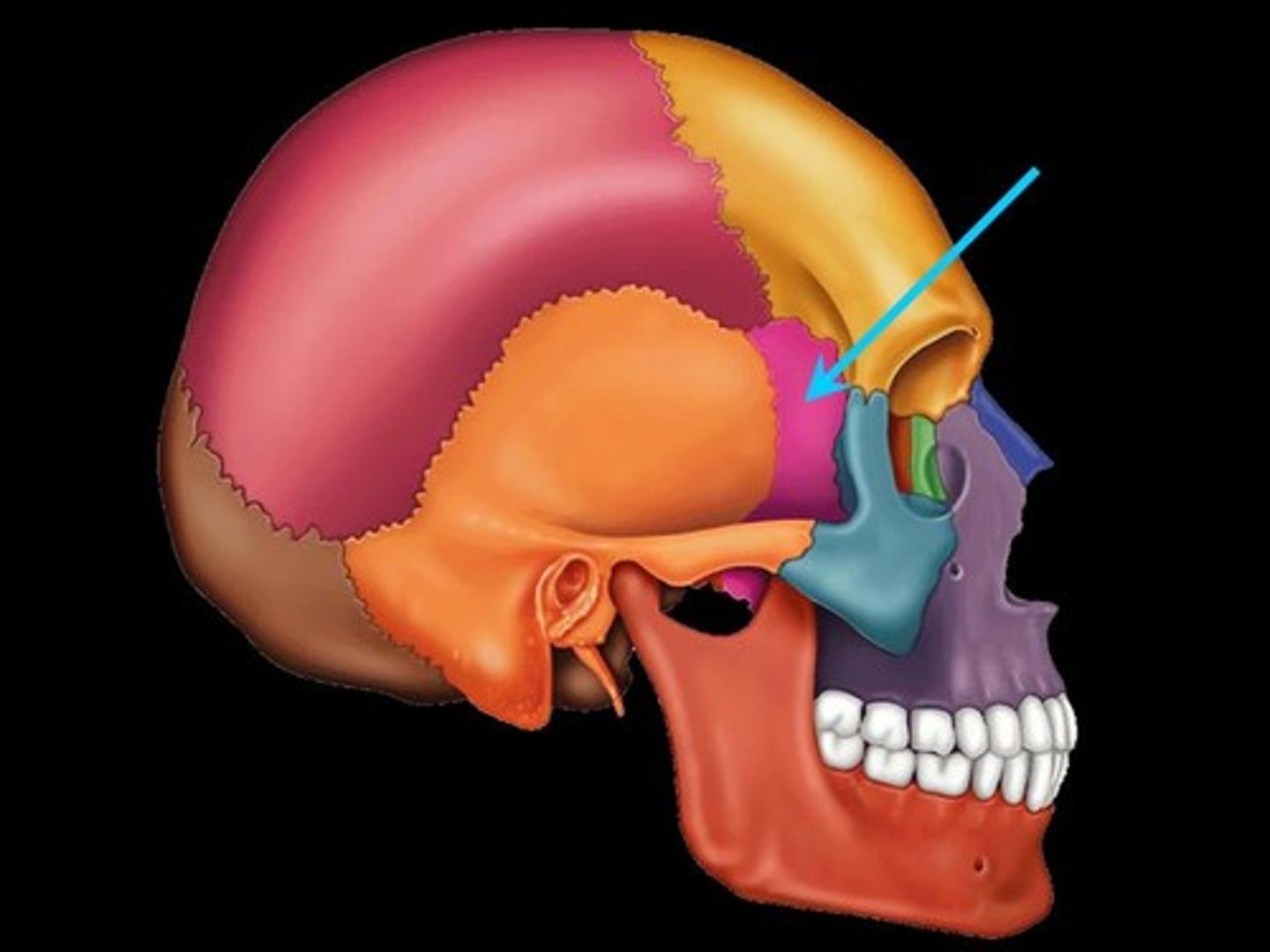
Where is the ethmoid bone?
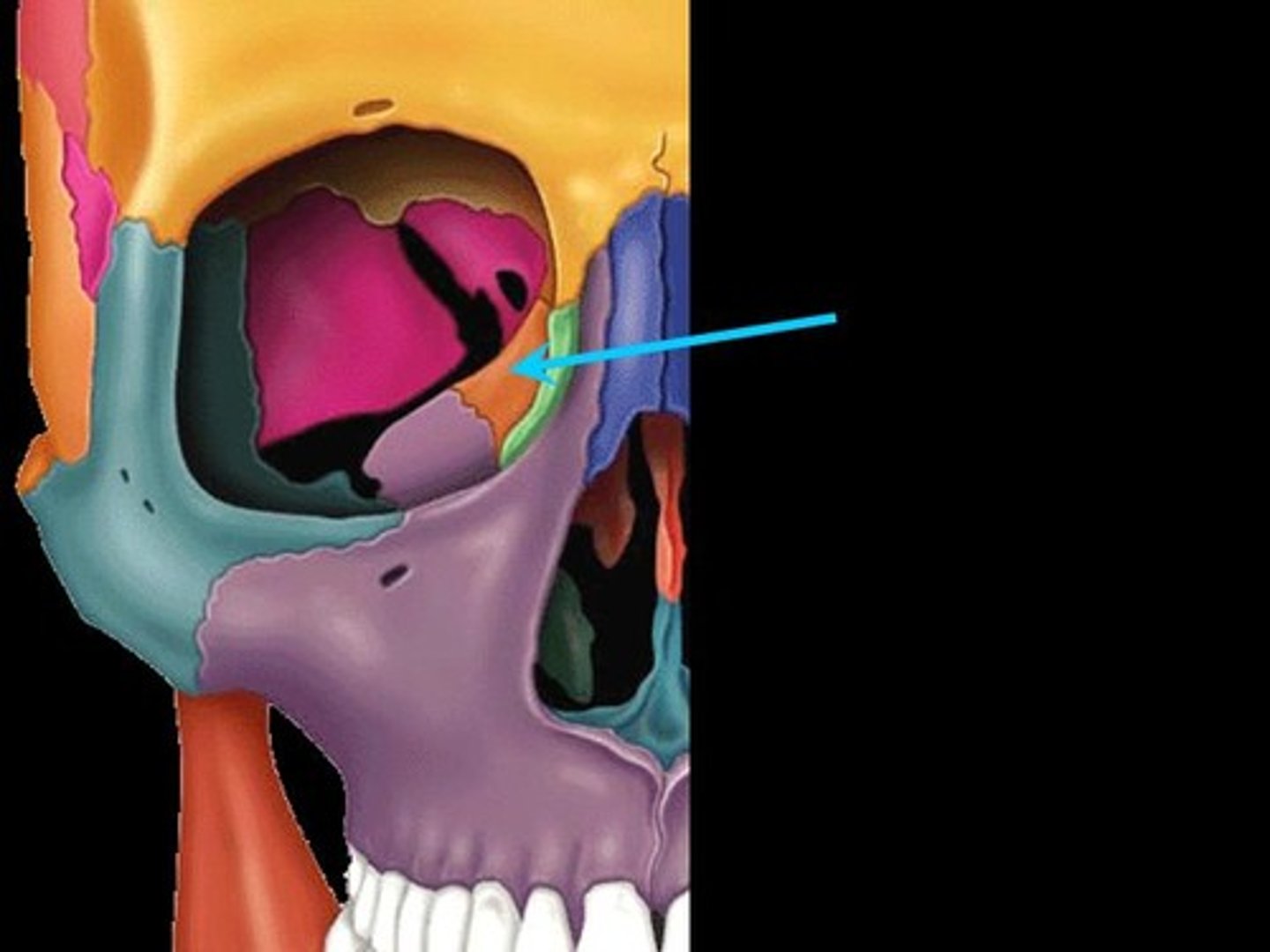
Where is the zygomatic bone?
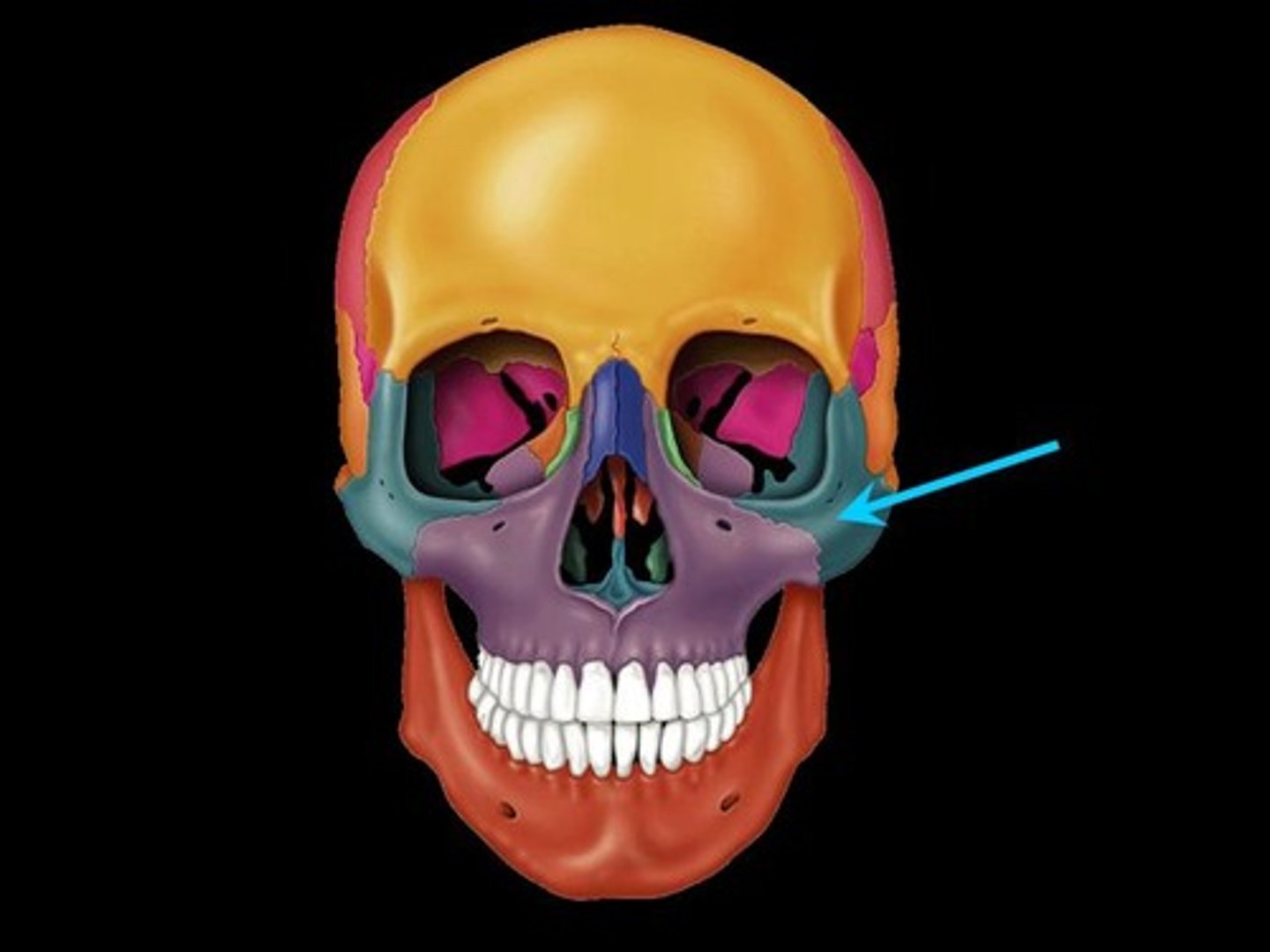
Where is the maxilla?
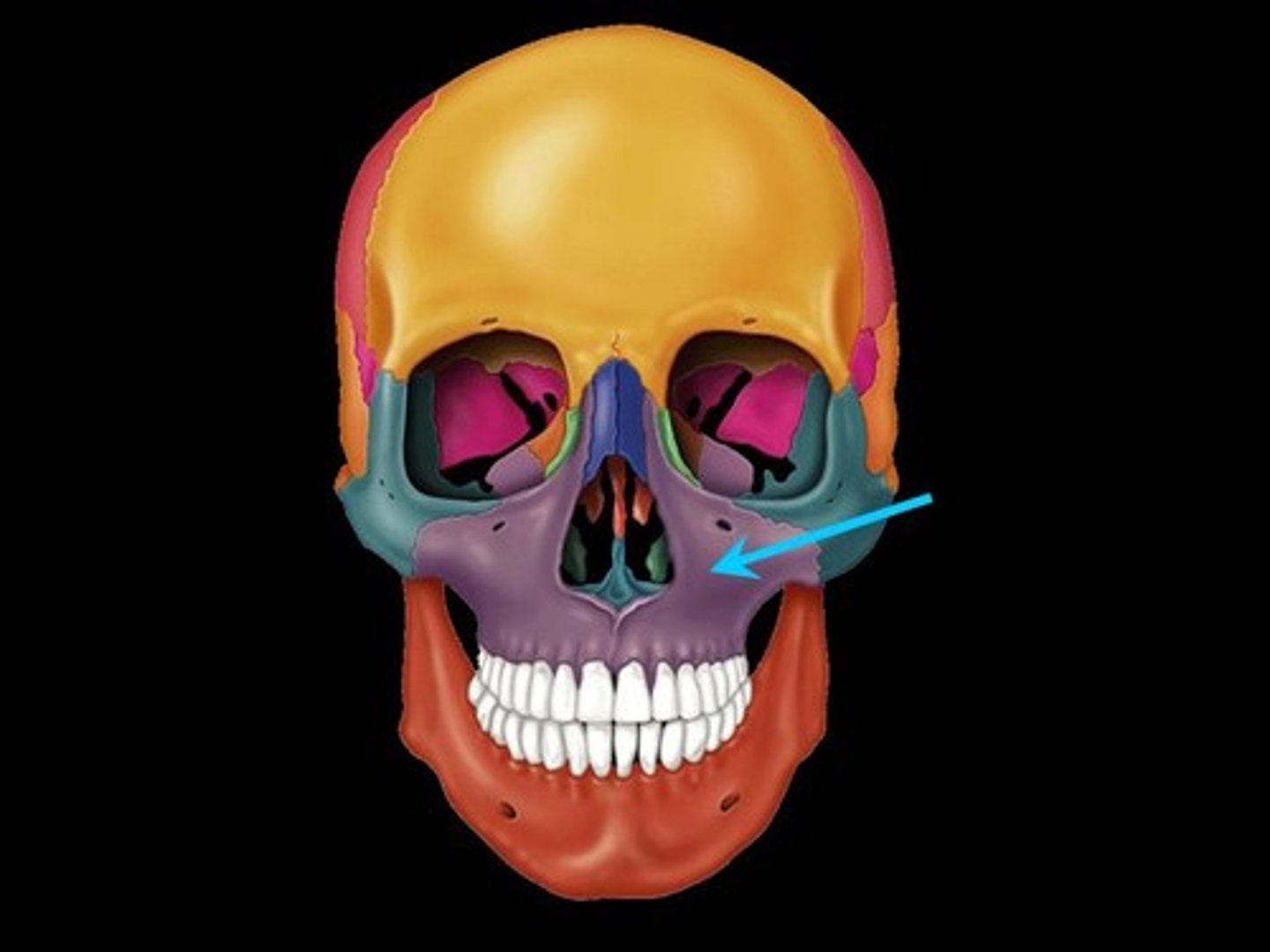
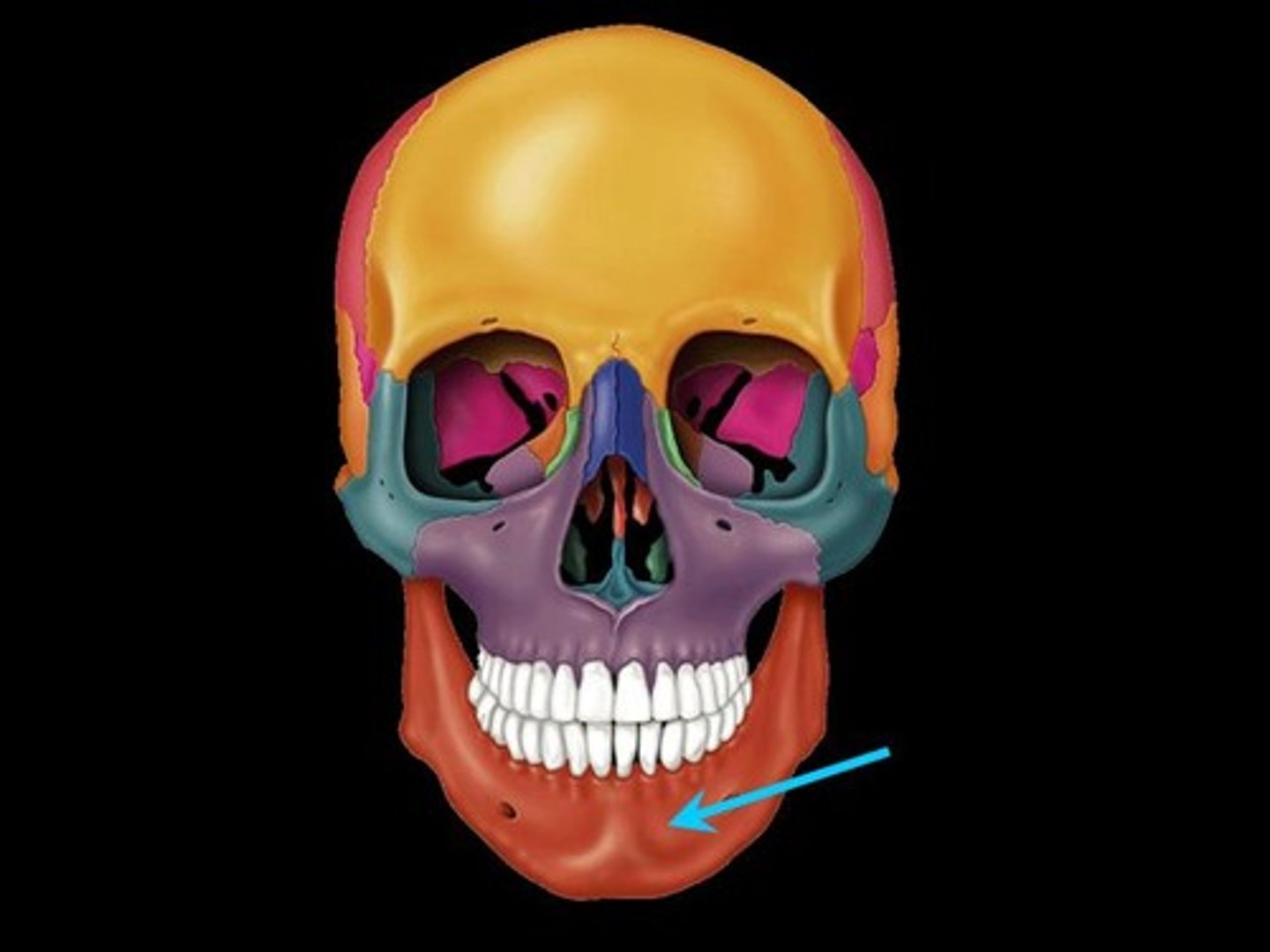
Where is the mandible?
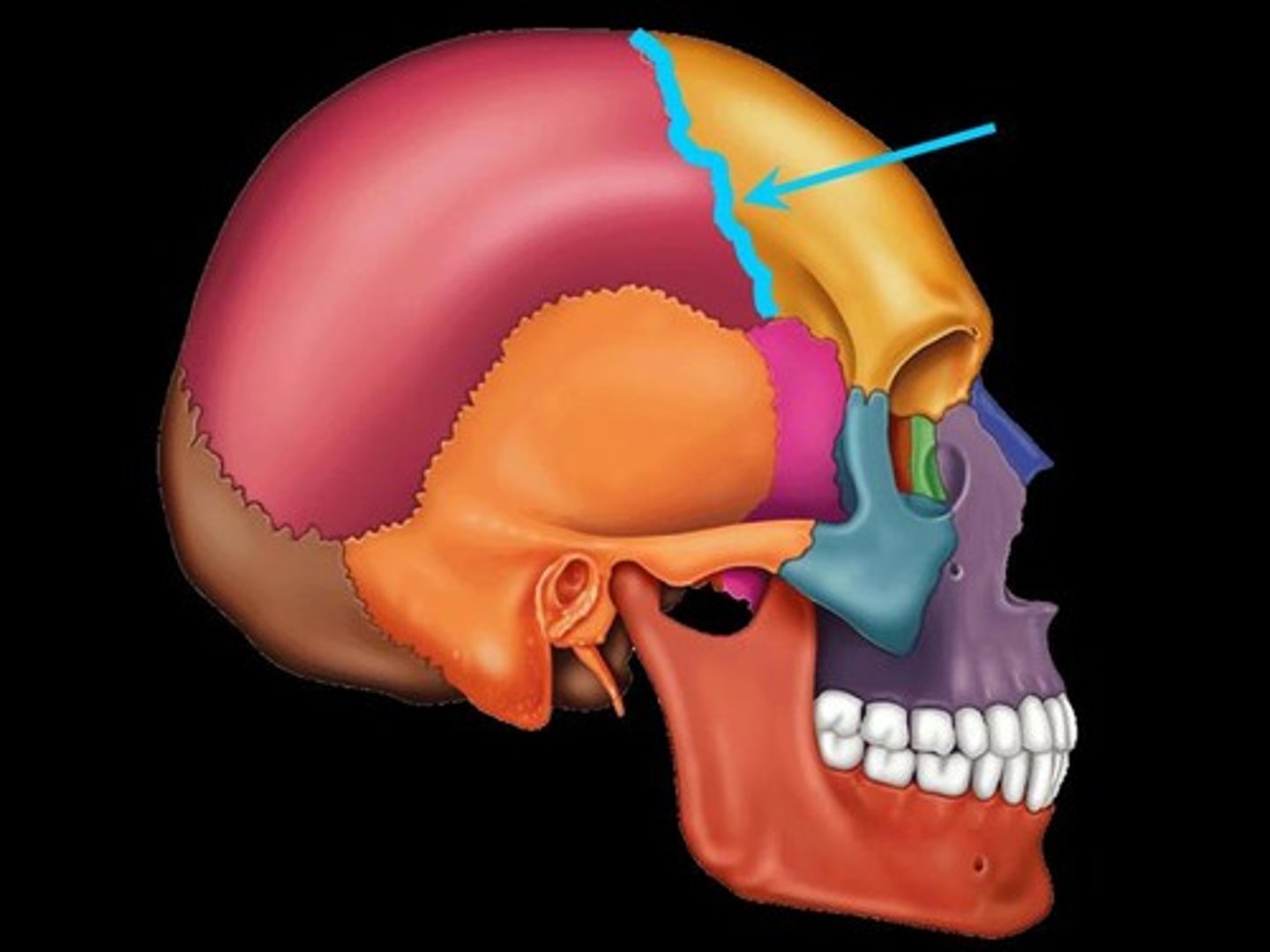
What bones make the coronal suture of the head?
Frontal with parietal
What bones make the sagittal suture of the head?
Parietal with parietal
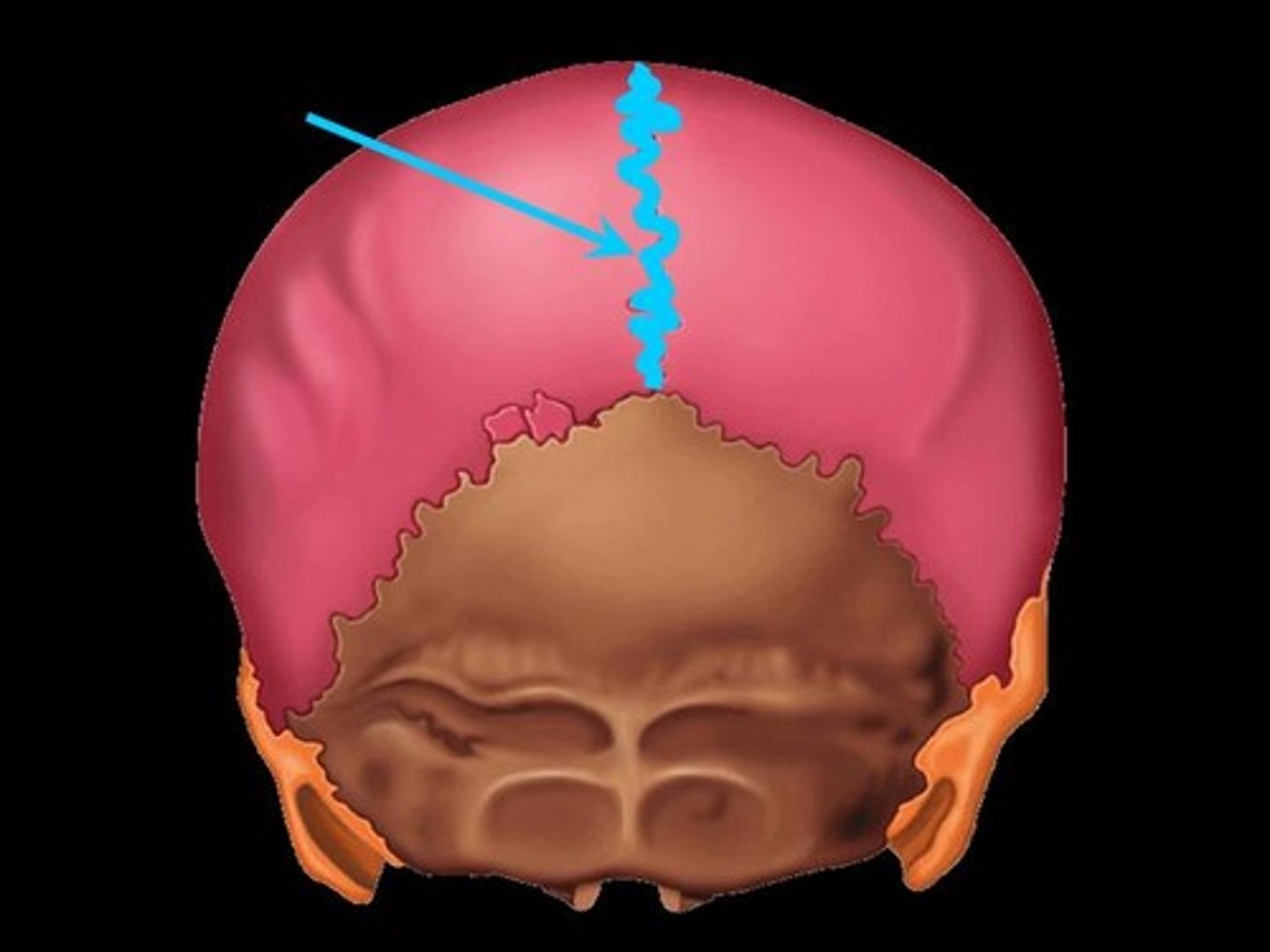
What bones make the lambdoid suture of the head?
Occipital with parietal
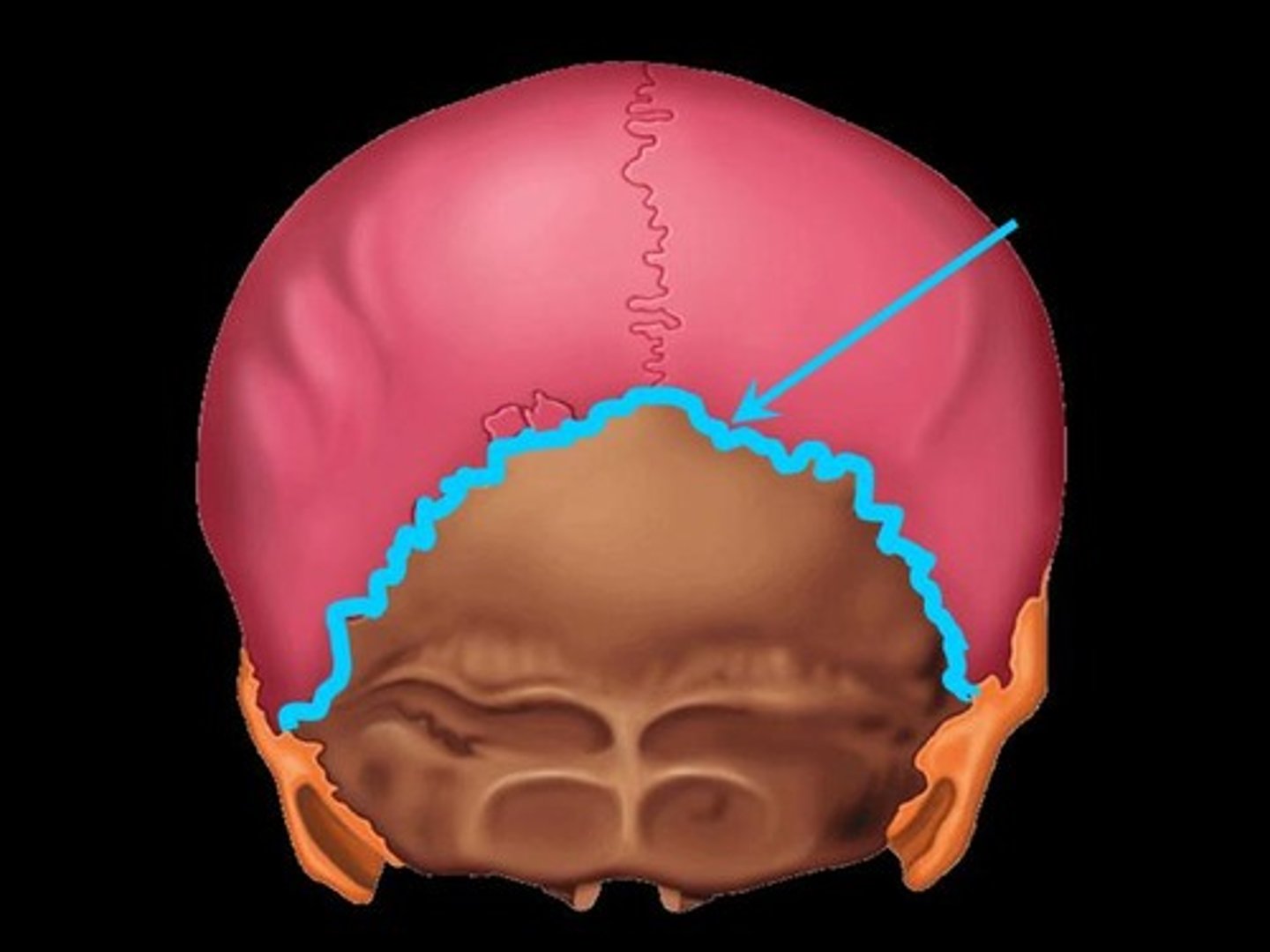
What bones make the squamous suture of the head?
Parietal with temporal
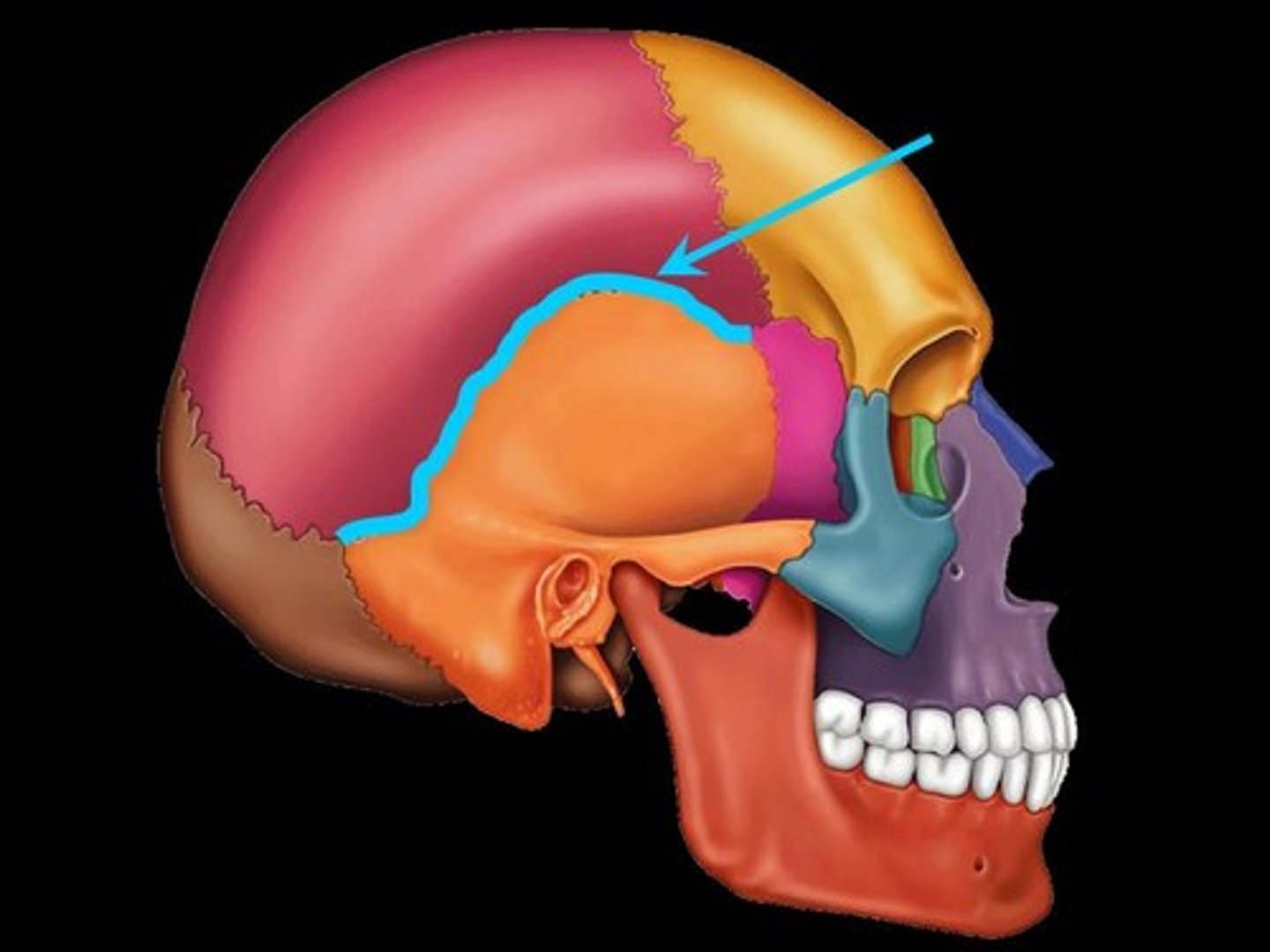
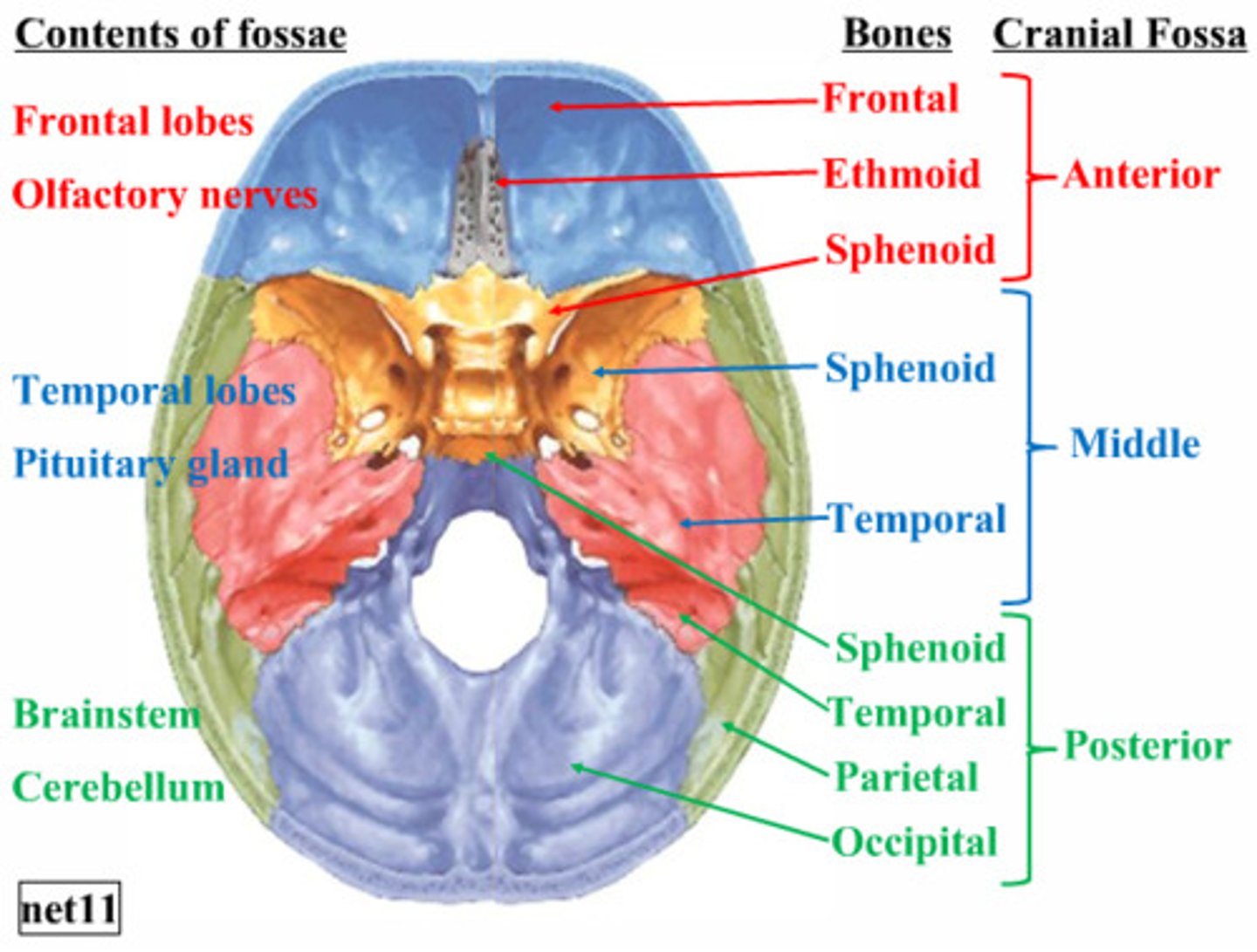
What are the three cranial fossa of the head?
What brains parts are held within them?
Anterior cranial fossa - Frontal lobe of cerebellum
Middle cranial fossa - Temporal lobe of cerebellum
Posterior cranial fossa - cerebellum
What does the term ganglion mean?
Cluster of neuronal CELL BODIES within PNS.
What does the term nerve mean?
Bundle of AXONS within PNS.
What does the term nerve plexus mean?
Network of nerves within PNS.
What does the term nuclei mean?
Cluster of neuron CELL BODIES within CNS.
What does the term tract mean?
Bundle of AXONS within CNS.
What does the term funiculus mean?
Group of TRACTS in a specific area of the SPINAL CORD
What does the term pathway mean?
CENTERS and TRACTS that connect the CNS with body organs and systems.
What does the term peduncle mean?
Stalk-like structure connecting two regions of the brain.
What comprises the gray matter of the brain?
Cortex
Motor neuron and interneuron cell bodies
Dendrites
Terminal arborizations
and unmyelinated axons.
Deep clusters of neuronal cell bodies in the gray matter are called CEREBRAL NUCLEI!!!
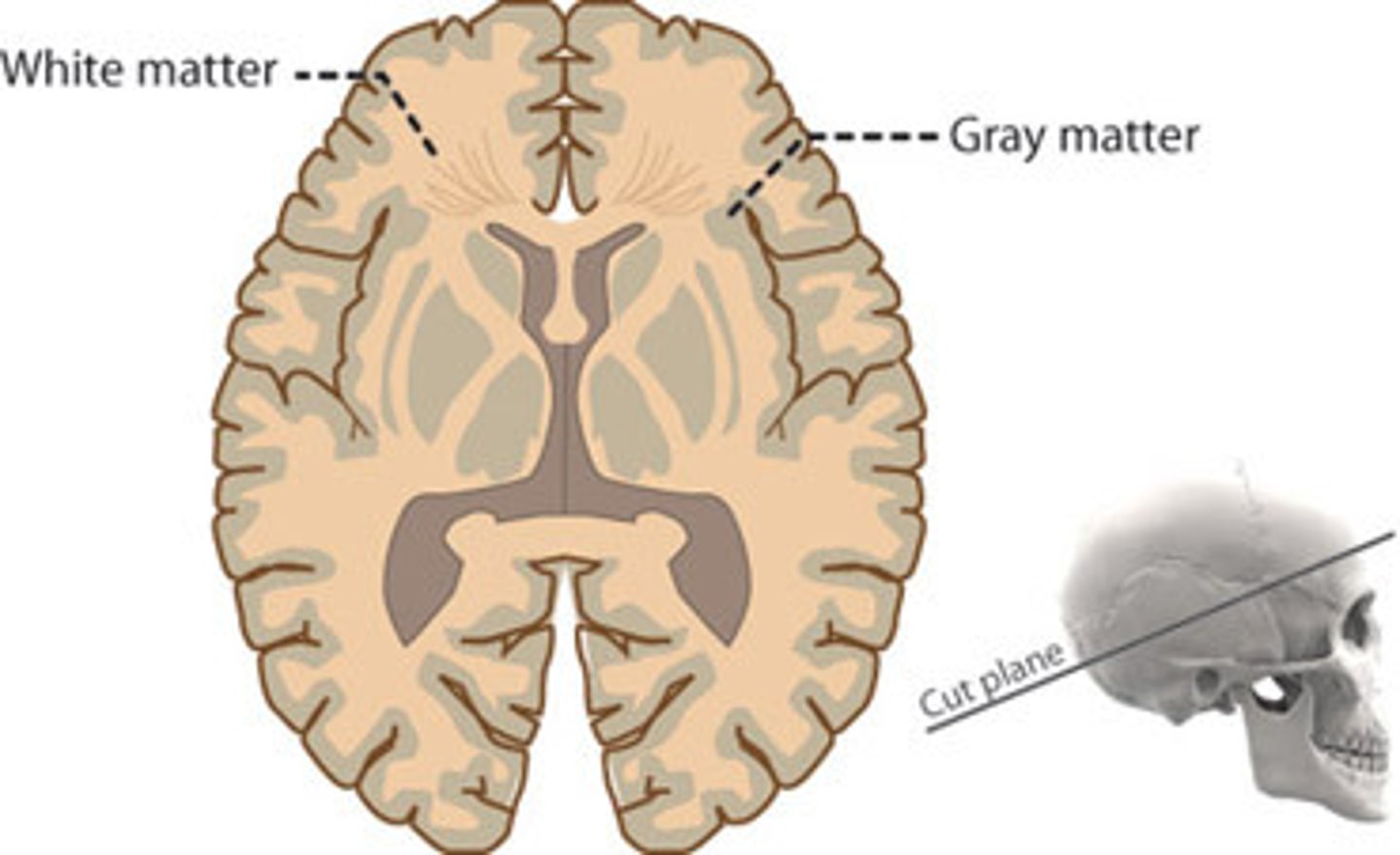
What comprises the white matter of the brain?
What is its position relative to the cortex?
Myelinated axons.
It is deep to the cortex.
The cerebrum is composed of what?
What is it divided by?
What is it connected by?
Cerebrum composed of two cerebral hemispheres.
They are divided by a longitudinal fissure
Connected to corpus callosum

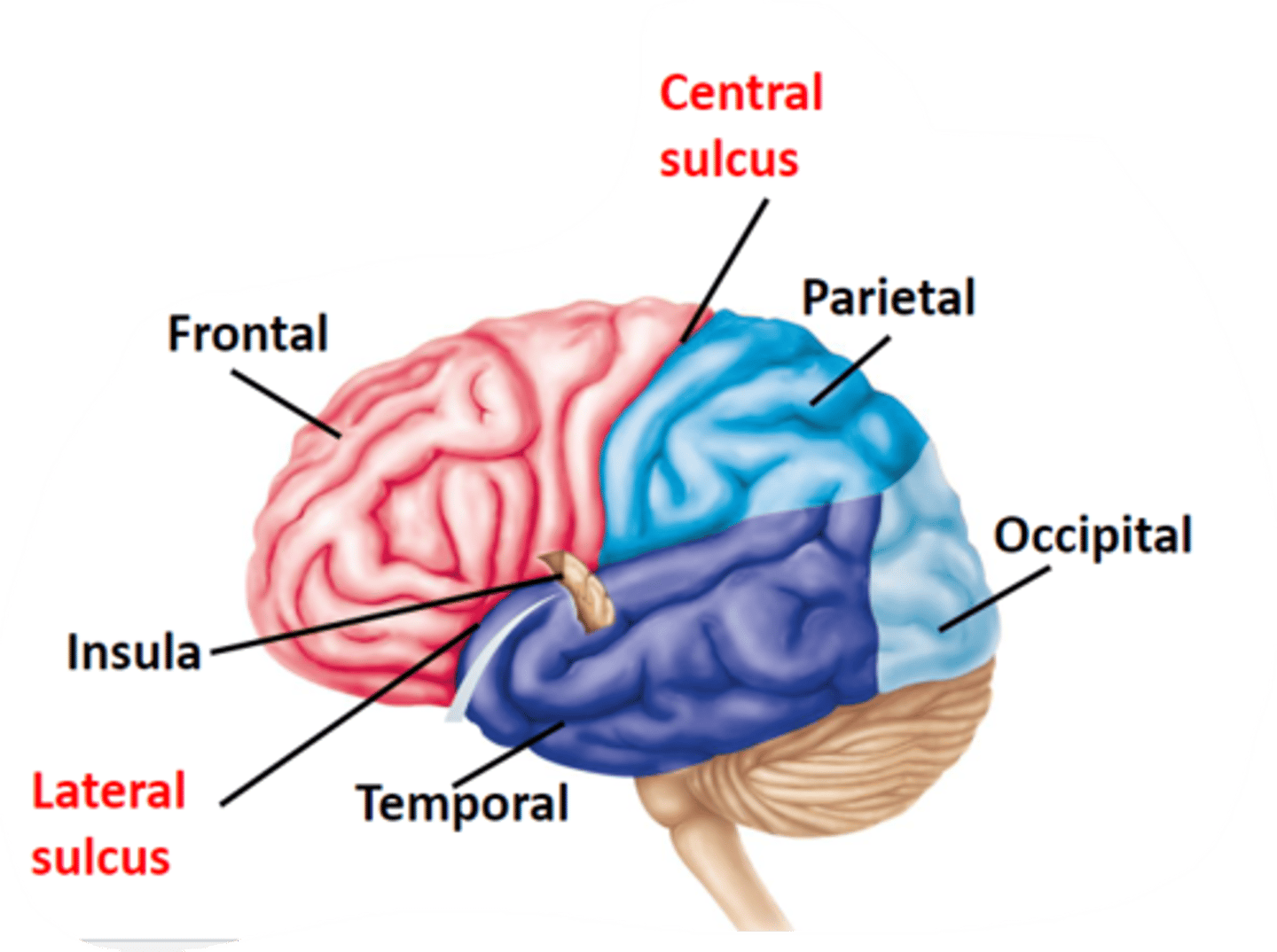
What are the five cerebral lobes in EACH cerebral hemisphere?
1) Frontal lobe
2) Parietal lobe
3) Occipital lobe
4) Temporal lobe
5) Insula (Deep within lateral sulcus)
What are the four general functions of the cerebral hemispheres?
1) Contralateral control
2) Hemispheric lateralization
3) Considerable overlap of functions in each region.
4) Separate except where tracts allow for communication. (The largest is the corpus callosum).
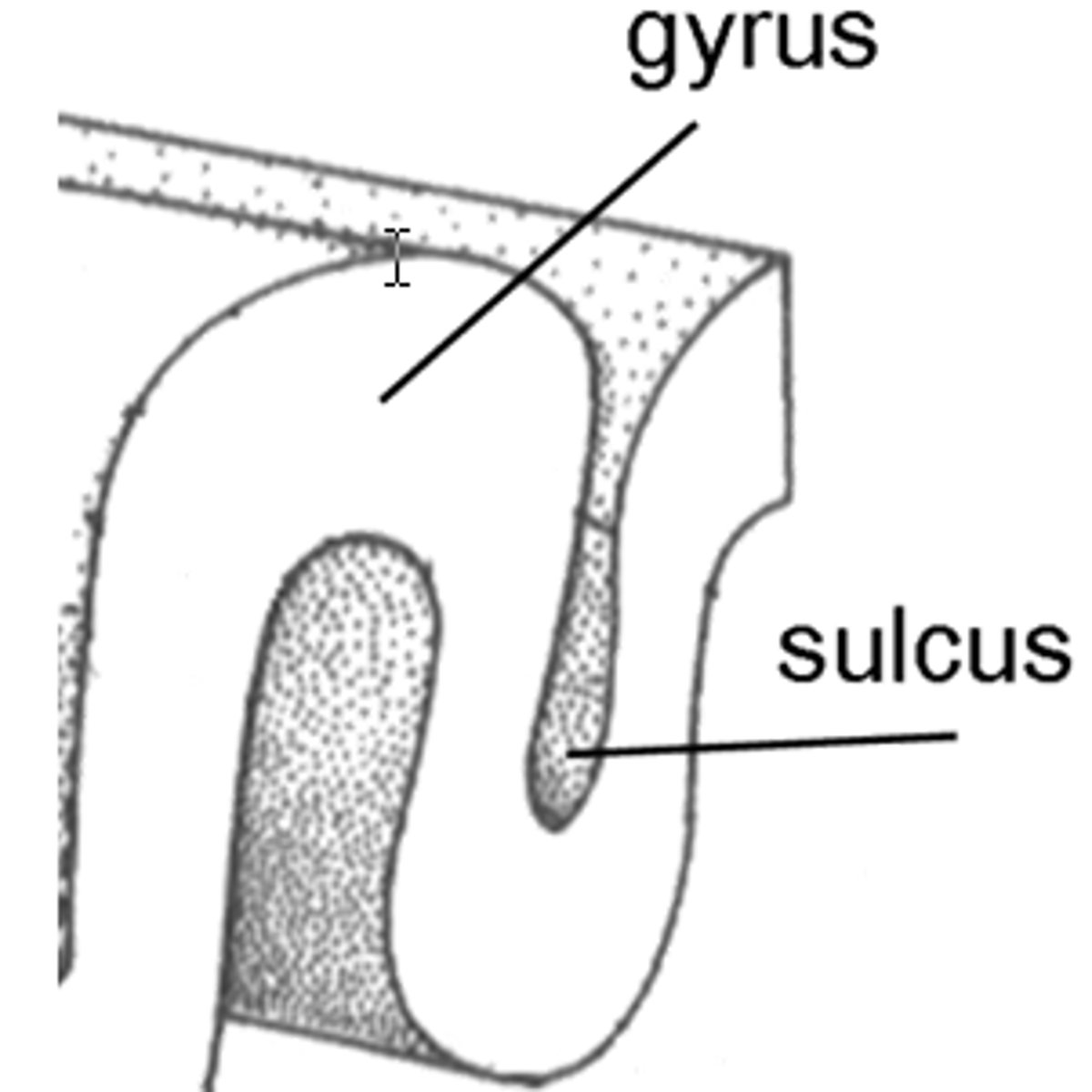
What is the gyrus and sulci of the brain?
Gyrus - Hump in the fold of the brain
Sulci - Dip in the fold of the brain.
What are the functions of the frontal lobe? Where is it located?
PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX (controls skeletal muscle movement).
Located in the precentral gyrus
Voluntary muscle movement, concentration, verbal communication, decision making, planning, and personality.
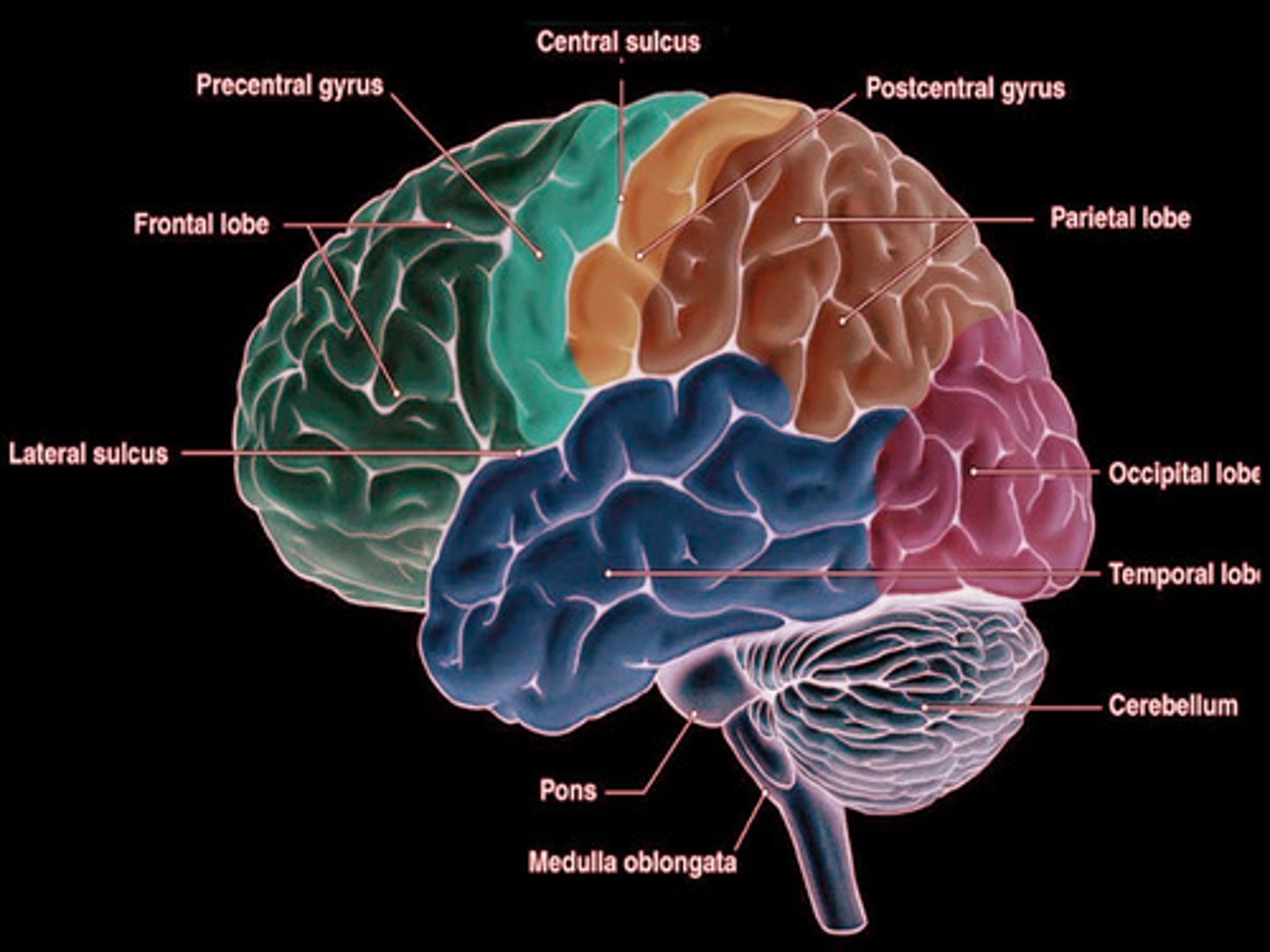
What are the functions of the parietal lobe? Where is it located?
PRIMARY SOMATOSENSORY CORTEX.
Located in the postcentral gyrus
General sensory functions; receives somatic sensory information from touch, pain, pressure, and temperature receptors.
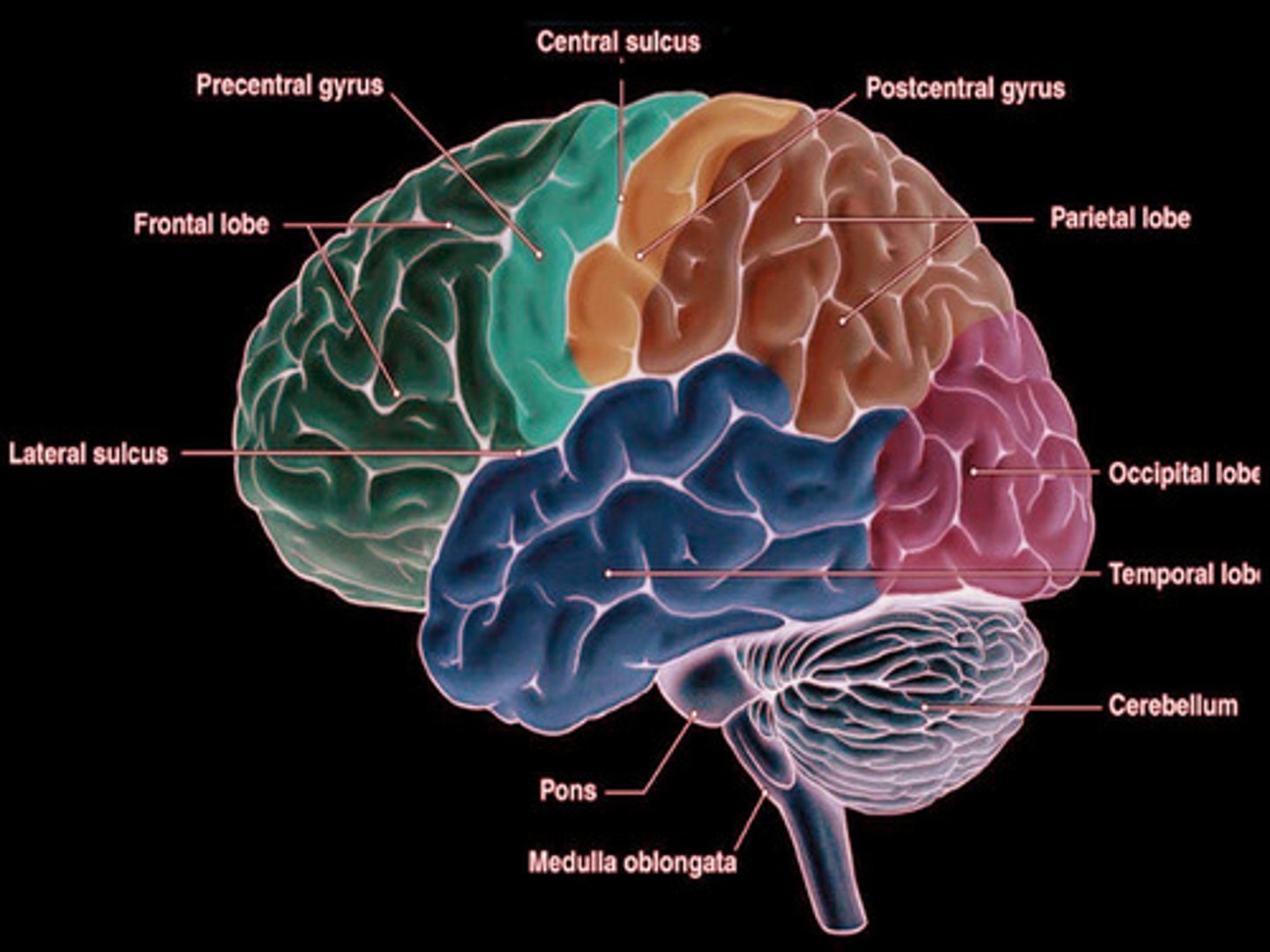
What are the functions of the temporal lobe? Where is it located?
Primary auditory cortex: Hearing
Primary olfactory cortex: Smell
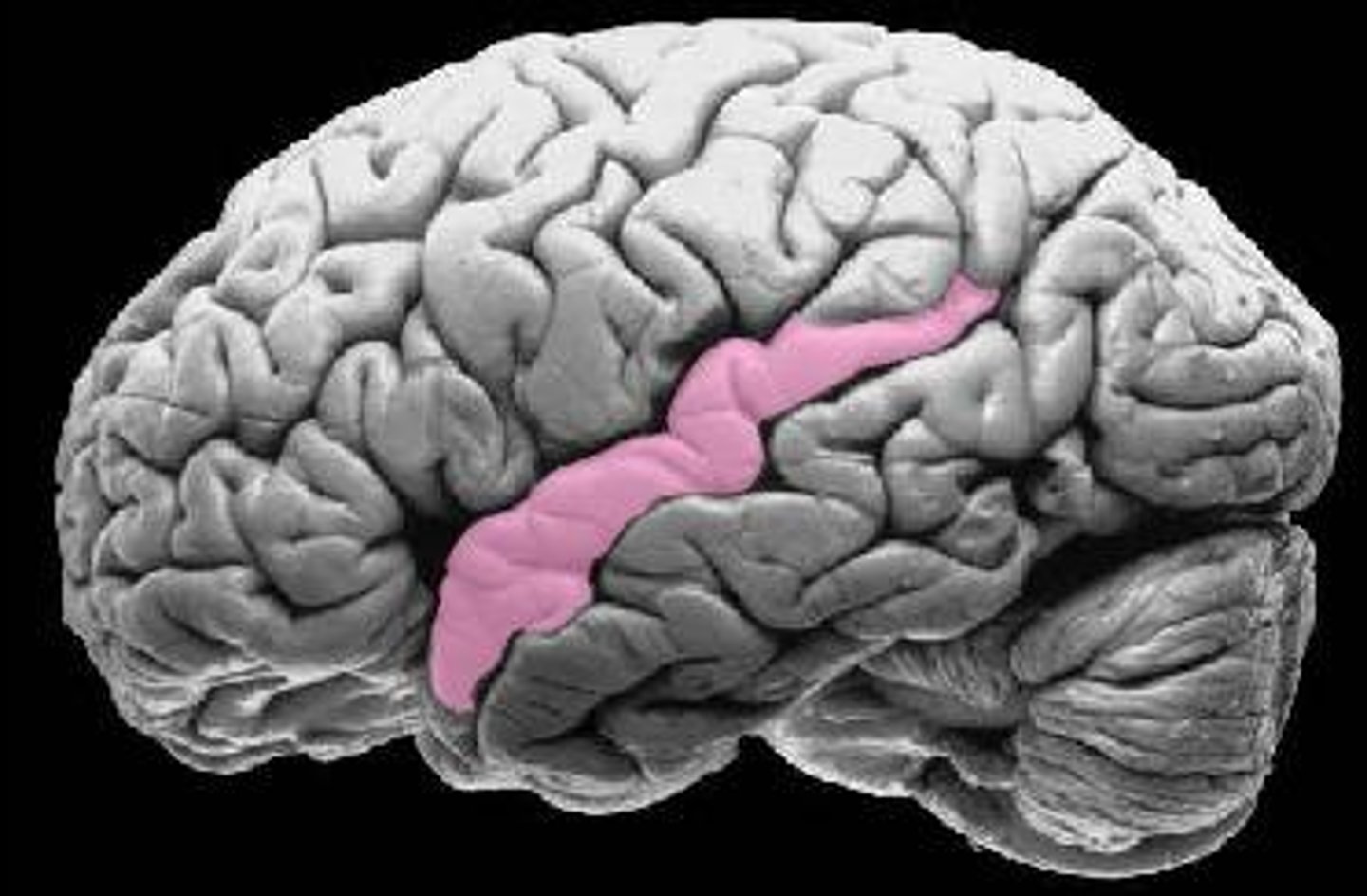
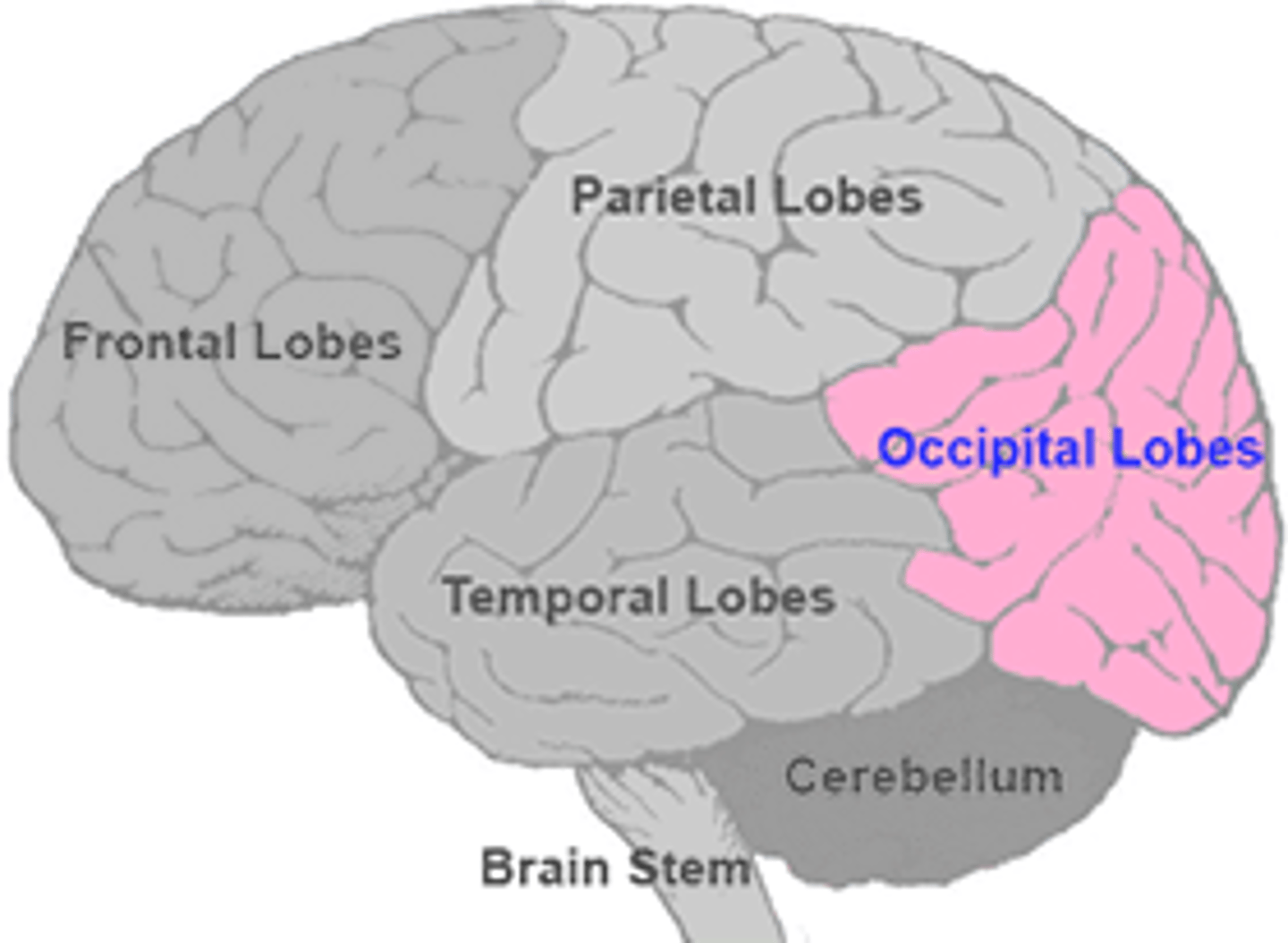
What are the functions of the occipital lobe? Where is it located?
Primary visual cortex
Processes incoming visual information and stores visual memories
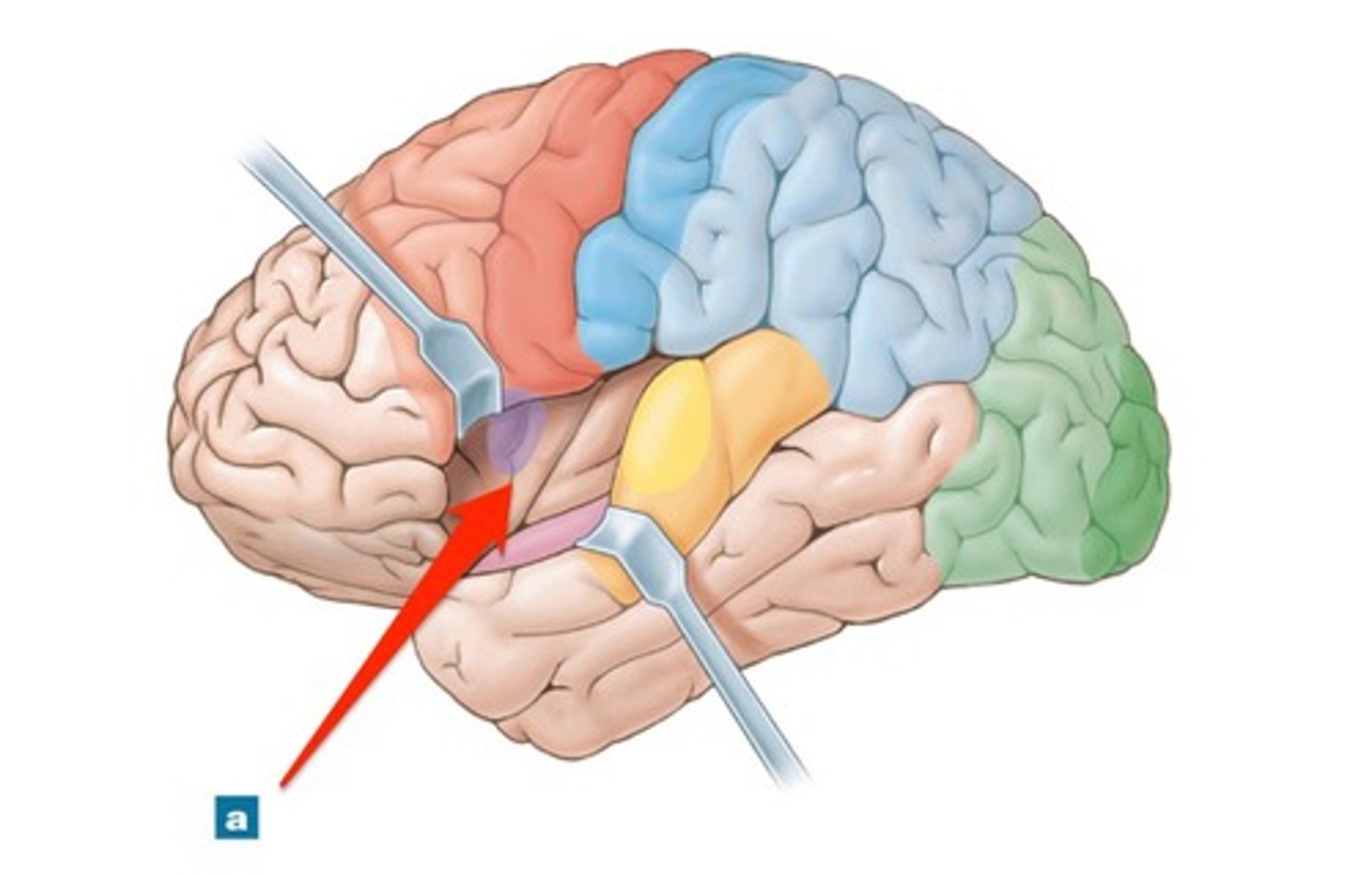
What are the functions of the insula lobe? Where is it located?
Primary gustatory cortex: Taste
Involved in emotional responses, empathy, and taste
What are the three tracts that exist in the white matter of the brain? What does it connect/extend between?
1) Association tracts - connect regions of the cortex WITHIN the same hemisphere.
2) Commissural tracts - extend between cerebral hemispheres
3) Projection tracts - link the cerebral cortex to the inferior brain regions and the spinal cord.
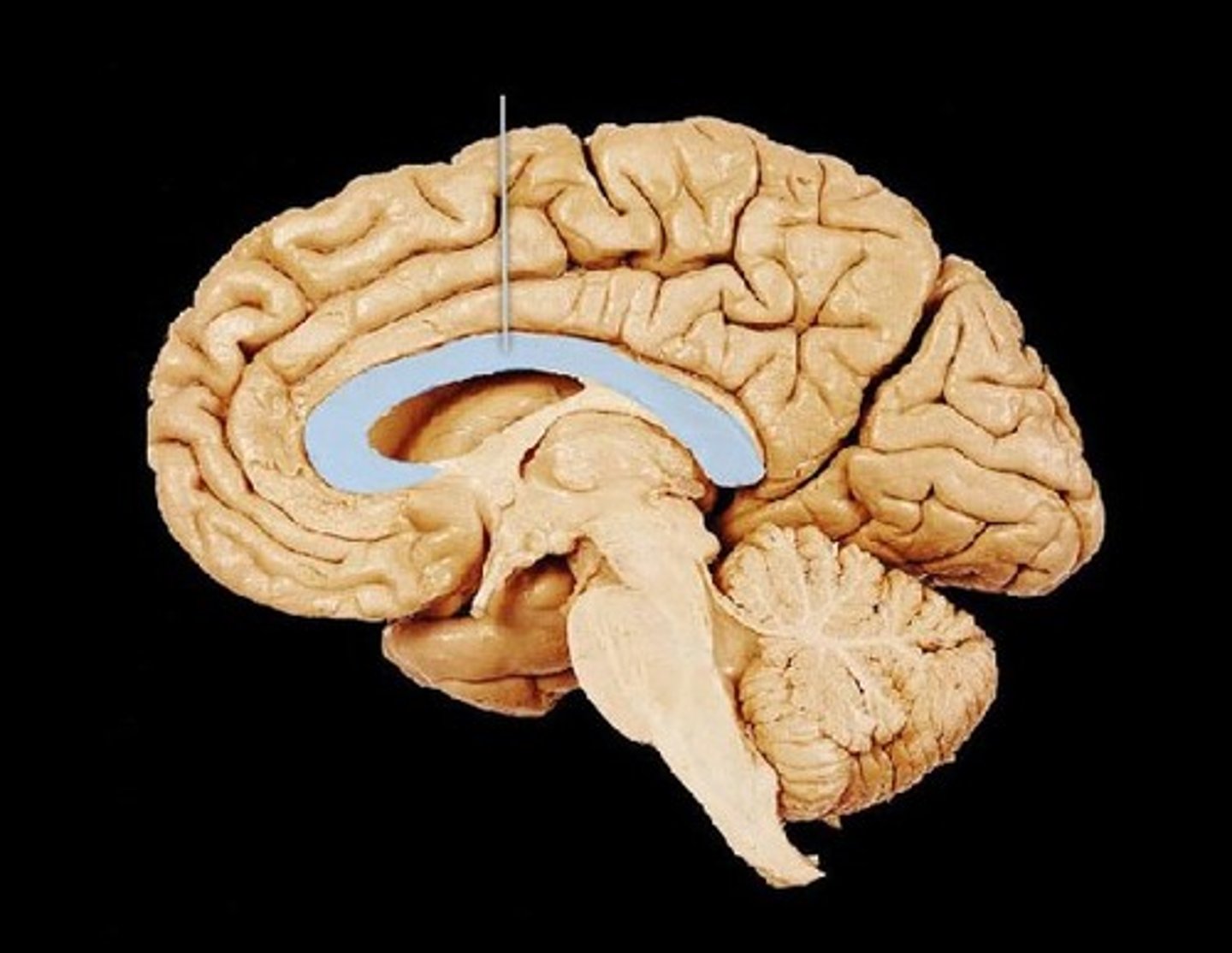
What is the commissural tract called in the brain?
CORPUS CALLOSUM