Aromatic chemistry
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
From closest to furthest to a given substituent, what are the names given to the carbons on a benzene ring?
ipso, ortho, meta, para
What are the four criteria an aromatic compound must satisfy?
planar
fully conjugated
cyclic
Follows Huckel’s rule; has (4n)+2 π electrons
How to determine Huckel’s rule
every double bond has 2π electrons. n= any number
eg. with benzene: 3db therefore 6π electrons, 6= (4×1)×2
a) Is benzene stable and b) why and c) what does this mean for electrophiles?
a) yes very
b) delocalised π bonds
c) must be very strong and reaction must be with Lewis acid
electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism
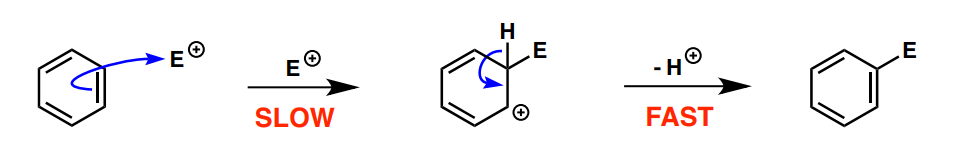
What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate?
A transition state unlike an intermediate cannot be spectroscopically observed of isolated and is higher in energy
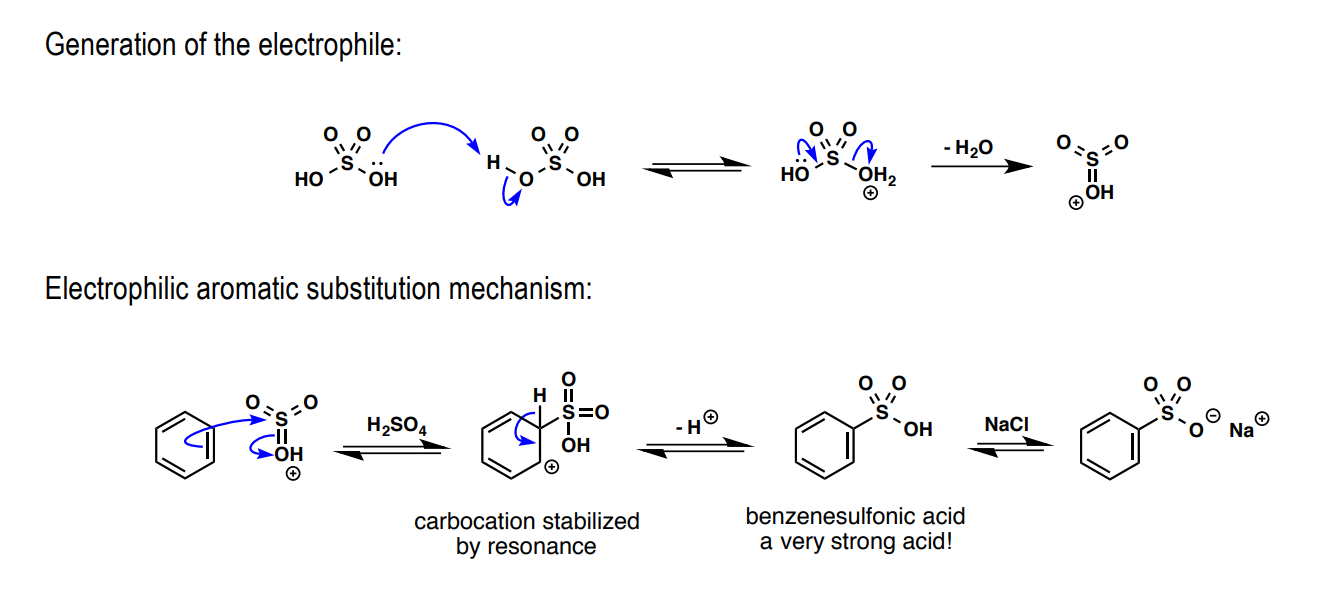
How is benzene sulfonated: a) electrophile preliminary, b) Lewis acid, c) substitution product
a) H2SO4
b) H2SO4
c) SO3H
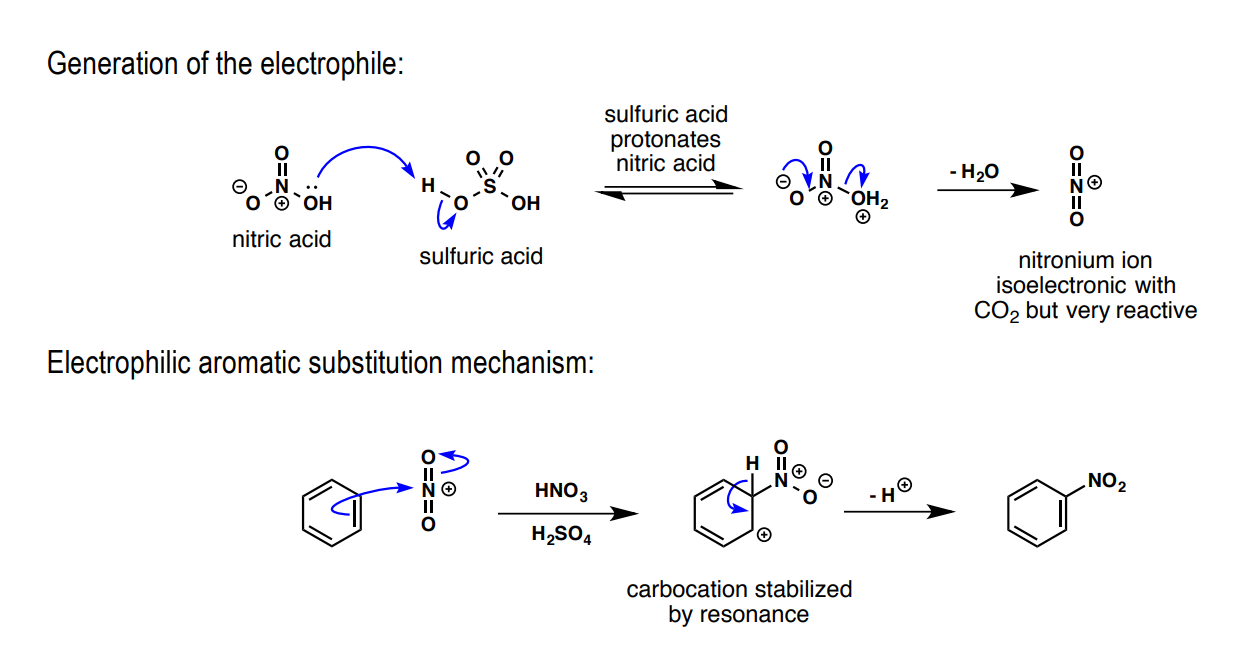
How is benzene nitrated: a) electrophile preliminary, b) Lewis acid, c) substitution product
a) NO3H
b) H2SO4
c) NO2
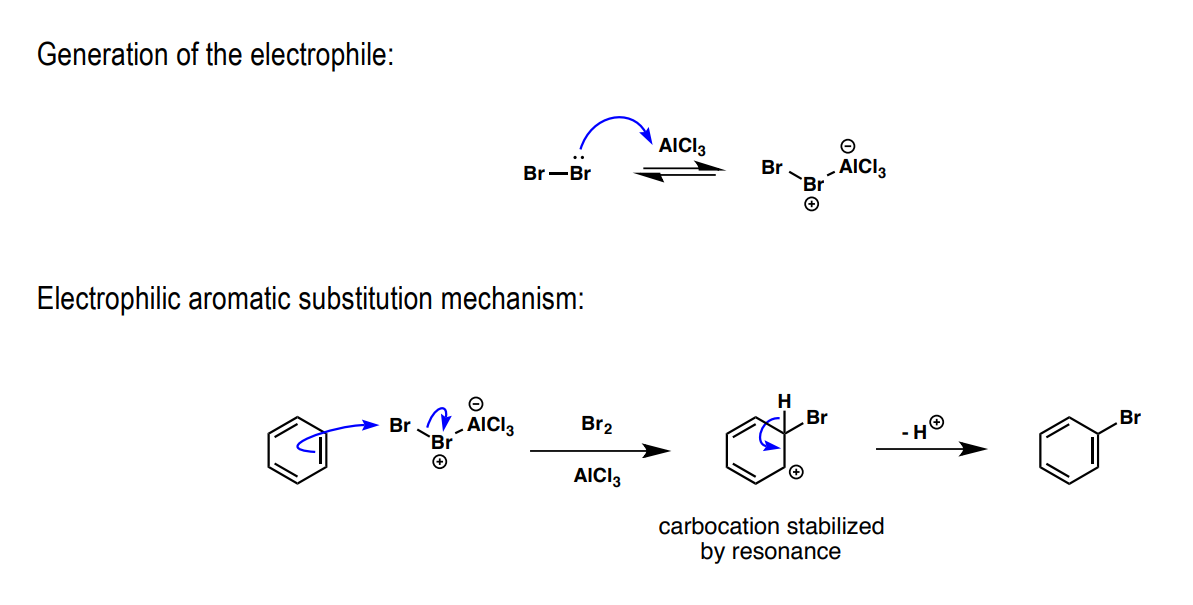
How is benzene brominated: a) electrophile preliminary, b) Lewis acid, c) substitution product
a) Br2
b) FeBr3 / AlCl3
c) Br
Friedel-Crafts alkylation: a) electrophile preliminary, b) Lewis acid, c) substitution product
a) R3CCl
b) AlCl3
c) R3C
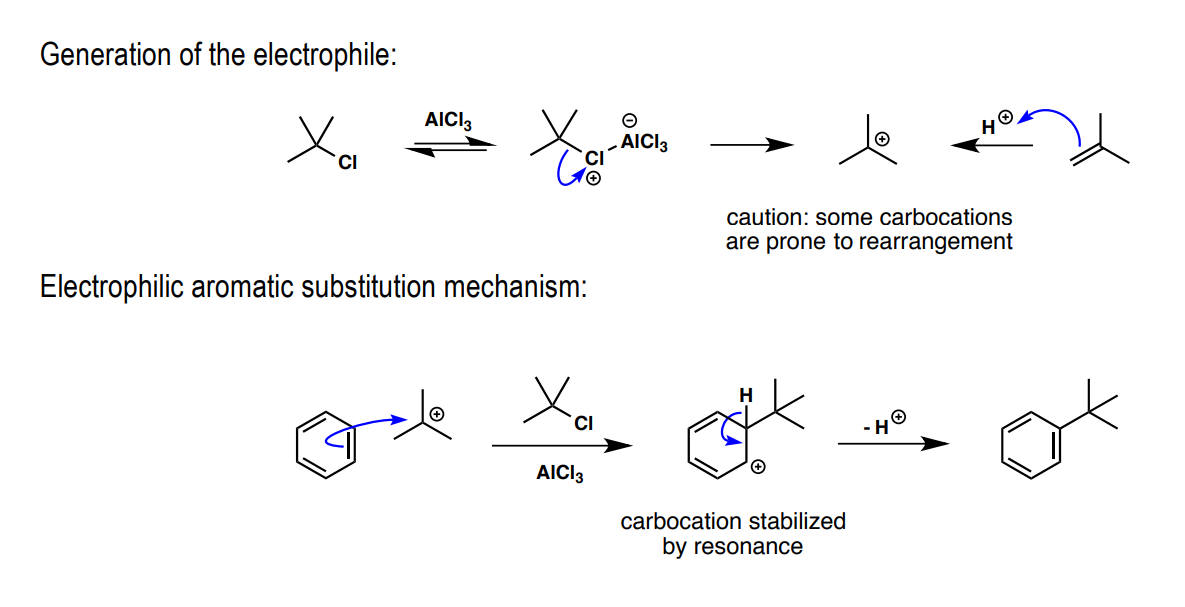
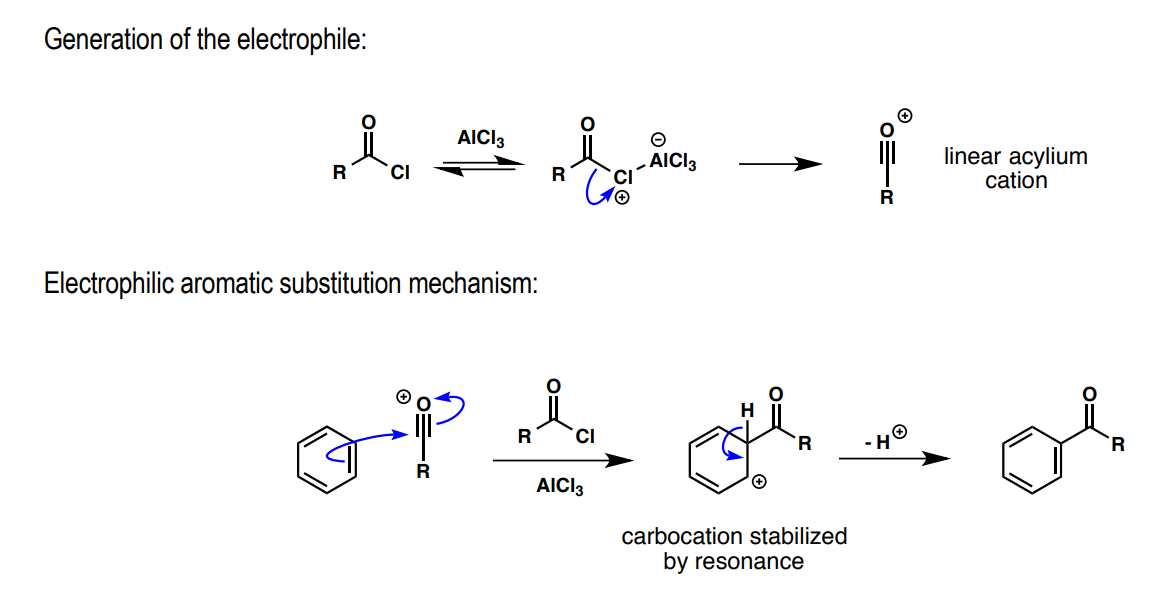
Friedel-Crafts acylation: a) electrophile preliminary, b) Lewis acid, c) substitution product
a) RC=OCl
b) AlCl3
c) RC=O
a) Are phenols (Ph-OH) more acidic than other alcohols and b) why?
a) yes
b) delocalization: lone pair on O- conjugate base perpendicular to the plane of the benzene ring, so it can overlap with the π-system. Similar effect to resonance.
inductive effect: sp2 carbon is more electronegative and more electron-withdrawing than sp3 carbon due to having higher effective nuclear charge
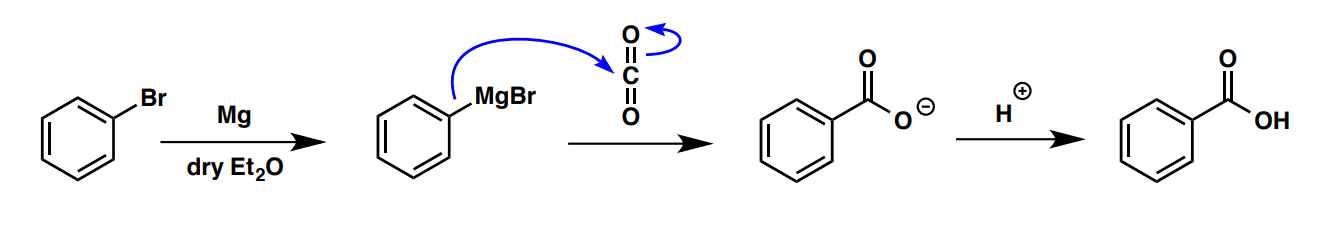
What are two methods that can be used to prepare benzoic acids (Ph-CO2H)?
oxidation of toluene (Ph-Me) with KMnO4
Grignard with CO2 (image)
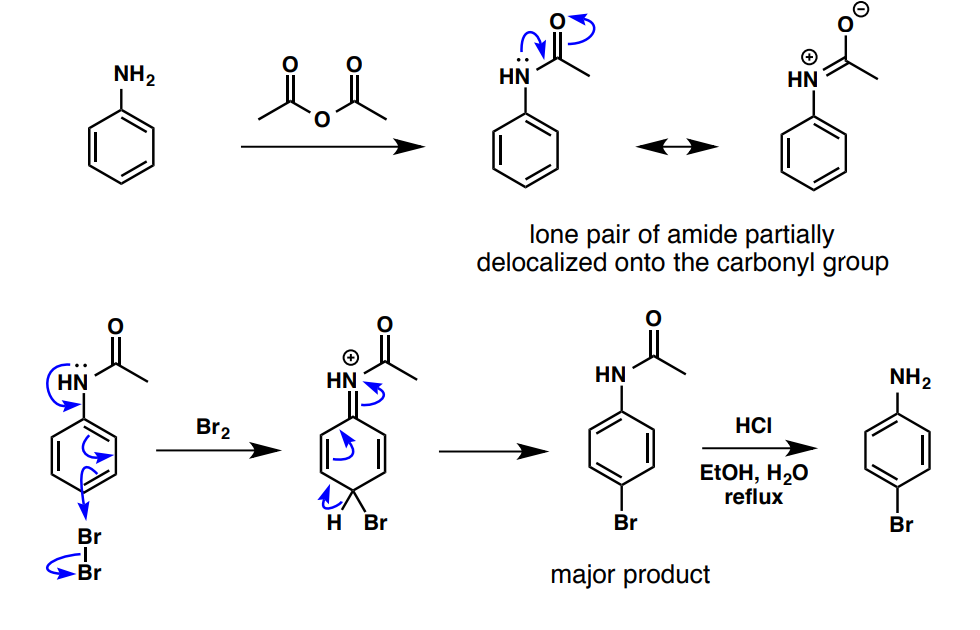
What are the reagents that can be used to prepare aniline (PhNH2)?
NO2→NH2
using Sn/HCl or Pd/H2
What are the 3 possible regioselective products of electrophilic aromatic substitution?
ortho, meta, para
What does a) activating and b) deactivating group mean?
a) reaction faster than benzene
b) reaction slower than benzene
Ortho, para-directing and activating groups (6)
alkyl
NH2
NR2
NHCOR
OH
OR
Why is ortho, para preferred for electron donating groups (with N: or O:)?
intermediate carbocation can be stabilized by/located on the O or N
List the following in order of reactivity: benzene, phenol, aniline, alkyl benzene
aniline>phenol>alkyl benzene>benzene
EXTRA INFO: nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen, so its lone pair of electrons is even more readily donated to the benzene π system
How can the para addition of Bromine to an aniline be favoured?
meta directing, deactivating groups (7)
NO2
SO3H
CO2H
CO2R
CHO
COR
CF3
Are aromatics with Meta-directing and deactivating (electron withdrawing) groups or ortho,para-directing and activating groups more likely to react?
ortho,para-directing and activating
What are the Ortho,para-directing and deactivating groups
halogens (group 7)
List the types of substituents in decreasing directing order therefore dominant effect (higher= directing effect overwhelms)
ortho,para with N or O>alkyl and halogen>meta directing
What happens to the location of substitution if the directing substituents are in a) same and b) different classes?
a) mixture of all products
b) higher directing power dominates
What molecular feature is required for nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
Electron withdrawing group (note: meta directing) ortho or para to the leaving group
What is the mechanistic difference between nucleophilic and electrophilic aromatic substitution?
electrophilic: double bond electrons are the nucleophile, creates cations
nucleophilic: incoming substituent is the nucleophile, creates anions (centered on ortho/para C to LG)
How does the nature of the leaving group impact the a) rate of reaction of an aromatic nucleophilic substitution and b) why?
a) more electronegative= quicker; F>Cl>Br
b) inductively withdraw electron density from the high energy anionic intermediate
TRUE OR FALSE: Pyridine does not need an EWG to undergo nucleophilic aromatic substitution
TRUE: N acts as the EWG
What is needed for making aromatic compounds undergo an SN1 reaction?
N≡N which is a really really good leaving group
What are two mechanisms for the creation of N≡O+?
NaNO2 + H+ (acid)
BuNO2 + H+ (acid)
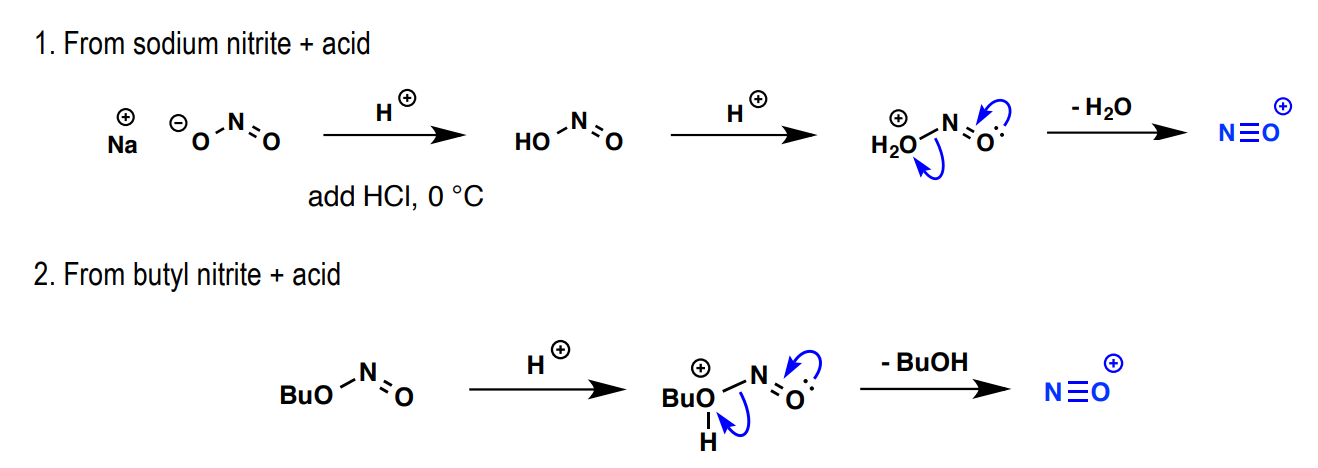
What are the reagents and process of creating a diazonium salt?
primary amine (R-NH2) and N≡O+
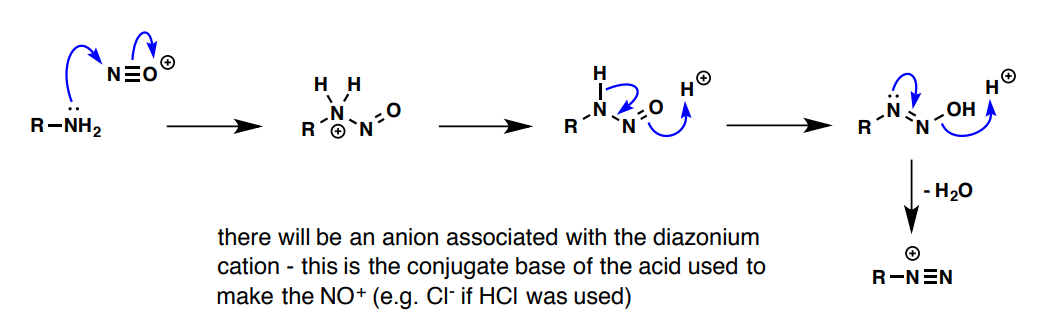
(aryl; CnH2xn+1)N≡N reaction
decomposition to give a planar C+
What is the process for creating a phenol (substituents)?
NO2→NH2→N≡N+ -X→HO
nitration, reduction, diazotization, hydration
TRUE OR FALSE: Diazo groups can be replaced by other nucleophiles
TRUE: especially halogens associated with K (I) or Cu (Br, Cl)
TRUE OR FALSE: aryl halides cannot be substituted
FALSE: a strong base is needed and it will proceed through a benzyne mechanism
Benzyne mechanism (4)
deprotonation ortho- to the leaving group by base
carbanion eliminates halogen, creating benzyne
base attacks benzyne and reforms carbanion
carbanion removed by conjugate acid of base (from first step)
What dictates regioselectivity of a benzyne reaction? (2)
sterics
inductive effect: if electron withdrawing substituent present it stabilizes carbanion formed during addition step
a) How many products can para-Disubstituted halides give in a benzyne reaction and b) why?
a) 2
b) only one benzyne intermediate can be formed and it is too far from the other group for it to exert steric effects
a) What position will the base be added in a benzyne reaction with an electron repelling anion substituent and b) why?
a) meta
b) puts anions furthest from each other
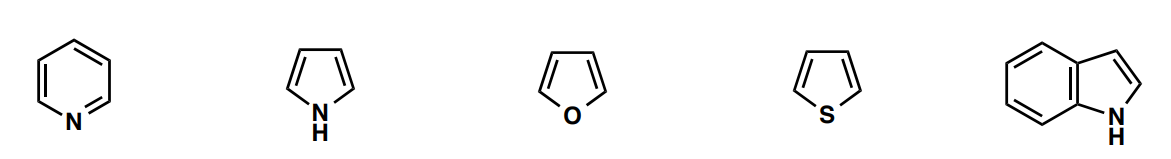
From left to right, name the heterocycles
pyridine, pyrrole, furan, thiophene, indole
Pyridine and DMAP are used as a) what and how and b) which is better and why?
a) nucleophile for carbonyl groups: N knocks out leaving group and makes C more electrophilic
b) DMAP is more nucleophilic due to NMe2 electron donating group
TRUE OR FALSE: Pyridine is a good substrate for electrophilic and nucleophilic aromatic substitution
FALSE: It sucks at electrophilic but is good at nucleophilic
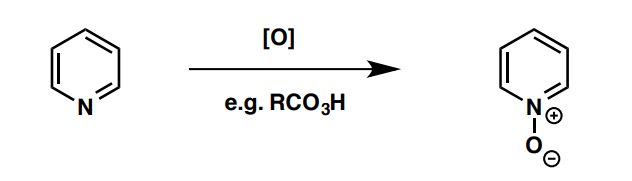
a) How can unsubstituted pyridines undergo electrophilic substitution and b) what substitution product will be formed?
a) pyridine N-Oxide (see image), which can be reverted to pyridine after by P(OMe)3
b) para substitution
a) What halogenated pyridine can be made and b) how?
a) chloropyridine
b) pyridine N-oxide and PCl3
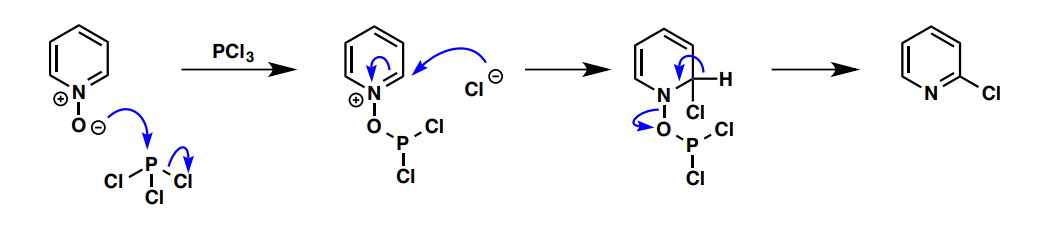
a) How can substituted pyridines undergo electrophilic substitution and b) why?
b) if the substituents are electron donating
b) override pyridine’s unreactivity
a) What are the pyridones’ tautomers and b) which is preferred?
a)
b) keto
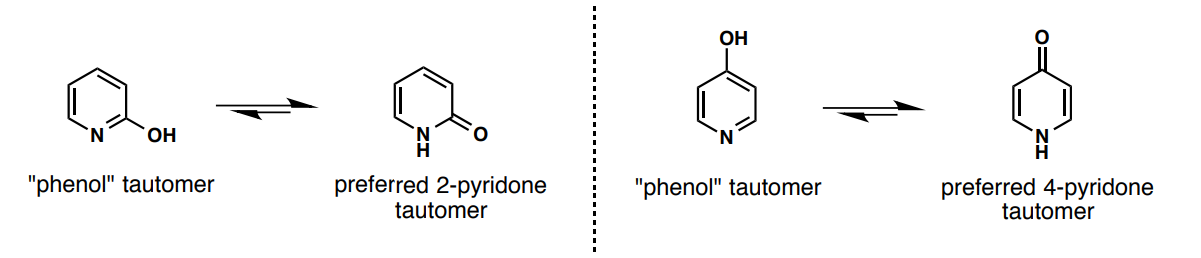
How can pyridone be converted into chloropyridines?
POCl3 reacting with keto (db to O)→ N in ring acts as nucleophile
What is the a) electron rich part of a pyrrole and b) why?
a) the ring
b) delocalization
TRUE OR FALSE: pyrroles are amphoteric
FALSE: moderately acidic
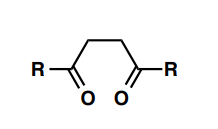
What reagents would you use to synthesize a) pyridine, b) pyrrole, c) thiophene and d) furan from the pictured (or similar) molecule?
a) NH2OH / HCl, EtOH
b) RNH2 or NH3
c) H2S / HCl
d) H+
Electrophilic aromatic substitution of pyrroles is (difficult/easy), but nucleophilic aromatic substitution is (difficult/easy).
Electrophilic aromatic substitution of pyrroles is (difficult/easy), and nucleophilic aromatic substitution is (difficult/easy).
In pyridine, the (ring/N) reacts with electrophiles, in pyrrole, the (ring/N) reacts.
In pyridine, the (ring/N) reacts with electrophiles, in pyrrole, the (ring/N) reacts.
In order of reactivity: furan, pyrrole, thiophene
pyrrole > furan > thiophene
Vilsmeier reaction
POCl3 + RCONMe2
H2O + RCClN+Me2 + pyrrole
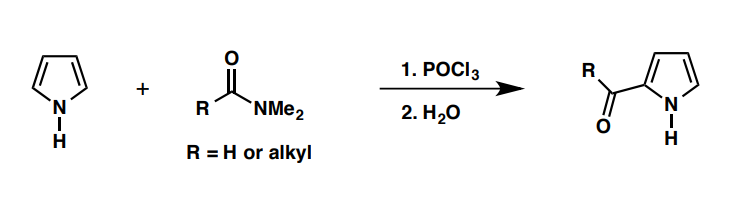
What can be used to imitate the Vilsmeier reaction with (R=Me) in a) thiophene and b) furan?
a) Ac2O, ZnCl2, 100oC
b) Ac2O, ZnCl2, 100oC
Furan + Br2 in a) aprotic solvent and b) MeOH
a) substitution (4 Br on ring)
b) addition (1 OMe added to each C closest to O)
How can C-C bond formation be promoted in thiophene and furan?
use Bu--Li+ to perform lithiation on C closest to O/S