Photosynthesis Test (Ch 10)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Photosynthesis Equation
6Co2 + 6H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + chemical energy
Light-dependent reactions overview
Photosynthesis begins with the light-dependent reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast. These reactions require light and water to produce ATP, NADPH, and oxygen.to generate energy for the light-independent reactions.
Takes in water and splits into oxygen
Calvin Cycle overview
Occurs in stroma, doesn’t require light directly
ATP + NADPH + CO2 → sugar
ATP broken down to release energy
NADPH donates electrons to convert carbon dioxide into sugars
Uses carbon dioxide to make G3P
Redox reaction
Acronym: OIL RIG (oxidizing is losing, reducing is gaining)
H₂O is oxidized → Becomes O₂ (loses electrons).
CO₂ is reduced → Becomes C₆H₁₂O₆ (gains electrons).
Light dependent reaction pictures

Chemiosmosis
the driving of ATP production as H+ ions flow down their gradient
Isn’t the specific process of production of ATP, but the process by which H+ ions flow
H+ ions first flow into thylakoid, increasing concentration and decreasing pH —> creates proton gradient that creates potential energy
H+ ions then flow back into stroma thru ATP synthase
Provides energy to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi)
Separate from photophosphorylation
When do chloroplasts seem to switch from linear to cyclic electron flow?
when the ratio of NADPH to NADP+ is too high (when too little NADP+ is available to accept electrons)
Especially since Calvin Cycle requires 18 ATP molecules, vs. the 12 NADPH, to create 2 G3P molecules (enough to make a glucose)
The 2:3 ratio of NADPH and ATP produced by linear electron flow may be insufficient
may also prevent excess light from damaging photosystem proteins and promoting repair of light- induced damage.
Effect of absence of photosystem 1
Rate of biomass produced by photosynthesis will be lower b/c insufficient ATP/NADPH produced for the synthesis of carbohydrates
Chlorophyll purpose
absorbs light energy, receiving electrons from water
Step 1 of Light-Dependent Reactions: Photosystem II
light energy (photons) excited electrons in PSII, which are transferred to ETC
This movement helps generate ATP through chemiosmosis, where protons (H+) flow through ATP synthase into stroma
Step 4 of Light-Dependent Reactions: Photosystem I
Electrons from PSII re-energized in PSI and passed through another ETC (Fd → NADP+ reductase)
No proton gradient → no ATP production
The enzyme NADP+ reductase catalyzes the transfer of electrons from Fd to NADP+ (2 electrons gained for reduction to NADPH)
Electrons in NADPH at higher energy level than in water, so more readily available for reactions of Calvin Cycle
H+ also removed from stroma
Step 2 of Light - Dependent Reactions: Photolysis
To replace lost electrons, water molecules split
Produces electrons to replenish ETC
Produces protons to help create gradient for ATP production
Produces oxygen (byproduct)
Electrons and Protons purpose
electrons transfer energy
Protons help make ATP
Alternate Names for Photosystems
Photosystem II - P680 (pigment is best at absorbing light with a wavelength of 680 nm)
Photosystem I - P700 (pigment is best at absorbing light with a wavelength of 700 nm)
Role of NADPH in photosysnthesis
carries high-energy electrons to Calvin Cycle for sugar production
Photophosphorylation
process of ATP production in the light-dependent reactions using light energy
Via chemiosmosis - process by which protons (H+ ions) flow across a membrane through an enzyme called ATP synthase
Non-cyclic vs. cyclic photophosphorylation
Non-cyclic - produces both ATP and NADPH (involves P1 and P2)
Cyclic - produces only ATP (only P1)
Enzyme responsible for carbon fixation in Calvin cycle
RuBisCo
Why do C4 and CAM plants have adaptations for photosynthesis?
to reduce photorespiration and survive in hot, dry environments where stomates are often closes
What type of plants use the C4 pathway?
Grasses and plants with a specialized leaf anatomy (bundle sheath cells)
What type of plants use the CAM pathway?
Cacti, succulents, and pineapples
Step 2 of Light-Dependent Reactions:
Step 4 of Light-dependent reactions: H+ Gradient Formation
the protons (H+ ions) built up inside thylakoid space after coming in from stroma
Protons diffuse out through ATP synthase, leading to ATP production
Chemiosmosis
Plant anatomy
Thylakoids - membrane-bound compartments where light reactions occur
Grana - stacks of thylakoids
Stroma - fluid surrounding thylakoids (where Calvin Cycle occurs)
Mesophyll Cells - in plant leaf tissue, contain chloroplasts
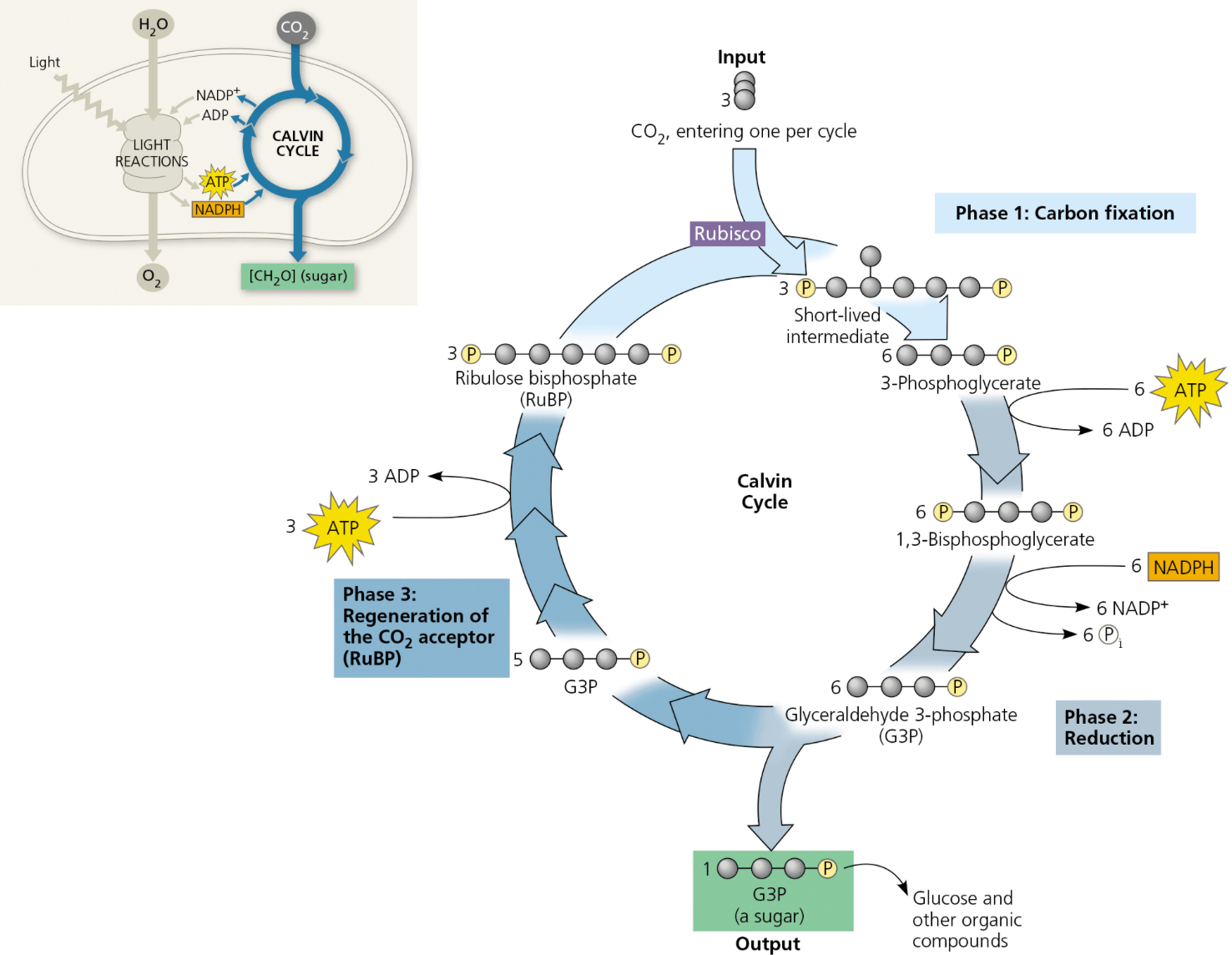
First Step of Calvin Cycle: Carbon Fixation
Technically occurs thrice to produce one G3P molecule from one CO2
enzyme RuBisCo attaches 3 CO2 to 3 RuBP (a 5-carbon molecules), forming a short-lived, unstable 6-carbon compound (6 carbons with a phosphate on each end)
Quickly splits into 6 3-carbon molecules (3-PGA) (3 carbons with a phosphate on one end)
Steps of Calvin Cycle
Carbon Fixation
Reduction Phase
Regeneration of RuBP
Carbon fixation definition
“ the initial incorporation of CO2 into organic material”
Step 2 of Calvin Cycle: Reduction Phase
6 ATP turns into 6 ADP, contributing a phosphate to form 6 Bi-PGA (now three carbons with 1 phosphate on each side)
6 NADPH contributed, leaving as 6 NADP+ and taking added phosphate with it
Removal converts 6 3-PGA into 6 G3P (a 3-carbon sugar)
1 G3P leaves cycle to become glucose and other carbohydrates
Step 3 of the Calvin Cycle: Regeneration of RuBP
5 G3P molecules stayed in cycle to be recycled
Using 3 ATP, 5 G3P molecules turned into 3 RuBP molecules
15 carbon total
ATP leaves as ADP
Photo of Calvin Cycle
Photorespiration
process that occurs in plants when RuBisCo reacts w oxygen instead of carbon dioxide
Tends to occur in an oxygen-rich, carbon-dioxide-low environment
Leads to production of 2-carbon molecule (G2P) instead of normal 3-carbon molecule
Inefficient because it doesn’t contribute to production of sugars and consumes energy
Reduces plant’s overall efficiency
Plant may draw on stored carbohydrates, reducing plant’s energy reserves, growth, and survival
First Step of C4 Pathway
In mesophyll cells
enzyme PEP carboxylase adds CO2 to PEP, forming Oxaloacetate, then Malate
Has much higher affinity for CO2 than rubisco and no affinity for O2
PEP carboxylase can fix carbon efficiently when rubisco can’t
2nd Step of C4 Pathway
the four- carbon products moves into a bundle-sheath cell via plasmodesmata
Third Step of C4 Pathway
The 4-carbon compounds CO2 is released
CO2 re-fixed into organic material by rubisco and the Calvin Cycle
Same reaction regenerates pyruvate, which is transported to mesophyll cells
ATP used to convert pyruvate to PEP, which can accept addition of another CO2
Overview of C4 Pathway
mesophyll cells pump CO2 into bundle-sheath cells, keeping CO2 concentration high enough for rubisco to bind CO2, not O2
O2 kept away from RuBisCo
spends ATP energy to fix carbon dioxide, minimize photorespiration, and enhance sugar production
Overview of CAM
crassulacean acid metabolism
Mesophyll cells store organic acids they make during night in vaculoes until morning, when stomata close
during day, when light reactions can supply ATP and NADPh, CO2 released from organic acids made night before to become incorporated into sugar
Rather than structural/physical separation in C4 plants, CAM plants have came 2 steps but different times.
First Step of CAM Pathway
In mesophyll cells
enzyme PEP carboxylase adds CO2 to PEP, forming Oxaloacetate, then Malate
Has much higher affinity for CO2 than rubisco and no affinity for O2
PEP carboxylase can fix carbon efficiently when rubisco can’t
Occurs during night, organic acids stored in vacuoles (stomates open during night)
Second Step of CAM Pathway
Daytime (stomates closed)
the four- carbon products moves out of vacuoles
Third Step of CAM Pathway
The 4-carbon compounds’ CO2 is released
CO2 re-fixed into organic material by rubisco and the Calvin Cycle
Same reaction regenerates pyruvate, which is transported to mesophyll cells
ATP used to convert pyruvate to PEP, which can accept addition of another CO2
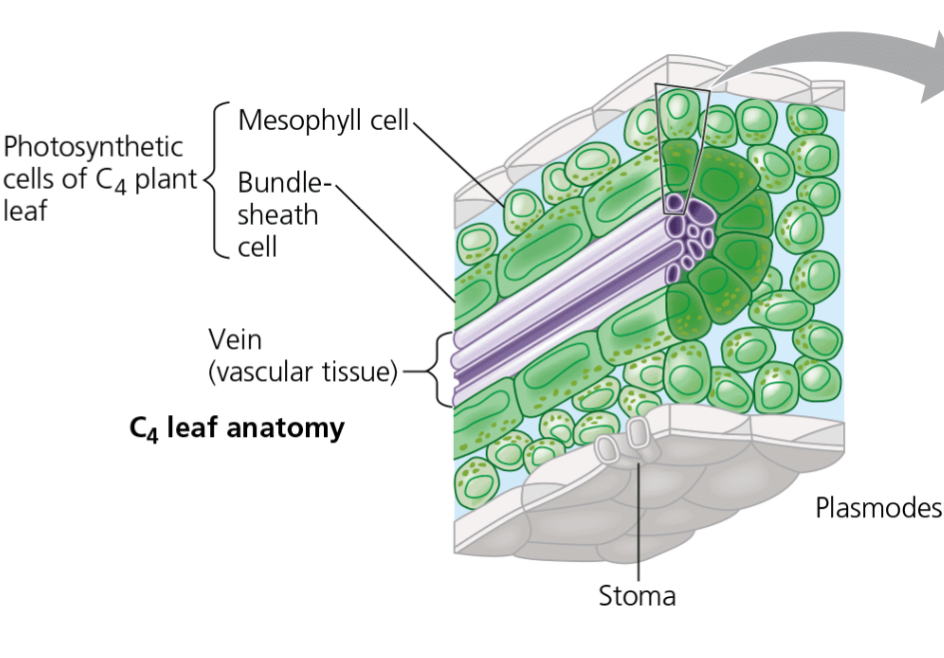
C4 Leaf Anatomy
Bullseye
inner tube of vein (vascular tissue)
surrounding layer of bundle sheath cell (photosynthetic cells)
surrounding layer of mesophyll cell (photosynthetic cells)
stoma on top and bottom
Which photon color would carry the most energy?
Blue (the smaller the wavelength/closer to purple → the more energy)
What is the range of wavelengths pigments capture?
blue-violet and red-orange