EL 2 How do we know so much about outer space?
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is spectroscopy?
The study of how substances absorb or emit electromagnetic radiation to identify their structure.
What types of electromagnetic radiation are studied in spectroscopy?
Infrared visible ultraviolet
What does absorption spectra show?
Missing frequencies of light absorbed by particles in a star’s chromosphere.
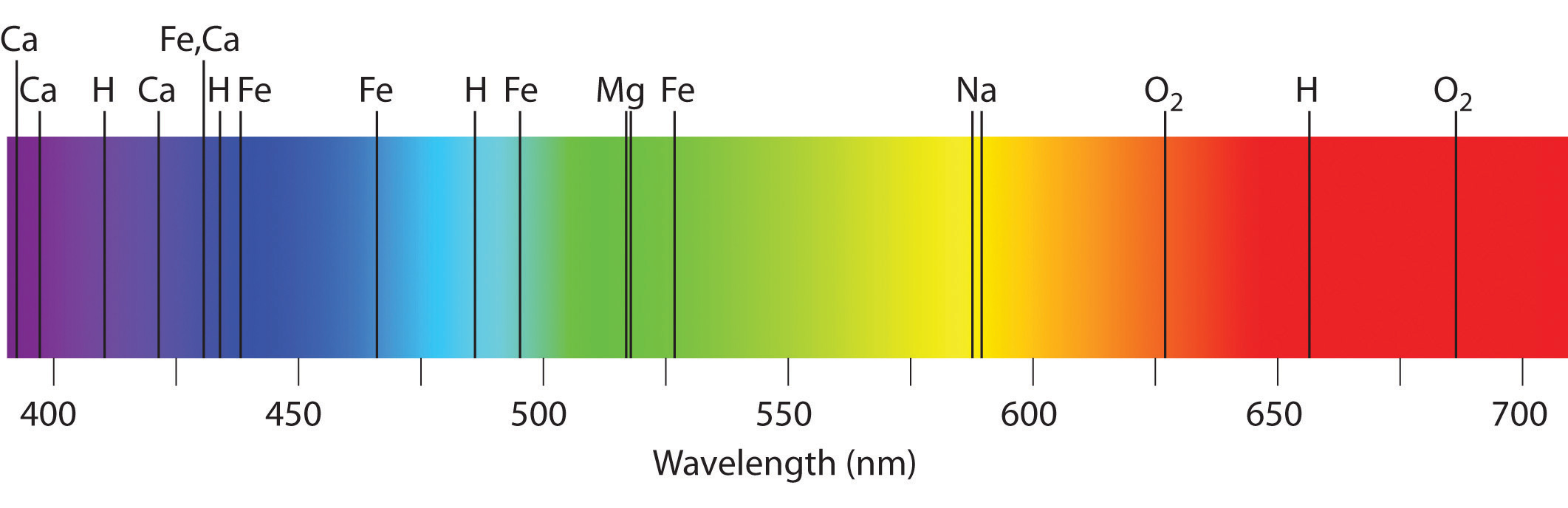
What is the absorption spectrum of a star?
dark lines where specific wavelengths of light are absorbed by elements
on a continuous background
What happens in emission spectra?
Atoms or molecules release energy when
electrons fall to lower energy levels emitting light.
What is the difference between absorption and emission spectra?
Absorption spectra shows missing frequencies
emission spectra shows frequencies emitted by excited atoms
What can scientists detect from absorption spectra?
presence of elements in stars
their energy levels and
their composition.
What is the Bohr model?
electrons in atoms occupy discrete energy levels
emitting light when they transition
How do hydrogen atoms produce emission spectra?
Electrons jump to higher energy levels and emit light when falling back to lower levels.
What is the Lyman series?
The series of hydrogen emission lines in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum.
What does the wave theory of light describe?
Light behaves as a wave with properties like frequency and wavelength.
What does the particle theory of light describe?
Light behaves as a stream of photons each with energy related to its frequency.
What are the features of the atomic spectrum of hydrogen?
Distinct lines corresponding to specific wavelengths of light emitted as electrons transition between energy levels.
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
inversely proportional
What is the Planck constant?
It is a fundamental constant (h = 6.63 x 10^-34 J·s) used in calculating the energy of photons.
What is the formula relating energy to frequency?
E = h v
What is the frequency of visible light?
Visible light has a frequency range from 4.3 x 10^14 Hz to 7.5 x 10^14 Hz.
What is the role of spectroscopy in determining the composition of stars?
It helps identify the elements in stars by analysing absorption and emission lines.
What happens to the energy of an electron in an atom when it jumps to a higher level?
absorbs energy
What is the significance of absorption lines in a star's spectrum?
They indicate the presence of specific elements and provide information about their concentration and state.
What is the purpose of flame tests?
To identify metal ions based on the characteristic colour they emit when heated.
What is the flame colour for lithium?
Red.
What is the flame colour for sodium?
Yellow-orange.
What is the flame colour for potassium?
Lilac
What is the flame colour for calcium?
Orange-red.
What is the flame colour for copper(II) ions?
Green
What are quanta?
Discrete energy levels that electrons can occupy with energy changes between them corresponding to photon emission or absorption.
How does the atomic spectrum relate to the energy levels of an atom?
shows the energy differences between the atom's energy levels
What are the main features of atomic spectra?
Characteristic lines that correspond to transitions between specific energy levels in atoms.
How do flame tests relate to atomic spectra?
emit characteristic colours that match specific wavelengths of light emitted by atoms
What is the result of the Bohr model’s predictions for hydrogen's emission spectrum?
It accurately predicted the wavelengths of light emitted by hydrogen when its electrons transition between energy levels.
What are the similarities between absorption and emission spectra?
Both involve electron transitions between energy levels and result in characteristic lines corresponding to specific wavelengths of light.
What is the energy of a photon?
E = hv.
What is the significance of the Bohr model for understanding atomic spectra?
It explains why atoms emit only certain frequencies of light and how electron transitions produce spectral lines.
How can we identify the presence of elements in stars?
By analysing the absorption lines in the star’s spectrum and matching them to known wavelengths of light absorbed by specific elements.
What does the particle theory of light explain?
It explains the dual nature of light as both a wave and a particle particularly in the context of quantum theory and photons.
How are emission spectra used in the analysis of stars?
They reveal which elements are present in the star's atmosphere based on the specific wavelengths of light emitted by excited atoms.
What are the characteristics of the absorption spectrum of a star?
It consists of dark lines corresponding to wavelengths of light absorbed by elements like hydrogen and helium in the star’s atmosphere.
What is the relationship between energy
frequency
What happens when an electron returns to a lower energy level?
It emits electromagnetic radiation in the form of light
How can flame tests identify metal ions?
By producing specific flame colours that correspond to the wavelengths of light emitted by different metal ions.
What is the formula for calculating the speed of light?
c = λ v
How does the absorption spectrum of a star help identify the elements present in its atmosphere?
The absorption spectrum shows dark lines at specific wavelengths which correspond to light absorbed by elements like hydrogen and helium in the star’s atmosphere. What is the Bohr model of the atom and how does it explain the emission spectrum of hydrogen?