10. Antigens and Immunogens
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are the 5 types of antigens
Proteins: best type of molecule that elicits a response
The bigger, more complex and more visible the better
Polysaccharides: their repetitive structure elicits a response
Typically need to be bound to a protein
Typically T-cell independent B cell activation
Nucleic acids: Fairl poor activators unless bound to proteins
Lupus is an example where patients produce antibodies against native dsDNA
Lipids: Rarely elicit a response unless bound to protein or polysaccharide
LPS is one of the most potent stimulators of the immune system
Superantigens: activate T cells regarding of specificity
Creates uncontrollable activation of T cells
Binds to MHC Class II outside of peptide groove
Binds to outer surface of TCR
Ex. Staph aureus
Antigen vs. Immunogen
Antigen: Any molecules that can be bound by an antibody and or T cell
Immunogen: an antigen that can elicit an immune response
Anything can be an antigen but not all antigens are immunogens
What are Adjuvants?
What is the relationship in solution when adjuvants are added?
Added to immunogenic antigens in order to maximize an immune response
Making the antigen bigger
Making antigen precipitate
Adjuvants are added to a solution with Immunogen but they do not form stable linkages to each other
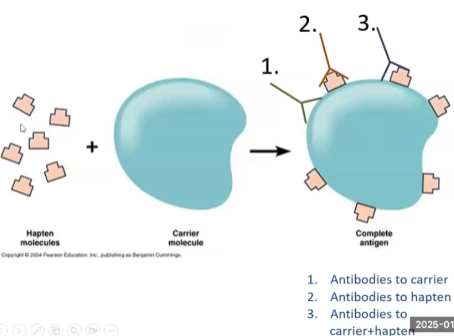
What are haptens?
What is one instance in which they CAN elicit an immune response?
They are antigens that can be bound by antibodies, but do not elicit an immune response
ANTIGENIC, NOT IMMUNOGENIC due to small size and simplicity
They can elicit an immune response if bound to an immunogenic carrier protein
Explain the antibody production in relation to the following situations
Hapten
Carrier Immunogen
Hapten + carrier
Hapten → No antibodies
Carrier immunogen → antibodies against carrier
Hapten + Carrier → antibodies against Hapten, carrier AND hapten and carrier at the same time
Example of drug-induced haptenation
IV Pen G acts as hapten and binds to RBC surface proteins (acts as carrier) and induces hemolytic anemia
______ molecular structures do not elicit much of an immune response
Maximum stimulation occurs with ____ molecules because they are ___ soluble and more _____ for APCs to phagocytose
_______ molecules are more easy to distinguish as foreign
Homopolymers are ____ immunogens, while Heteropolymers are ___ immunogens
Charge counts, charged molecules are ____ than uncharged neutral molecules
HYdrophilic is ___ than hydrophobic
Immunogens must be __________ so they can be processed and presented to T cells, this is why prosthetic devices are not immunogenic
Small molecular structures do not elicit much of an immune response
Maximum stimulation occurs with larger molecules because they are less soluble and more visible for APCs to phagocytose
Complex molecules are more easy to distinguish as foreign
Homopolymers are bad immunogens, while Heteropolymers are good immunogens
Charge counts, charged molecules are better than uncharged neutral molecules
Hydrophilic better than hydrophobic (bc we are hydrophobic)
Immunogens must be degradable so they can be processed and presented to T cells, this is why prosthetic devices are not immunogenic
The more ______, the more antibodies that can bind, the more immunogenic
The more unlike ____ molecules, the better
Dosage is important (goldilocks effect) because too low ____ ___ elicit a response and too high may elicit _____
Route of administration determines which _____ and ______ will activate and ____ of antibody produced
Some ______ defects confer non-responsiveness or decreased responsiveness
Age also affects responsiveness as _____ have a still developing immune system and immunity ____ with age
The more epitopes, the more antibodies that can bind, the more immunogenic
The more unlike our molecules, the better
Dosage is important (goldilocks effect) because too low will not elicit a response and too high may elicit anergy
Route of administration determines which cells and organs will activate and isotype of antibody produced
Some genetic defects confer non-responsiveness or decreased responsiveness
Age also affects responsiveness as infants have a still developing immune system and immunity wanes with age
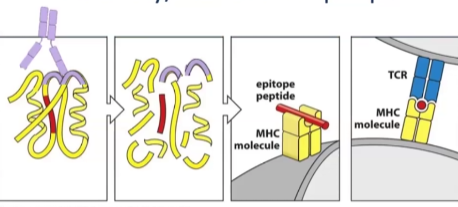
BCR binds native molecules that are _______ around _____ of cells
TCR binds to ____ that are presented on _____ complexes
TCR and BCR can have the same _____ but not always the same _____
BCR binds native molecules that are floating around outside of cells
TCR binds to peptides that are presented on MHC complexes
TCR and BCR can have the same antigen but not always the same epitope
Characteristics of BCR
Binds proteins or peptides?
Sequential or discontinuous binding?
Epitope must be outside or inside?
Recognizes what kinds of antigens?
Binds anything, proteins, peptides
Binding may be sequential or discontinuous
Epitope must be on antigen external surface
Recognizes nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and polysaccharides
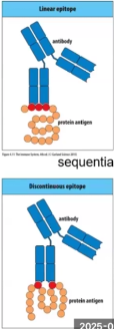
Characteristics of TCR
Binds proteins or peptides?
Sequential or discontinuous binding?
Epitope must be outside or inside?
Recognizes what kinds of antigens?
Binds peptides presented on MHC only
Binding is sequential
Epitope can be inside or outside, it doesn’t matter bc it will be broken down into peptides
Recognizes almost always proteins