05 Concrete, Mortar, Hardware & Adhesives
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Finish Hardware
Exposed hardware serving a decorative as well as a utilitarian purpose, as the locks, hinges, and other accessories for doors, windows, and cabinetwork
Hinge
A jointed device, usually consisting of two leaves joined together by a pin, on which a door, gate, or shutter swings, turns, or moves
Loose Pin Hinge
Hinge having a removable pin so that the door can be enough by separating the two leaves
Ball Bearing Hinge
The hinge equipped with ball bearing between the knuckles to reduce friction and ensure ease of operation
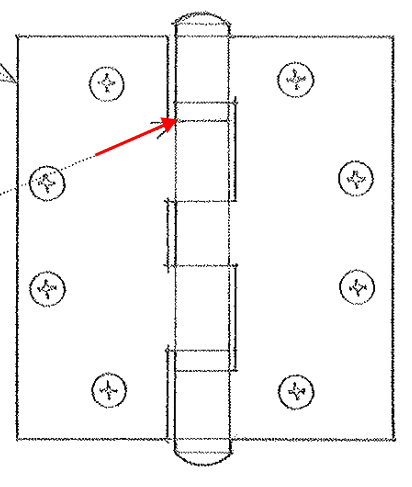
Gravity Hinge
A hinge that closes automatically by means of gravity
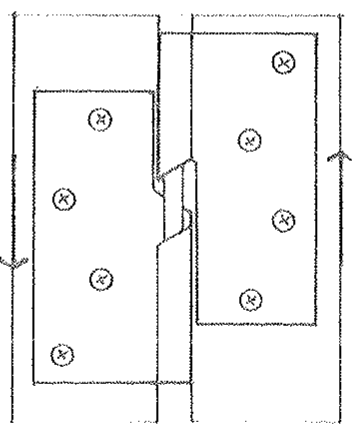
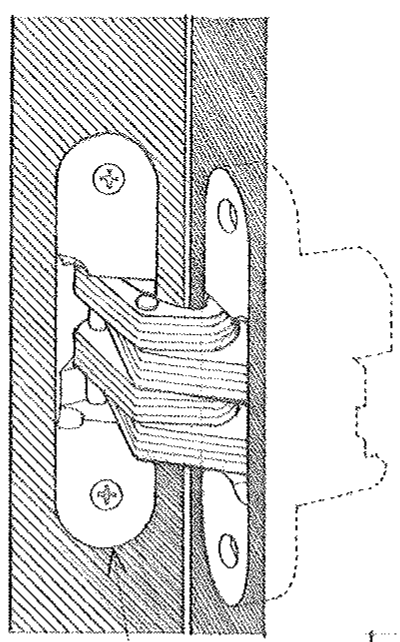
Concealed Hinge
A hinge consisting of a number of flat plates rotating about a central pin, with shoulders mortised into the door edge and doorframe so as to be concealed when closed
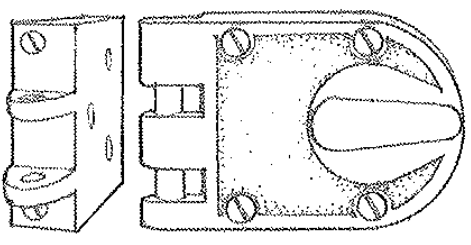
Lock
A device for securing a door, drawer, or lid in position when closed, consisting of a bolt or combination of bolts propelled and withdrawn by a key- or combination-operated mechanism
Lockset
An assembly of parts making up a complete locking system including knobs, plates and a locking mechanism
Cylindrical Lock
Also known as Bored Lock and Latch; A lock housed withing two holes bored at right angles to each other, one through the face of the door and the other in the door edge
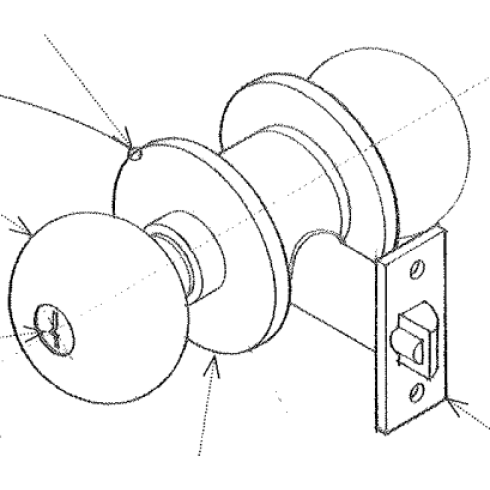
Mortise Lock
A lock housed within a mortise cut into a door edge so that the lock mechanism is covered on both sides
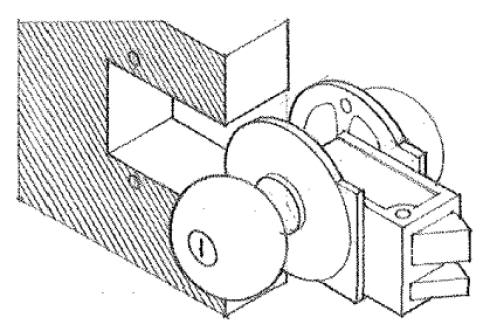
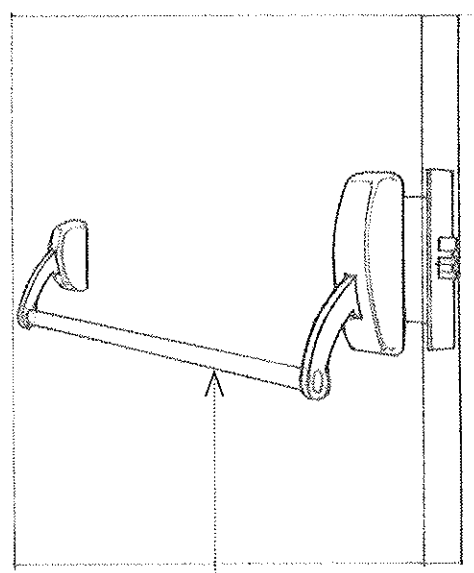
Panic Hardware
A type of door hardware specifically designed to provide safe and quick egress during emergencies
Weatherstrip
A material or device used to seal gaps around windows, doors, and other openings in buildings to prevent air, water, dust, and noise infiltration
Door Threshold
Horizontal strip or plate that spans the bottom of a door frame; Primary function is to provide a transition between the interior floor and the exterior or adjacent space
Drawer Glides
Mechanisms that enable drawers to move smoothly in and out of cabinets, furniture, or other storage units
Sliding Door Rollers and Tracks
Components of sliding door systems, facilitating smooth and effortless movement of doors along a designated path
Cabinet Lid Stay
A hardware device used to support and control the movement of cabinet doors or lids, particularly those that open upward, such as flip-up cabinet doors or lids on storage benches
Door Closer
A mechanical device that automatically closes a door after it has been opened, controlling the speed and force of the closing action
Door Latch/Barrel Bolt
Mechanism that consists of a metal bolt or bar that slides into a receptacle or strike plate mounted on the door frame or adjacent surface.
Door Stopper
Device used to prevent a door from swinging too far open and damaging nearby walls, furniture, or fixtures
Push Plate
A protective plate of metal or plastic mounted vertically on the lock stile of the door
Kick Plate
A protective metal plate fastened to the bottom of a door to resist blows and scratches
Rough Hardware
Bolts, screws, nails, and other metal fittings that are concealed in a finished construction
Nail
A straight, slender piece of metal having one end pointed and the other enlarged and flattened for hammering into wood or other building materials as a fastener
Expansion Bolt
An anchor bolt having a split casing that expands mechanically to engage the sides of a hole drilled in masonry or concrete
Heavy Work
What are large nails used for?
Finish Work
What are light nails used for?
Hardwood
What are thinner nails used for?
Screws
A metal fastener having a tapered, helically threaded shank and a slotted head, designed to be driven into wood or the like by turning, as with a screwdriver
3mm
What is the recommended length of a wood screw when joining boards together?
Hardwood
What are fine-threaded screws used for?
Softwood
What are course-threaded screws used for?
Bolt
A metal bar or rod in the mechanism of a lock that is propelled or withdrawn, as by turning a knob or key
Washer
A perforated disk of metal, rubber or plastic used under the head of a nut or bolt or at a joint to distribute pressure, prevent leakage or relieve friction
Lock Washer
A washer specially constructed to prevent a nut from shaking loose

Astragal
Vertical members used between double doors to seal the opening, act as a door stop, or provide extra security when the doors are closed
Adhesives
Used to secure the surfaces of two materials together; May be supplied in the form of a solid, liquid, powder, or film
White or Polyvinyl Glue (PVA)
Glue that sets quickly and does not stain and is slightly resilient (ex: Elmer’s, Wood Glue, Stikwel)
Cement, Aggregate, Water
What is concrete made of?
Cement
A powder material which when combined with water possesses adhesive and cohesive properties; Type of binder that hardens in place
Aggregates
Inert granular material such as sand and gravel which when mix with cement and water result in concrete
Water
Combines with cement to form a paste, which coats and surround the inert particles of aggregates and upon hardening, binds the entire mass together
Concrete
A plastic mass which can be cast, molded, or formed into predetermined size or shape; Becomes stone-like in strength upon hydration
In Situ
Term refers to concrete that is poured in place
Stripping
The process of removing concrete form works
Setting
What is the hardening of concrete called?
Mortar, Stucco, or Cement Plaster
What is produce when mixed with water and fine aggregate of less than 6mm are combined?
Concrete
What is produced when water, fine aggregate, and a large aggregate of more than 6mm in size are combined?
Plain or Mass Concrete
What is the product called when concrete is made without reinforcement?
Reinforced Concrete
Concrete in which steel reinforcement is embedded in such a manner that the two materials act together in resisting forces
Cement
A calcined mixture of clay and limestones, finely pulverized and used as an ingredient in concrete and mortar
Gypsum
A kind of cementing material used by Egyptians, Greeks, and romans; Source of the word plaster; Can be more plastic if hydrated lime is added
Pozzolan Cement
A kind of cementing material first developed by the Romans; Mix of slaked lime with pozzolana (volcanic ash) which hardens under water
Portland Cement
A kind of cementing material produced by heating a mixture of limestone and clay minerals in a kiln to form clinker, which is then ground into a fine powder
John Aspdin
Who patented the Portland Cement in 1824?
Type I: Normal
A type of Portland Cement for general purpose commonly used for structural work, bridges, pavements, and concrete masonry units
Type II: Modified Portland Cement
A type of Portland Cement that generates less heat and at a slower rate during the hydration process; Provides moderate resistance to sulfate attack and is used in large piers and heavy abutments to minimize detrimental effects of heat and hydration
Type III: Highly Early Strength Cement
A type of Portland Cement used where high strength is desired at early periods, usually within a week or less; Used in cold weather construction to reduce time required for protection from low temperatures
Type IV: Low-heat Cement
A type of Portland Cement that generates less heat of hydration than normal Portland cement; Used in massive structures such as large gravity dams
Type V: Sulfate Resistance Cement
A type of Portland Cement that is used when high sulfate resistance attack is desired; Gains strength at a slower rate than Type I
White Portland Cement
A type of Portland Cement manufactured using selected raw materials so that the finished product will be white rather than gray; Used for decorative architectural concrete, stucco, white, or pigmented grout
Air-entraining Portland Cement
A type of Portland Cement introduced minute air bubbles in the concrete mix to increase its resistance to freezing; Makes the concrete more durable and lighter in color
Fine Aggregates
Aggregates that are smaller than 6mm in diameter (ex: Sand)
Coarse Aggregates
Aggregates that are larger than 6mm in diameter (ex: Gravel)
Potable
What kind of water must be used in concrete mixing?
Admixtures
Substances added to a concrete mix to alter or enhance a specific property
Air-Entraining Agents
Introduces minute air bubbles in the concrete mix to increase its resistance to freezing
Accelerators
Used to speed up setting time and reduces the length of time for curing and protection
Retarders
Slows down the setting of a concrete mix in order to allow more time for placing and working the mix
Reducers
Reduces water requirements of concrete for a given consistency; Also known as plasticizers
Reinforcing Boards
Reinforcement changes the basic strength properties of concrete and consequently its behavior as a structural material
Concrete
A material strong in handling compression forces, but very weak against tension; More durable, fireproof, and requires little maintenance
Steel
A material strong in handling both compression and tensile forces; More expensive and requires fire proofing and maintenance against rust
Water-Cement Ratio
Amount of water used per bag of cement
Less
The ________ water used in mixing, the better the quality of concrete
1:2:4
What is the standard cement-sand-gravel ratio for portioning concrete?
1
Each bag of cement is equivalent to how many cubic foot?
Class AA
A type of concrete for concrete under water, retaining walls; Has a ratio of 1 : 1.5 : 3
Class A
A type of concrete for suspended slabs, beams, columns, arches, stairs, walls of 100mm thickness; Has a ratio of 1 : 2 : 4
Class B
A type of concrete for walls thicker than 100mm, footings, steps, reinforced concrete slabs on fill; Has a ratio of 1 : 2.5 : 5
Class C
A type of concrete for concrete plant boxes, and any non-artificial concrete structures; Has a ratio of 1 : 3 : 6
Class D
A type of concrete for mass concrete works; Has a ratio of 1 : 3.5 : 7
Adhesives
Used to secure the surface of two materials and may require a catalyst to activate their adhesive properties
Animal or Fish Glue
Also known as hide glue or protein glue; A type of adhesive derived from collagen-rich tissues of animals or fish; Primarily for indoor use where temperature and humidity do not vary greatly but may be weakened by exposure to heat or moisture
White or Polyvinyl Glue (PVA)
A type of synthetic adhesive commonly used in woodworking, crafts, and general household applications; A thermoplastic polymer that becomes adhesive when dissolved in water and forms a strong bond as the water evaporates
Stikwel
A type of PVA that is specifically formulated for bonding wood surfaces; A synthetic polymer that forms a strong bond when applied to wood surfaces and allowed to dry
Epoxy Resin
A type of thermosetting polymer resin valued for its strong adhesive properties, excellent chemical resistance, and durability; widely used as a structural adhesive for bonding metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites in various industries (ex: Mighty Bond)
Marine Epoxy Resin
A specialized type of epoxy resin formulated for use in marine environments; Designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by exposure to water, moisture, salt, and other harsh conditions encountered in marine applications
Resorcin Resin
A synthetic resin derived from resorcinol, a benzenediol compound; Used primarily as a bonding agent in various applications, particularly in the production of engineered wood products and high-performance adhesives
Contact Cement
A type of adhesive known for its strong and permanent bond, versatility, and ease of use; Used to secure large sheet materials such as plastic laminate and vinyl tiles (ex: Rugby)
Liquid Nail
A construction adhesive known for its strong bonding properties and versatility; Premium-grade, solvent-based, synthetic rubber multipurpose construction adhesive; Adhesive used to install laminate flooring
Vinyl Adhesive
A water-based type of adhesive specifically formulated for bonding vinyl materials; Used for resilient tiles and sheets, wood parquet, linoleum and carpets
Stone Adhesive
A type of adhesive specifically formulated for bonding natural and engineered stone materials; Designed to provide a strong and durable bond for various stone applications, including countertop installation, stone veneer, stone tile, and stone repair
Tile Adhesive
A type of adhesive specifically formulated for bonding ceramic, porcelain, glass, and natural stone tiles to various substrates; Crucial component in tile installations, providing a strong and durable bond between the tiles and the underlying surface (ex: ABC)
Wood Sash Putty
It is a putty mixture that is composed of carbon silicate and oil
Mortar
A plastic mixture of lime or cement, or a combination of both, with sand and water, used as a bonding agent in masonry construction
Cement Mortar
A mortar made by mixing portland cement, sand, and water
Lime Mortar
A mixture of lime, sand, and water that is rarely used because of its slow rate of hardening and low compressive strength
Cement-Lime Mortar
A cement mortar to which lime is added to increase its plasticity and water-retentivity
Type M Mortar
A high-strength mortar recommended for use in reinforced masonry below grade or in contact with the earth, such as foundation and retaining walls subject to frost action or to high lateral or compressive loads
Type S Mortar
A medium-high-strength mortar recommended for use in masonry where bond and lateral strength are more important than compressive strength