Rivers, Estuaries, and Deltas
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Hydrologic Cycle
the movement and interchange of water between the sea, air, and land
Steps in the Hydrologic Cycle
Evaporation
Precipitation
Transpiration
Runoff
Infiltration
Running Water
most important geologic agent in eroding, transporting, and depositing sediment
Stream
a body of running water, confined to a channel, that runs downhill under the influence of gravity
Parts of a Stream
Headwaters
Mouth
Channel
Banks
Bed
Floodplain
flat valley floor composed of sediment deposited by the stream
Drainage Basin
the total area drained by a stream and its tributaries
Tributary
a small stream flowing into a larger one
Divide
ridge or high ground that divides one drainage basin from another
Continental Divide
separates the streams that flow into the Pacific from those that flow into the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico
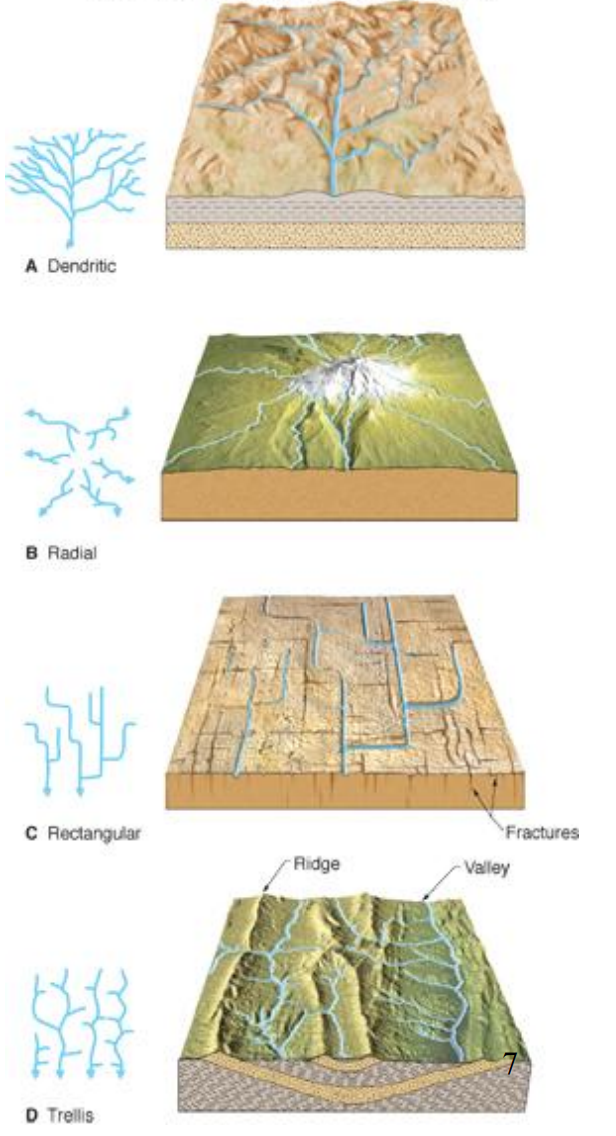
Drainage Pattern
the arrangement, in map view, of a stream and its tributaries
Types of Drainage Patterns
Dendritic
Radial
Rectangular
Trellis
Stream Erosion is controlled by
flow velocity and discharge
Stream Velocity is controlled by
stream gradient (slope)
channel shape
channel roughness
Stream gradient
downhill slope of the streambed
Channel shape and roughness
both effect stream velocity due to drag
Stream Discharge
volume of water flowing past a given point in a unit of time
Stream Erosion occurs by three mechanisms:
hydraulic action
solution
abrasion
Categories of Sediment load
Bed load
Suspended load
Dissolved load
Bed Load
large or heavy particles that travel on the streambed
divided into traction load and saltation load
Suspended Load
sediment that is small/light enough to remain above the stream bottom by turbulent flow for an indefinite period of time
Dissolved Load
dissolved ions produced by chemical weathering of soluble minerals upstream
Sediment Deposition
sediment temporarily deposited along stream as bars and floodplain deposits and at/near its end as deltas or alluvial fans
Bars
ridges of sediment (usually sand or gravel) deposited in the middle or along the sides of a stream
can create braided streams if sediment is deposited in middle
Meandering Streams
flow faster along the outside of bends and more slowly along the inside, depositing point bars on the insides of the meanders
Meander Cutoffs (Oxbow Lakes)
form when a new, shorter channel is cut through the narrow neck of a meander
Delta
body of sediment deposited at the mouth of a river when flow velocity decreases
Alluvial Fan
large, fan- or cone-shaped pile of sediment that forms where stream velocity decreases as it emerges from a narrow mountain canyon onto a flat plain
Types of Deltas
wave-dominated
tide-dominated
stream-dominated
Methods of Flood Control
Dams
Artificial levees
Wise land-use planning
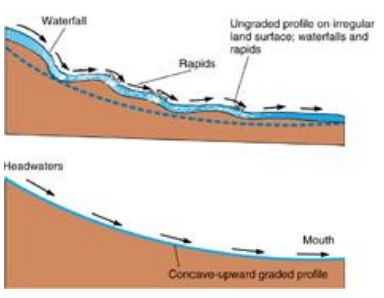
Downcutting
process of deepening a valley by erosion of the streambed
typically form v-shaped valleys
Streams cannot erode below their
base level
Graded Streams
characteristic concave-up longitudinal profile
Lateral Erosion
widens stream valleys by undercutting of stream banks and valley walls as a stream swings from side to side across the valley floor
Headward Erosion
the slow uphill growth of a valley above its original source by gullying, mass wasting, and sheet erosion
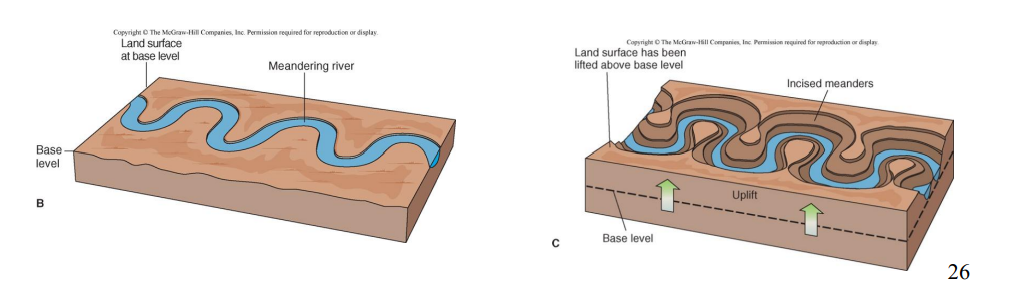
Stream Terraces
step-like landforms found above a stream and its floodplain
occurs when river rapidly cuts downward into its own floodplain
Stream Terraces can be caused by
rapid uplift
drops in base level
climate changes
Incised Meanders
retain sinuous pattern as they cut vertically downward
Estuary
semi-enclosed coastal environment where freshwater and ocean water meet and mix
Types of Estuaries
Coastal Plain
Fjord
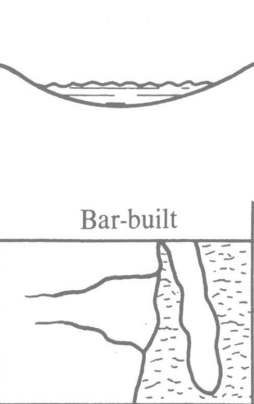
Bar-built
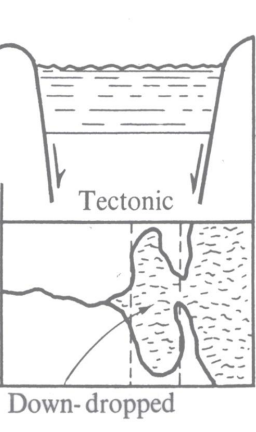
Tectonic
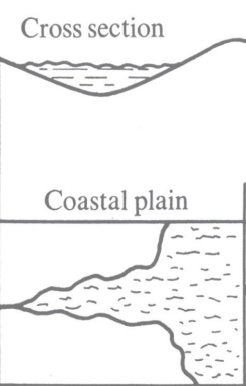
Coastal-Plain Estuary (drowned river valley)
V shape in cross-section
result of fluvial erosion
Fjord (drowned glacial valley)
U shape in cross-section, deep
result of glacial erosion
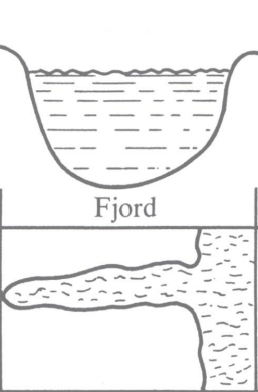
Bar-built Estuary (lagoon)
sand spit or barrier island encloses embayment
shallow
Tectonic Estuary
down-dropped basin (due to plater tectonics)
located near ocean and seawater floods basin
Why are estuaries particularly susceptible to hypoxia?
Highly productive
Stratified
Most are heterotrophic