Class 2: Chemistry of Life
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
LOW electronegativity
Hydrogen
Carbon
HIGH electronegativity
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Ionic Bonds
bonds formed when negative and positive atoms are attracted to each other (exchange of atoms)
BUT dissolves easily in water
IMF
Covalent Bonds
When 2 atoms share electrons
# of electrons that can be shared:
1 = H
2 = O
3 = N
4 = C
Single, double, triple bonds
1 = 2 shared e-
2 = 4 shared e-
3 = 6 shared e-
# of e- pairs → # covalent bonds!!!
INTRAMOLECULAR BONDS
Non Polar Covalent Bond
equal sharing of e-
Polar Covalent Bond
unequal sharing of e-
creates slightly positive and slightly negative areas around atoms
higher e- density area → partial NEGATIVE (because e- are neg. → area becomes neg.)
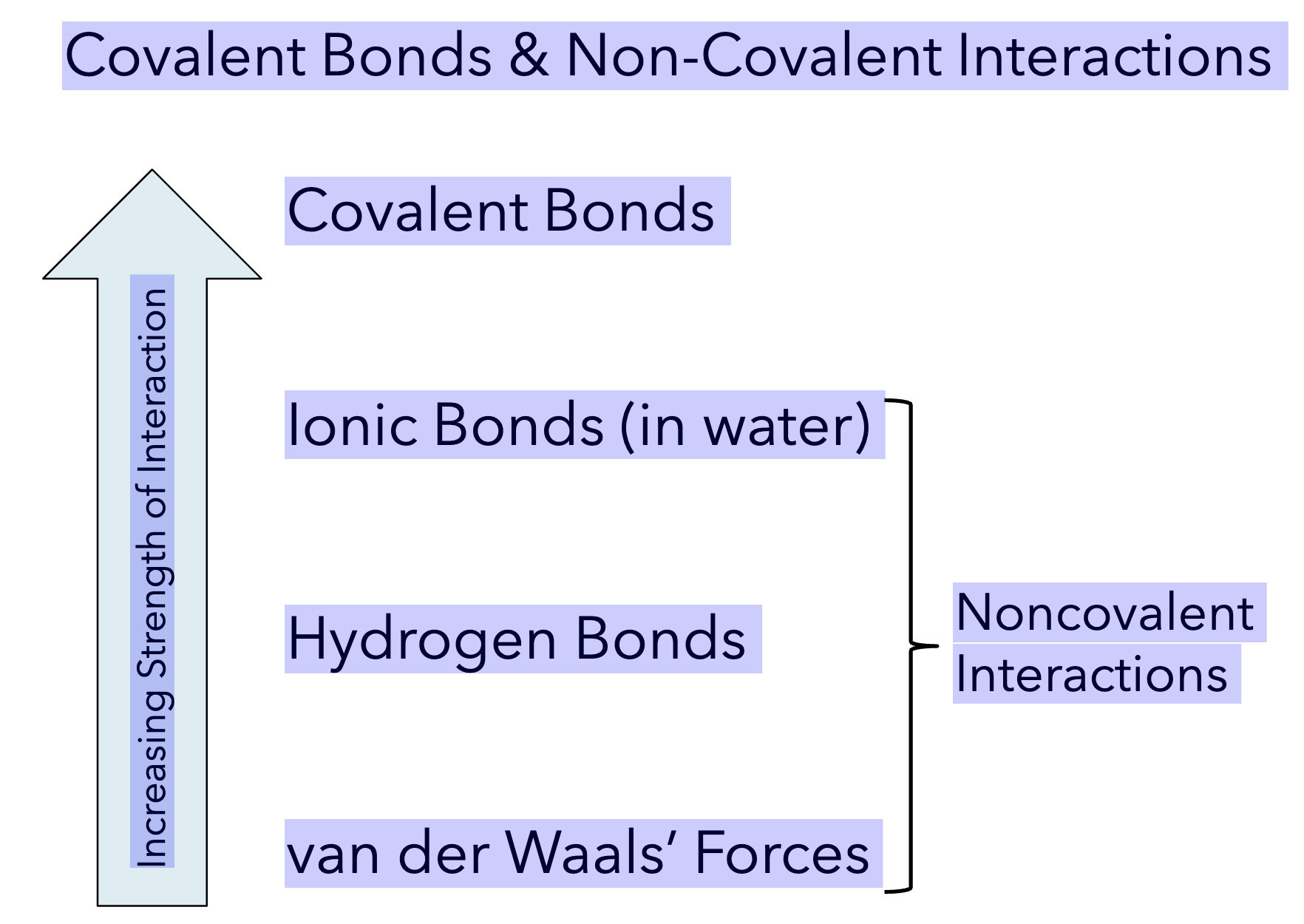
weakest → strongest bonds
van Der Waals’ Forces → Hydrogen bonds → Ionic bonds → Covalent bonds
Van der Waals
Electrostatic interactions → temporary partial charges
weak, but a lot → STRONG
geckos
IMF
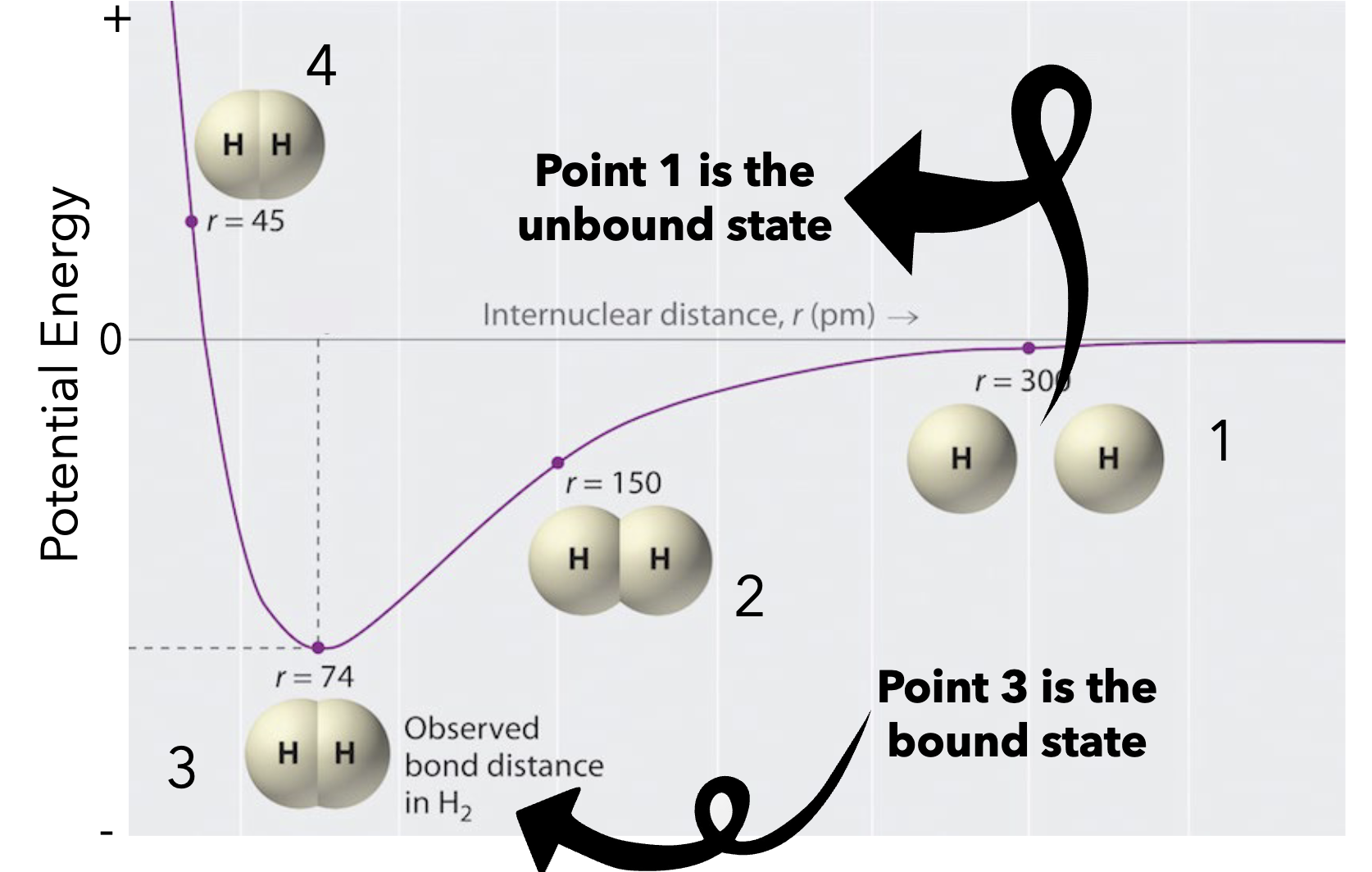
Potential E and Strength = INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL
Higher potential energy in a chemical bond actually means the bond is weaker, while stronger, more stable bonds have lower potential energy. The potential energy of a bond is inversely proportional to its strength; breaking a weak, high-potential energy bond requires less energy than breaking a strong, low-potential energy bond.
Hydrogen Bond
Intermolecular Force
H bonds form when H δ+ interacts with O δ- or N δ- OR ANY ELECTRONEGATIVE atom
more of an association, not a true bond