Epithelium Structure and Function - Lab - Lecture 1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Describe the histological characteristics of a simple squamous cell.
Simple means mono-layer or 1-layer
Squamous means flat-like cells
Describe the histological characteristics of a stratified squamous cell.
Stratified means multi-layered cells
Squamous means flat-like cells
Explain a key difference between non-keratinized and keratinized cell.
keratinized cells do not contain nuclei as of non-keratinized cells do.
Explain a histological characteristic associated with simple cuboidal.
Simple means mono-layer
Cuboidal is a cube-shaped cell that is known for secretions.
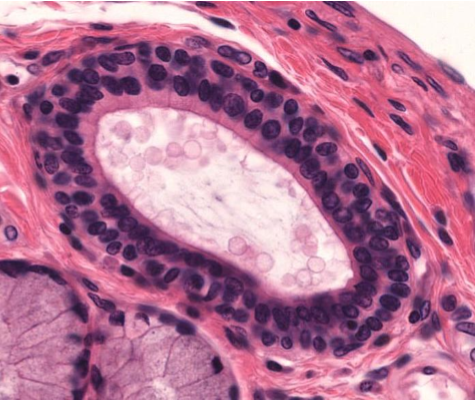
What type of epithelium is present in the image?
Stratified cuboidal

What is the type of epithelium present in the image?
Simple Columnar
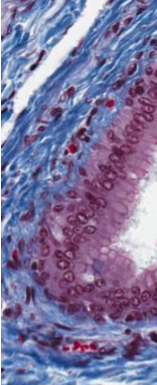
What is the type of epithelium present in the image?
Stratified Columnar
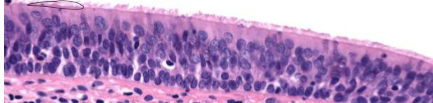
What is the type of epithelium present in the image?
Pseudostratified columnar
What does pseudo mean?
All cell touch the basement membrane but it appears stratified.
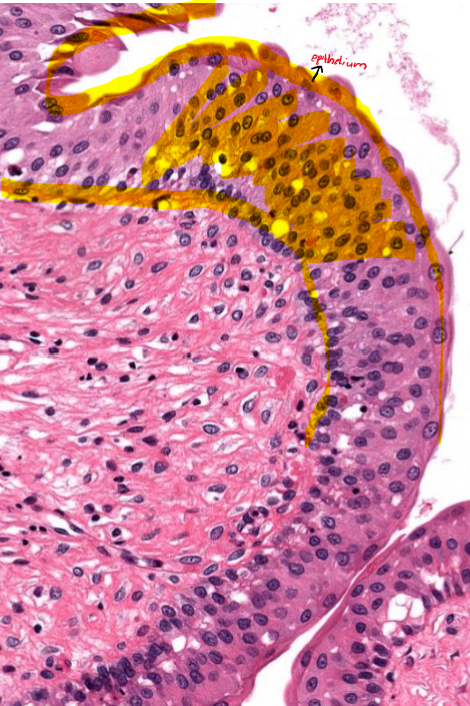
What is the type of epithelium present in the image?
Urothelium or Transitional
Describe some characteristics of the Exocrine glands.
Organization: Unicellular or multicellular
Structure: Nature of the duct system
Simple or compound and shape secretory units
tubular, acinar or alveolar, tubuloalveolar
Product secreted - serous (proteins), mucous (mucus) or mixed (seromucous)
Mode of secretion - Merocrine (exocytosis), Holocrine (apoptosis), or apocrine (packged secured in membrane from the cell)
What is the main function of mucous glands?
Protects and lubricates cell surfaces with viscous secretions.
What is the main function of serous secretions?
Watery secretions often rich in enzymes.
What is the main function of mixed secretions?
Mucus (viscous) and serous (watery) substances
Is mixed secretions associated with unicellular or multicellular?
Only multicellular glands can have mixed secretions
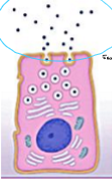
What is the name of this secretion mechanism?
Merocrine

What is the name of this secretion mechanism?
Apocrine

What is the name of this secretion mechanism?
Holocrine
Describe the merocine secretion mechanism.
Cells will secrete substances via exocytosis.
Describe the apocrine secretion mechanism.
Cells will release substances with pieces of the cell membrane
Describe the holocrine secretion mechanism.
Substances will release through the cell rupturing.
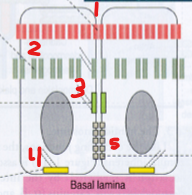
Label each section that is numbered in the image.
Occluding junction (Zona occludens)
Belt desmosome (Zonula ahderens)
Spot desmosome (Macula adherens)
Hemidesmosome
Gap or Communicating junction
Describe Occluding junctions or tight junctions.
Defines cell polarity and control the passage of substances between adjacent cells.
Haves a beltlike distribution like a ribbon internally bracing the cells
Describe belt desmosomes or zonula adherens.
Anchorage junction that has a beltlike distribution and is associated with actin filaments.
Describe spot desmosome or macula adherens.
Anchorage jucntion has a spotlike distribution and is associated with intermediate filaments.
Describe Hemidesmosomes.
Links the basal domain of an epithelial cell to the basal lamina.
Intermediate filaments are associated with plaque.
Describe gap or communicating junctions.
Connect functionally two adjacent cells
Formed by connexons, channel-like structures that enable the passage of small molecules
Describe microvillii.
For area, absorption, and secretion.
Describe cilia
Moves fluid, cells and mucus, and sensory
Describe stereocilia.
Enhancing sensibility (ear) and absorption (epid.)
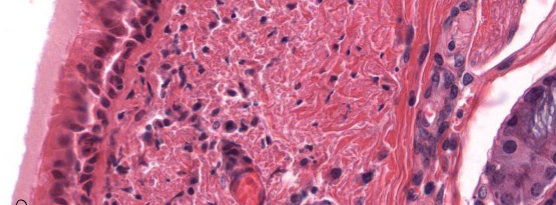
What surface mechanism is this?
Cilia
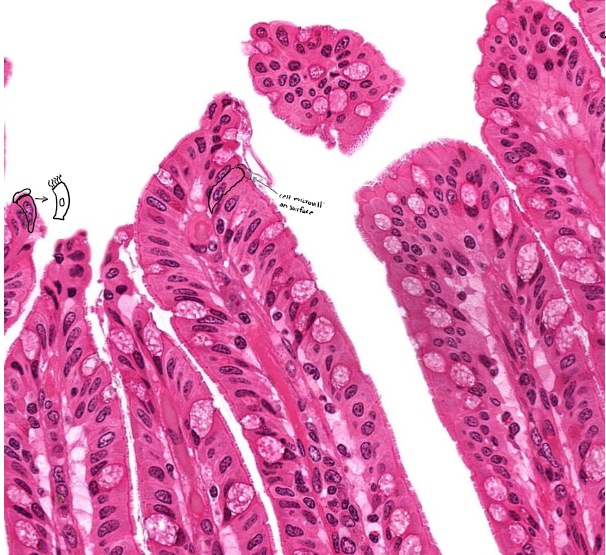
What surface mechanism is this?
Microvilli
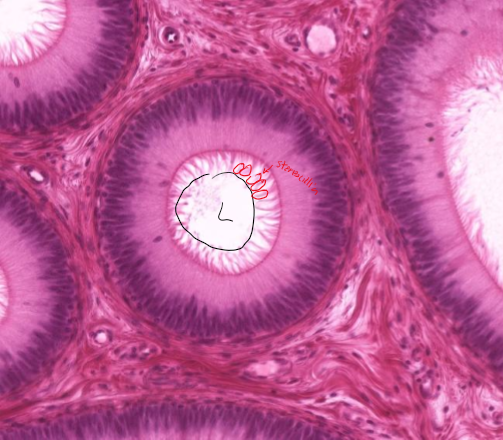
What surface mechanism is this?
Stereocilia
What is the two types of simple columnar epithelium?
Supporting cells seen in the basal area of the epithelium
Sensory cells that project to the surface of the epithelium
Describe squamous epithelium.
Squamous epithelial cells are flat and sheet-like in appearance.
Describe cuboidal epithelium.
Cuboidal epithelial cells are cube-like in appearnace, meaning they have equal width, height and depth.
Describe columnar epithelium.
Columnar epithelial cells are column-like in appearance, meaning they are taller than they are wide.
Describe simple.
A simple epithelium means that there’s only one layer of cells.
Describe stratified.
A stratified epithelium is made up of more than one layer of cells
Describe pseudostratified.
A psuedostratified epithelium is made up is closely packed cells that appear to be arranged in layers because they’re different sizes, but there’s actually just one layer of cells.
Describe transitional epithelium.
A transitional epithelium (also known as urothelium) is made up of several layers of cells that become flattened when stretched.
It lines most of your urinary tract and allows your bladder to expand.
Describe simple squamous epithelium.
This type of epithelium typically lines blood vessels and body cavities and regulates the passage of substances into the underlying tissue.
Describe Simple cuboidal epithelium.
This type of epithelium is typically found in glandular (secreting) tissue and kidney tubules.
Describe Simple columnar epithelium
This type of epithelium is often specialized for absorption and usually has apical cilia or microvilli.
These cells line your stomach and intestines.
Describe Stratified squamous epithelium.
This type of epithelium usually has protective functions, including protection against microorganisms from invading underlying tissue and or protection against water loss.
The outer layer of your skin (the epidermis) is made of stratified squamous epithelial cells.
Describe stratified cuboidal epithelium.
This type of epithelium is not as common and is found in the excretory ducts of your salivary and sweat glands.
Describe straitified columnar epithelium.
This type of epithelium is not as common and is seen in the mucous membrane (conjunctive) lining your eyelids, where it’s both protective and mucus-secreting.
Describe Psuedostratified columnar epithelium.
This type of epithelium lines your upper respiratory tract and usually has a lot of cilia.