Natural Resources in the Crust & Rocks, Soil, and Sediment
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Ancient sea creatures, dust, mud, vegetation, and animal life.
What materials make up marble?
The remains of a forgotten desert.
What material makes up sandstone.
Space rocks and space dust (asteroids).
Where does Iridium come from?
75% of all life
How much life was wiped out by the asteroid?
South Africa
In what country is the world’s deepest mine found?
Iron impurities
An amethyst contains what elemental impurity in quartz.
5,500 meters below the crust.
At what depth do we find oil?
Dead plankton, mud, silt, and sand.
What materials make up black shale crude oil?
Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic
What are the 3 rock families?
Obsidian, rhyolite, andesite, basalt, granite, diorite, gabbro, periodotite, pegmatites, pumice, scoria, and tuff
What are examples of Igneous rocks?

Sandstone, Limestone, Shale, Conglomerate, and Gypsum.
What are examples of Sedimentary rocks?

Marble, Slate, Quartzite, and Gneiss
What are examples of Metamorphic rocks?
1.Weathering 2. Erosion and transport 3. Deposition 4. Deformation and metamorphism 5. Solidification 6. Uplift. (Burial and uplift can happen at any point.)
What are the six steps of the rock cycle?
Sedimentary rocks
Formed by time and pressure and from dirt.
Chemical weathering (dissolution, hydrolysis, oxidation, biological activity); Physical Weathering (Biological activity, frost and wedging, fracturing, and glacial erosion); and transport.
How is dirt (sediment) made?
Dissolution, Hydrolysis, Oxidation, and Biological activity.
What are the types of chemical weathering?
Biological activity, Frost and wedging, Fracturing, and Glacial erosion.
What are the types of physical weathering?
Dissolution
Minerals dissolve in making sediment. (Dissolving of ionic compounds in water.)
Hydrolysis
Converts original materials to clay + splitting of molecules using water.
Oxidation
Transfers electrons, adds oxygen. (Breaking down minerals using water over time).
Biological activity (Chemical weathering)
Acid production through decomposition.
Biological activity (physical weathering)
Worm tunneling and root wedging
Frost and wedging
Water contracts/expands.
Fracturing
Breaks away from the source.
Glacial erosion
Strips away layers. It moves in a circular motion + Abrasion deepens the hollow.
Transport
Movement from one place to the next.
Bedrock (Bedrock and parent material), Soil (Subsoil-clay) + Topsoil, Vegetation (surface layers)
What is the structure of the crust?
Steam Deposition (Transport process)
1.Headwater streams swiftly flow down steep mountain slopes and cut deep, y-shaped valleys. Waterfalls and rapids occur in this zone. 2. Lower-elevation streams merge to flow down gentle slopes. (Large sediments) 3. At the lowest elevations a river meanders across a broad, nearly flat valley and floodplain. The costal plain and delta are made of river sediments. (Small sediments)
Clast, Shape, and sorting
How are sedimentary rocks classified by?
Clast
Fragment of a rock or mineral.
Boulder, Cobble, Pebble, Sand, Silt, Clay
6 categories of clasts? (Largest —> Smallest)
Angular, Partially rounded, and Rounded
What are the clast shapes?
Poorly sorted (Angular), Moderately sorted (Partially rounded and rounded), and Well-sorted (Sand)
What are the 3 types of class sorting?
Clastic and NonClastic
2 types of sedimentary rocks?
Clastic
Contains visible chunks of other rocks (clasts)? Ex: Conglomerate/Breccia, Sandstone, and Shale
Conglomerate
What rock is this?

Breccia
What rock is this?

Sandstone
What rock is this?

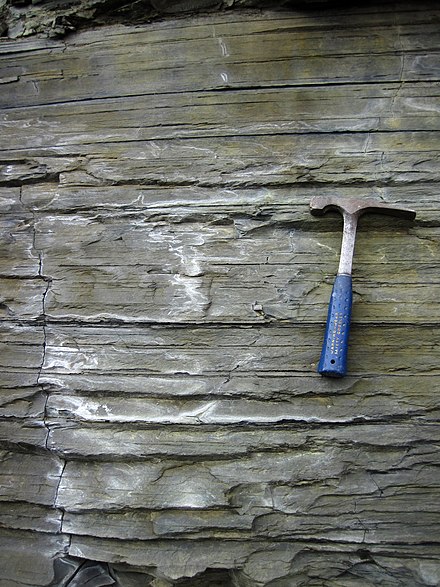
Shale
What rock is this?

Nonclastic
Does not contain visible chunks of rock? (2nd group of sedimentary rocks). Ex: Salt, Limestone/Chalk, Chert, Iron Formation, Coal.
(Rock) Salt
What type of nonclastic sedimentary rock is this?

Limestone
What type of nonclastic sedimentary rock is this?

Chert
What type of nonclastic sedimentary rock is this?

Iron formation
What type of nonclastic sedimentary rock is this?

Coal
What type of nonclastic sedimentary rock is this?

Igneous rock
What type of rock comes about when hot molten rock crystallizes and cools?
Intrusive (plutonic) and extrusive
2 types of igneous rock?
Intrusive (plutonic)
Cools slowly below the surface and large crystals form. Classified based on texture and composition. Ex: Granite, Peridotite, Pegmatites, Diorite, Gabbro.
Extrusive (volcanic)
Cools quickly above the surface and tiny crystals form. Based on texture and composition. Ex: Rhyolite, Obsidian, Basalt, and Andesite
Granite (Felsic)
What type of intrusive igneous rock is this?

Peridotite (Ultra
What type of intrusive igneous rock is this?

Pegmatite
What type of intrusive igneous rock is this?

Diorite (Intermediate)
What type of igneous intrusive rock is this?

Gabbro (Mafic)
What type of intrusive igneous rock is this?

Mafic
Means dark colors in terms of igneous rocks.
Rhyolite (Felsic)
What type of extrusive igneous rock is this?

Andesite (intermediate)
What type of extrusive igneous rock is this?
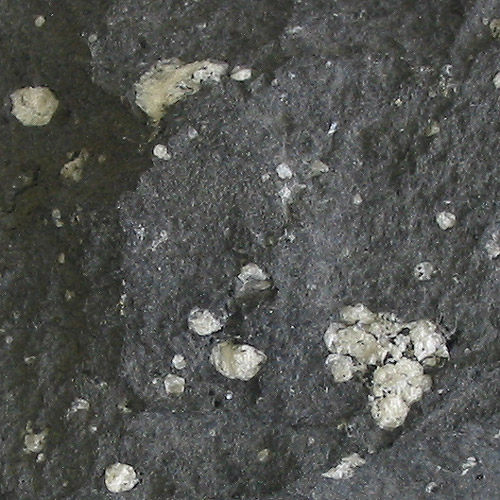

Obsidian (Volcanic glass)
What type of extrusive igneous rock is this?

Basalt
What type of extrusive igneous rock is this?

Pumice
What type of other igneous rock is this?

Scoria
What type of other igneous rock is this?

Tuff
What type of other igneous rock is this?

Metamorphic rocks
Rocks that were some other type of rock.
Some heat (not enough to melt), Pressure, and Chemical processes.
How are Metamorphic rocks modified?
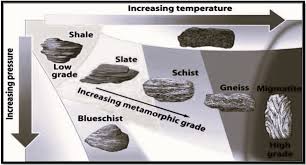
Shale (Low grade pressure and heat), Slate (more heat and pressure than shale), Schist (More heat and pressure than shale), Gneiss (More heat and pressure than Schist), and Migmatite (High pressure and high heat).
Chart of Increasing Temperature and increasing pressure.
Contact and regional
2 types of metamorphism
Contact metamorphism
Small pockets of magma increases surrounding rock temperatures. Involves low stress (no foliation). Due to concentrated heat, different rocks form in the same area.
Regional metamorphism
Associated with major Earth dynamics. General heating over a large area. Involves high stress (foliation).
Foliated
A simple classification of metamorphic rocks. Due to parallel arrangement of minerals. Occurs from directed pressure and some heat. Rocks develop a sheet-like structure.
Slate, Schist, Gneiss, and Migmatite
Types of foliated metamorphic rock
Slate
What type of foliated metamorphic rock is this?

Schist
What type of foliated metamorphic rock is this?

Gneiss
What type of foliated metamorphic rock is this?

Sandstone becomes quartzite and limestone becomes marble.
What does sandstone and limestone become?
Non-foliated (Non-banded)
Type of metamorphic rock that has no shearing, and not enough heat and pressure to align crystals. Ex: Lapis Lazuli, Hornfels, and Ruby in marble
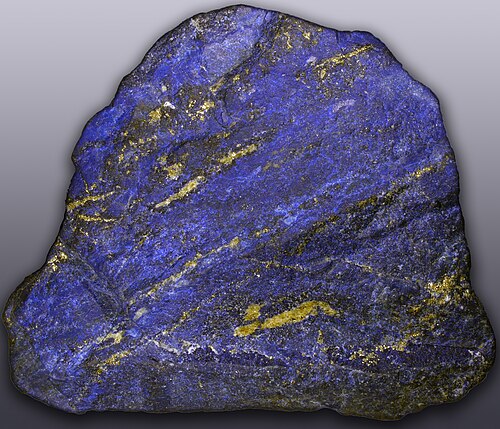
Lapis lazuli
What type of non-foliated metamorphic rock is this?

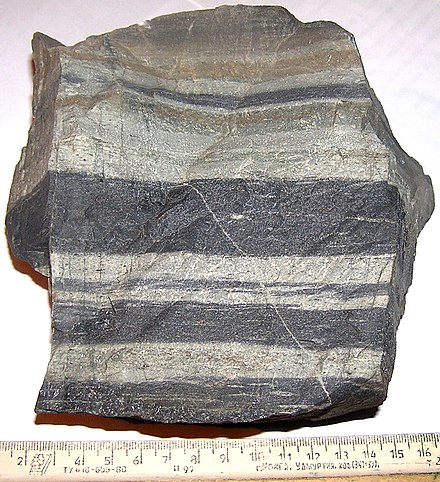
Hornfels
What type of non-foliated metamorphic rock is this?

Ruby in Marble
What type of non-foliated metamorphic rock is this?

Minerals
A solid inorganic substance of natural occurrence with a specific chemical composition.
Natural, solid, inorganic, and crystalline.
4 qualifications of minerals.
Metals and Nonmetals
2 types of minerals?
Color, Streak, Luster, Physical characteristics
How are minerals classified?
Color
Which qualification of minerals is not-useful, can be caused by elements, other materials, and impurities, and its value can be affected by perception?
Streak
Deals with if a mineral streaks and is the truer color; qualification of mineral?
Luster
How shiny a mineral is?
Crystalline
Which structure of minerals is more uniform, has a more definitive structure when it cooled. Ex: Quartz
Non-crystalline
Which structure of minerals is amorphous and chaotic. Ex: Silicon dioxide.
Isometric (Flourite), Tetragonal (wulfenite), Orthorhombic (Tanzanite), Monoclinic (Azurite), Triclinic (Amazonite), Hexagonal (Emerald), and Trigonal (Rhondochrosite)
What are the structures of the crystal systems?
Lustrous, Conductors, High melting point, High density, Malleable, Ductile, Solid at room temp, opaque as a thin sheet, noisy (sonorous)
Characteristics of a metal (mineral)?
Dull, Poor conductors, Nonductile, Brittle, Solids/liquids/gasses at room temp, transparent, and not noisy (not sonorous).
Characteristics of a nonmetal (mineral)?
Runs from 1 to 10. Talc being (1) also the softest. Diamond being a (10) being the hardest.
Mohs scale of Mineral Hardness?
Torbernite, Monazite, Autunite, Uranocircite, Zippeite, Metatorbernite, Uraninite, and Carnotite.
Types of radioactive minerals?
Olivine, Ca-Plagioclase Feldspar, Halite, Pyroxene, Na-Plagioclase Feldspar, Gypsum, Amphibole, Orthoclase Feldspar, Limonite, Biotite, Hematite, Muscavite, Quartz, Calcite.
Examples of minerals?
