Cleaning, Disinfection, and Decon and biocontainment
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What does -cide mean?
Killing action
What does -static mean?
Growth inhibition/prevention
What is cleaning?
Removal of foreign material
What is sanitization?
Any cleansing technique that mechanically removes microbes
What is antiseptic?
Disinfectants applied directly to exposed body surfaces
What is disinfection?
Process to destroy vegetative pathogens on inanimate objects (not endospores)
What is sterilization?
A process that destroys all viable microbes including viruses and endospores. Microbiocidal
What is the rate of bacterial growth?
Exponential
What is the rate of bacterial death?
Constant
What are easily susceptible pathogens/
Enveloped virus, Gram positive and negative bacteria, large non-enveloped viruses, fungi
What are the hardest to destroy pathogens?
Prions, coccidia, bacterial spores, Mycobacterium, Protozoan cysts, non-enveloped viruses
What what does a higher number of microorganism mean?
Increases necessary contact time
How can the location of microorganisms impact disinfection and sterilization?
Pores can be hard to get through. Flat solid surfaces are easier
What disinfectant gets better the more it is diluted?
Iodophors because free iodine concentration is higher
What happens to the efficacy of most disinfectants as concentration increases?
It gets stronger
Increase in temp causes what for disinfection?
Improves it
T/F pH changes can improve or hinder an antimicrobial?
True
What is the most important factor to maintain efficacy of gaseous disinfectants?
Relative humidity
What can water hardness do to disinfection efficacy?
Divalent cations like Mg2+ or Ca2+ can cause insoluble precipitates with disinfectant
How can organic matter prevent disinfection or sterilzation?
They act as a physical carrier
Why feces in a footbath bad?
It becomes a physical barrier to the boot from disinfectant. This is why cleaning should be done before disinfection
What is filtration?
Passage of a liquid or gas through a filter with pores to retain microbes (common in vaccines or injectables)
What are the physical methods of microbial control?
Filtration
Osmotic pressure
Radiation
Desiccation
Temperature
What is osmotic pressure used to prevent bacterial growth?
High concentrations of salt and or sugar to create a hypertonic solution
What organisms have a greater availability than bacteria to survive hypertonic environments?
Fungi
What type of wavelength is better for penetration and has more energy?
Shorter
What are the ionizing radiation types?
Electron beams, gamma rays, x-rays
What is the nonionizing radation we use?
UV light
T/F UV lights are the only necessary disinfection in a BSC?
False, humidity can impact effectiveness, temperature is important, and dust can accumulate on the bulb
What is the human risk of UV light?
Causes pyrimidine dimers that can lead to eye, skin, or other melanomas
What is desiccation?
State of extreme dryness
What is lyophilization?
Freeze drying to preserve microbial cultures
What does desiccation and lyophilization do?
It creates a microbiostatic environment
What does high temperature do?
Denatures proteins
Interferes with cytoplasmic membrane and cell walls
Disrupts nucleic acids
What is thermal death point?
Lowest temp that kills all cells in 10 minutes
What is thermal death time?
Time to sterilize volume of liquid at set temp
T/F moist heat is more effective than dry heat?
True, water is a better conductor of heat than air
What are methods of using moist heat for disinfection, sanitation or sterilization?
Boiling, autoclaving, pasteurization, ultrahigh-temp sterilization
What does the pressure allow for in an autoclave?
Prevents team from escaping
When do you use dry heat over moist heat?
Moist heat will damage the item
What type of heat requires higher temperatures for a longer time?
True
What is the ultimate means of sterilization?
Incineration (dry heat)
What is dry heat most effective against?
Enveloped viruses, vegetative cells of bacteria, fungi, protozoa
What are ideal traits for a disinfectant?
Broad spectrum, fast-acting, stable, water soluble, not effected by environment, non-corrosive, non-toxic, easy to use, odorless, cleaning, environmentally friendly, inexpensive
What are the steps of cleaning and disinfection?
Remove all grossly visible debris
Rinse thoroughly
Allow area to dry
Apply appropriate disinfectant
Allow for proper contact time
Rinse thoroughly
Allow area to dry
What is risk group 1?
Does not cause disease in healthy human adults
What is risk group 2?
Limited and treated disease of minimal community risk with usually fecal-oral spread
What is risk group 3?
Causes serious disease with limited treatments and moderate to high community risk, typically aerosol spread
What is risk group 4?
Life-threatening with no treatments and high community risk
What factors goes into your risk assessment?
Risk, likelihood, hazard severity
What happens at BSL1?
Low risk work with minimal design features, programs
Required basic training
What is BSL-2?
Moderate risk work with some safety features and equipment
Task-specific training
What is BSL-3?
High risk work with more features and safety equipment
Must demonstrate proficiency and there are required training programs
What is BSL-4?
Extreme work risk with extensive features, redundant safety equipment, extensive programs and extensive training and demonstrated proficiency
What are some engineering controls to prevent incidents?
Sealed concrete walls, directional airflow, biosafety cabinet use, , vacuum lines that are filtered, PPE
What are some administrative controls to prevent incidents?
SOP training, security background checks, risk assessments, minors are not allowed, PPE
What is an example of a primary barrier?
Tube of ebola
What is an example of a secondary barrier?
Ebola in a tube in a BSC
What does 0.3um mean in a HEPA filter?
It is the most penetrating size of a particle. Smaller and larger particles are collected with higher performance
What can HEPA not filter?
Gases and vapors
What does HEPA stand for?
High Efficiency Particulate Air filter
How do HEPA filters work?
Straining, inertia impaction, interception, and diffusion
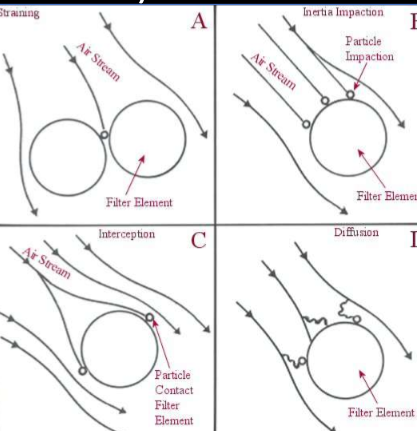
When do HEPA filters need replacement?
When they are loaded to the extend that sufficient airflow can not be maintained
Must be decontaminated before removal in high BSLs
Where are HEPA filters typically located?
Just outside of the room you are filtering air for
What hood protects the inside from the outside (product)?
Laminar flow hoods
What hood protects you from the inside?
Chemical fume hood
What BSCs protect the environment and you while working?
Class 1
What BSCs protect you, the product, and the environment?
Class 2, 3, and isolators
What is required PPE based on?
Project risk assessment
T/F PPE can be reusable or single use?
True
When should you use two gloves?
Working with infectious agents that you do not what on your skin
What does ABSL mean?
Animal biosafety level
What are two major animal biocontainment challenges?
Necropsy and sample transport
What is the mechanism of action for oxidizing agents?
Forms hydroxyl radicals leading to DNA damage
Attacks membrane lipids
Addition of metal ions will increase efficacy
What are the pros and cons for
Pros: Hard water friendly, kills spores, (also viruses, fungi, anaerobes and gram+)
Cons: Mildly corrosive, respiratory irritant, short shelf life, can leave a residue
What is the practical usage for oxidizing agents?
Very good for room decontamination and foot baths and effective against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores