MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE | 1.1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Mechanics
The branch of physics involving the motion of an object and the
relationship between that motion and other physics concepts.
kinematics / dynamics
two branches of mechanics
Kinematics
deals with the description of motion.
- 1D motion - Projectile motion
- Circular motion - Relative Motion
Dynamics
deals with causes of motion.
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Momentum and Energy
One-dimensional (1D) Motion
considering objects to travel along a flat and narrow straight
line (rectilinear motion)
object is considered as point particle
One-dimensional (1D) Motion
considering objects to travel along a flat and narrow straight
line (rectilinear motion)
object is considered as ______
Reference Frame
a physical entity to which the motion and position
of objects are referred.
Distance
➢ scalar quantity
➢total length traveled
➢ denoted by s
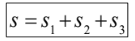
distance formula
Displacement
➢ vector quantity
➢shortest distance from initial to final position
➢ change in position denoted by Δx or Δy
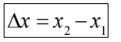
displacement formula
Speed (Average Speed)
➢ scalar quantity
➢ “how fast the object is moving?”

Speed (Average Speed) formula
Velocity (Average Velocity)
➢ vector quantity
➢ “the rate at which an object changes its position”
➢ denoted by v

Velocity (Average Velocity) formula
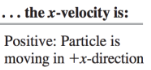

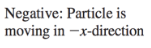
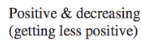
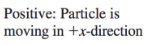
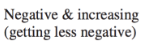
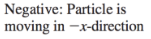

Average Speed
➢Total distance traveled,
regardless of direction
➢Cannot have a negative
average speed
Average Velocity
➢Needs info on origin
and positive x-axis
➢Displacement is
important, NOT
distance.
➢Can have a negative
average velocity

average speed formula
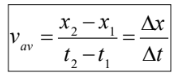
average velocity
Slow
rightward (+x)
Fast
rightward (+x)
Fast
leftward (-x)
Slow
leftward (-x)
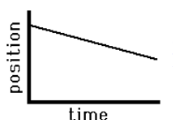
Instantaneous velocity
defined as
the limit of the average velocity as the
time interval becomes infinitesimally
short, or as the time interval
approaches zero
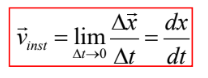
Instantaneous velocity formula
Acceleration
The magnitude of the velocity is changing whether
increasing or decreasing.
✓ The magnitude of the velocity is constant but the there
is a change in direction.
✓ Change in velocity magnitude and direction.
Acceleration
➢ vector quantity
➢ “The rate at which the object changes it velocity.”
➢ denoted by a
Uniformly Accelerated Rectilinear Motion (UARM)
➢UARM means motion in straight with constant acceleration
(g= -9.8 m/s^2)
acceleration due to gravity value