Chapter 2: Chromosomes and Cellular Reproduction
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 2 video assignments, homework, & adaptive quiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What are the two major phases of the cell cycle?
interphase and M phase
During which phase of the cell cycle would each cell be undergoing biochemical events required to prepare for cell division, and each chromosome consist of two identical chromatids?
G2
In which portion of the cell cycle do chromosomes begin to condense and the spindle fibers begin to form from the centrosomes?
prophase
If a cell normally has 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes are present in the G2 phase of the cell cycle?
12
A cell starts out in G2 phase with 12 chromosomes, but after mitosis, each of the daughter cells has only 11 chromosomes in G1 phase. What event provides the most likely explanation for this scenario?
During prometaphase in the original cell, one of the chromosomes failed to attach to a spindle fiberor was improperly segregated during mitosis.
If a cell starts out in G2 phase with 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would you expect in each of the daughter cells if one of the chromosomes failed to separate in anaphase?
One daughter cell will have 11 chromosomes, and the other will have 12
In which phase of meiosis do homologous chromosomes initiate pairing?
prophase I
During which phase of meiosis do homologous chromosomes separate?
anaphase I
During which type of cell division does each daughter cell contain half the amount of DNA as did the cell just prior to cell division?
meiosis I, meiosis II, and mitosis
If a cell normally has 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would be present in each cell at the end of meiosis II if a single pair of homologous chromosomes failed to separate during anaphase I?
2 daughter cells will each have five chromosomes and two daughter cells will each have seven chromosomes.
During which phase of meiosis does independent assortment occur?
metaphase I
Which process results in sister chromatids that are no longer identical?
crossing over
During which phase of meiosis does crossing over occur?
prophase I
What are the two processes in meiosis that create genetic differences among cells?
independent assortment and crossing over
In female animals, the cell capable of being fertilized is the ___________
ovum
All of the following make meiosis different from mitosis EXCEPT ___________
a) meiosis comprises two divisions
b) chromosome number is reduced by half in meiosis
c) resulting cells from meiosis are genetically different from the parent cell
d) meiosis lacks a preceding S phase
e) pairing of homologous chromosomes usually occurs only in meiosis
meiosis lacks a preceding S phase
Which event of meiosis explain genetic variation among the gametes?
a) crossing over
b) random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes
c) distribution of differing numbers of chromosomes to daughter cells
d) both a and b
e) all of the above
both a and b
unicellular, no membrane- bound organelles
eubacteria and archaea
prokaryotes
both unicellular and multicellular with membrane-bound organelles
yeast
eukaryotes
what’s the difference between prokaryote and eukaryote DNA?
prokaryote - not complexed with histones in bacteria and not as organized; usually one circular DNA molecule
eukaryote - complexed with histones to help with sorting; has multiple linear DNA molecules
neither prokaryotic nor eukaryotic with an outer protein coat surrounding nucleic acid
viruses
simple division
has an origin of replication and high rate of replication
prokaryotic cell reproduction
separation of replicated circular chromosome
simple division
goes through a cell cycle, has homologous pairs and structures of chromosomes, and has genetic consequences of the cell cycle
eukaryotic cell reproduction
cells carry two sets of genetic information
aka somatic cells (mitosis)
diploid (2n)
cells carry one set of genetic information
aka gametes (meiosis)
haploid (n)
two version of a gene encode a trait
allele
two sets of chromosomes (2 versions of same genes)
homologous pairs
tips/ends of a linear chromosome
protective capes so as replication occurs, genes don’t degrade
telomeres
attachment point for spindle microtubules (how cells pull chromosomes apart with spindle fibers)
centromere
where the DNA attaches to the spindle
kineochore

submetacentric
metacentric

telocentric

acrocentric
an extended period between cell divisions, DNA synthesis, and chromosome replication phase
cell is growing and getting ready to split
interphase
mitotic phase (splitting)
M phase
key transitions points in the cell cycle
phase checkpoint
cell is growing and doubles in size; proteins necessary for cell division are synthesized
G1
DNA synthesis (double the DNA)
S phase
checkpoints before M phase; biochemical preparation of cell division
G2
nuclear and cellular division (separation of sister chromatids)
M phase/mitosis
actual split of cells/ separation of cytoplasm
cytokinesis
regulated decision point (cell can sit in this phase, go through apoptosis, or go on)
G1/S checkpoint
only passed if DNA is fully replicated undamaged
G2/M checkpoint
mitosis: not condensed chromosomes
interphase
mitosis: condensed chromosomes and developing spindle
prophase
mitosis: break nuclear envelope and interact with spindle fibers
prometaphase
mitosis: chromosomes line up down the middle and attach to spindle fibers
metaphase
mitosis: break sister chromatids apart
anaphase
mitosis: make nuclear envelope and dissolve spindle fibers
telophase
stable; nondividing period of variable length
G0 phase
What are the genetic consequences of the cell cycle?
produces 2 cells that are genetically identical to each other and with the original cell. Each new cell contains a full complement of chromosomes and about half the cytoplasm and organelle content of the original parental cell
the production of haploid gametes
meiosis
the fusion of haploid gametes
fertilization
consequences of meiosis
genetic variation
meiosis: DNA synthesis and chromosome replication
interphase
meiosis: separation of homologous chromosome pairs, and reduction of the chromosome number by half
meiosis I
meiosis: separation of sister chromatids, also known as equational division
meiosis II
Prophase I: close pairing of homologous chromosomes
synapsis
Prophase I: closely associated four chromatids of two homologous chromosomes
tetrad
Prophase I: exchange of genetic information of chromosome segments from non-sister chromatids within the synapsed chromosome
crossing over
random alignment of homologous pairs of chromosomes along the __________ plate
metaphase I
separation of homologous chromosome pairs, and the random distribution of chromosomes into two newly divided cells — second mechanism of generating genetic variation in the newly formed gametes
anaphase I
nuclear envelope back
telophase I
the period between meiosis I and meiosis II
interkinesis
If 8 chromosomes in metaphase II, then how many chromosomes in _______
a) prophase of mitosis
b) metaphase of meiosis I
c) anaphase of mitosis
d) anaphase II of meiosis
e) anaphase I of meiosis
f) after cytokinesis that follows mitosis
g) after cytokinesis that follows meiosis II
a) 16 chromosomes, 32 DNA molecules
b) 16 chromosomes, 32 DNA molecules
c) 32 chromosomes, 32 DNA molecules
d) 16 chromosomes, 16 DNA molecules
e) 16 chromosomes, 32 DNA molecules
f) 16 chromosomes, 16 DNA molecules
g) 8 chromosomes, 8 DNA molecules
what are the 3 sources of genetic variation in meiosis?
four cells are produced from each original cell
chromosome number in each new cell is reduced by half
newly formed cells from meiosis are genetically different from one another and from the parental cell
which genetic diseases or disorders result from errors in mitosis or meiosis?
down syndrome - extra chromosome 21
turner syndrome - single X
cancers - errors in mitosis
how do errors in mitosis or meiosis bring about these diseases and disorders?
abnormal separation of chromosomes so that cells have too many or too few chromosomes
comparison of mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis II: cell division
yes
comparison of mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis II: reduction in chromosome number
no, yes, no
comparison of mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis II: genetic variation produced
no, yes, no
comparison of mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis II: crossing over
no, yes, no
comparison of mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis II: random distribution of maternal and paternal chromosomes
no, yes, no
comparison of mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis II: metaphase
individual chromosomes line up
homologous pairs ling up
individual chromosomes line up
comparison of mitosis, meiosis I, and meiosis II: anaphase
chromatids separate
homologous chromosomes separate
chromatids separate
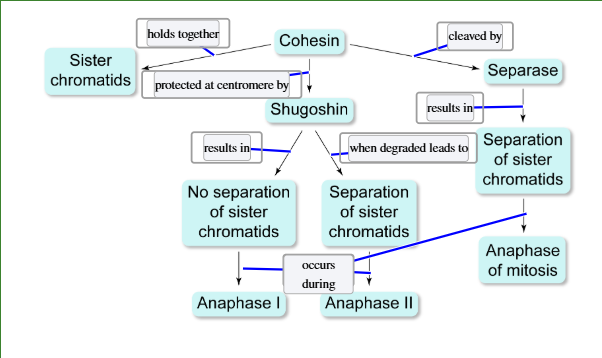
a protein that holds the chromatids together
key to the behavior of chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis
controls separation of chromatids and chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis
cohesin
protects cohesin at the centromeres from the action of separase, so the sister chromatids remain together
shugoshin in anaphase I
breaks down and the centromeric cohesin is cleaved by separase, so the sister chromatids separate
shugoshin during anaphase II
male gamete production
spermatogenesis
female gamete production
oogenesis
The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster has four pairs of chromosomes, whereas the housefly Musca domestica has six pairs of chromosomes.
How many different combinations of chromosomes are possible in the gametes of the fruit fly?
How many different combinations of chromosomes are possible in the gametes of the house fly?
Based on chromosome number, in which species would you expect to see more genetic variation among the progeny?
16
64
the house fly
Suppose a scientist measures the amount of DNA per cell of a particular diploid species at various stages of meiosis. She finds that the meiotic cells contain 3.7 pg, 7.3 pg, or 14.6 pg of DNA.
What stages of the cell cycle would correspond to the different amounts of DNA contained within a cell at that stage?
3.7 pg - after cytokinesis of meiosis II
7.3 pg - metaphase II, G1
14.6 pg - prophase I, telophase I before cytokinesis, G2
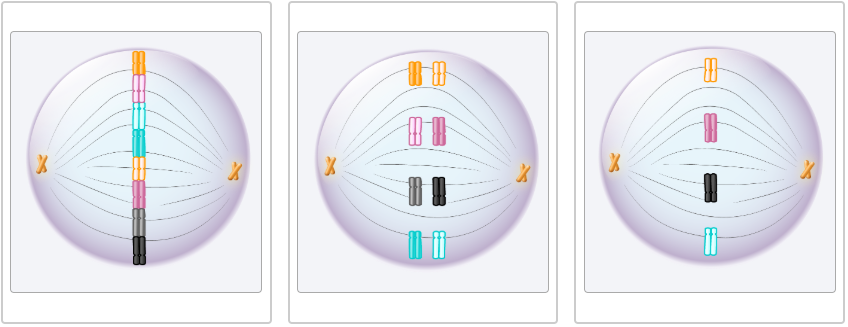
Identify the images as a cell in metaphase of mitosis, meiosis I, or meiosis II. All cells come from from an organism that has a diploid (2n) chromosome number of eight.
mitosis, meiosis I, meiosis II
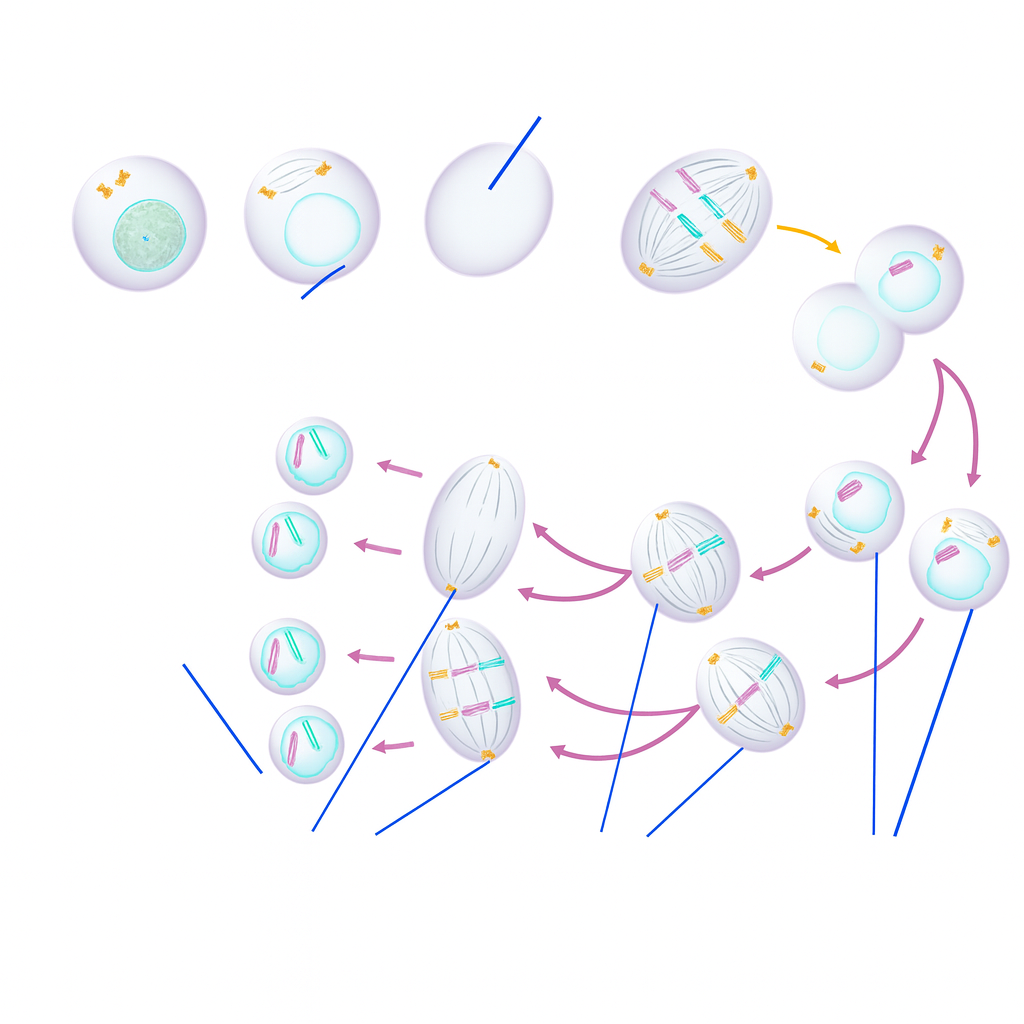
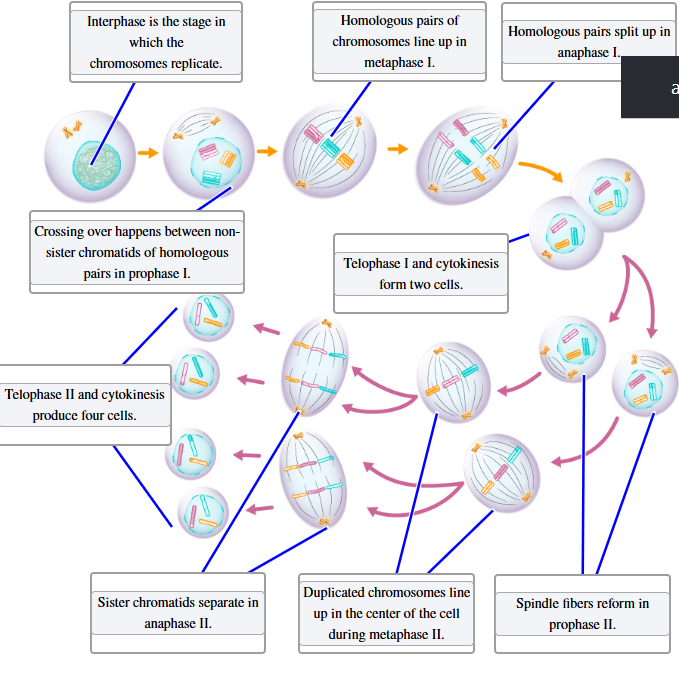
Identify the stages of meiosis.
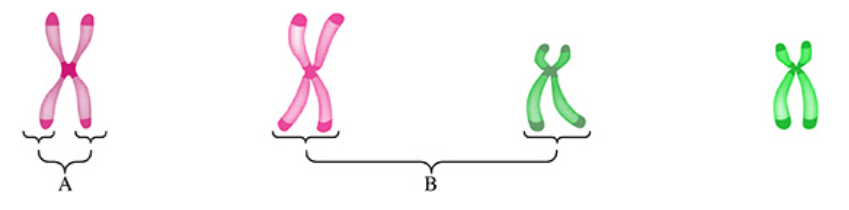
The given chromosomes are derived from a diploid cell.
Which set of terms describes the chromosomes labeled A and B?
The chromosomes labeled A are sister chromatids and the chromosomes labeled B are nonhomologous chromosomes.
Suppose a diploid European wild raspberry is completely heterozygous at all 14 of its chromosomes (2n = 14).
How many different combinations of gametes can be produced by this European wild raspberry, assuming no homologous recombination between chromosomes? (*remember gametes are haploid when using the 2n formula*)
128
The somatic cell of a cat contains 38 chromosomes (2n = 38). How many chromosomes and how many DNA molecules would the secondary spermatocyte of this cat have?
Using the formula 2n, where n equals the number of chromosome pairs, the answer is:
19 chromosomes
38 DNA molecules
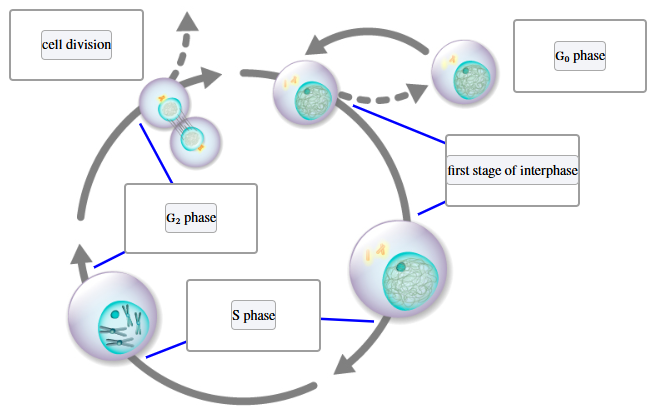
Label each phase of the cell cycle with the appropriate name.
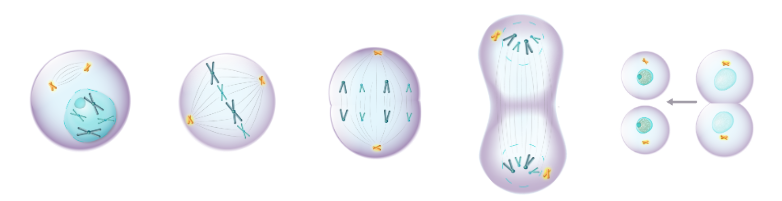
Identify each stage of M phase.
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
Cell division by mitosis is a mechanism of cell replication. Some single-celled organisms reproduce by cell division, and cell division enables multicellular organisms to grow and to repair damaged cells.
What is a product of cell division by mitosis?
two cells genetically identical to the original cell
A cell has a circular chromosome and histone proteins associated with its DNA but lacks a nuclear membrane.
Choose the domain of the cell with the best justification.
The cell belongs to Archaea because it has histone proteins, which are present in Archaea and Eukaryota, but absent in Eubacteria.
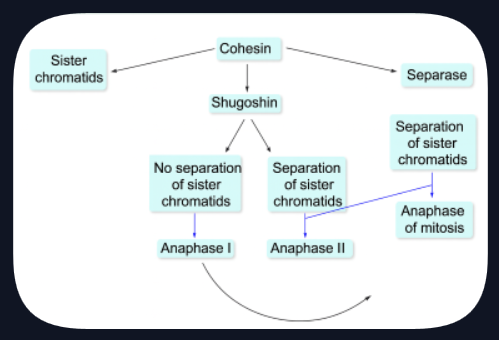
Match the relationships to the best corresponding concepts.