Exam 1 - Pearson Q's
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
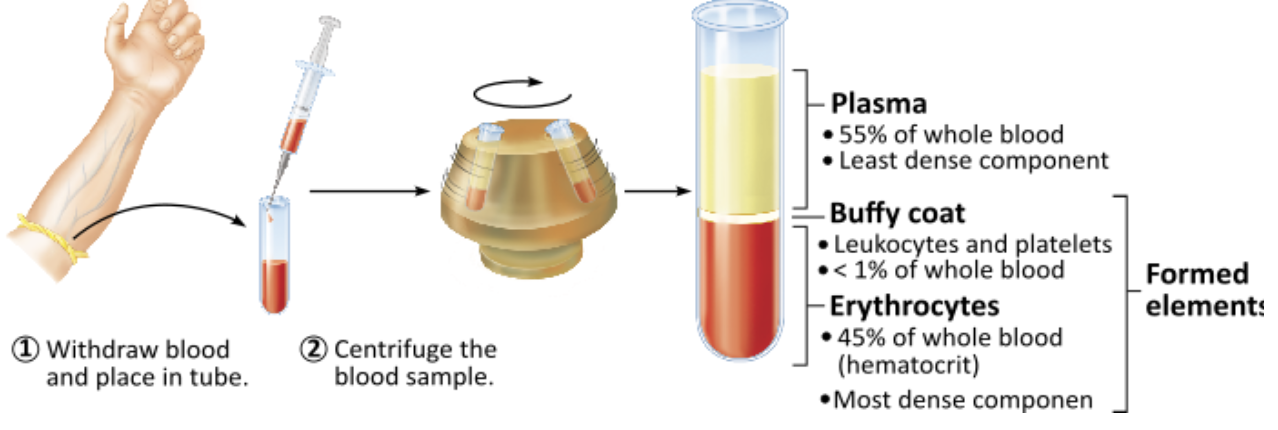
Which of these makes up the greatest portion of whole blood by volume?
platelets
leukocytes
plasma
erythrocytes
plasma
What is a hematocrit?
A hematocrit is the percentage of leukocytes & platelets in a whole blood sample
A hemocrit is the percentage of all formed elements in a whole blood sample
A hemocrit is the percentage of plasma in a whole blood sample
A hematocrit is the percentage of erythrocytes in a whole blood sample
A hematocrit is the percentage of erythrocytes in a whole blood sample
What is the average normal pH range of blood?
4.65-4.75
7.75-7.85
7.35-7.45
8.35-8.45
7.35-7.45
Which of the following is not a function of blood?
transport of metabolic wastes
protection from infection
hormone production
homeostatic regulation
3.hormone production
give the word of this definition:
Makes up most of plasma protein
ALBUMIN
give the word of this definition:
The major contributor to plasma osmotic pressure
Albumin
give the word of this definition:
forms the structural framework of a blood clot
Fibrinogen
give the word of this definition:
Thrombin catalyzes the activation of these molecules present in plasma
Fibrinogen
Prostaglandin derivates such as Thromboxane A2 is produced by ___.
platelets
What is the fibrous protein that gives shape to an RBC plasma membrane?
SPECTRIN
Erythropoietin is a hormone that stimulates production of __.
RBCs
What 2 things stimulates WBC production?
Interleukins
CSFs
__ is a natural anticoagulant found in basophils
Heparin
With a patient that is administered an injection of erythropoietin (EPO) you would expect to see ________.
decreased white blood cell count
increased white blood cell count
increased hematocrit
decreased hematocrit
increased hematocrit
Which plasma constituent is the main contributor to clotting?
albumin
beta globulins
alpha globulins
fibrinogen
4.fibrinogen
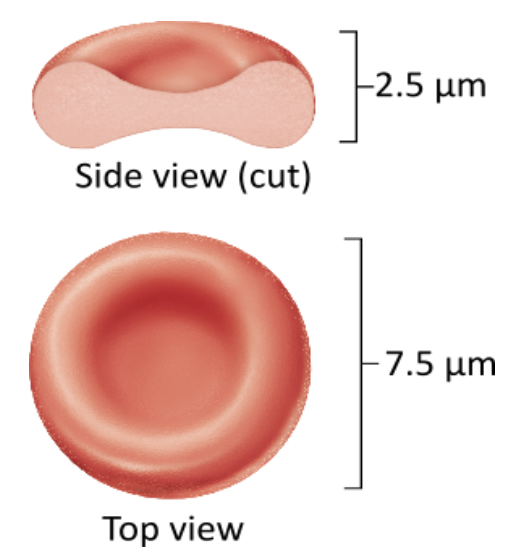
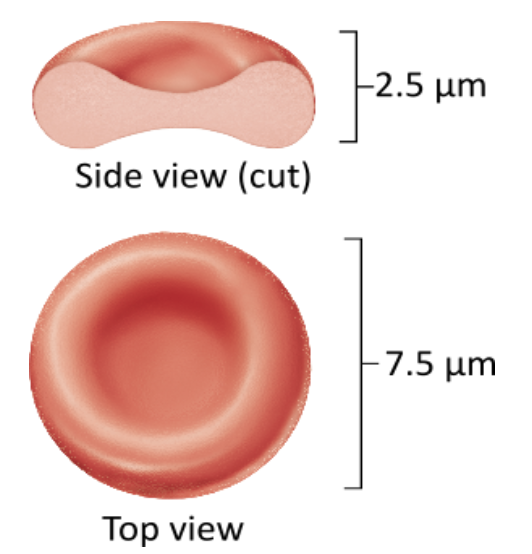
Which of the following is true of the structure of an erythrocyte?
Erythrocytes are nucleated cells.
Erythrocytes can bend and twist to fit through vessels.
Erythrocytes are larger than other cells in the blood.
Erythrocytes are cell fragments.
Erythrocytes can bend and twist to fit through vessels.
What is the name of the protein found in erythrocytes that transports respiratory gases and provides the red color?
fibrinogen
antibody
albumin
hemoglobin
hemoglobin
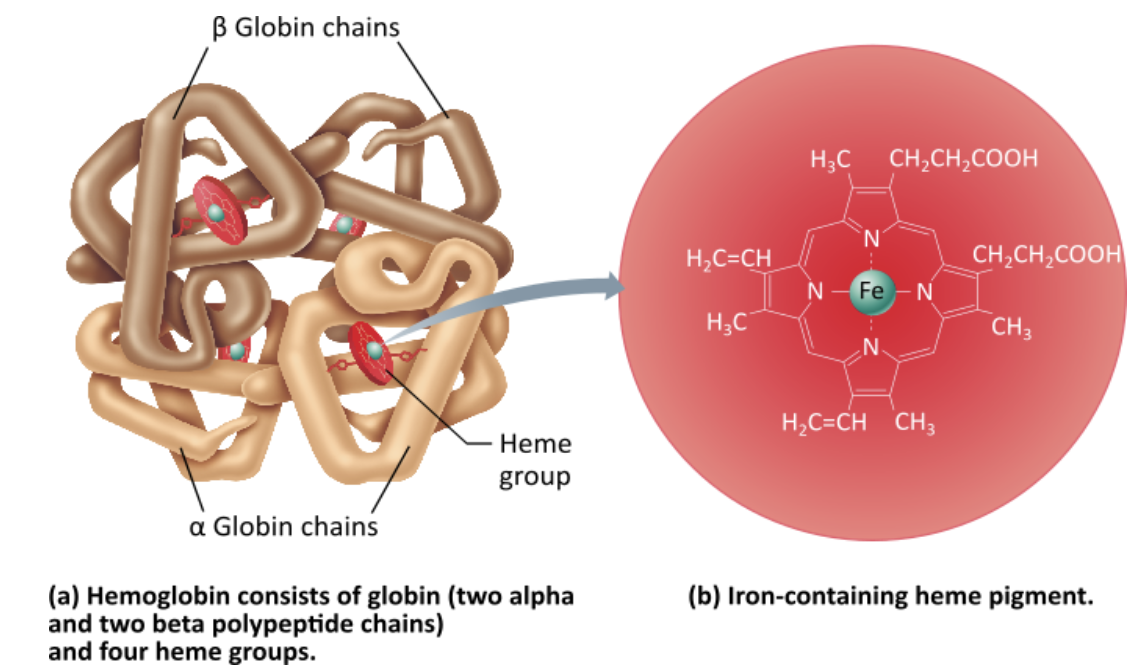
How many oxygen molecules can be transported by one hemoglobin molecule?
two
four
eight
2.four
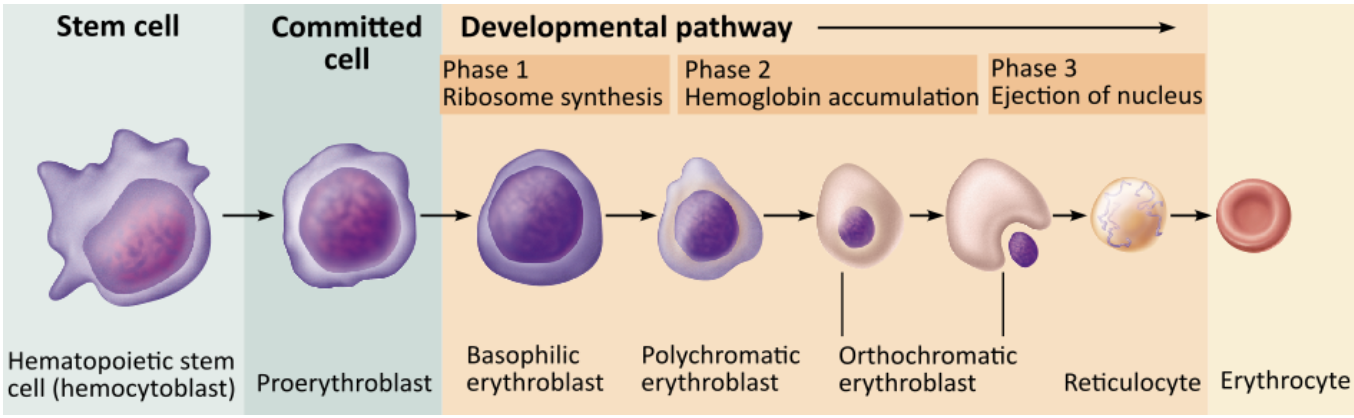
Erythropoietin (EPO) stimulates the developmental process shown here. What part of the body does erythropoietin (EPO) target to increase erythropoiesis?
bone marrow
lungs
kidneys
liver
Bone marrow
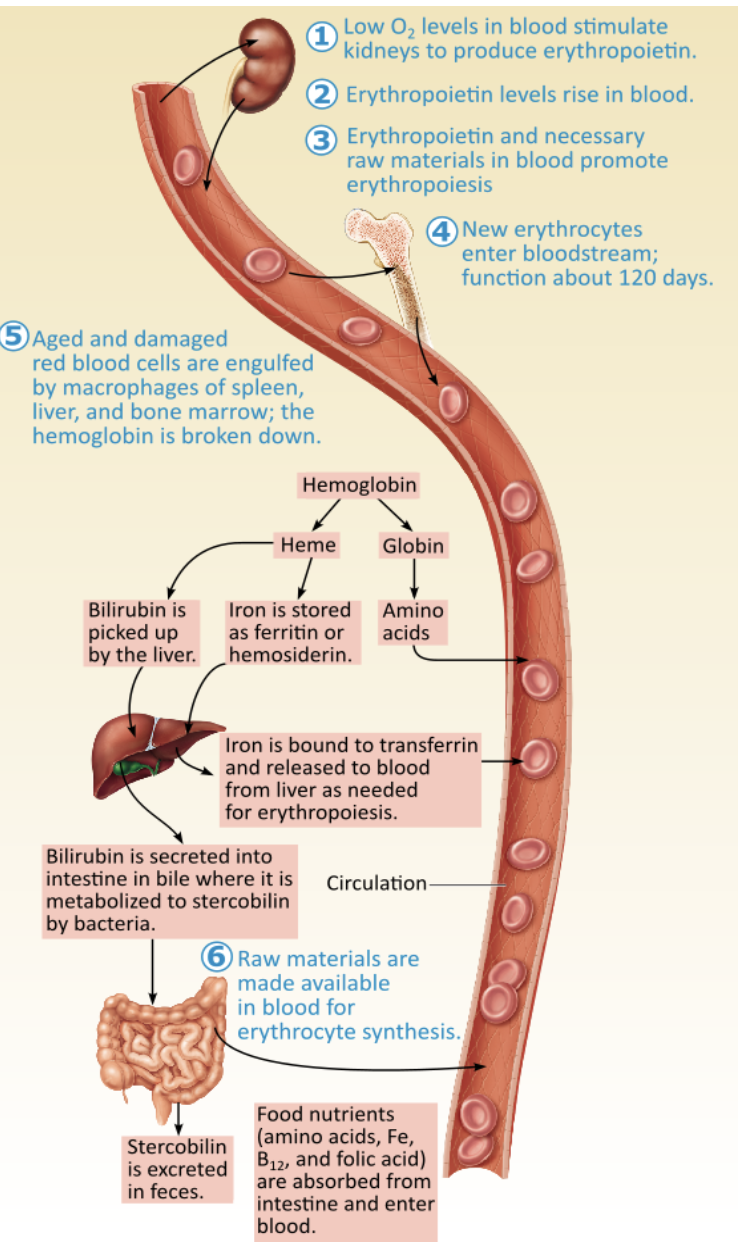
What part of the hemoglobin molecule is eventually metabolized to stercobilin in the feces?
iron
transferrin
a portion of the heme group
globin
3.a portion of the heme group
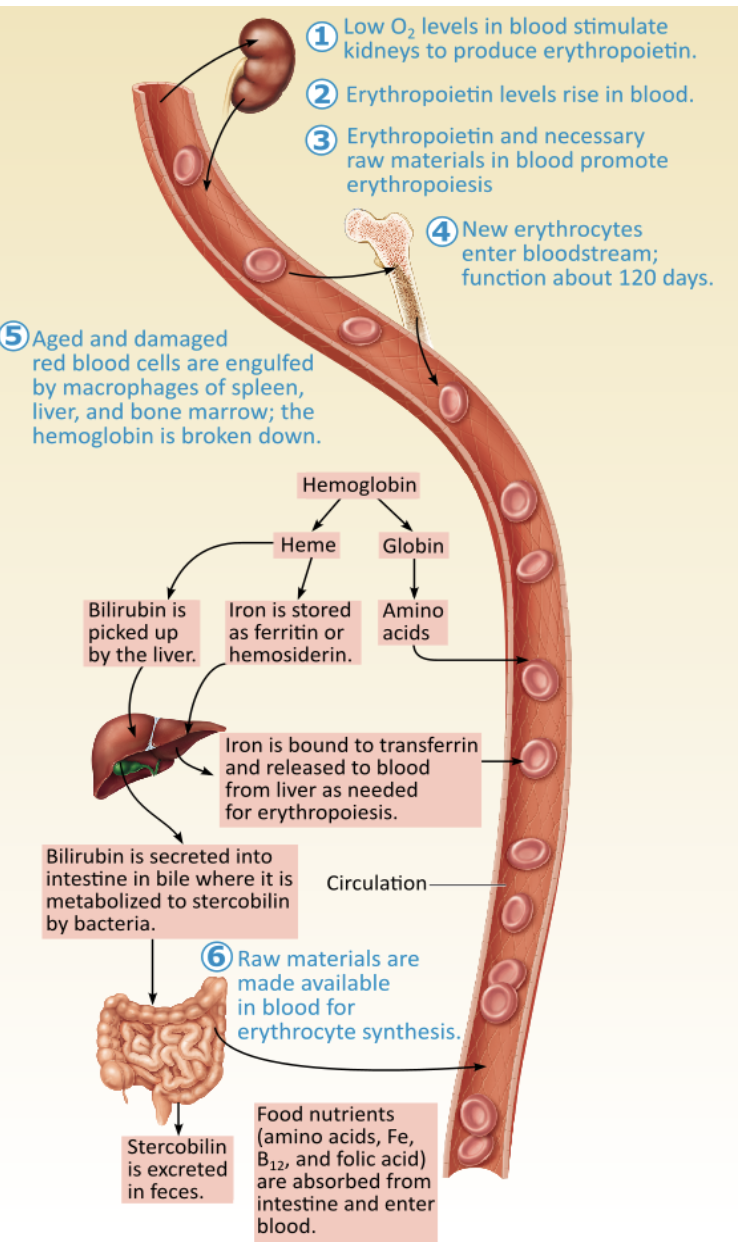
What erythrocyte production disorder results from an autoimmune disease associated with insufficient vitamin B12 absorption (step 6)?
renal anemia
pernicious anemia
aplastic anemia
hemorrhagic anemia
pernicious anemia
Mature erythrocytes do NOT contain mitochondria or a nucleus.
True
False
True
Which of the following does NOT stimulate erythrocyte production?
a drop in blood oxygen levels
erythropoietin
testosterone
hyperventilating
hyperventilating
Which of the following anemias is correctly matched with its description?
aplastic anemia: results from excessive blood loss
hemolytic anemia: results from inadequate iron intake
hemorrhagic anemia: results from red blood cells rupturing
pernicious anemia: results from a vitamin B12 deficiency
4.pernicious anemia: results from a vitamin B12 deficiency
Higher viscosity of blood will increase the amount of stress placed on the heart while it is pumping. Viscosity of blood is highest when ________.
hemoglobin levels are lowest
HbA1C levels are lowest
hematocrit is highest
plasma levels are highest
hematocrit is highest
Which of the following might trigger erythropoiesis?
hypoxia of EPO-producing cells
moving to a lower altitude
an increased number of RBCs
decreased tissue demand for oxygen
hypoxia of EPO-producing cells
t/f:
The primary source of RBCs in the adult human being is the bone marrow in the shafts of the long bones.
false
t/f:
Fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin.
true
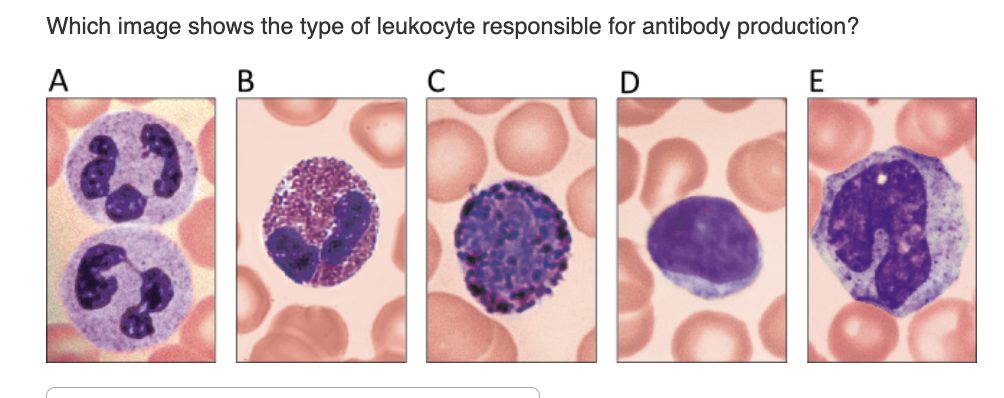
C
D
B
E
D
t/f:
Leukemia refers to cancerous conditions involving white blood cells.
true
T/F:
Leukopenia is an abnormally low number of leukocytes.
true
T/F:
Granulocytes called neutrophils are phagocytic and are the most numerous of all white blood cell types.
True
What factor stimulates platelet formation?
PDGF
G-CSF
thrombopoietin
erythropoietin
Thrombopoietin
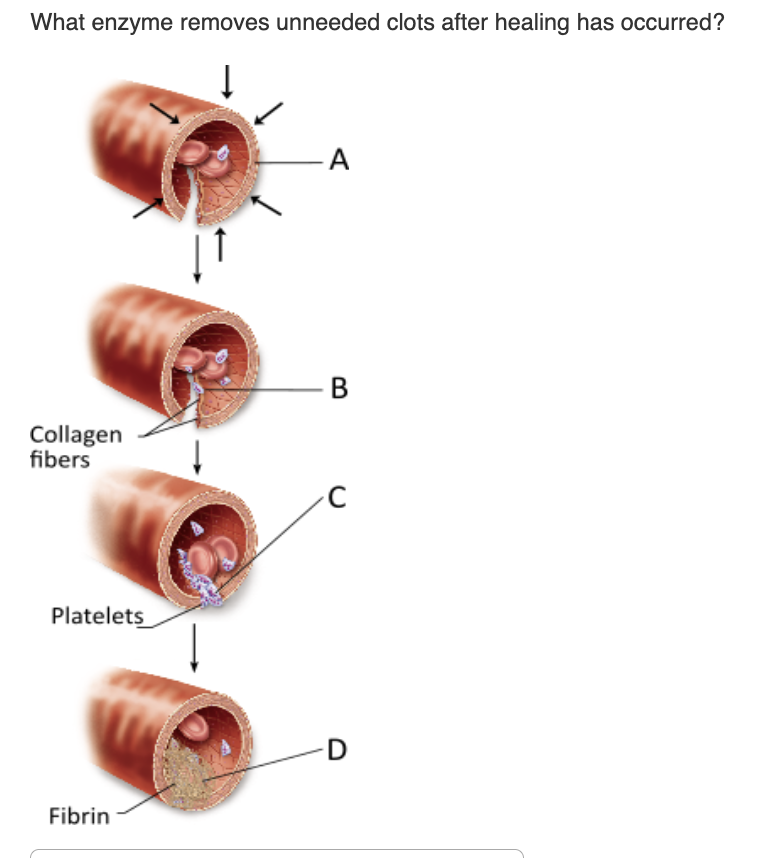
plasminogen
plasmin
fibrin
thrombin
plasmin
Hemostasis is important for __________.
stoppage of bleeding
red blood cell recycling
red blood cell production
white blood cell production
stoppage of bleeding
A person who lacks agglutinogen A but has agglutinogen B would have blood type __________.
B
AB
O
A
B
Which of the following scenarios could result in HDN (hemolytic disease of the newborn)?
O-positive female pregnant with a B-positive baby
AB-negative female pregnant with an AB-negative baby
B-negative female pregnant with an AB-positive baby
A-positive female pregnant with a B-positive baby
B-negative female pregnant with an AB-positive baby
Choose the incompatible transfusion.
Donate type B blood to a recipient with type AB blood.
Donate type A blood to a recipient with type AB blood.
Donate type B blood to a recipient with type O blood.
Donate type O blood to a recipient with type AB blood.
Donate type B blood to a recipient with type O blood.
When neither anti-A serum nor anti-B serum clot on a blood plate with donor blood, the blood is type ________.
A |
AB |
O |
B |
type O
cuz type O has both anti b and anti a antibodies
__ is the abnormal excess of erythrocytes resulting in an incr. in blood viscosity
POLYCYTHEMIA
Thrombocytopenia is platelet deficiency/surplus resulting in spontaneous bleeding from small blood vessels.
deficiency
Anemia is a condition in which blood has abnormally low __ __ capacity
oxygen carrying capacity
Leukemia is cancerous condition involving RBCs/WBCs
WBCs
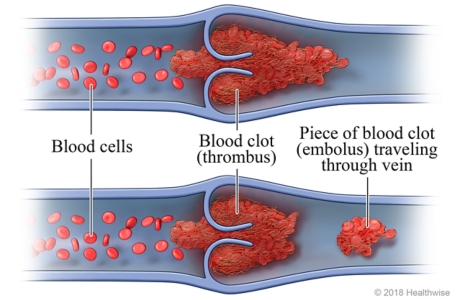
__ is a free floating thrombus in the bloodstream
Embolus
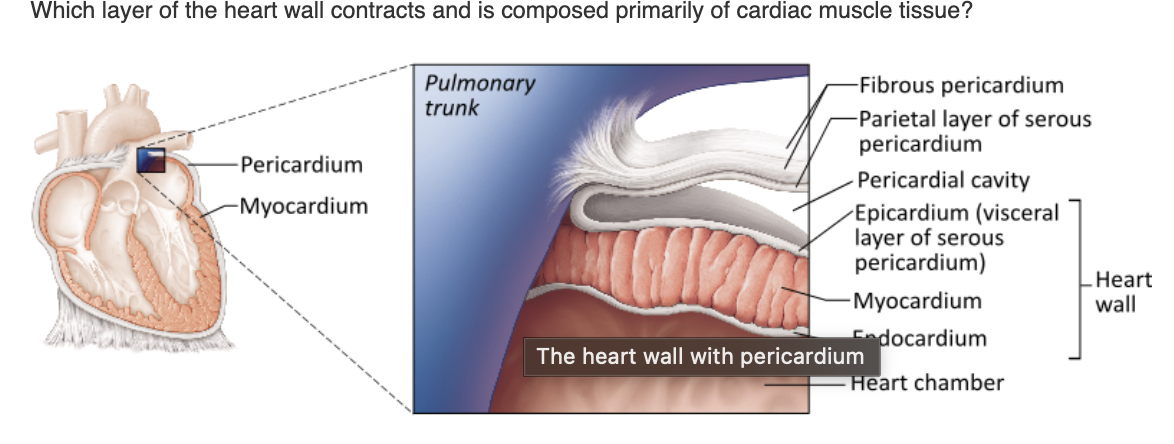
endocardium
epicardium
myocardium
visceral layer of the serous pericardium
myocardium
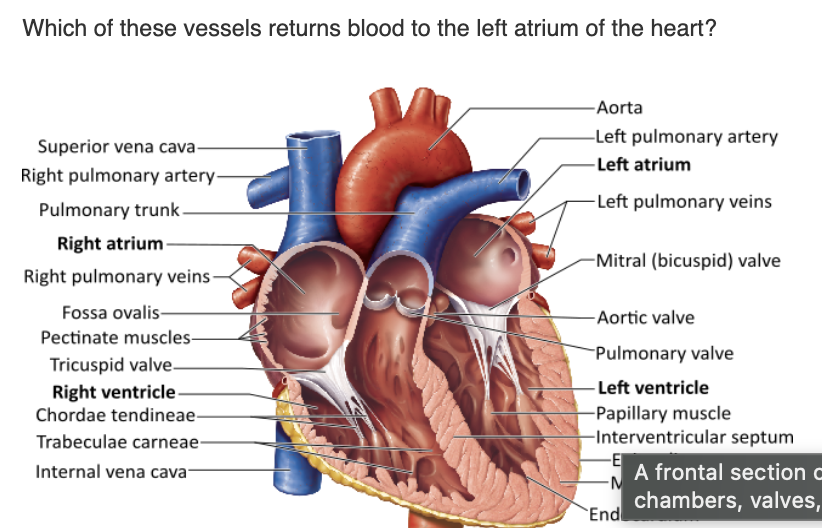
1.superior vena cava
2.pulmonary trunk
3.coronary sinus
pulmonary veins
pulmonary veins
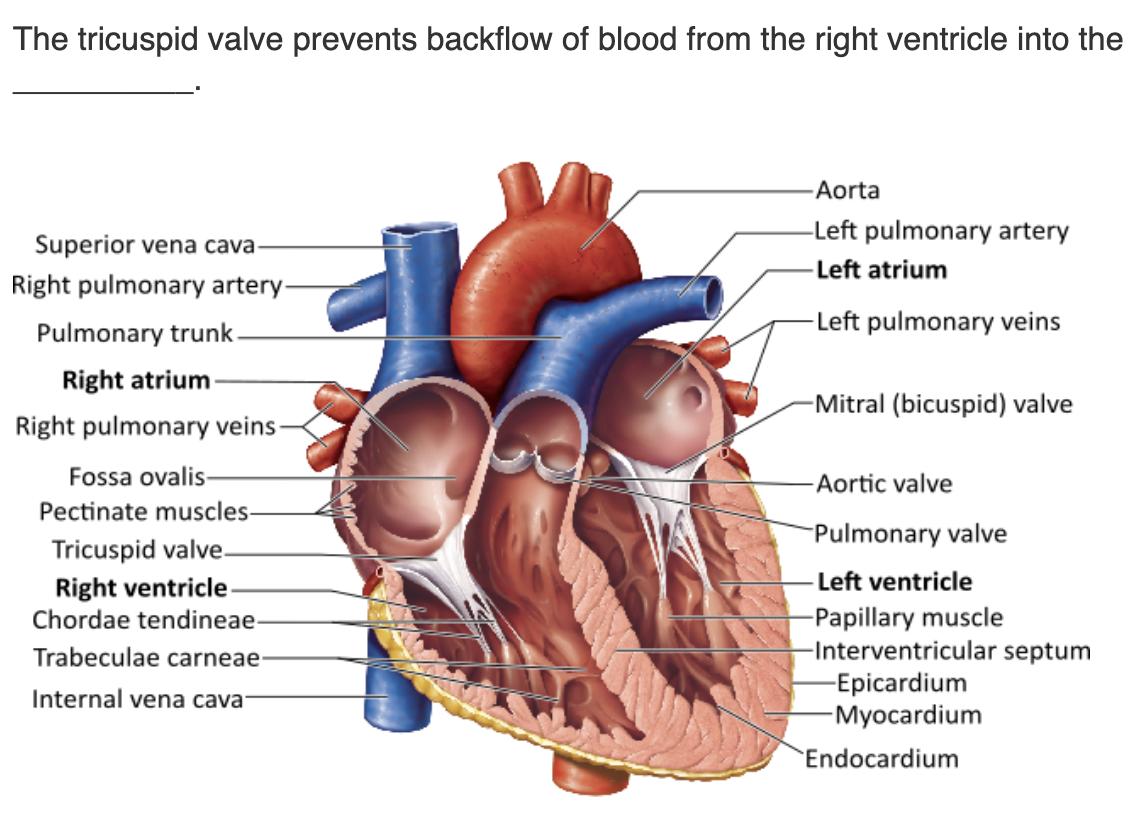
left ventricle |
pulmonary trunk |
left atrium |
right atrium |
right atrium
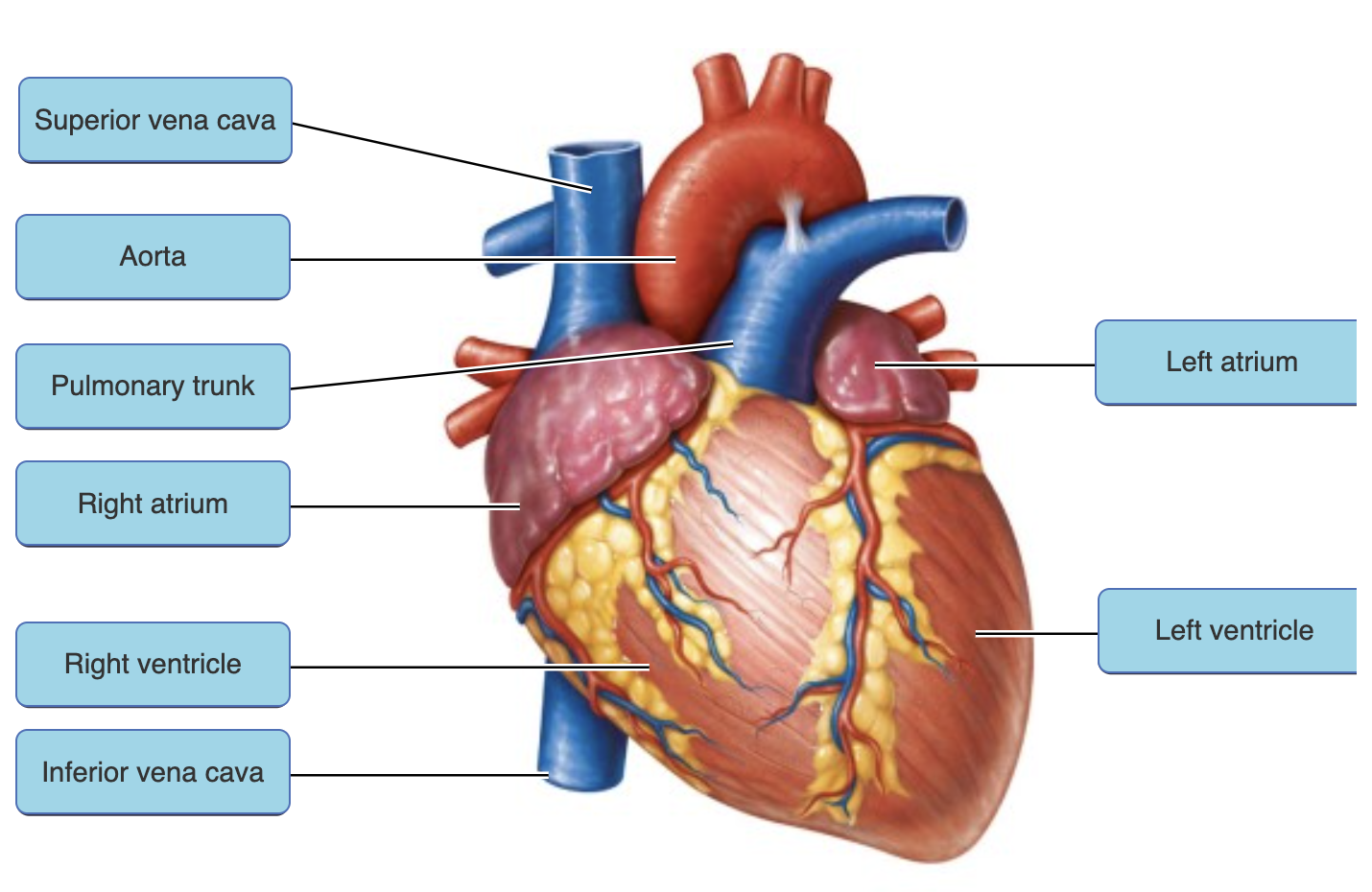
just know locations
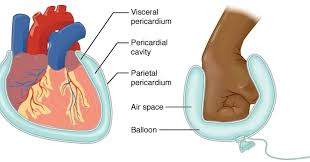
Cardiac tamponade results in ineffective pumping of blood by the heart. This is because the excessive amount of fluid in the pericardial cavity will ______.
prevent the visceral layer of the serous pericardium from properly surrounding the heart |
prevent the heart from filling properly with blood |
prevent proper oxygenation of the blood |
interfere with the ability of this fluid to lubricate the serous membranes |
prevent the heart from filling properly with blood |
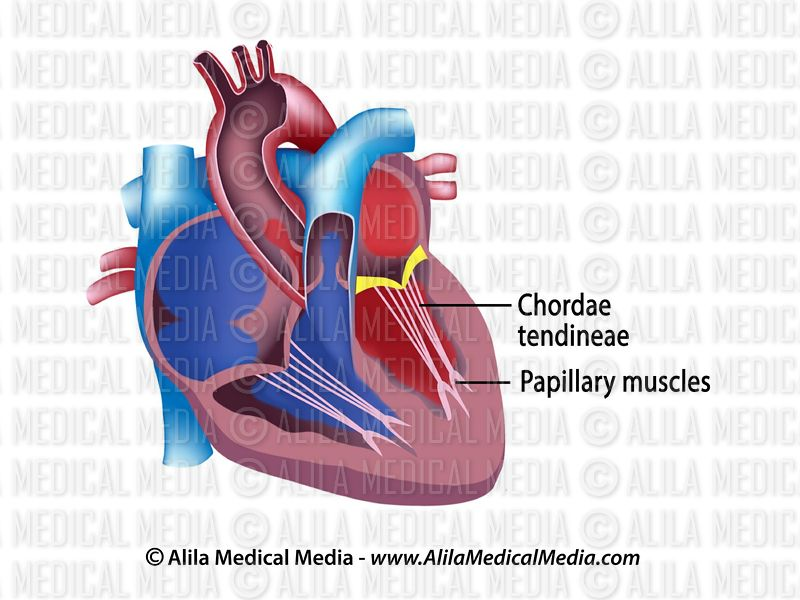
T/F:
The role of the chordae tendineae is to open the AV valves at the appropriate time.
False; they hold the AV valves in place so they don’t flip backward.
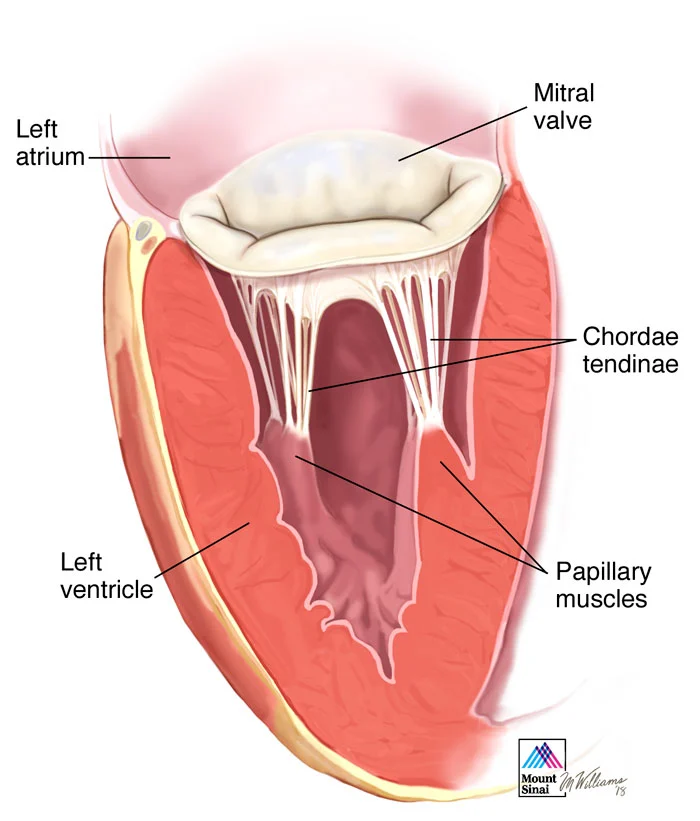
Select the correct statement about the heart valves.
Aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves control the flow of blood into the heart. |
The mitral (bicuspid) valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle. |
The tricuspid valve divides the left atrium from the left ventricle. |
The atrioventricular (AV) valves prevent backflow of blood added into the atria during ventricular contraction. |
The atrioventricular (AV) valves prevent backflow of blood added into the atria during ventricular contraction. |
Name the ridged bundles of muscle found projecting inside the right atrium.
View Available Hint(s)for Part A
Trabeculae carneae |
Pectinate muscles |
Papillary muscles |
Intercalated discs |
Pectinate muscles |
Identify the right atrioventricular valve.
Pulmonary valve |
Tricuspid valve |
Bicuspid valve |
Aortic semilunar valve |
Tricuspid valve |
Identfiy the valve located at the exit of the right ventricle.
Bicuspid valve |
Pulmonary semilunar valve |
Tricuspid valve |
Aortic semilunar valve |
Pulmonary semilunar valve |
T/F:
The moderator band is found on both the right and left side of the heart.
False
T/F:
Oxygenated blood flows through the right side of the heart.
False
Identify the most muscular chamber.
View Available Hint(s)for Part A
Left atrium |
Right atrium |
Left ventricle |
Right ventricle |
Left ventricle |
Name the inner lining of the heart.
View Available Hint(s)for Part B
Epicardium |
Myocardium |
Endocardium |
Pericardium |
Endocardium
Identify the valve found between the left atrium and left ventricle.
View Available Hint(s)for Part C
Bicuspid (mitral) valve |
Aortic valve |
Tricuspid valve |
Pulmonary valve |
Bicuspid (mitral) valve |
What heart chamber pushes blood through the aortic semilunar valve?
Left ventricle |
Right ventricle |
Left atrium |
Right atrium |
Left ventricle |
Name the irregular ridges of muscle lining the ventricles that are not indirectly connected to the atrioventricular valves.
Pectinate muscles |
Trabeculae carneae |
Papillary muscles |
Chordae tendineae |
Trabeculae carneae |
What fibrous structure functions to anchor the atrioventricular valves in a closed position?
Trabeculae carneae |
Chordae tendineae |
Papillary muscle |
Moderator band |
Chordae tendineae |
T/F:
Blood on the right never mixes with blood on the left, once the heart is fully developed.
TRUE
What is the function of the coronary circulation?
Provide a blood supply to the heart |
Provide a blood supply to the pericardium |
Provide a blood supply to the aortic arch |
Provide a blood supply to the lungs |
Provide a blood supply to the heart |
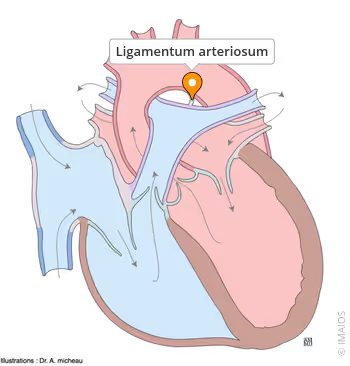
What is the ligamentum arteriosum?
A ligament securing the aorta |
A remnant of the ductus arteriosus |
A remnant of the foramen ovale |
A ligament attaching the aorta to the superior vena cava |
A remnant of the ductus arteriosus |
Which chamber of the heart exits into the pulmonary trunk?
Right atrium |
Right ventricle |
Left ventricle |
Left atrium |
Right ventricle |
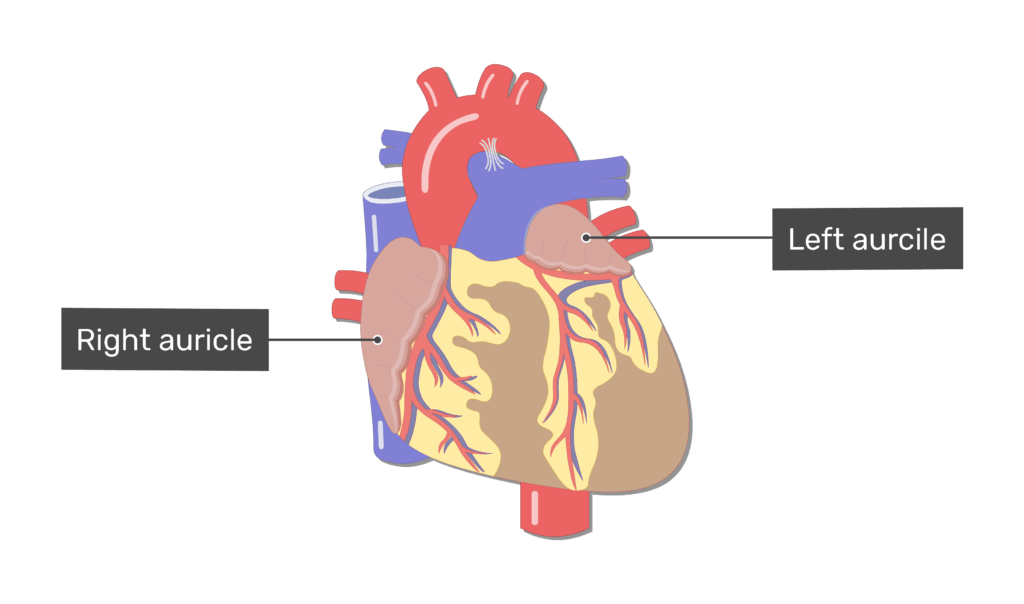
Identify the ear like flaps that are attached to the top chambers of the heart.
Pectinate muscles |
Coronary sinus |
Atrium |
Auricle |
Auricle |
t/f:
The first branch off the arch of the aorta is the brachiocephalic artery in both the sheep and the human.
True
t/f:
The base of the heart is located at the bottom of the heart.
false
right ventricle |
left atrium |
right atrium |
left ventricle |
right atrium |
pulmonary semilunar valve |
right atrium |
left ventricle |
right ventricle |
left ventricle |
t/f: The right side of the heart is considered the systemic circuit pump.
FALSE
The term for pain associated with deficient blood delivery to the heart that may be caused by the transient spasm of coronary arteries is ________.
pericarditis |
angina pectoris |
myocardial infarct |
ischemia |
angina pectoris |
t/f:
The myocardium receives its blood supply from the coronary arteries.
TRUE
T/F: The left side of the heart pumps the same volume of blood as the right.
TRUE
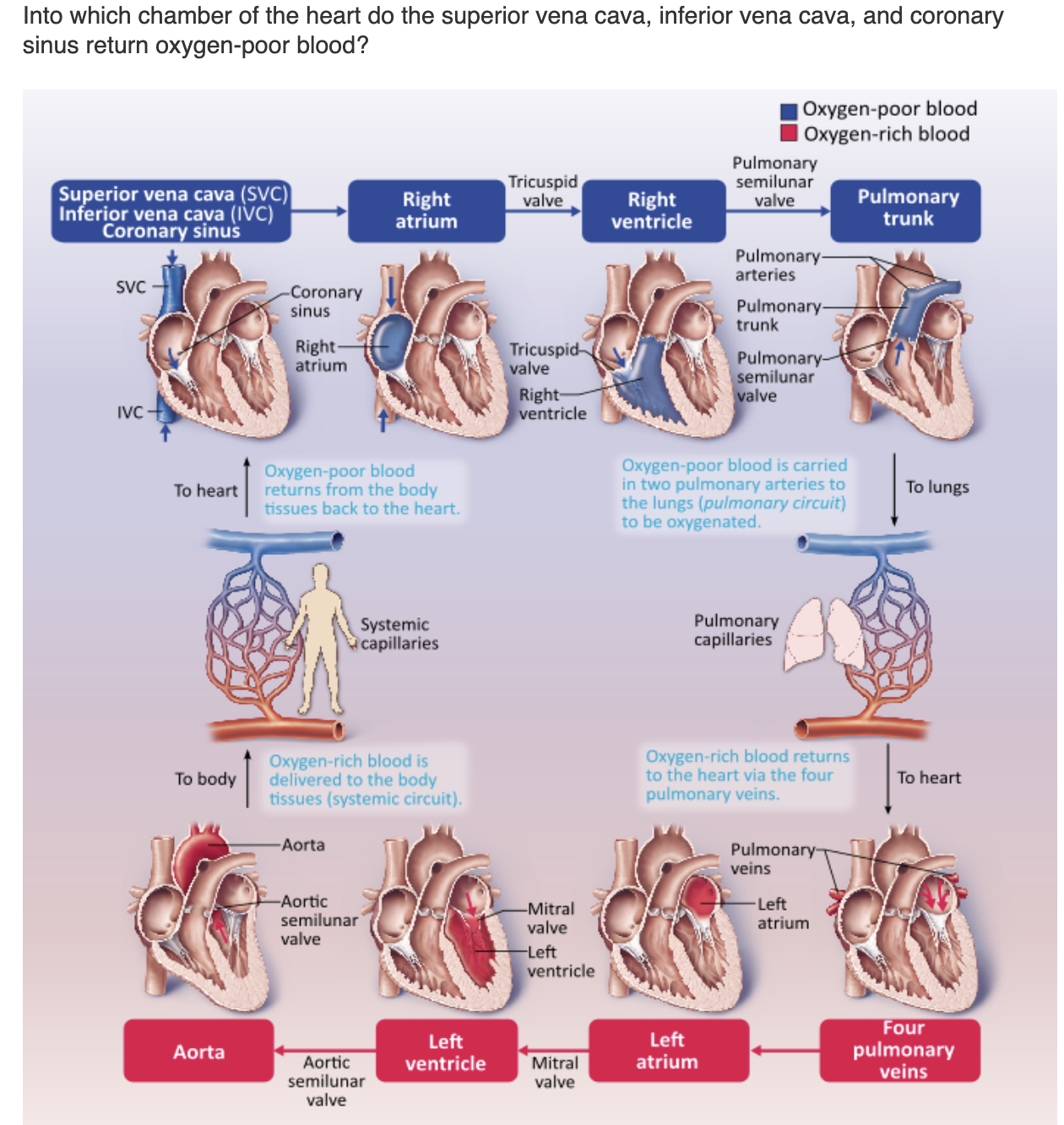
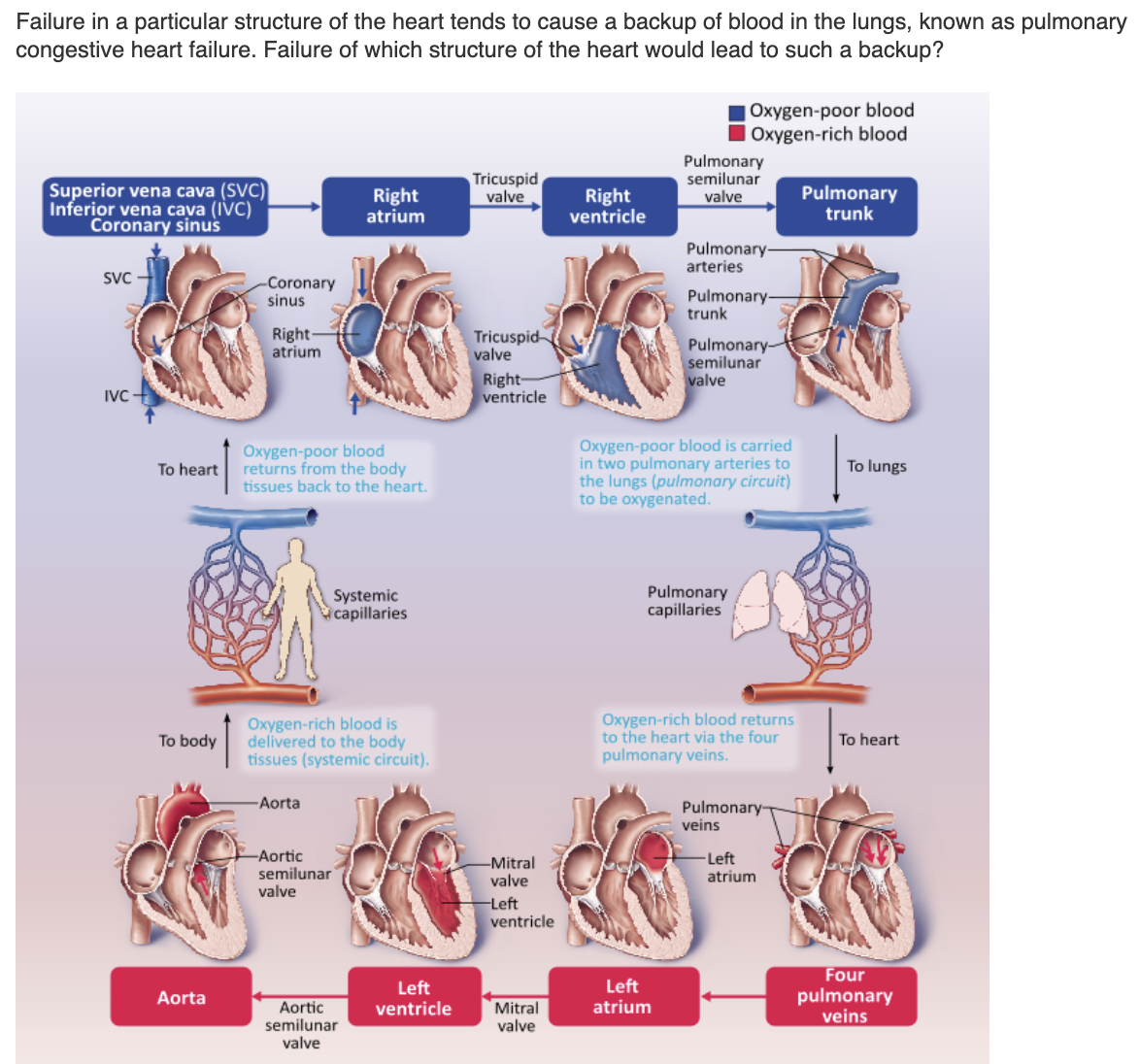
The __ __ __ carries o2 poor venous blood from above the diaphragm from areas of the upper body & extremities into the right atrium
superior vena cava
The __ __ carries O2 poor venous blood of the coronary circulation into the right atrium
Coronary sinus
The ___ __ cava carries O2 poor venous blood from below the diaphragm from the areas of the lower body & extremities into the right atrium.
inferior vena cava
know names
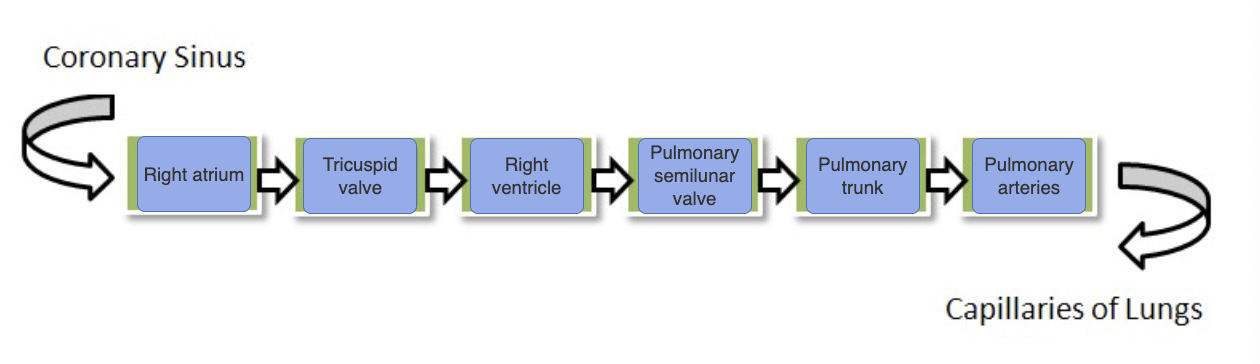
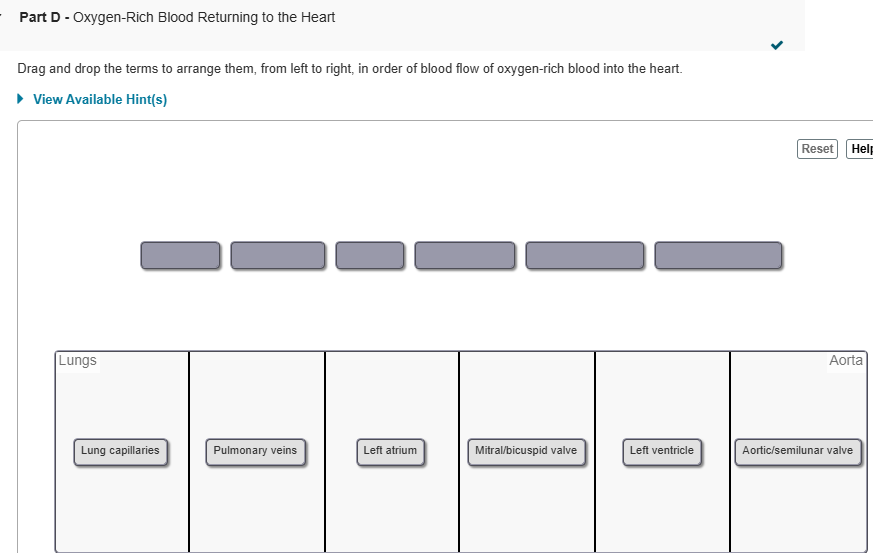
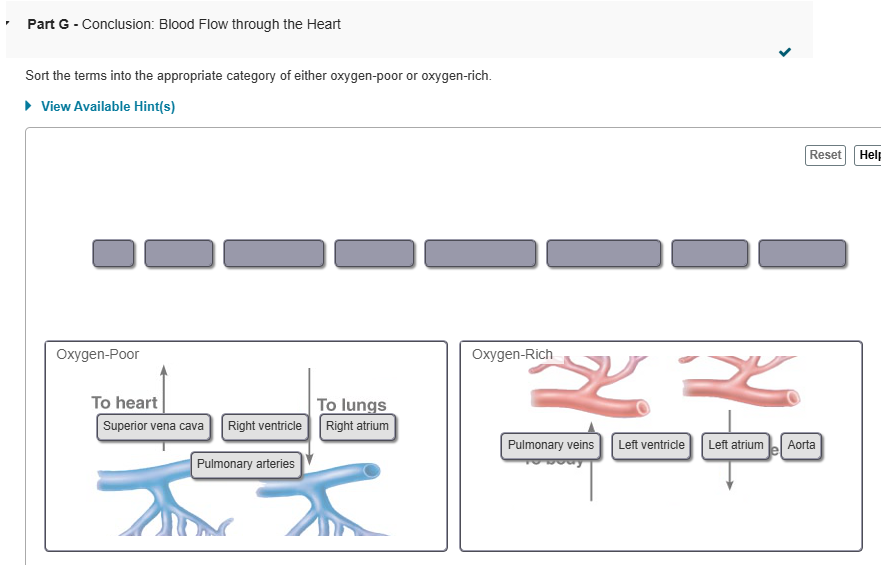
Assume that blood is flowing from the coronary sinus to the lung capillaries. Place the anatomical labels in order of flow in the target boxes. Not all labels are used.
just study picture
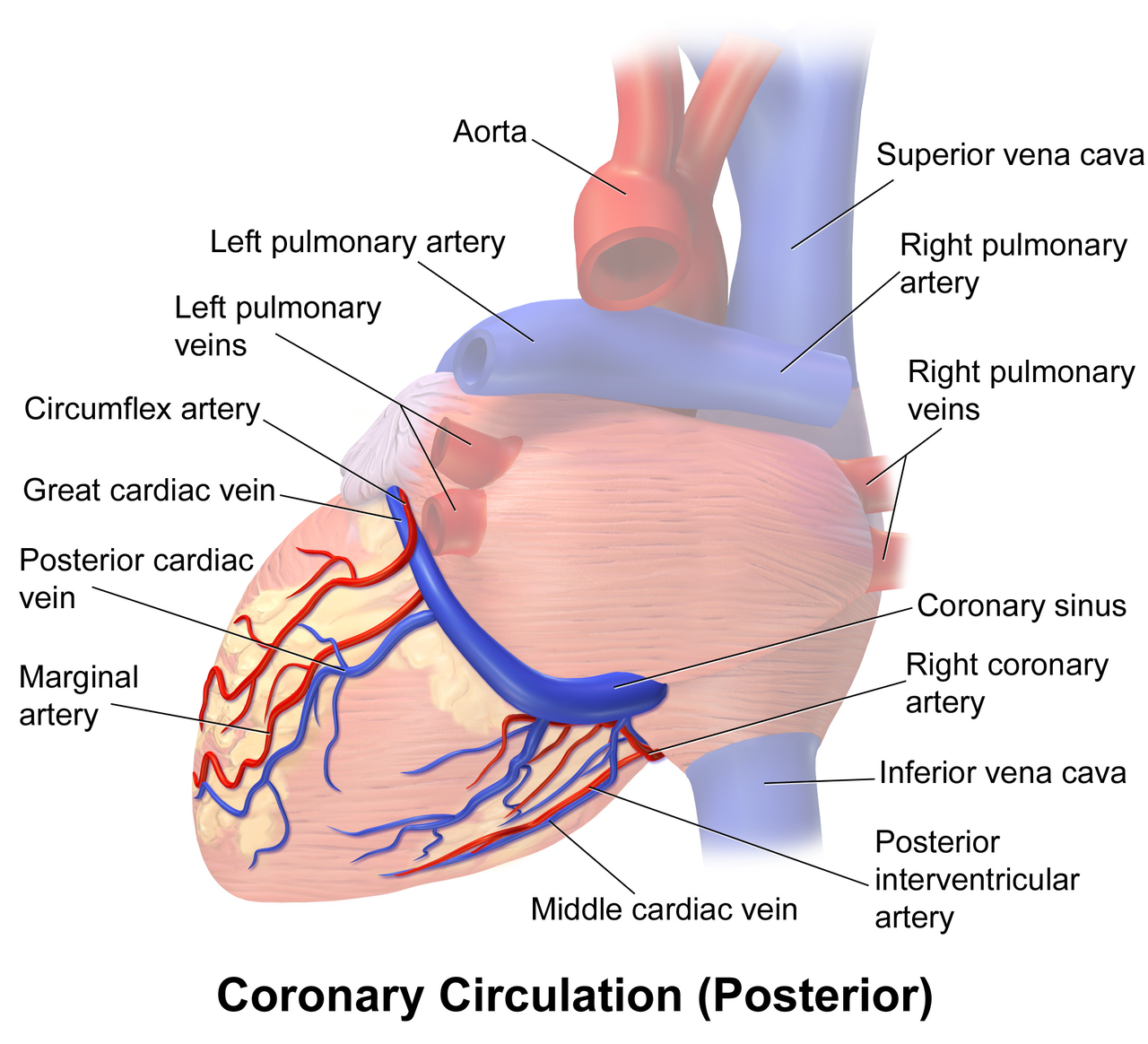
just know
Which structure prevents backflow of blood into the left atrium
mitral (biscuspid) valve
The vessel that carries O2-rich blood to tissues is the…
aorta
Systemic capillaries are capillaries receiving blood flow from the right/left side of the heart
left
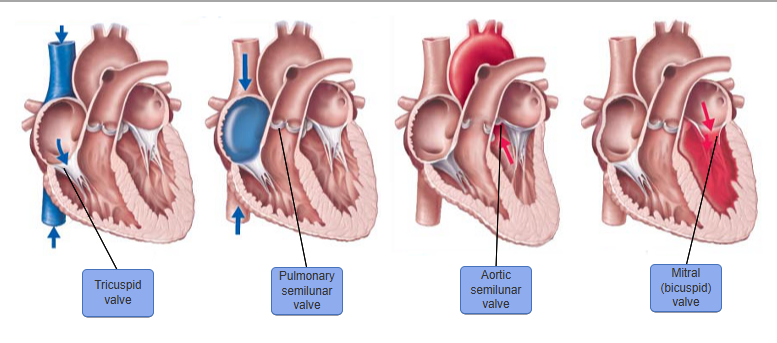
Structure that’s located anatomically btwn aorta & left ventricle is the
aortic semilunar valve
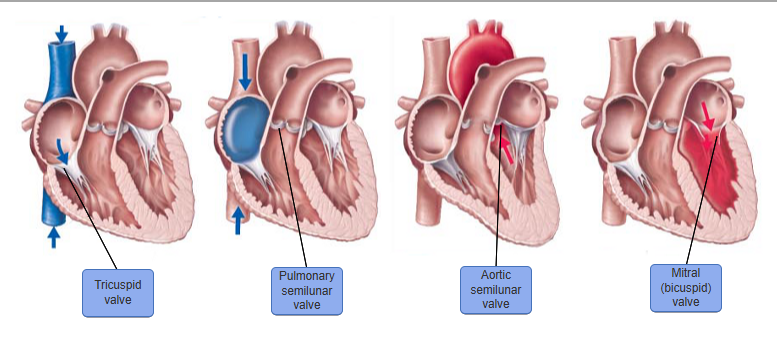
just know
just know
Select the correct partial path. This path is part of the complete blood flow pathway. You should be able to trace flow starting in any location.
Blood moves from the pulmonary artery into the left atrium. From there, it passes through the mitral valve into the left ventricle. |
Blood moves from the aorta, through smaller systemic arteries, and into systemic capillaries. From there it moves through systemic veins, into the right atrium, and through the tricuspid valve. |
Blood from the systemic veins returns to the heart through the left atrium. Blood then passes through the mitral valve. |
Blood moves from the pulmonary trunk, through the pulmonary arteries, and into the pulmonary capillaries. From there it moves through the pulmonary veins into the right atrium. |
Blood moves from the aorta, through smaller systemic arteries, and into systemic capillaries. From there it moves through systemic veins, into the right atrium, and through the tricuspid valve.
Which of the following descriptions does not describe atrioventricular (AV) valves?
formed from pocket-like cusps |
flap-like |
open based on pressure changes in the atria versus the ventricles |
anchored inferiorly by specialized connective tissue |
formed from pocket-like cusps |
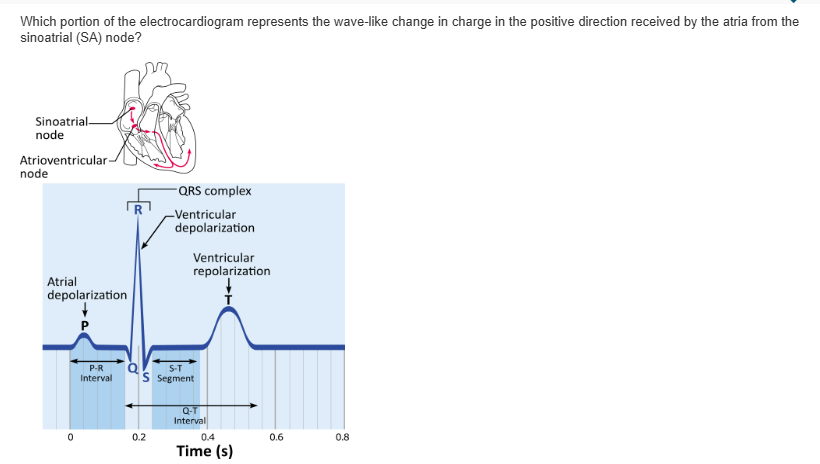
S-T segment |
QRS complex |
T wave |
P wave |
P wave |
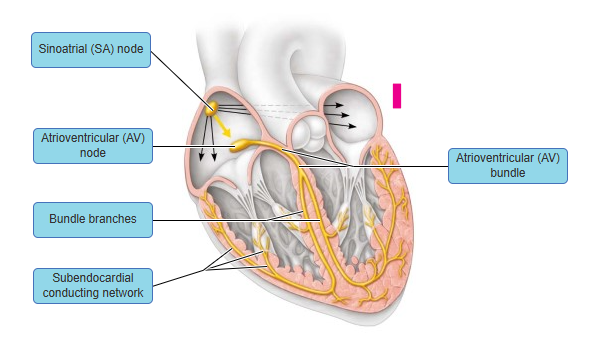
just know
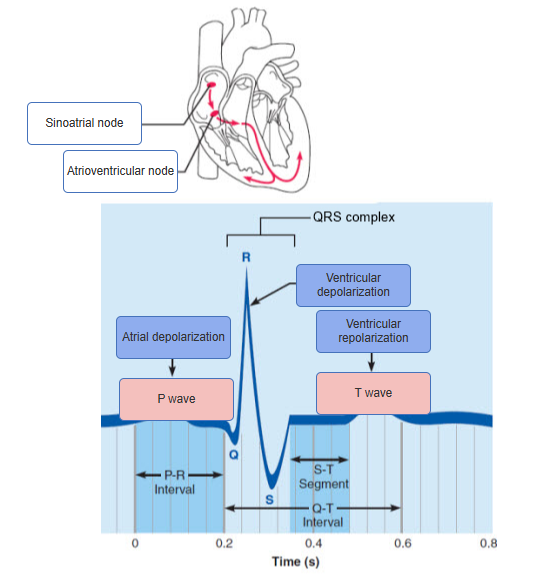
just know
Which of these is a condition marked by premature ventricular contraction?
extrasystole |
heart block |
arrhythmia |
fibrillation |
extrasystole |
The P wave on an electrocardiogram represents __________.
ventricular repolarization |
atrial depolarization |
ventricular depolarization |
atrial repolarization |
atrial depolarization |
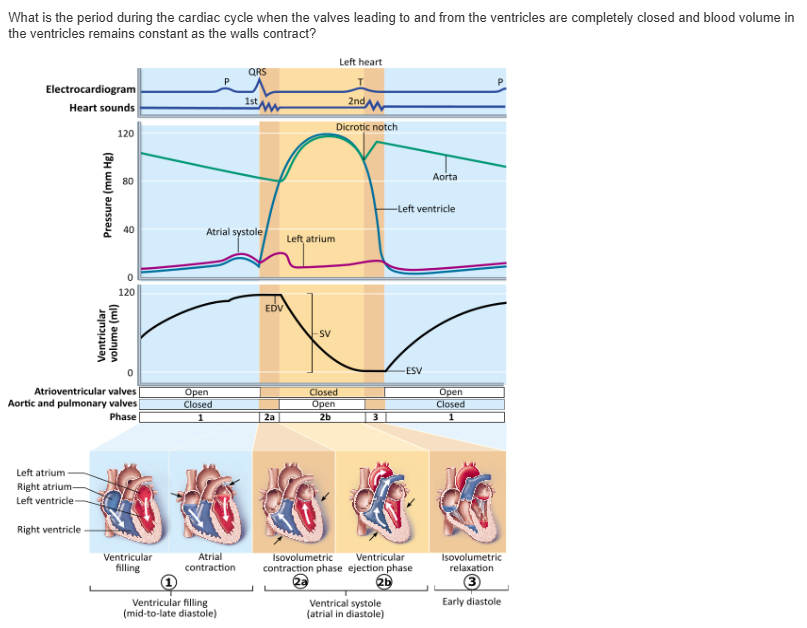
ventricular ejection |
isovolumetric relaxation phase |
ventricular filling |
isovolumetric contraction phase |
isovolumetric contraction phase |
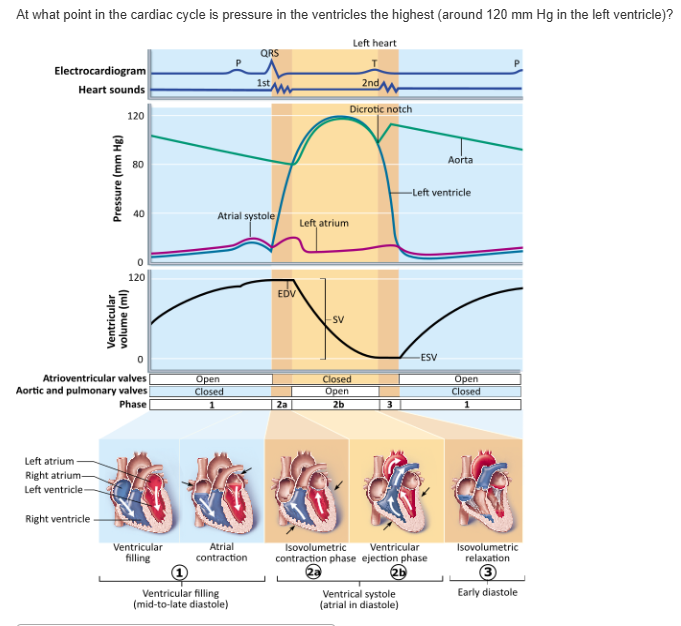
ventricular filling |
ventricular systole |
mid-to-late diastole (atrial contraction) |
early diastole (isovolumetric relaxation) |
ventricular systole
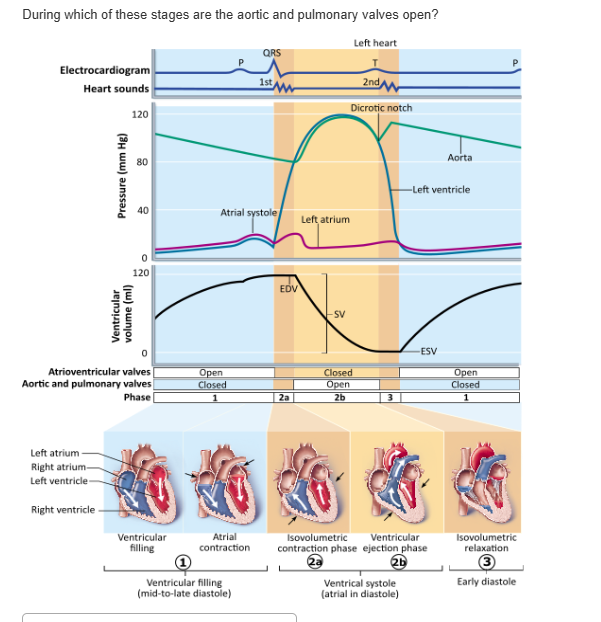
phase 1 |
phase 2a |
phase 2b |
phase 3 |
phase 2b |
Normal heart sounds are caused by which of the following events?
closure of the heart valves |
excitation of the sinoatrial (SA) node |
friction of blood against the chamber walls |
opening of the heart valves |
closure of the heart valves |
Isovolumetric relaxation and ventricular filling (two phases of the cardiac cycle) take place during __________.
ventricular diastole |
ventricular systole |
ventricular diastole |