hybridisation and electronic effects
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what is hybridisation
the mixing of atomic orbitals in order to change their energies
explain sp3 hybridisation with a diagram. what type of bonds are formed?
in order for C to form 4 single bonds, each valence electron has ¼ s orbital character and ¾ p-orbital character. without it, carbon would have only 2 unpaired electrons but hybridisation gives it 4 to make 4 bonds.
sigma bonds formed.
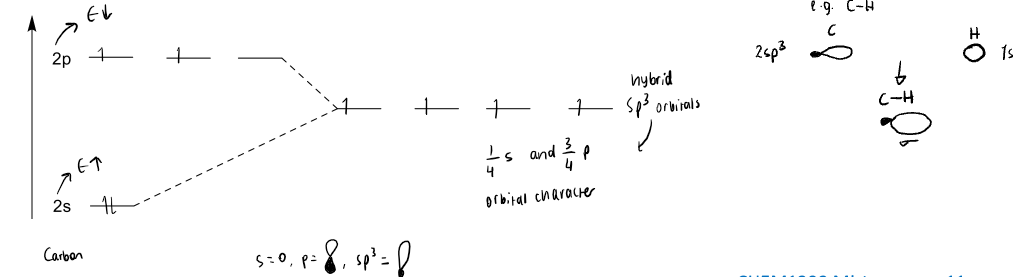
explain sp2 hybridisation with a diagram. what types of bonds are formed?
the s orbital and 2 of the p orbtials become hybridised to have 1/3 s orbital and 2/3 p orbital character. the 3rd p orbital stays at its original energy. this allows for 2 sigma bonds and 1 pi bond (from the p orbital that doesnt hybridise which overlaps with the same p orbital of another atom).
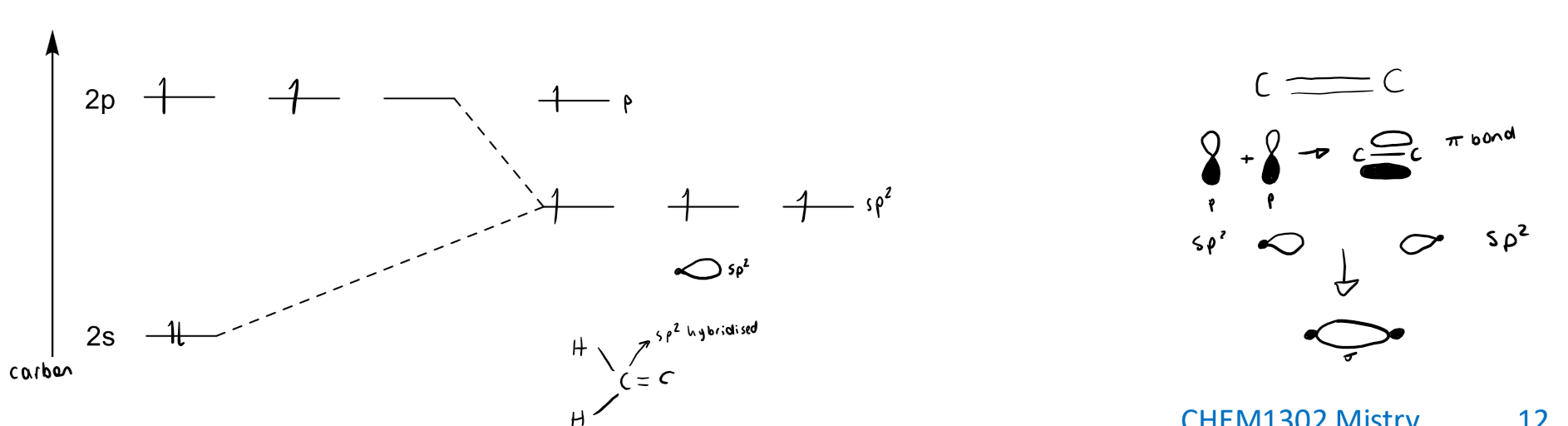
explain sp hybridisation with a diagram. what types of bonds are formed.
the s orbital and one p orbital hybridise to have half s and p character each and allow 2 sigma bonds to form. the remaining p orbtials allow 2 pi bonds to be formed
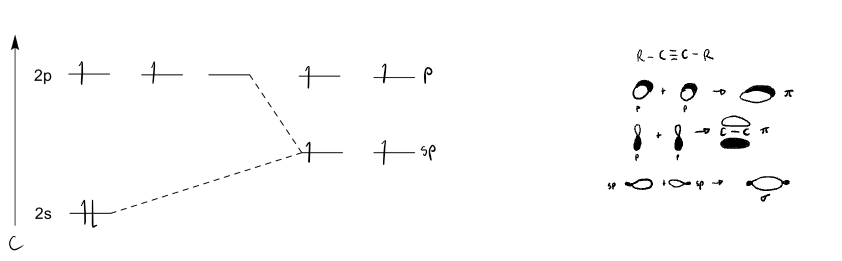
what type of bonds do hybridised orbitals form
sigma
what are inductive effects
the way in which electronegative atoms polarise electron density in the sigma bond framework of a molecule
what are the 2 types of inductive effects and with what sort of atoms do they occur
-I = electron-withdrawing effects - the atom is more electronegative than carbon
+I = electron-donating effects - the atom is less electronegative than carbon

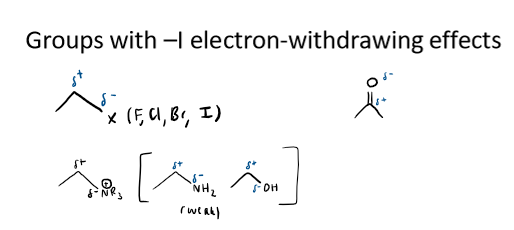
examples of -I groups
halogens, X (F, Cl, Br, I)
C=O
NR3, (weakly) NH2 and OH
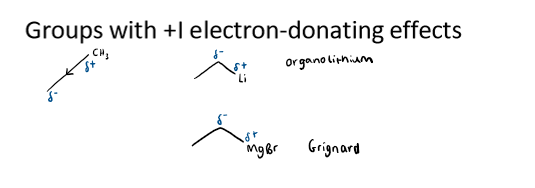
examples of +I groups
CH3
organolithium
Grignard (MgBr)
what are carbocations
organic intermediates with a positive charge
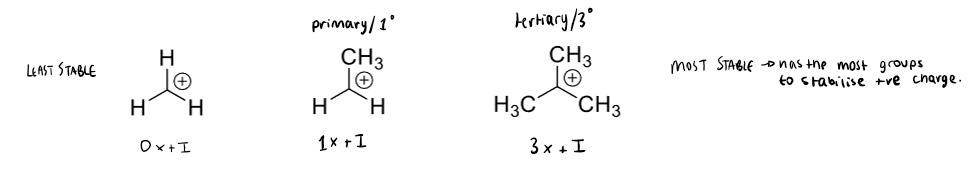
how are carbocations stabilised
having more +I groups
hyperconjugation
how do +I groups stabilise carbocations
eg C-H bonds are slightly polar with the C having the partial negative charge. this effect can add up and result in the carbon atoms bonded to the carbocation donating electron density to it and stabilising it.
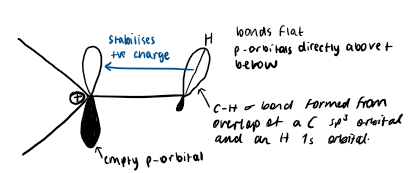
how does hyperconjugation stabilise carbocations
hyperconjugation is the donation of electrons from nearby C-H or C-C σ bonds to the empty unhybridized p-orbital of the carbocation
the carbocation is planar, the p-orbital is perpendicular to it. when a C-H bond is adjacent to a carbocation, it orientates itself to be parallel with the empty p-orbital.
the carbocation is stabilised as it now has greater electron density and the positive charge is delocalised onto other carbon atoms as well. there is greater stabilisation the more adjacent C-H/C-C σ bonds there are to align with the empty p-orbital
what is conjugation
π-electrons on adjacent bonds can delocalise their electrons across the π system.
why are conjugated systems flat
orbital overlap is most effective when the p-orbitals are parallel
what are nodes
how are these represented by orbital diagrams
nodes are regions where electron probability density is zero
in orbital diagrams this is shown by a crossing point where the wave function changes sign, ie the orientation of the orbital flips
draw the orbitals including nodes, HOMO and LUMO for butadiene

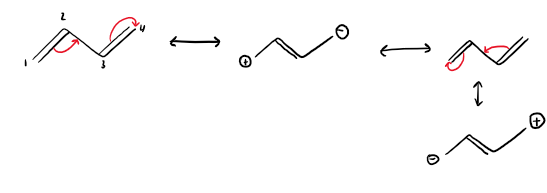
draw resonance forms of butadiene
effect of increasing number of double bonds on conjugation (think orbitals)
HOMO-LUMO gap gets smaller
as conjugated systems absorb light when electrons jump from HOMO to LUMO, changing this energy gap will alter the frequency absorbed
highly conjugated systems absorb light in the visible region
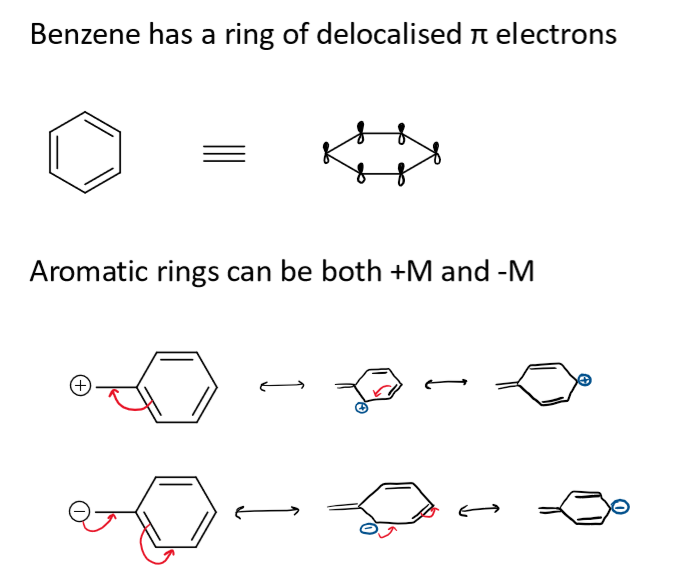
what are mesomeric effects
the movement of electron density within the π system of a molecule by resonance conjugation
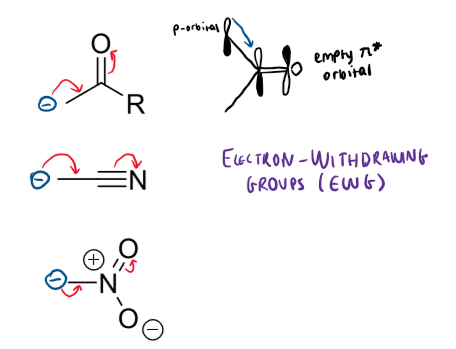
-M mesomeric effect meaning and groups
electron withdrawing groups (EWG)
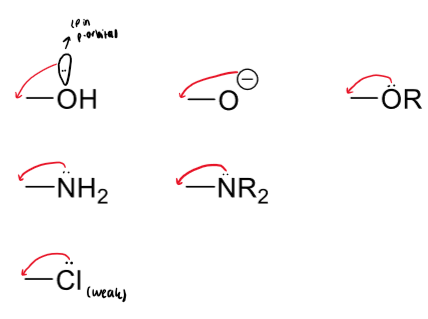
+M mesomeric effect meaning and groups
electron donating groups (EDG)
these are forming double bonds with the atom the electrons are being donated to
mesomeric effects in aromatic rings
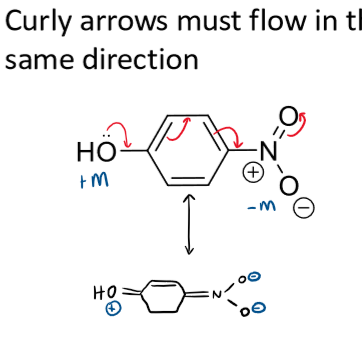
rule for drawing resonance in aromatic rings
mesomeric effects of carbonyl groups
type of effect
orbitals?
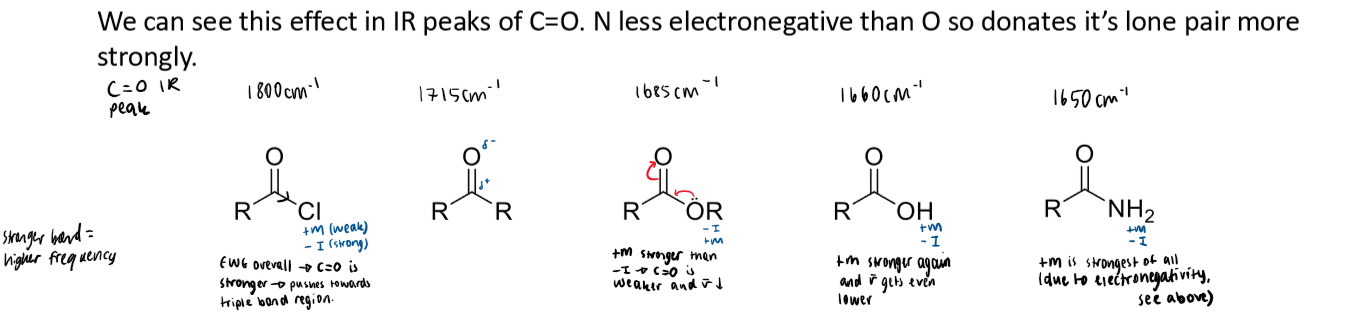
how is this observed with 5 different C=O groups + explain the differences
-M groups
the π* orbital of the C=O can overlap with lone pairs in p-orbitals of heteroatoms
this is observed in the IR peaks of C=O
N is less electronegative than O so donates its lone pair more strongly