EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING THEORY BY KOLB
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Experiential Learning Theory
States that people learn best through experience—by doing, reflecting, thinking, and applying
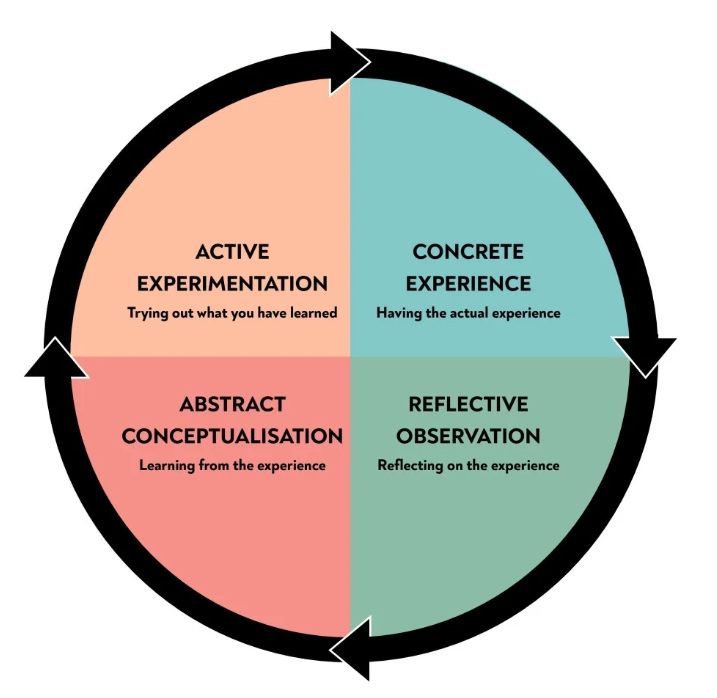
Concrete experience
Reflective observation
Abstract conceptualization
Active experimentation
4-Stage Learning Cycle
Concrete experience
4-Stage Learning Cycle
The learner encounters a concrete experience
This might be a new experience or situation, or a reinterpretation of existing experience in the light of new concepts.
Reflective Observation
4-Stage Learning Cycle
the learner reflects on the new experience in the light of their existing knowledge
Abstract Conceptualization
4-Stage Learning Cycle
reflection gives rise to a new idea, or a modification of an existing abstract concept (the person has learned from their experience)
Active Experimentation
4-Stage Learning Cycle
the newly created or modified concepts give rise to experimentation
the learner applies their idea(s) to the world around them to see what happens
T
(T/F) Learning occurs when an individual passes through all stages
He or she experiences a new event, leading to reflection and interpretation of that event, forming some conclusion, assumption, or generalization from this event, and then testing this conclusion or assumption by applying it in the real world.
Summary of the cycle
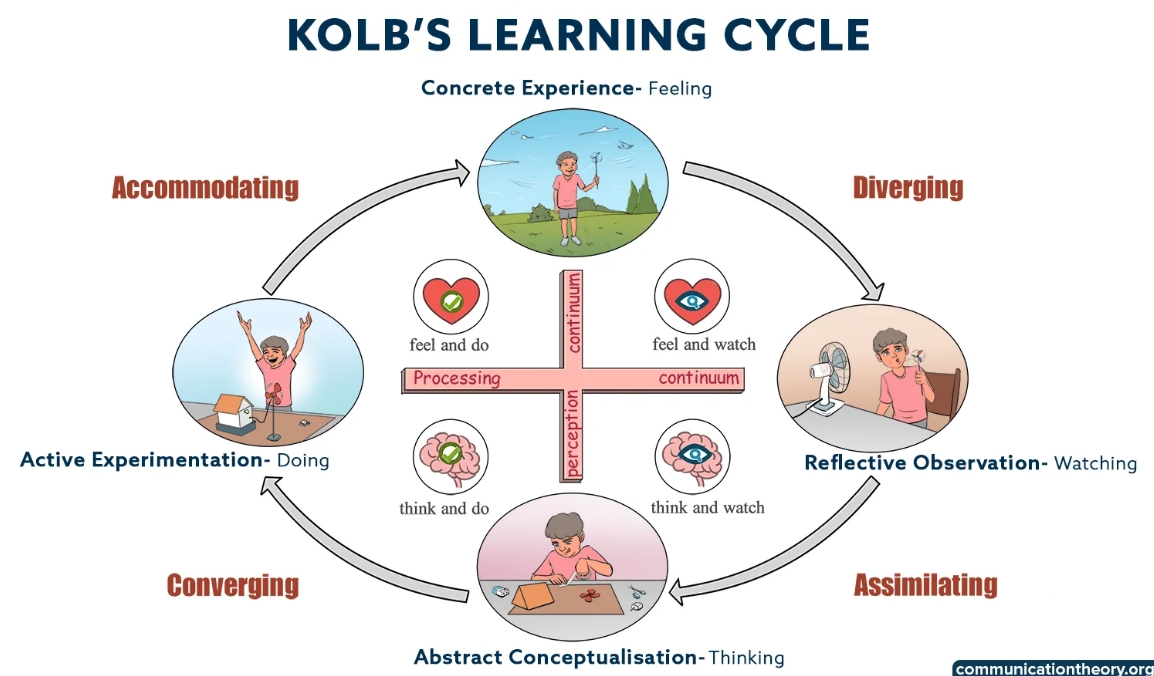
4 Basic learning styles
Diverging
Basic Learning Styles
Concrete Experience (feel) + Reflective Observation (watch)
includes observing and reflecting on a situation before taking any action
this style included generating multiple ideas, and they tend to like knowing about different cultures and traditions and are open to different perspectives
Prefer to work in groups, listening w/ an open mind, and receiving personalized feedback
Assimilating
Basic Learning Styles
Reflective Observation (watch) + Abstract Conceptualization (think)
includes using a logical and analytical approach to solve problems or reach conclusions
prefer to use theories and logic rather than practicality to understand concepts
Prefer reading theories or research papers, lectures, and exploring analytical models
Ex: solving sudoku or puzzles that require logical thinking and reasoning
Converging
Basic Learning Styles
Abstract Conceptualization (think) + Active Experimentation (do)
includes solving issues or problems by applying learnt knowledge or skills
Prefer to experiment w/ new ideas, simulations, and lab experiments
Ex: using previous knowledge about addition and subtraction to solve multiplication and division problems
Accommodating
Basic Learning Styles
Active Experimentation (doing) + Concrete Experience (feel)
involves using practicality to solve problems and reach conclusions
enjoy new challenges and tasks and often use intuition to come to conclusions.
Prefers to do field work, and test out different approaches to completing a project
Ex: using ‘guts’ to come to conclusions about another person’s behavior