Exam 2 Review
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms

In Chapter 7 Motor output variability who is the person in the slide
Carl Lewis
What is motor output variability
The Unintentional variations in the output of motor contractions
What are 2 dimensions of motor output variability
Unsteadiness
Inconsistency
What are variables to unsteadiness
Trajectory Variability
Tremor
What are variables to inconsistency
Endpoint Variability
Trial to Traal Variability
What is a functional consequence of unsteadiness
Tremors
Explain Inconsistency when infant age
There is significant motor inconsistency along with unpredictability
Explain inconsistency at adolescence
People are typically in health range of motor inconsistency and innaccuracy
Explain inconsistency at maturity with movement disorders
Movement disorders can play a significant role in motor inconsistency
Why do we care about factors that influence motor output variability
Practical ways to reduce Motor output variability
Mechanisms of variability
Ways to manipulate it experimentally and examine its affects on motor performance
Does motor variability increase with level of effort
Yes for Standard deviation
Is it proportional to the level of effect
No, because coefficient of variation is greater at low force levels
How does CNS plan and execute complex movement
Central command
HOw do we accomplish accurate movemnts
Sensorimotor transformations
How do we accomplish theres sensorimotor transformations
CNS determines locations of end effector and target
Computes a difference vector that specifies the amplitude and direction
CNS uses difference vector to develop motor plan
Explain Motor plan
Determines the joint torques or muscle activities that are necessary to achieve the desired joint trajectories
Depend on the dynamic properties of the arm such as the mass of the segments
How do we know that voluntary motor commands derive from sensorimotor transformations
motor equivalence
What is motor equivalence
The ability of different systems to achieve the same behavior

Who painted this painting
Peter longstaff with his feet
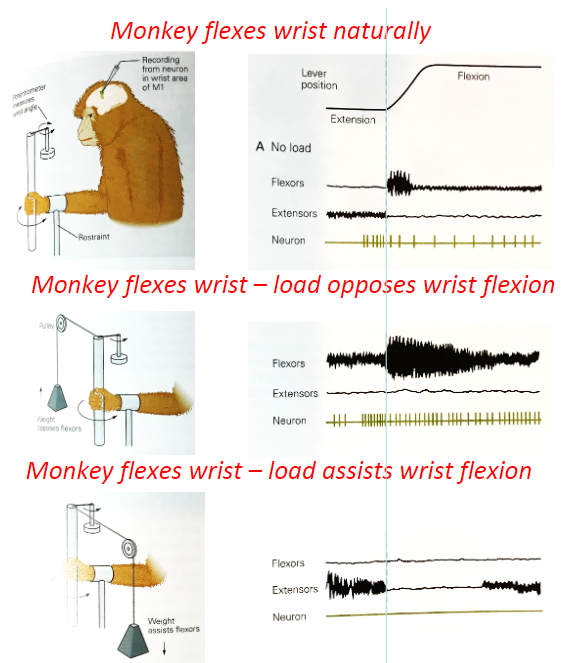
What is significant about Evarts experiement
The activity of a primary motor cortex neuron relates to the direction and level of force and muscle activity exerted during the movement than simply to the direction of wrist displacement
How does the CNS learn to repeat movements with accuracy
Efference copy
What are spinal reflexes
Fast responses that involve an afferent signal into the spinal cord and an efferent signal out to the muscle
What combo makes up for spinal reflexes
Sensory receptor, interneuron, efferent neuron
How do we know our own muscle length during movements
Muscle spindles
What does the muscle spindle comprise of
2-12 miniature skeletal fibers referred as intrafusal fibers
When does Ia neurons discharge
Intensely when stretch of the muscle is occurring, dynamic phase
When does II neurons discharge
Intensely when magnitude of stretch changes, Static phase
What happens during alpha gamma coactivation
CNS activates both the MNs during contraction concurrently
What would happen if only alpha MN activation
Slack of intrafusal fibers
Diminished or no feedback from the muscle regarding its change in length
What are monosynaptic reflexes
When a sensory neuron synapses, or a nerve impulse is transmitted, directly to a motor neuron, resulting in an automatic reflex
Explain how Hoffman reflex can be evoked
An application of electrical stimulus to a peripheral nerve and recorded the twitch or muscle activity of the muscle that innervates
When is M wave existent
At high voltage
When is H-reflex greatest
When M wave is small
Define muscle fatigue
An acute exercise–induced reduction in force and power output of the involved muscles that dictate performance.
What is Central Fatigue
Reduction in capacity of the central nervous system to voluntarily activate muscles
What is peripheral fatigue
Decrease in contractile strength in muscle fibers
Explain voluntary activation
Electrical stimulation at the motor nerve during a maximal contraction to examine how much extra force can be evoked
What is cortical fatigue
Disruption of processes that generate the motor output at the cortical level
Explain Spinal activation
Disruption of processes that generate motor output at the spinal level
What is muscle wisdom
Ability of the brain to adapt without us knowing it
Why would mechanical state change in spinal activation
The relaxation rate of the twitch lengthens
Degree of fusion of the twitches increases
Muscle wisdom is
The reduction in discharge rate of MUs to match the change in the mechanical state of the muscle
What is motor fatigability
Voluntary activation
contractile funciton
What is considered perceptual fatigability
Excitement
Apathy
Depression
Which task reaches task failure first, force or position.
Position
Why does position task reach failure first
More rapid recruitment of MUs, as indicated by faster increase in EMG
More frequent bursts
What does glands are part of HPA axis activation
Hypothalamus
Pituitary
Adrenal
What is the differences in younger and older adults when observing feedback
Younger adults observe visual feedback better than older adults
When does motor output variability increase
With more visual information in older adults
Is it the amplitude or the speed of visual feedback that increases force output variability in older adults
Increased speed but not amplitude of visual feedback increases force variability in older adults
Explain Motor unit Reorganiation
Large MNs die
Sprouting occurs
Small MNs innervate more muscle fibers
What are functional implications of the increase in motor output variability for older adults
Endpoint accuracy decreases
Motor learning is inhibited
Impairs reactive driving
Slows reaction time
What should rehabilitation innervations focus on in older adults
Reducing motor output variability
What are hypokinetic disorders
Slowness of movement
What are hyperkinetic movements
Excessive involuntary movement
What is essential tremor
involuntary rhythmic sinusoidal oscillations (4-8 Hz; shaking movements) of one or more parts of the body.
What is Deep brain stimulation
involves implanting electrodes within the thalamus. The electrodes produce electrical impulses that affect brain activity to treat certain medical conditions.
How does health aging affect motor variability
Older adults are less steady at very low forces. Older adults are more variable in repeating the same voluntary command.
Does motor variability vary with contraction type
Yes, When eccentric contractions are less steady and more variable when repeating the same voluntary command.
Predictability of the motor command is
Safety
How do we know about our own muscle force during movements
Tendon organ (Ib afferent)
When do tendon organs get excited
By a pinch of collagen
Increase GTO leads to…
excitation of the Ib inhibitory interneuron