Burn Injury Skin and Occupational Therapy: Anatomy, Assessment, and Interventions
1/213
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
214 Terms
What is the largest organ of the body?
The skin
What protein forms hair, nails, and callused skin?
Keratin
What type of skin covers the palms and soles?
Glabrous (hairless) skin
Why are deep 2nd or 3rd degree burns painless?
The nerve endings are burned off
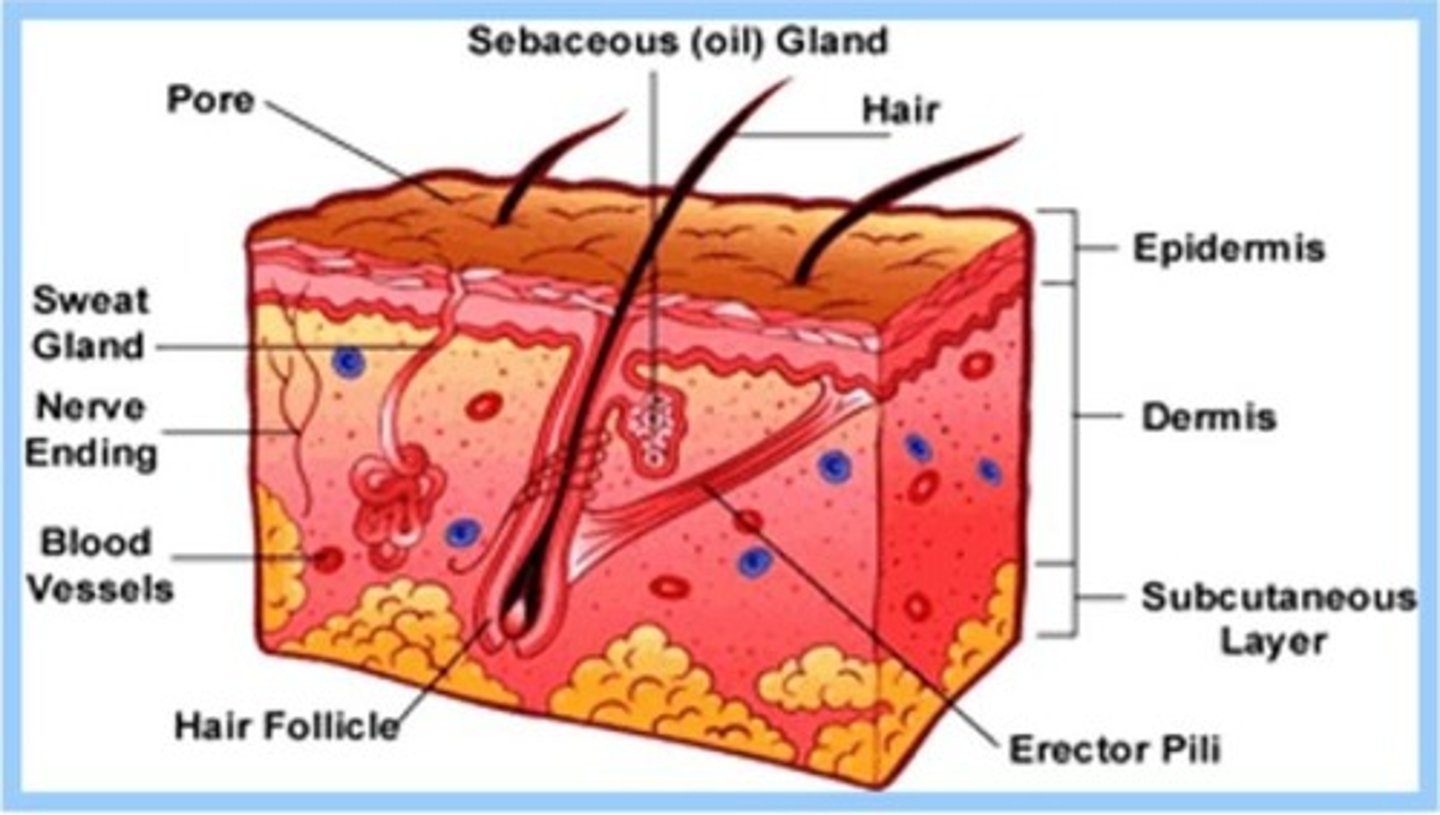
What are the two primary layers of the skin?
The dermis and epidermis
What is contained within the dermis layer?
Fibrous connective tissue, capillaries, lymphatics, nerve endings, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands
What is the outermost layer of the epidermis called?
Stratum corneum
What happens in the stratum granulosum of the epidermis?
Cells flatten, lose nuclei, and become nonviable and keratinized
What is the function of the skin?
To serve as a barrier against UV rays, chemicals, bacteria, and to regulate temperature
What is a major consequence of burn injuries on skin function?
Destruction of the protective barrier, leading to heat and fluid loss
What psychological impact can burn injuries have?
They can affect body image, personal identity, and social interaction
How is burn severity determined?
By mechanism, depth, extent, and affected areas
What does %TBSA stand for?
Percentage of Total Body Surface Area
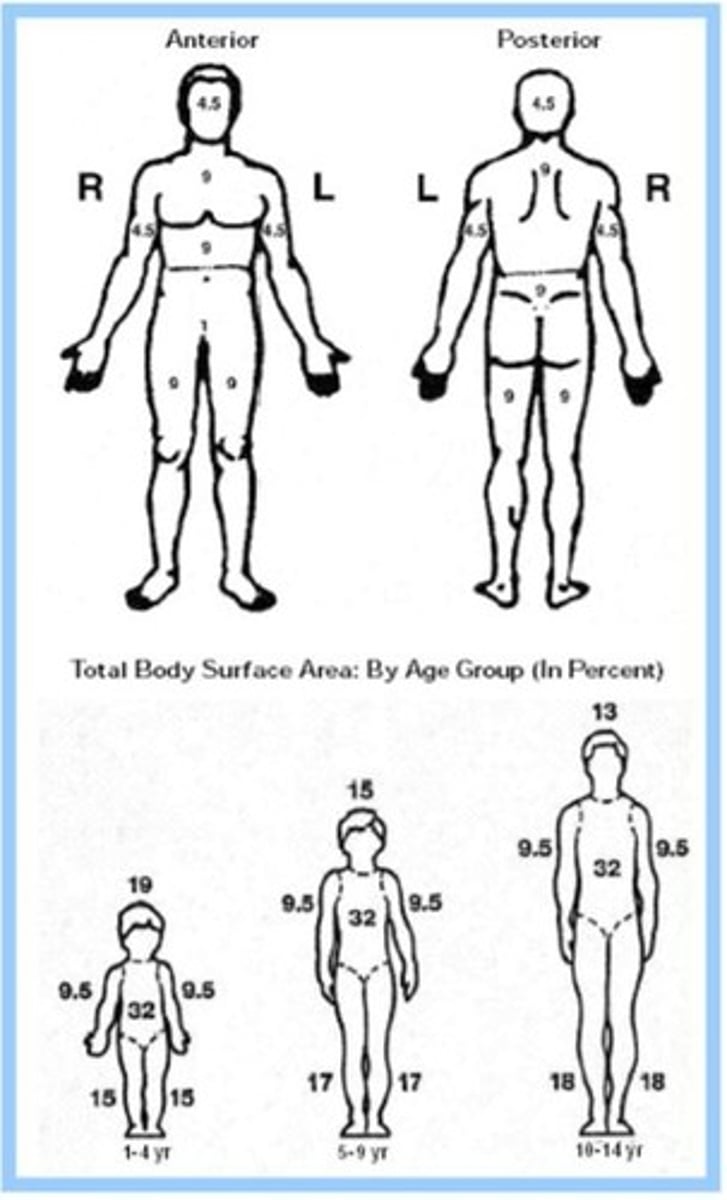
What are the two common methods for estimating %TBSA?
Rule of Nines and Lund & Browder Chart
What is the Rule of Nines used for?
To estimate the percentage of body burned for 2nd degree burns or higher
What factors determine the severity of a burn injury?
Size, depth, location, age, medical history, functional ability, and pain level
What are the four phases of wound healing?
Hemostasis, Inflammatory Phase, Proliferation Phase, Maturation/Remodeling Phase
What occurs during the Hemostasis Phase?
Vasoconstriction, platelet aggregation, and clotting factor release to stop bleeding
What characterizes the Inflammatory Phase?
Swelling, pain, redness, and a vascular and cellular response to attack bacteria
What happens during the Proliferation Phase?
Revascularization, reepithelialization, and wound contraction occur
What is the purpose of compression garments during the Maturation Phase?
To prevent hypertrophic scarring and keloids
What are hypertrophic scars?
Thick, rigid, red scars that develop 6-8 weeks after closure
What is the significance of the stratum germinativum?
It forms keratinocytes
What can happen if the skin cannot regulate temperature after a burn?
The body can go into shock
What is the role of occupational therapy in burn recovery?
To support individualized care and address functional impacts of burns
What is the impact of inhalation injuries on burn severity?
They increase severity and mortality risk due to damaged lungs
What is the typical duration for scar maturation?
6 months to 2+ years
What is a worst-case scenario for hypertrophic scarring?
It may require surgery to release contractions.
What are keloid scars?
Scars that extend beyond the original wound and may take years to mature, impacting function.
What are some occupational therapy (OT) interventions for minimizing contractures?
Positioning, stretching, splinting, and compression.
How do scars influence psychological and social aspects of a patient's life?
They can affect self-image, identity, and social reintegration, leading to isolation due to appearance-related anxiety.
What role does OT play in the psychological impact of scarring?
OT provides coping strategies and encourages reengagement in daily and social roles.
What is crucial for recovery in burn patients?
Education on skin care, range of motion (ROM) exercises, moisturization, and sun protection.
What is the focus of initial medical management in the emergent phase of burn treatment?
Life-saving interventions and preventing complications.
What are key priorities in the emergent phase of burn management?
Fluid resuscitation, respiratory support, wound care, infection control, and psychological support.
What causes fluid leakage and edema in burn injuries?
Increased vascular permeability due to the burn injury.
What is the Parkland formula used for?
To guide fluid replacement based on the percentage of total body surface area (TBSA) burned.
What is a risk associated with circumferential burns?
Compartment syndrome, which may require escharotomy or fasciotomy to restore circulation.
What is a common secondary diagnosis related to burns?
Smoke inhalation.
What treatments are used for respiratory management in burn patients?
Intubation, ventilatory support, and respiratory therapy.
What is the purpose of tracheostomy in burn patients?
To improve comfort, allow oral care, and prevent laryngeal damage during prolonged ventilation.
What is essential for optimal healing in burn wound care?
Proper resuscitation and nutrition.
What types of treatments are included in wound care for burns?
Topical antibiotics, biological, or synthetic dressings.
What is the role of antibiotic ointments in burn care?
To help with hydration and reduce scarring.
What is Mafenide acetate used for?
To prevent infection in burn wounds.
What are silver-based solutions used for in burn treatment?
To reduce infection-related morbidity and mortality.
What is the benefit of biosynthetic dressings?
They provide antimicrobial protection and support wound healing until ready for grafting.
What is the purpose of hydrotherapy in burn management?
To remove debris and old topical antibiotics, cleanse the wound, and assess ROM.
What analgesics are administered during hydrotherapy?
Analgesics and anxiolytics to manage pain and anxiety.
What is the role of occupational therapy during hydrotherapy sessions?
To assess and facilitate range of motion exercises.
What are biologic dressings used for?
To serve as temporary coverings that close wounds and promote healing.
What is the function of enzymatic wound debriders?
To break down dead tissue and promote faster wound healing.
What are the limitations of modern biosynthetic products in burn care?
They cannot fully replicate real skin function and are subject to cost and expertise factors.
How are burns classified?
By depth and percentage of total body surface area (TBSA).
What are the four classifications of burns by depth?
First-degree (superficial), Second-degree (partial-thickness), Third-degree (full-thickness), Fourth-degree (electrical).
What characterizes a first-degree burn?
Involves only the epidermis; red, painful, blanches under pressure; heals within ~1 week.
What are the clinical features of a second-degree superficial partial-thickness burn?
Destroys epidermis and superficial dermis; red, blistering, very painful; heals within ≤3 weeks.
What is the healing process for second-degree burns?
Healing occurs in 7-day increments; moisture aids quicker healing.
What are the occupational therapy actions in the shock phase for first-degree burns?
Screen, educate on skin protection, hydration, and infection signs; gentle AROM as tolerated.
What are the occupational therapy actions in the acute phase for first-degree burns?
Educate on skin care, moisturization; progress ADL independence as pain subsides.
What are the clinical features of a second-degree deep partial-thickness burn?
Involves deeper dermal layers; red/tan/white, decreased sensation; healing takes >3-5 weeks.
What are the occupational therapy actions in the shock phase for second-degree deep partial-thickness burns?
Strict infection control, positioning to prevent contractures, gentle AROM/AAROM.
What are the clinical features of a third-degree burn?
Total dermal destruction, eschar dry/leathery, insensate to pinprick; requires grafting.
What are the occupational therapy actions in the shock phase for third-degree burns?
Do not move graft areas until cleared; rigid positioning to prevent contracture.
What are the occupational therapy actions in the acute phase for third-degree burns?
Post-graft immobilization for 3-5 days; then graded ROM; intensive scar management.
What characterizes a fourth-degree burn?
Complete tissue destruction from epidermis to bone; risks include deep muscle/nerve damage.
What are the occupational therapy actions in the shock phase for fourth-degree burns?
Monitor for compartment syndromes; protect limb; assess strength and sensation.
What is the importance of psychological support in burn treatment?
Given the severity and uncertainty of extent, early psychological support is crucial.
What is the significance of positioning in burn therapy?
Proper positioning prevents contractures and promotes healing.
What are the signs of infection to educate patients about?
Increased redness, swelling, warmth, and discharge at the burn site.
What is the role of hydrotherapy in burn rehabilitation?
Facilitates wound care and therapeutic exercise without dressing restriction.
What is the purpose of pressure garment therapy?
Prevents hypertrophic scarring and aids in scar management.
What is an escharotomy?
An incision made in eschar to release pressure and improve circulation.
What is the expected duration for scars to heal after a burn?
It takes approximately 24 months for scars to heal.
What is the importance of monitoring for heterotopic ossification?
To address joint mobility limitations and obtain imaging if ROM plateaus.
What are the goals of occupational therapy in burn rehabilitation?
To restore function, prevent complications, and promote independence in ADLs.
What is the significance of moisture in burn healing?
Moisture promotes quicker healing and reduces scarring.
What are the potential complications of deep partial-thickness burns?
Increased infection risk and potential conversion to full-thickness burns.
What is the recommended action for blisters in second-degree burns?
Protect blisters; do not pop unless necessary to allow for circulation.
What is the definition of sepsis in the context of burn injuries?
Sepsis is life-threatening organ dysfunction from a dysregulated host response to infection.
What are common pathogens associated with burn wound infections?
Bacteria, fungi, parasites, and mycobacteria, especially in immunocompromised patients.
What are the symptoms of septic shock?
Ischemia, hypotension, tachycardia, tachypnea, hypothermia, low urine output, confusion, and coma.
What is the primary goal of surgical intervention for burns?
To remove nonviable tissue and restore skin integrity via grafting.
When is surgery indicated for burn injuries?
When burns require more than 1 week to heal or pose a risk of infection or scarring.
What are the three main types of biological grafts?
Xenograft (processed pigskin), Allograft (human cadaver skin), and Autograft (patient's own skin).
What is the purpose of vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) therapy?
To use negative pressure wound therapy to remove fluid, decrease bacterial colonization, and stimulate granulation tissue.
What nutritional needs are essential for burn recovery?
High protein, calorie, and micronutrient intake (vitamin C, copper, selenium, zinc) due to increased metabolic needs.
What is the healing time for a 1st degree burn?
About 1 week.
What characterizes a 2nd degree superficial partial burn?
Red, blisters, painful, minimal scarring, and healing within 3 weeks.
What are the management strategies for a 3rd degree burn?
Immobilization for 3-5 days, gentle AROM once cleared, scar management, and ADL retraining.
What are the psychosocial considerations post-surgery for burn patients?
Anxiety, isolation, pain, and limited visitor access can increase emotional strain.
What is the healing time for a 2nd degree deep partial burn?
More than 3-5 weeks.
What is the role of occupational therapy post-surgery for burn patients?
To prevent contractures, maintain ROM, provide emotional support, and assist with ADL retraining.
What are the signs of infection in burn wounds?
Increased pain, redness, swelling, and discharge from the wound.
What is the importance of early compression garments for burn patients?
To prevent hypertrophic scarring.
What is the typical position for splinting a 3rd degree burn?
Strict positioning to prevent contractures, including neck extension and shoulder abduction.
What is the significance of dynamic hand orthoses for burn patients?
To prevent heterotopic ossification and support functional recovery.
What is the healing time for a 4th degree burn?
Healing time varies significantly due to extensive damage to muscle, nerve, and vascular structures.
What is the role of emotional support in burn recovery?
To help patients cope with anxiety and promote resilience and emotional well-being.
What is the purpose of hydrotherapy in burn rehabilitation?
To assist with wound care and promote mobility in affected areas.