biology homeostasis
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
what is homeostasis
the maintenance of a constant internal environment for optimum conditions for the cell’s activities
what does homeostasis control
temperature, blood sugar levels and water levels
what is a stimulus
change in an environment
what is a receptor
cell that detects a stimulus
what does a coordination centre do
receive and process information from receptors
what is an effector
muscle or gland that brings about a response
nervous system order
stimulus → receptor → sensory → relay → motor → effector → response
what are the three neurons in the nervous system called
sensory relay motor (science really matters)
what is the role of the sensory neuron
carries electrical impulses to the CNS
what is the role of the relay neuron
located in CNS and receives impulse
what is the role of the motor neuron
carries impulse to effector
what is the central nervous system made of
brain and spinal cord
what is the peripheral nervous system made of
nerves
label neuron
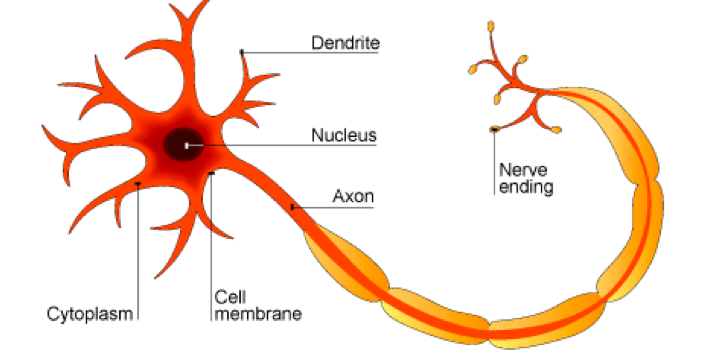
what is the axon surrounded by and why
myelin sheath to speed up nerve impulses
reaction time required practical
person A holds out their hand with gap between thumb and first finger
person B holds ruler at 0 at top of person A’s thumb
person B drops the ruler without telling person A and they must catch it
the number on the ruler at person A’s thumb is recorded and this is repeated 10 times
swap places and repeat steps 1-4
use conversion table to work out reaction time
brain diagram
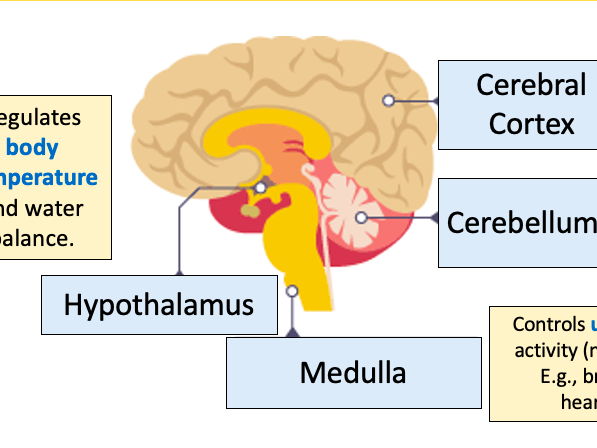
role of medulla
unconscious activities such as controlling heartbeat, breathing and digestion
role of cerebral cortex
consciousness, intelligence memory and language
role of cerebellum
coordinates how muscles work
how do we study the brain
studying patients with brain damage, electronically stimulating brain and MRI scans
MRI evaluation
provides brain map, non invasive painless observe live patients but may be unethical to experiment on healthy people
electrical stimulation evaluation
stimulate different parts of brain by using electricity- remove top of skull, communicate with patients painless, unethical invasive may be at risk of infection
problems with the brain
very complex and delicate, easily damaged and destroyed, difficult to investigate brain disorders, easy to cause unintended damage
eye diagram
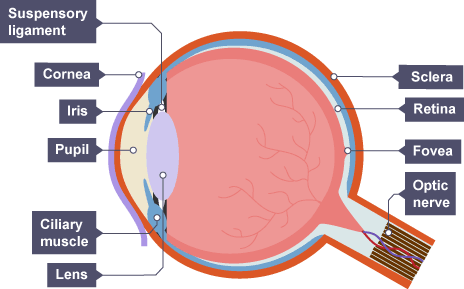
function of retina
made up of light, sensitive receptor cells, rod- black and white and cone- colour
function of optic nerve
carries impulses from retina to brain
function of sclera
tough outer layer which protects and holds eye in place
function of cornea
reflects light- bends as it enters
function of iris
has muscles that control size of pupil and regulate light reaching retina
function of lens
focuses light rays on retina
how does iris adapt to bright light
circular muscles contract and radial muscles relax causing pupil to constrict
what is accommodation
ability to change the shape of the lens to focus near or distant objects
accommodation of distant objects
ciliary muscles relax, suspensory ligaments tighten/contract, lens becomes thinner, light rays are refracted less, image focused on retina
accommodation of near objects
ciliary muscles tighten/contract, suspensory ligaments relax, lens becomes thicker, light rays are refracted more, image focused on retina
myopia evaluation
short sightedness, image is focused in front of retina because eyeball is too long- elongated, lens is too thick and curved, can be treated with concave lens glasses
hyperopia evaluation
long sightedness, image focused behind retina because eyeball is too short- lens becomes less elastic which is often age related, treated with convex lens glasses
what is reflex
fast automatic response to a stimulus
why do we need reflexes
to reduce chance of injury
synapse diagram

what is a synapse
small gap between two nerves
what does the thermoregulatory system contain
receptors sensitive to temperature change in blood and skin which send impulses to brain
how do the effectors work
antagonistically
what happens if body temperature gets too high
hair lies flat to prevent air from being trapped which is an insulator, blood capillaries get wider to allow for more blood flow near surface of skin so heat energy gets radiated and sweat glands will release sweat which will evaporate and remove heat from body
what happens if temperature gets too low
the hairs will stand up to trap air which is an insulator, the capillaries will contract so blood flow is further away from the surface of the skin so less energy is radiated and shivering occurs which is when the muscles contract to increase rate of respiration so more energy is released
what is vasoconstriction
when blood vessels become narrower
what is vasodilation
when blood vessels become wider
what is the endocrine system composed of
glands which secretes hormones into blood
what are hormones
chemical messengers which are transported through the blood to vital organs
endocrine system diagram
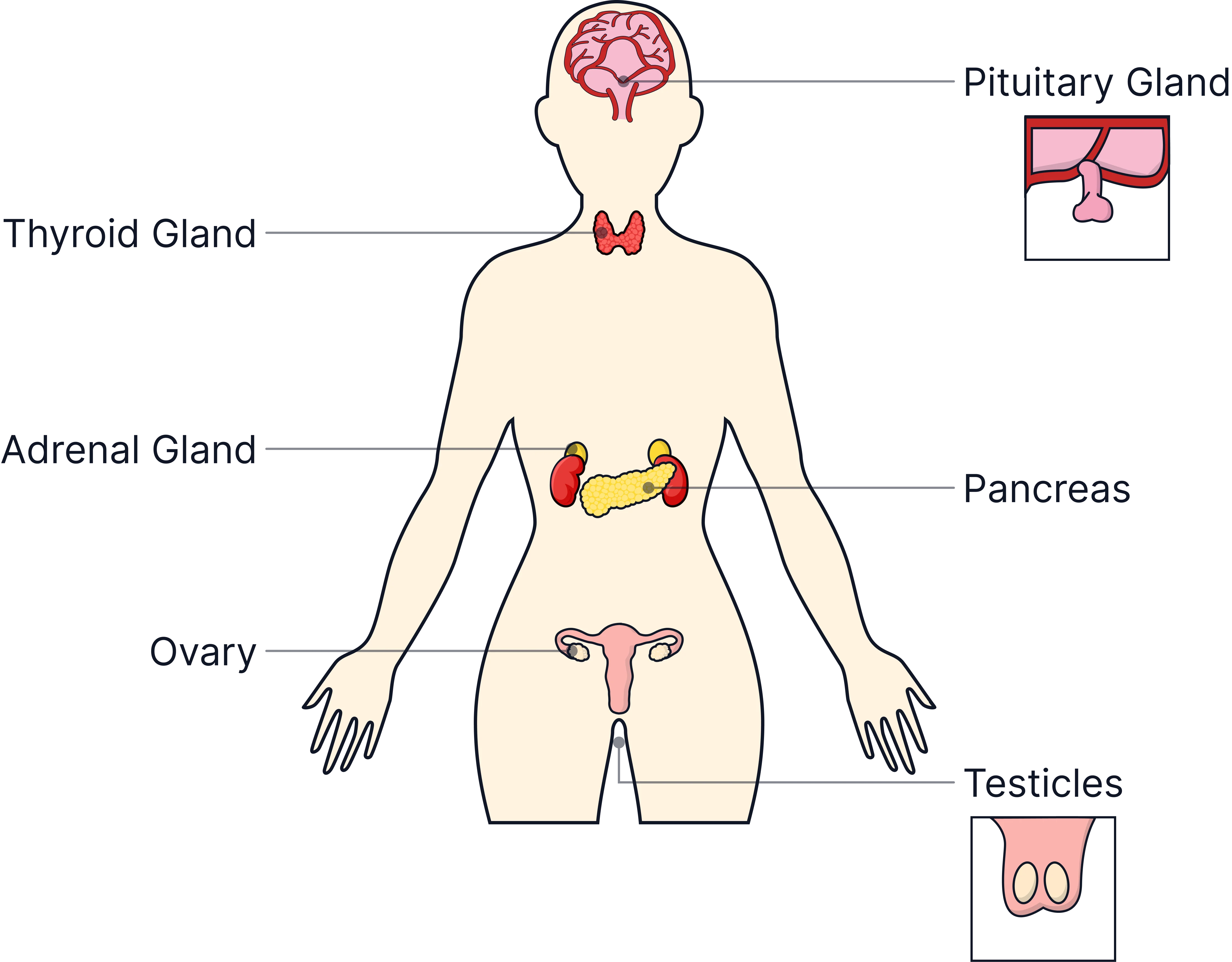
what is the role of the pituitary gland and what hormone is released
tells other glands to release hormones, releases FSH LH and ADH
what is the role of the thyroid gland and what hormone is released
regulates rate of metabolism growth and development, releases thyroxine
what is the role of the pancreas and what hormone is released
regulate blood glucose concentrations and released insulin and glucagon
what is the role of the adrenal gland and what hormone is released
increases heart rate, flight of fight response, releases adrenaline
why is there an increased heart rate due to the adrenaline hormone
more oxygen pumped around body
why is there an increased breathing rate due to the adrenaline hormone
more oxygen into blood and more carbon dioxide removed
why is there an pupil dilation due to the adrenaline hormone
more light in for sharper vision
why is it important that adrenaline doesn’t use a negative feedback loop
once the stress is over, normality is reestablished which reduces energy consumption
what is the role of the ovaries and what hormone is released
puberty and menstrual cycle, releases oestrogen
what is the role of the testes and what hormone is released
controls puberty and produces sperm, releases testosterone
what are the differences between the endocrine and nervous system
endocrine- responses are slow, messages are in form of chemical messengers and carried in bloodstream, effects last a long time
nervous- responses are fast, messages are in form of electrical impulses and carried along neurones, effects last a short time
what happens when glucose levels rise
insulin produced by the pancreas causes glucose to change to glycogen which is stored in the liver and muscles for later use
what happens when glucose levels fall
glucagon released by pancreas converts glycogen in liver back to glucose and is released into blood
one function of glucose in the body
provides energy
type 1 diabetes evaluation
effects younger people, caused by infection of pancreas/ genetics, immune system attacks pancreas, controlled with insulin pumps or injections
type 2 diabetes evaluation
effects people over 40, linked to poor diet/obesity, cells become resistant to insulin, controlled with a carbohydrate controlled diet
development of females
breasts develop, hips get wider, voice deepens slightly, ovaries start to release egg cells, menstruation starts, growth of hair under arms and pubic hair
development of males
voice breaks and deepens, testes start to produce sperm cells, sexual organs start to grow and develop, growth spurt, growth of hair under arms and pubic hair
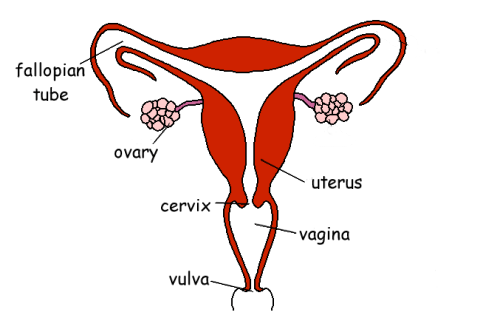
female reproductive system diagram
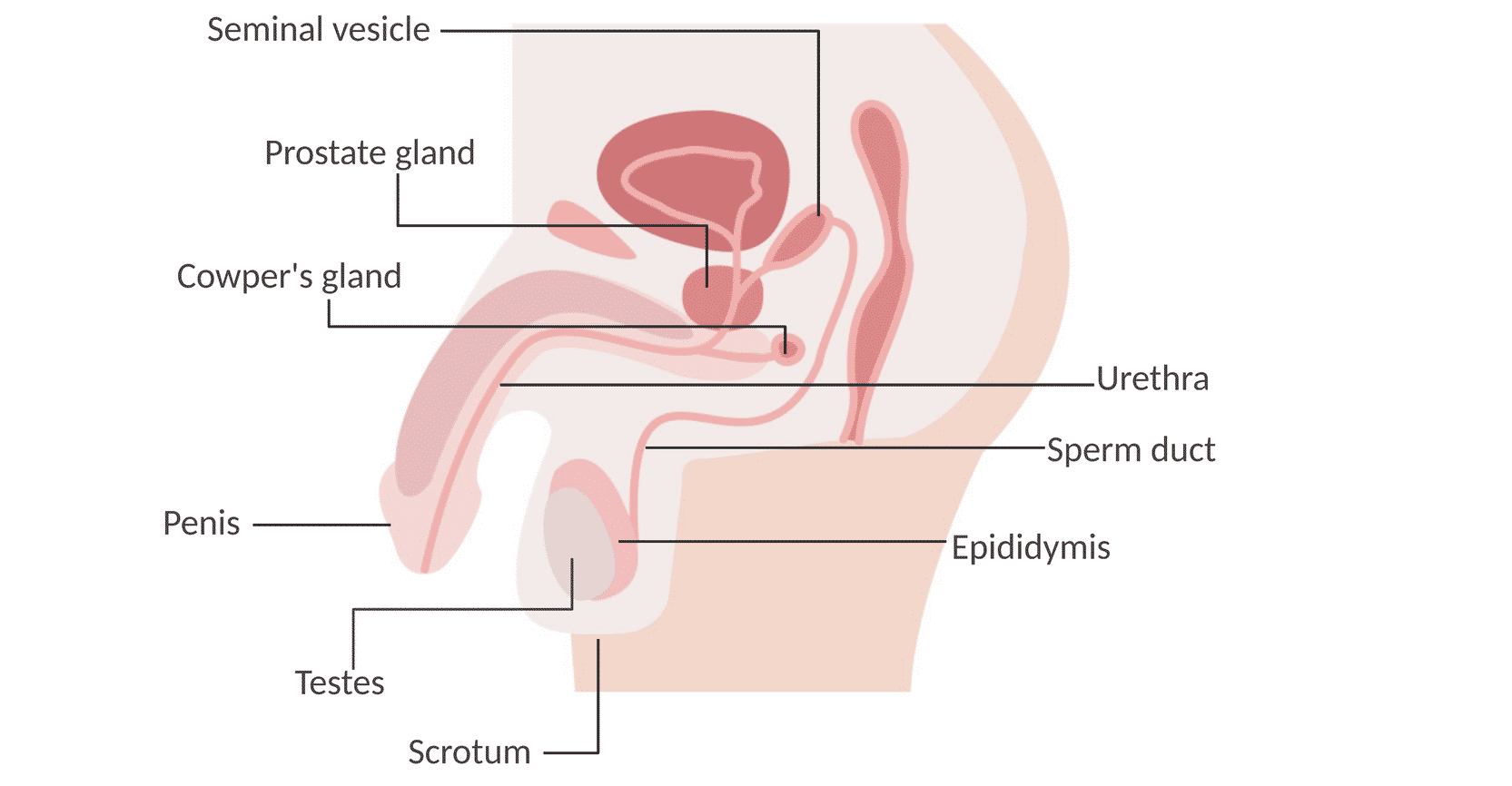
male reproductive system diagram
menstrual cycle process
day 1- lining of uterus starts to breakdown
day 4- womb begins to thicken: has lots of blood vessels
day 14 approx.- egg released from ovary (ovulation)
day 28- pregnancy will continue if fertilised egg is received or cycle will begin again if not
what does FSH do in the menstrual cycle
secreted by the pituitary gland it makes eggs mature in the ovaries and also stimulates the ovaries to produce oestrogen
what does oestrogen do in the menstrual cycle
secreted by the ovaries, stimulates the lining of the uterus to build up ready for pregnancy, slows down production of FSH and stimulates release of LH
what does LH do in the menstrual cycle
stimulates ovulation
what does progesterone do in the menstrual cycle
produced in the ovaries by the remains of the follicle after ovulation, maintains the lining of the uterus during the second half of the cycle and also inhibits the release of FSH and LH
oral contraceptives evaluation
inhibits FSH production to stop eggs maturing and prevent the release of an egg, very reliable easy to take, make cause side affects and affect fertility in future
injection/implant/skin patch contraceptives evaluation
slowly releases progesterone to inhibit maturation, lasts longer than pill, several side effects and doesn’t protect against STDs
barrier methods of contraception evaluation: condom and diaphragm
prevents sperm reaching egg, highly effective and has no side effects, may break and diaphragms need to be fitted by a doctor
IUD/coil contraceptive evaluation
t shaped device which gets inserted into uterus to stop fertilised eggs implanting, highly effective but doesn’t protect against STIs
abstinence contraceptive evaluation
people will not have sex around time of ovulation, no side effects, not very reliable can’t protect against STIs and can risk unexpected pregnancy
surgical methods of contraception
men get sperm ducts cut and women get fallopian tubes tied, permanent, difficult to reverse and no protection against STIs