Current & Circuits
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:47 PM on 9/1/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
Electric Current
The rate of flow of electric charge
2
New cards
Potential Difference (Voltage)
The work done per unit charge in moving a charge between two points in a circuit (the "push" driving current)
3
New cards
Resistance
The opposition to the flow of electric current
4
New cards
Material Effect on Resistance
Different materials have different resistivities
5
New cards
Length Effect on Resistance
Resistance is directly proportional to length
6
New cards
a longer wire has higher resistance
7
New cards
Cross-sectional Area Effect on Resistance
Resistance is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area
8
New cards
a thicker wire has lower resistance
9
New cards
Temperature Effect on Resistance (Metals)
In most metals
10
New cards
Ohm's Law
The current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage
11
New cards
V=IR
12
New cards
Series Circuit Current
The current is the same at all points
13
New cards
I_total = I_1 = I_2 = I_3...
14
New cards
Series Circuit Potential Difference
The total potential difference is shared between components
15
New cards
V_total = V_1 + V_2 + V_3...
the potential differenc across each component is dependant on it's resistance
16
New cards
Series Circuit Resistance
The total resistance is the sum of individual resistances
17
New cards
R_total = R_1 + R_2 + R_3...
18
New cards
Parallel Circuit Current
The total current splits between branches
19
New cards
I_total = I_1 + I_2 + I_3...
20
New cards
Parallel Circuit Potential Difference
The potential difference is the same across all components in parallel
21
New cards
V_total = V_1 = V_2 = V_3...
22
New cards
Parallel Circuit Resistance
The reciprocal of the total resistance is the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistances
23
New cards
1/R_total = 1/R_1 + 1/R_2 + 1/R_3...
and the total resistance is less than the smallest individual resistance
24
New cards
Resistor (Circuit Symbol)
A component that provides a fixed resistance
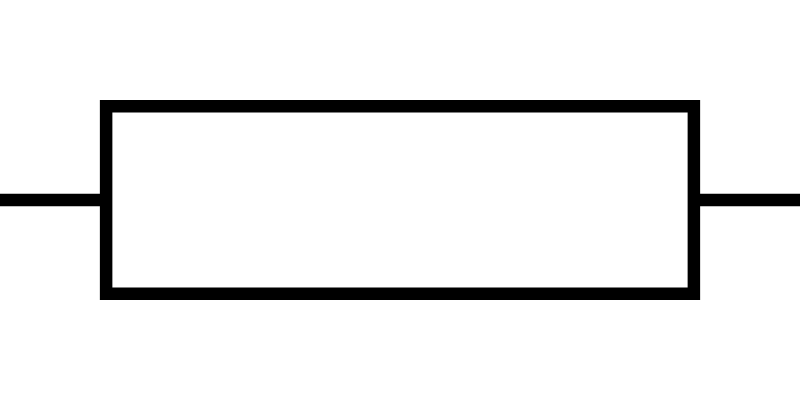
25
New cards
Filament Lamp (Circuit Symbol)
Provides resistance and emits light

26
New cards
its resistance increases with temperature (non-ohmic)
as current increase
27
New cards
Diode (Circuit Symbol)
Allows current to flow in practically only one direction (very high resistance in reverse)
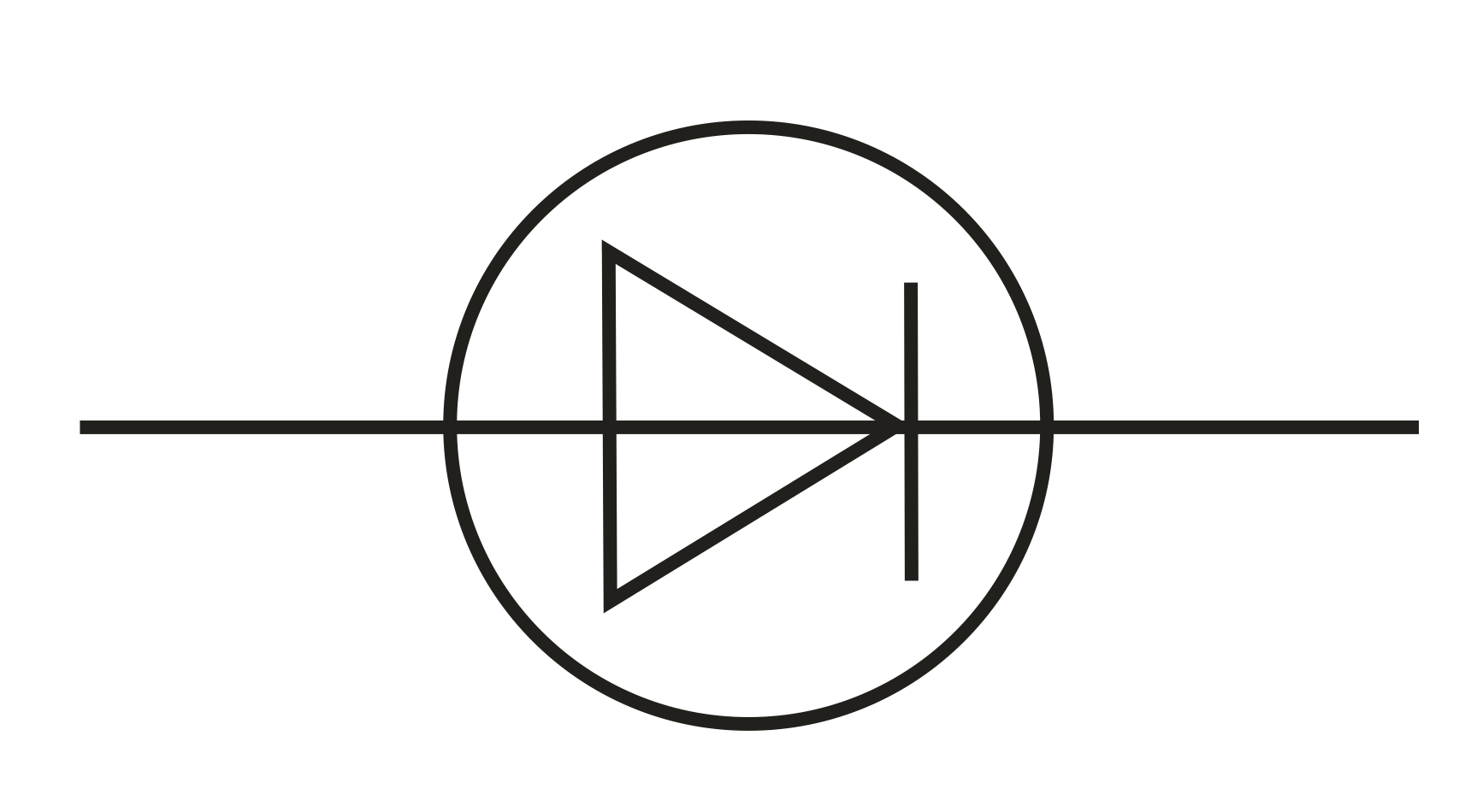
28
New cards
LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) (Circuit Symbol)
A resistor whose resistance decreases as light intensity increases
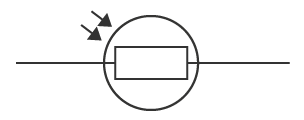
29
New cards
Thermistor (Circuit Symbol)
A resistor whose resistance decreases as temperature increases
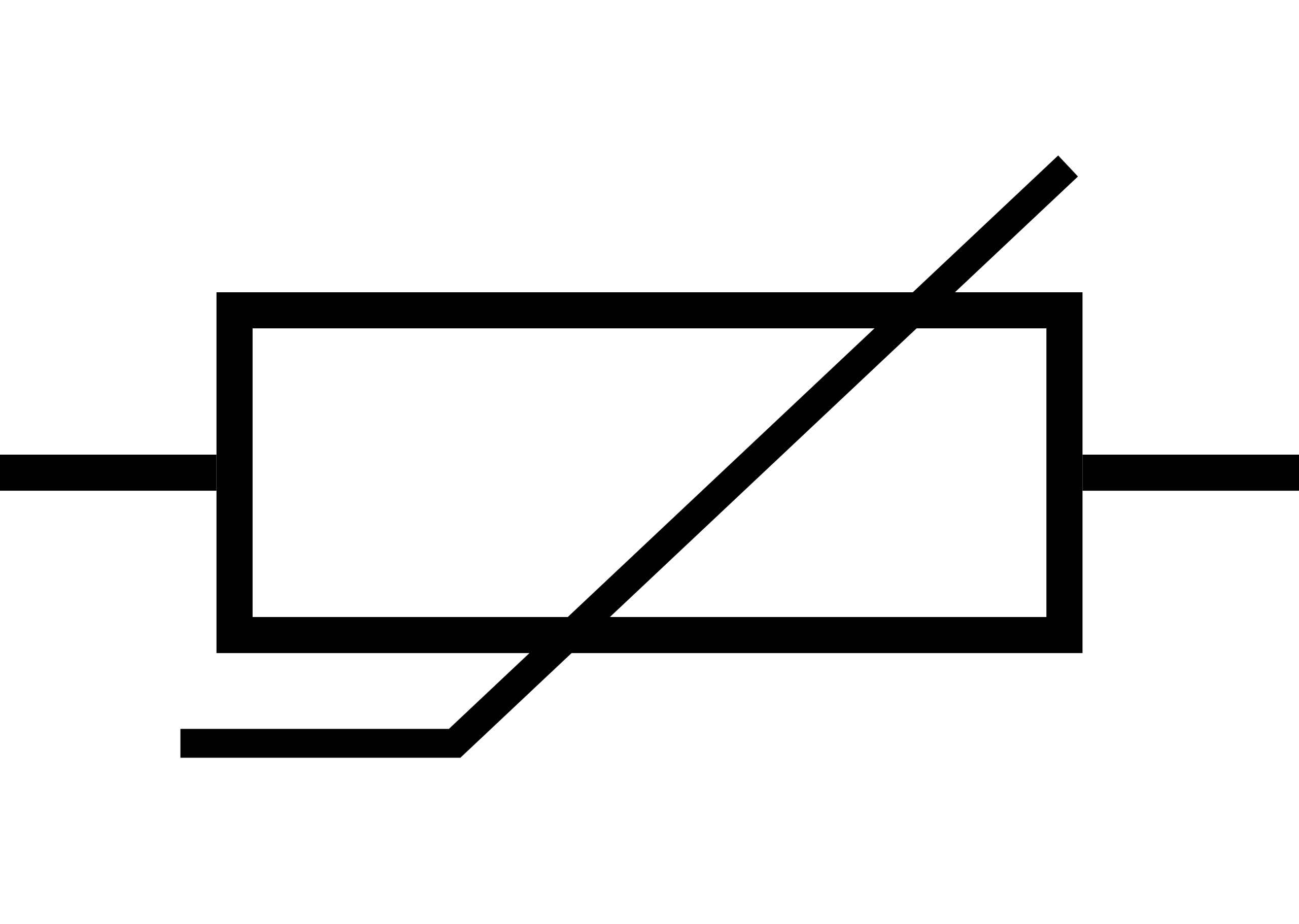
30
New cards
Energy Transferred Equation
E = IVt (Energy = Current x Voltage x Time)
31
New cards
Units for Energy Transferred
Joules (J) for energy
32
New cards
Power Definition
The rate at which energy is transferred or the rate at which work is done
33
New cards
Power Equation 1
P = E/t (Power = Energy / Time)
34
New cards
Power Equation 2
P = IV (Power = Current x Voltage)
35
New cards
Power Equation 3
P = I²R (Power = Current squared x Resistance)
36
New cards
Power Equation 4
P= V^2/R (Power=Voltage Squared / Resistance)
37
New cards
Power Unit
Watts (W)
38
New cards
AC (Alternating Current)
Current that constantly changes direction
39
New cards
Mains Electricity
AC supply (230V
40
New cards
DC (Direct Current)
Current that flows in only one direction
41
New cards
Battery/Cell Supply
DC
42
New cards
Live Wire (Color and Function)
Brown
43
New cards
carries the alternating potential difference (230V)
44
New cards
Neutral Wire (Color and Function)
Blue
45
New cards
completes the circuit
at 0V
46
New cards
Earth Wire (Color and Function)
Green and Yellow
47
New cards
safety wire
at 0V
48
New cards
Fuse Function
A safety device that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds its rating
49
New cards
Fuse Placement
Always connected in the live wire
50
New cards
Circuit Breaker Function
An automatic switch that trips (turns off) when current is too high
51
New cards
Circuit Breaker Advantages
Faster than fuses
52
New cards
Double Insulation
Appliances with plastic casings and no exposed metal parts
53
New cards
I-V graph
Shows the relationship between the current and the potential difference
54
New cards
Linear component
straight line on a I-V graph
55
New cards
Non-linear Component
Curved line on a I-V Graph
56
New cards
Charge calculation
charge = current x time
57
New cards
Charge unit
coulombs
58
New cards
Standard Test Circuit
Used to investigate I-V graph for a range of componants
59
New cards
Ammeter placing
In series
60
New cards
Voltmeter placing
In parallel
61
New cards
Power rating
Shows the maximum safe power.
62
New cards
Household fuses
Protect the wires in the house.
63
New cards
Potential difference defintion 2
The energy transfered per coloumb of charge that passes between two points in an electric circuit.
64
New cards
Current definition 2
Current is the flow of electrical charge.
65
New cards
Conventional Current
Current flows from +ve to -ve.
66
New cards
Electron flow
electrons flow from -ve to +ve.