Global midterms
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
The feudal system
Was the system of land ownership where rules divided land among their followers in return for loyalty and taxes
Blacksmith
Makes tools and weapons
Bailiff
Man who ran the Manor in the Lords absence. Responsible for collecting taxes and keeping law and order
Open field system
The land for crops was divided into three huge fields. Each field was divided into long stripes of land and tended by different families
Serfs
Belonged to their Lord. Worked 6 days a week farming the Lords lands. In return they received a small plot of land. They couldn’t leave the Manor or marry without the Lords permission. If they escaped and stayed free for a year and a day the became a freeman
Lords
They were very powerful
Foot soldiers
Made up the largest part of any medical army, fought with swords, daggers and spears. They were peasants
Archers
Fought with a bow and arrow, or sometimes a longbow or cross bow. Wore very little protective clothing
Knights
We’re minor nobles who fought on horseback and swore the oath of chivalry. Wore full body armour
Feudalism
The system of land ownership and hierarchy where the King granted land to nobles in exchange for loyalty, military service, and taxes.
Manorialism
it was the economic system of the Middle Ages where the Lord's estate (Manor) was the center of life and production.
What does mesopotamia mean
Land between the two rivers
What are the two rivers in mesopotamia
Tigris and Euphrates
All of the river valley civilizations
Polytheistic
Hammurabi’s code
The first written set of laws, strict and harsh punishments
Sumerians
made cuneiform, writing, wheel and plow
Neolithic revolution
change in diet and shelter, hunter and gather changed to farmic, permanent settlers
CAUSE AND EFFECT
Neolithic rev led to civilizations
Where did they settle
The river valley
The nile
Predictable flooding
Why did they build pyramids
tombs for the pharaohs who were viewed as gods, brought them to the afterlife with valuables
How did monsoons impact the lives of Indians?
If monsoons were late a drought happened, brought them water, flooding
How did Hinduism and Buddhism develop in India?
Buddhism came from hinduism, both found in India, The aryans brought the vedas to india, no founder
Grid planned cities
Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro
Writing system
Sanskrit
The castle system
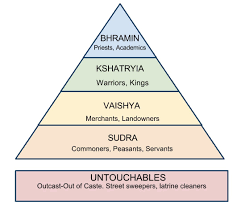
Karma
The Buddhist and Hindu belief that the sum of a person's actions in this life determines their fate in the next life.
Dharma
The responsibilities of each caste
Reincarnation
The belief of being reborn into a cycle
Founder of Buddhism
Siddartha, believed suffering was the result of desire, lived the middle way, rejected the castle system
The four noble truths
1. All life is suffering, 2. Suffering is caused by desire, 3. To end suffering, one must end desire, 4. To end desire, follow the Eightfold Path.
Eightfold path
The steps followed in Buddhism to achieve Nirvana, including right understanding, right speech, and right action.
Buddhism and Hinduism similarities
S: Enlightenment, Reincarnation, Karma, Dharma
D: Moksha, Nirvana, Can’t move classes (H), anyone can move (B), Buddhism has no social classes
Dynasties
Shang, Zhou, Qin, Han
Shang
First dynasty, oracle bones
Zhou
Mandate of heaven
Qin
Legalism, strict government and laws, the great wall of china
Han
silk road, trade routes that connected Asia to the western world, civil service exam, confucianism
Confucianism
Respected elders (Filial Piety), rulers are viewed as role models, all are equal besides ruler and parents, restore social order
Legalism
strict government and laws, similar to hammurabi’s code
Silk road
trade routes that connects china to the rest of the world
Geographies impact on greece
Isolated separate city states and kept Greece from uniting, different government in each city state, travel and trade based on water routes, they can’t unite or trade
Mountains impact on greece
Few natural resources, forced city states to expand, protection and isolation
How did democracy develop in Athens
Athens and Sparta were in a war and Athens citizens decided to make their own decisions and voted directly on laws
Most important contribution to the modern world
Trade increased
cultural diffusion, adopted the phoenician alphabet
differences between Athens and Sparta
S: Language, religion and culture
Athens: golden age, limited democracy, prioritized educations, prepare for times of peace and war, limited freedom of speech, women’s roles limited to managing the house
Sparta: oligarchy, based around the military, discipline and strength, women had freedoms
Alexander the Great
United the Greek city states, the son of one of the biggest rulers in greece, the empire collapsed after his death
Hellenistic culture
The combination of Egyptian, Greek, Persian and indian, CULTURAL DIFFUSION
Cultural Diffusion
The spreading of ideas and beliefs
Republic vs democracy
People voted for elected representatives in a republic, laws directly in a democracy
Patricians: Wealthy landowners, most power
Plebeians: Common people, no power
The punic wars
Rome vs Carthage, gave Rome the control of the Mediterranean sea
Julius Caesar
Led the Roman armies, dictator of Roman republic, assassination was end of the republic and the start of the Roman empire
Pax Romana
Golden age
Inventions in rome
Aqueducts, arches and domes, roads increased trade and transportation
Rome’s downfall
12 Tables
Law code of the Roman republic, law applies to everyone