Bio 269 lab exam 2
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
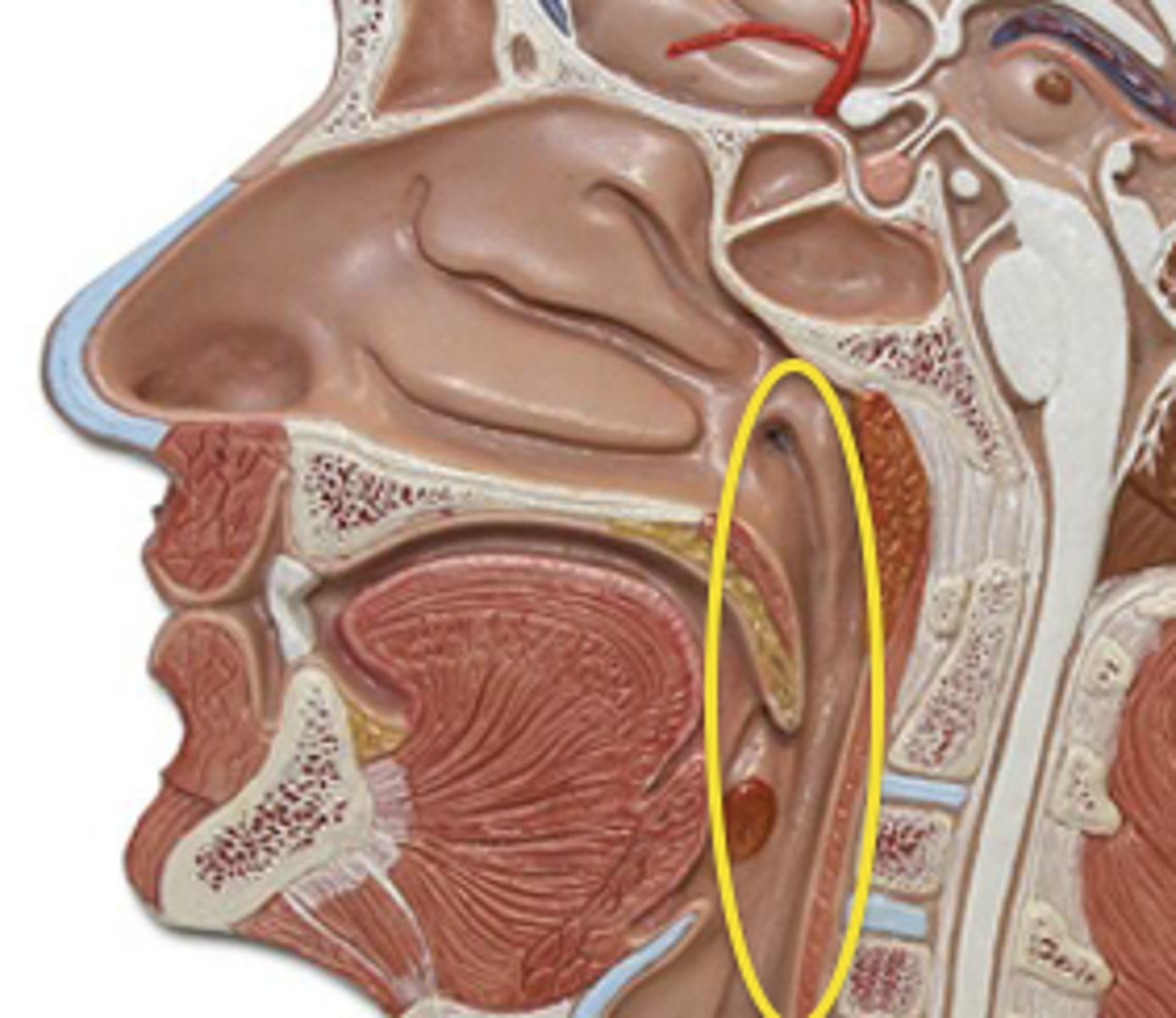
uvula
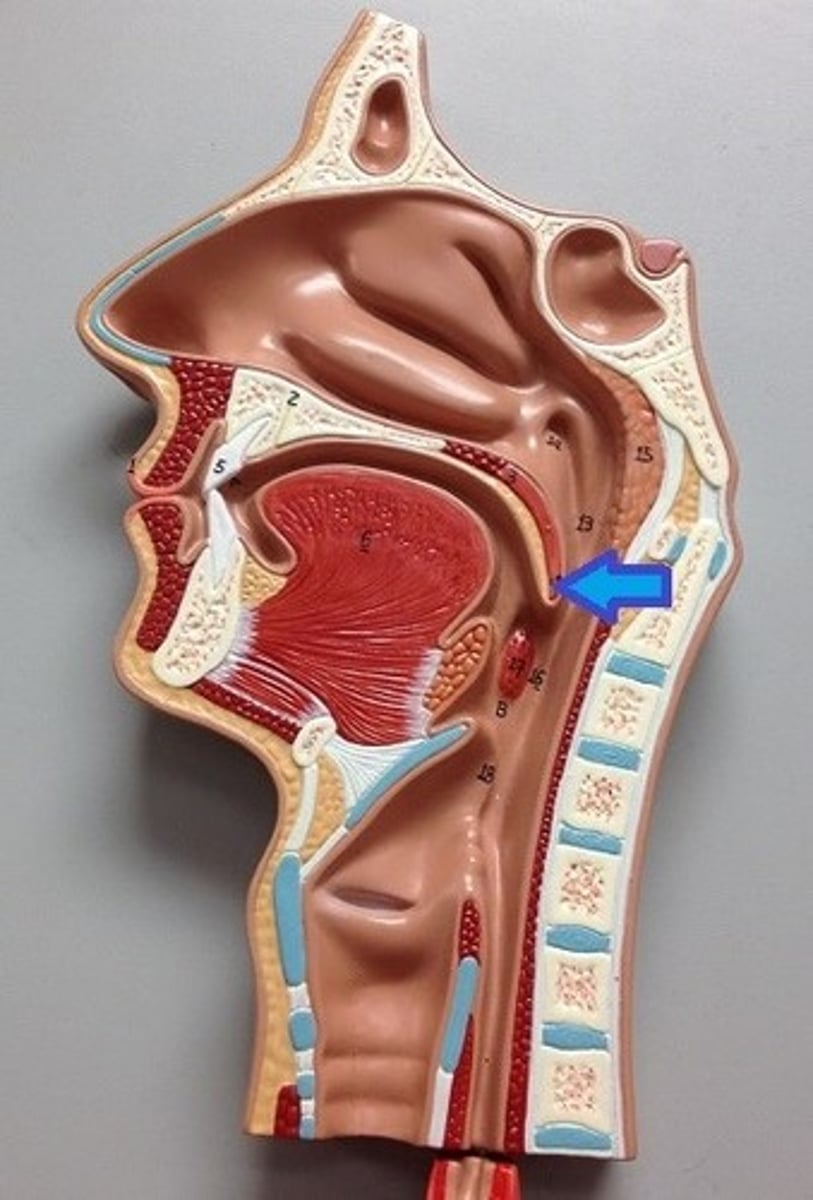
pharynx
esophagus
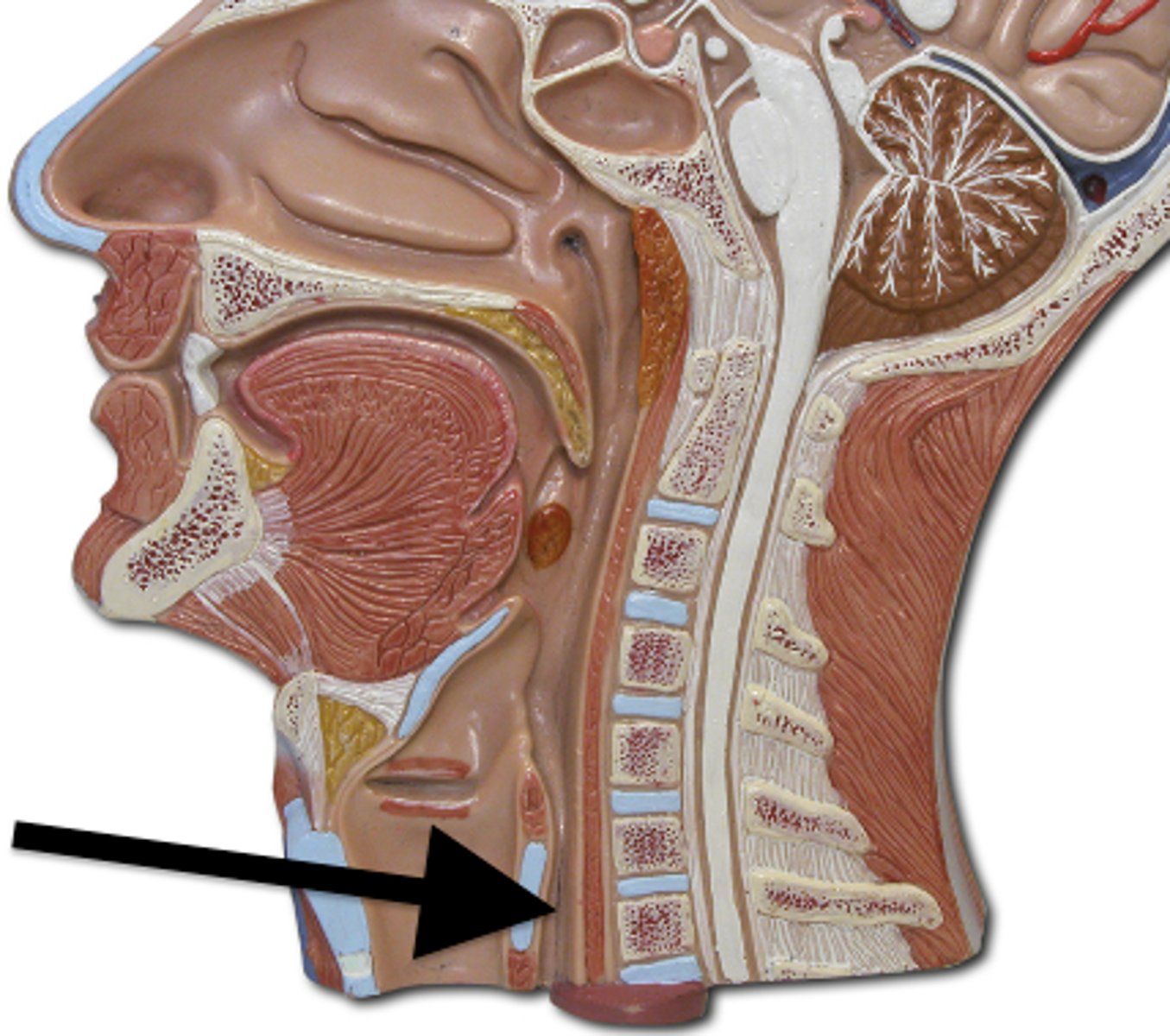
trachea
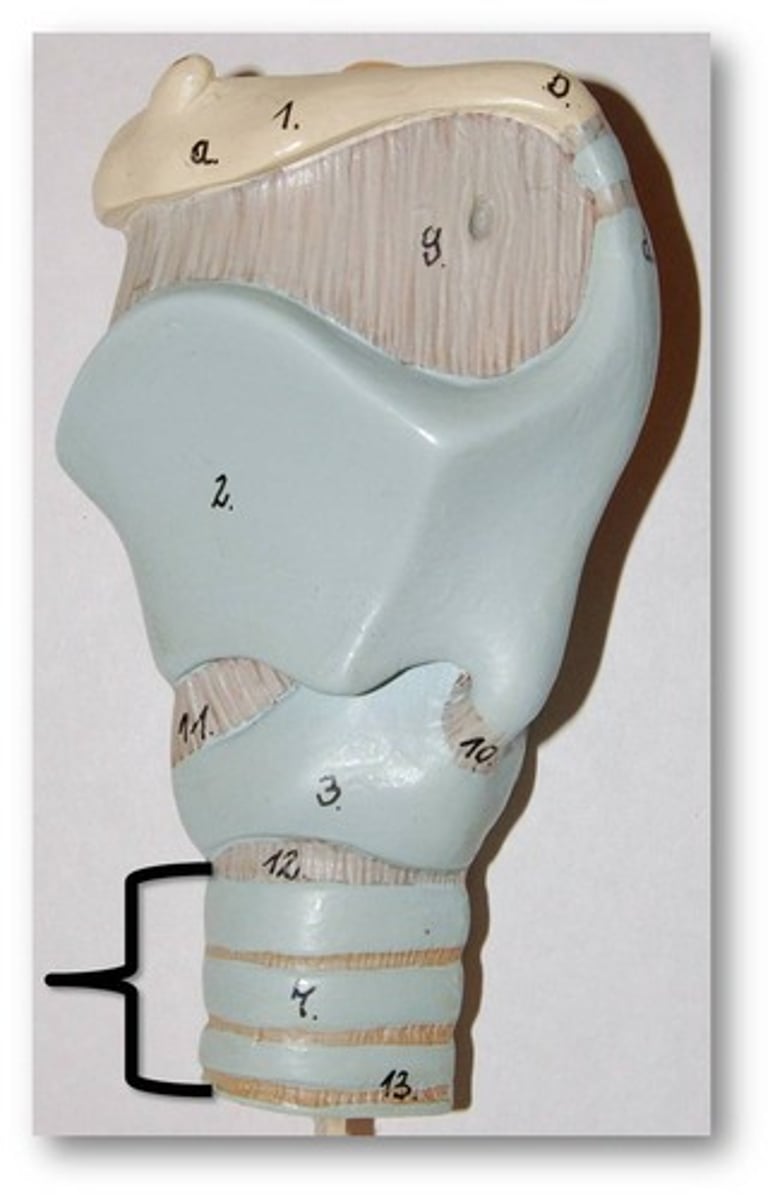
Larynx
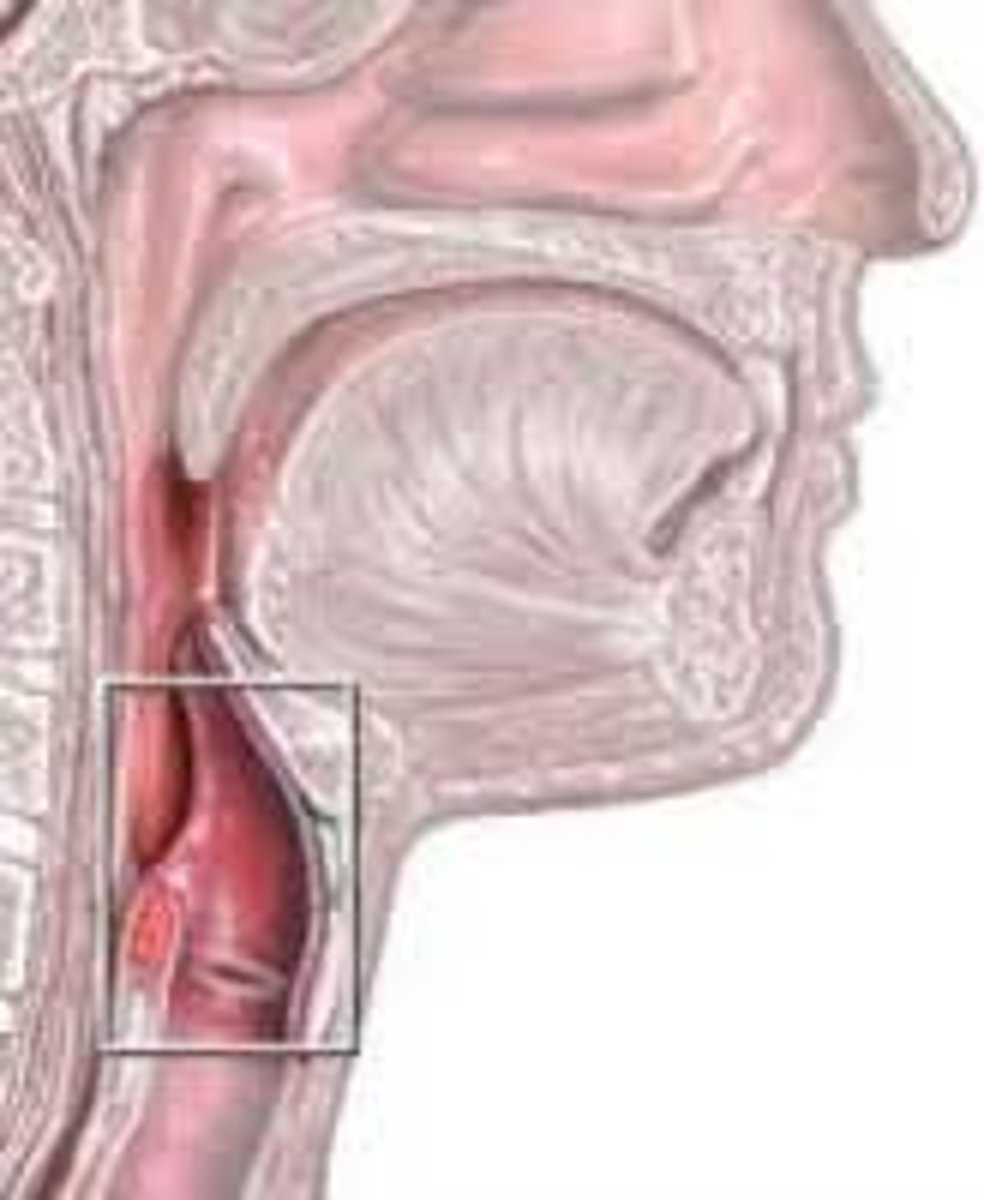
Epiglottis
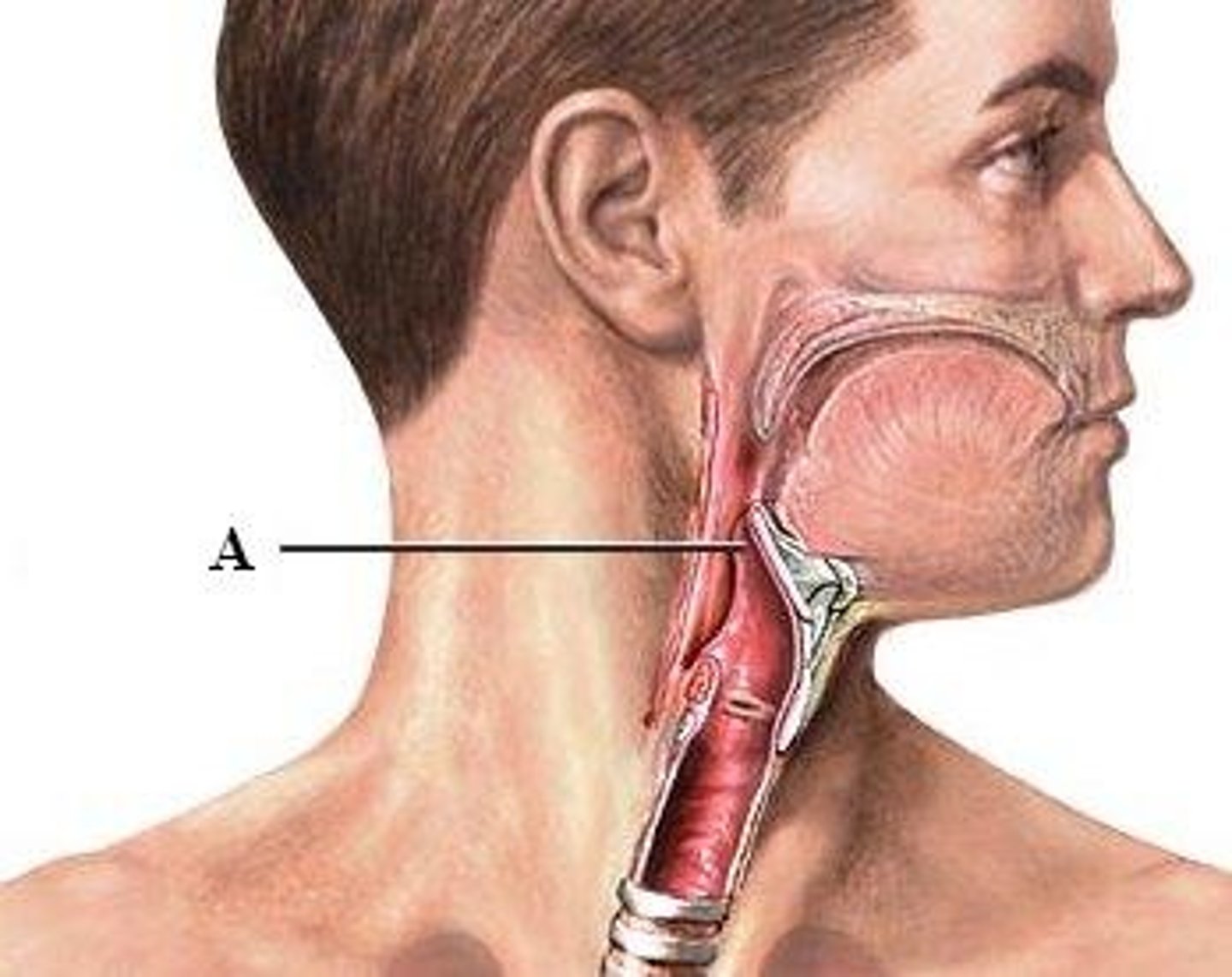
laryngeal prominence

tracheal cartilage
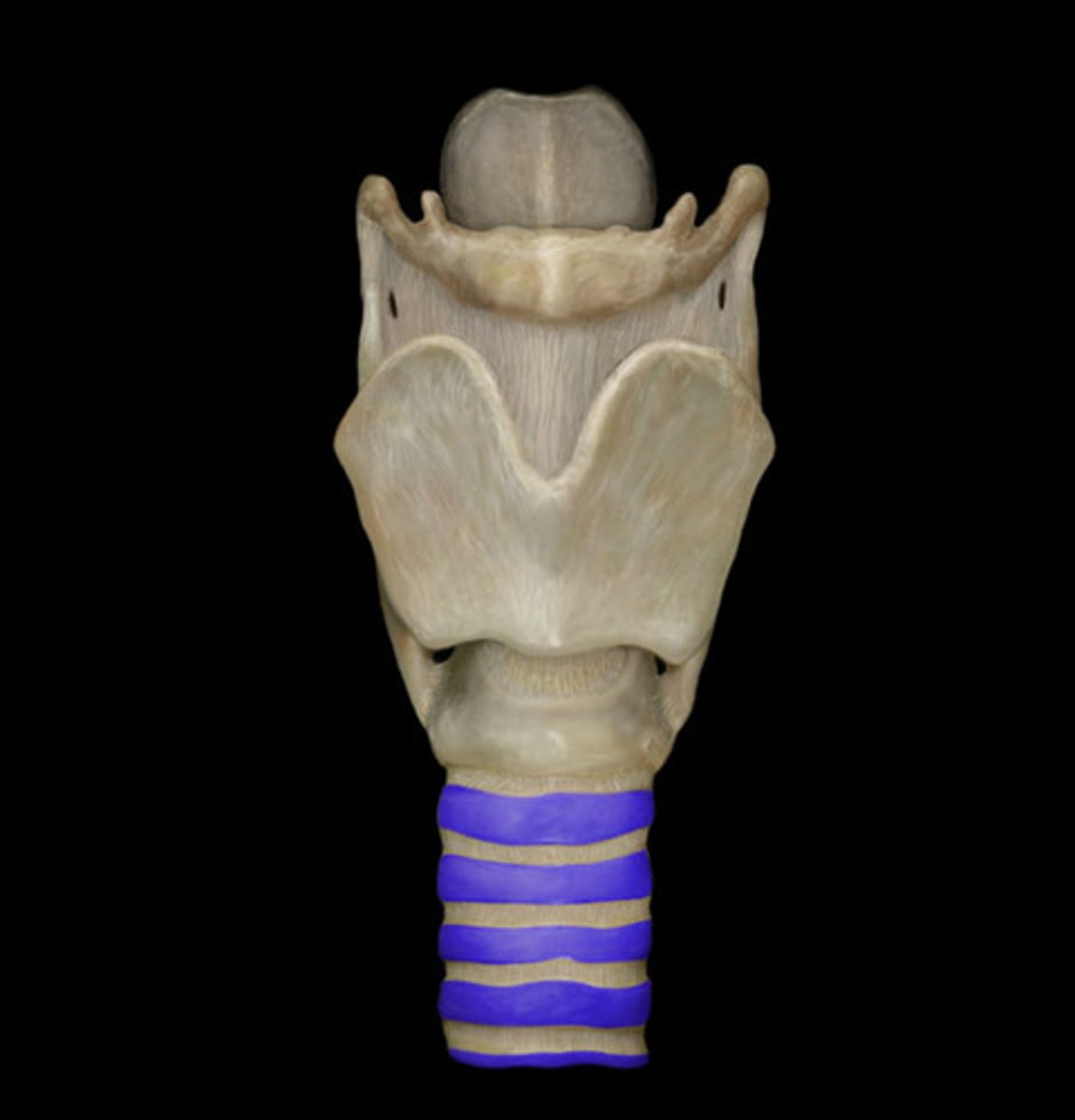
cricoid cartilage

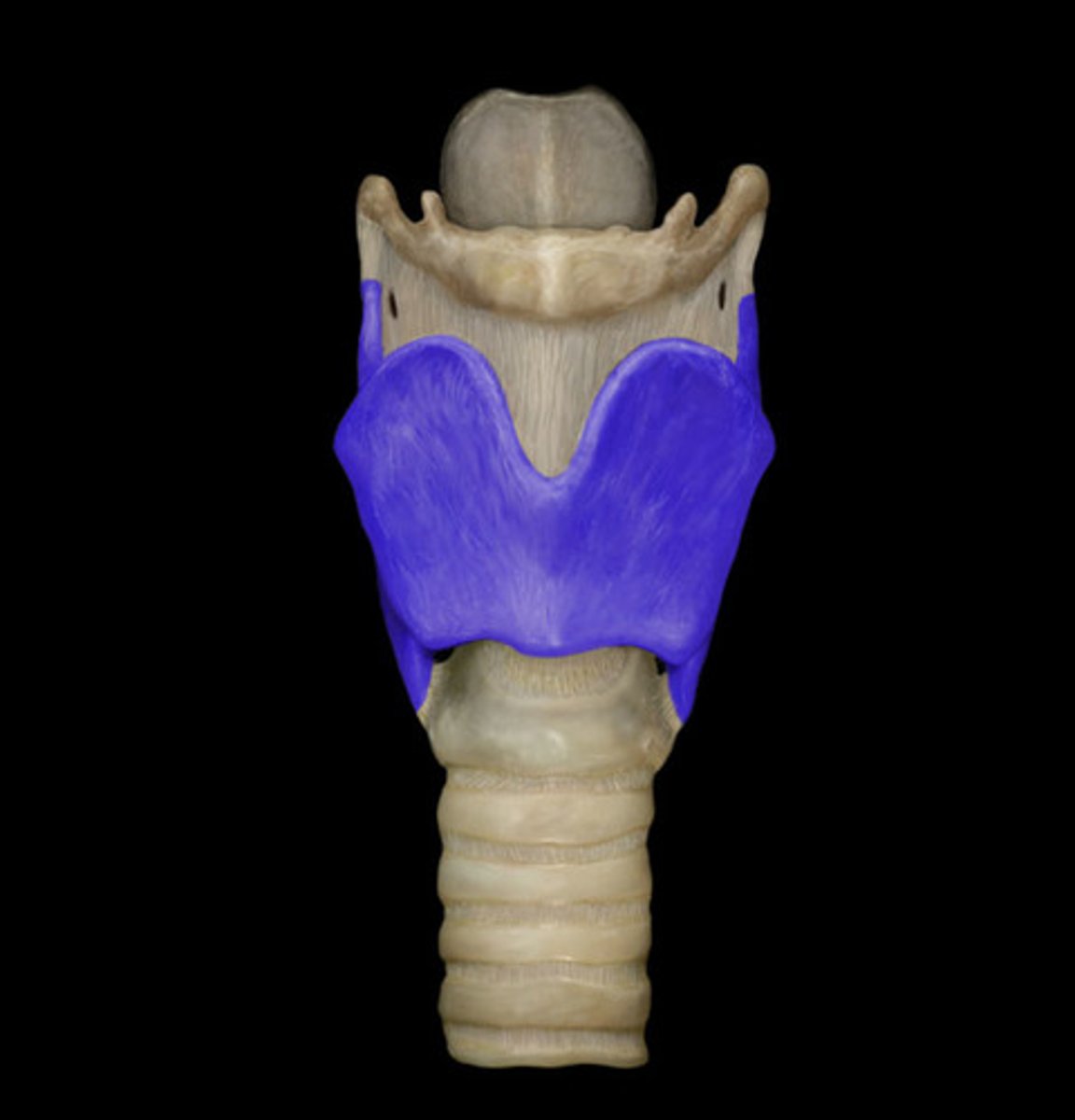
thyroid cartilage
hyoid bone
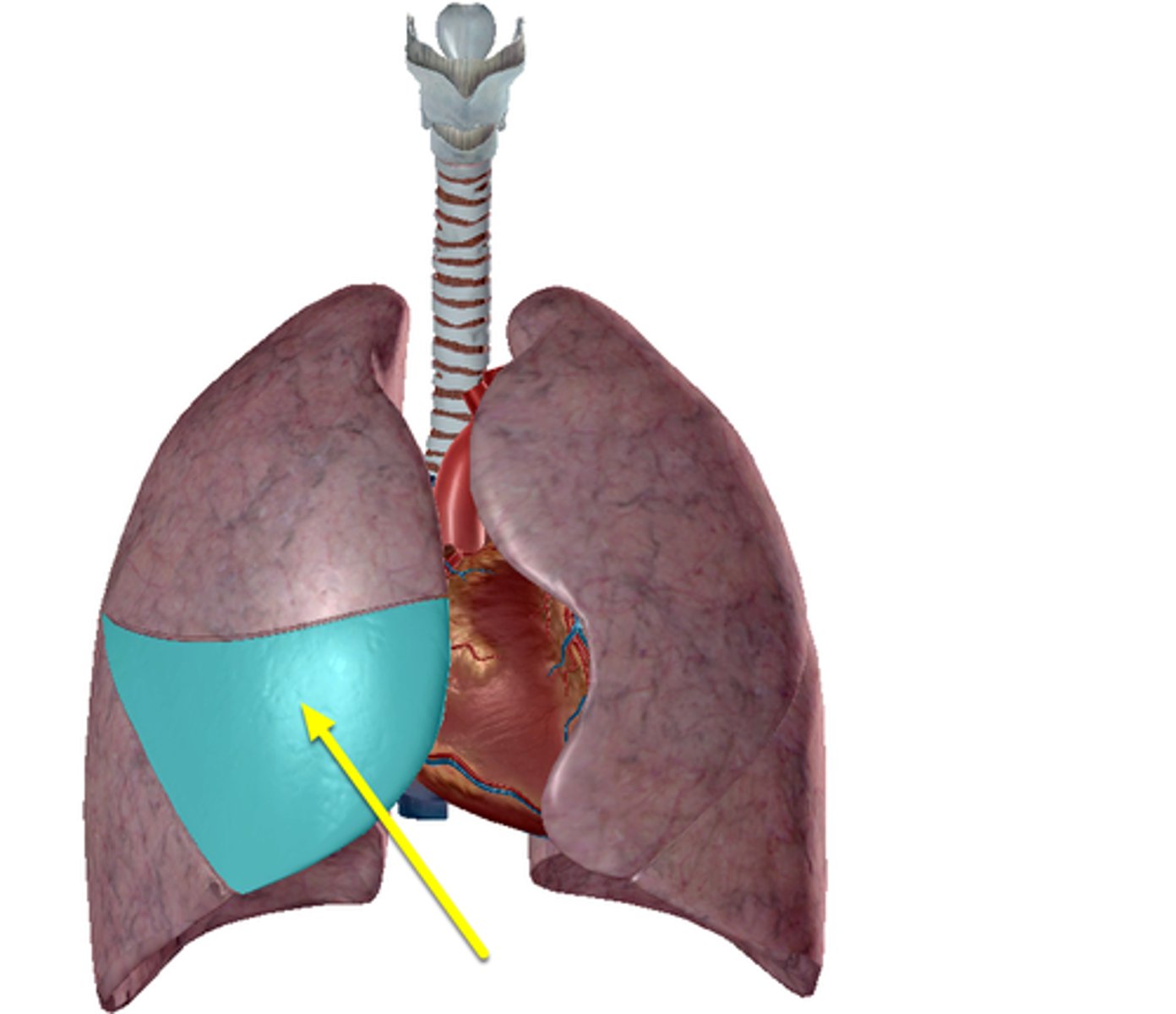
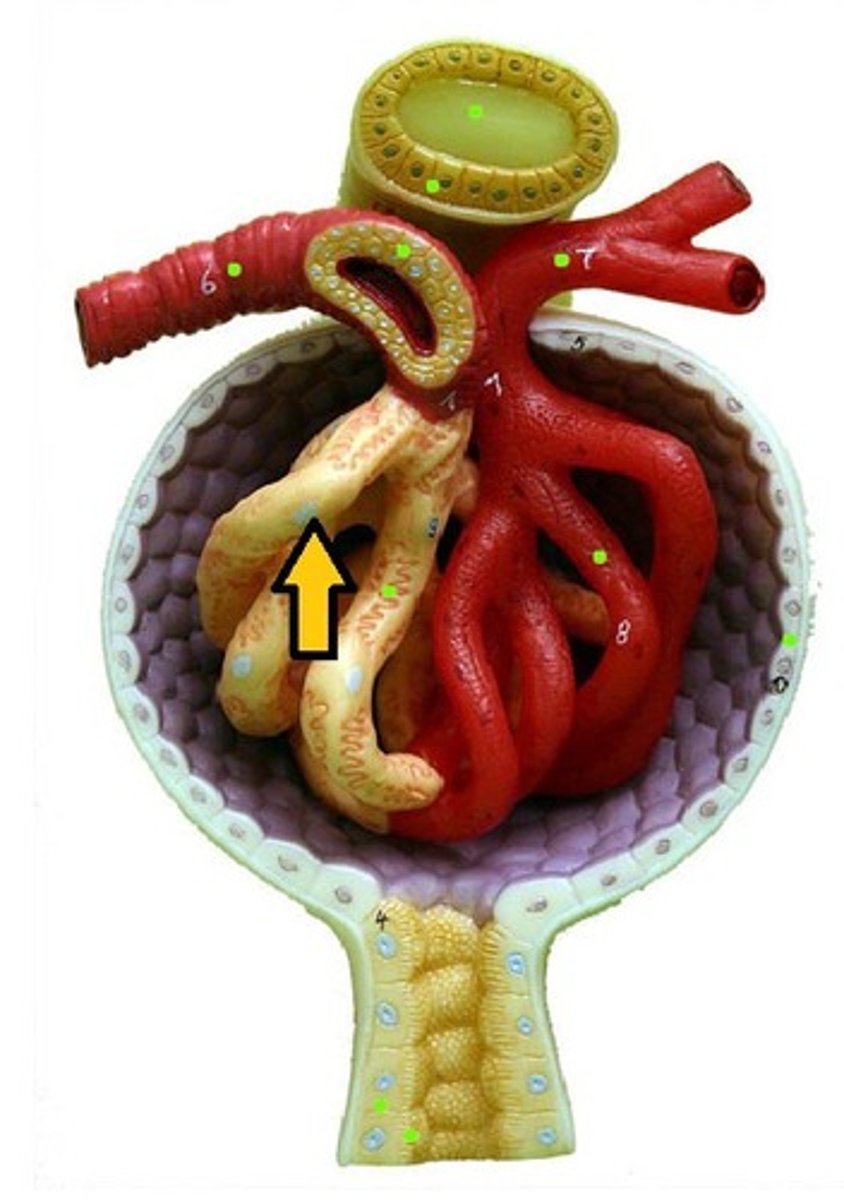
superior lobe of right lung

middle lobe of right lung
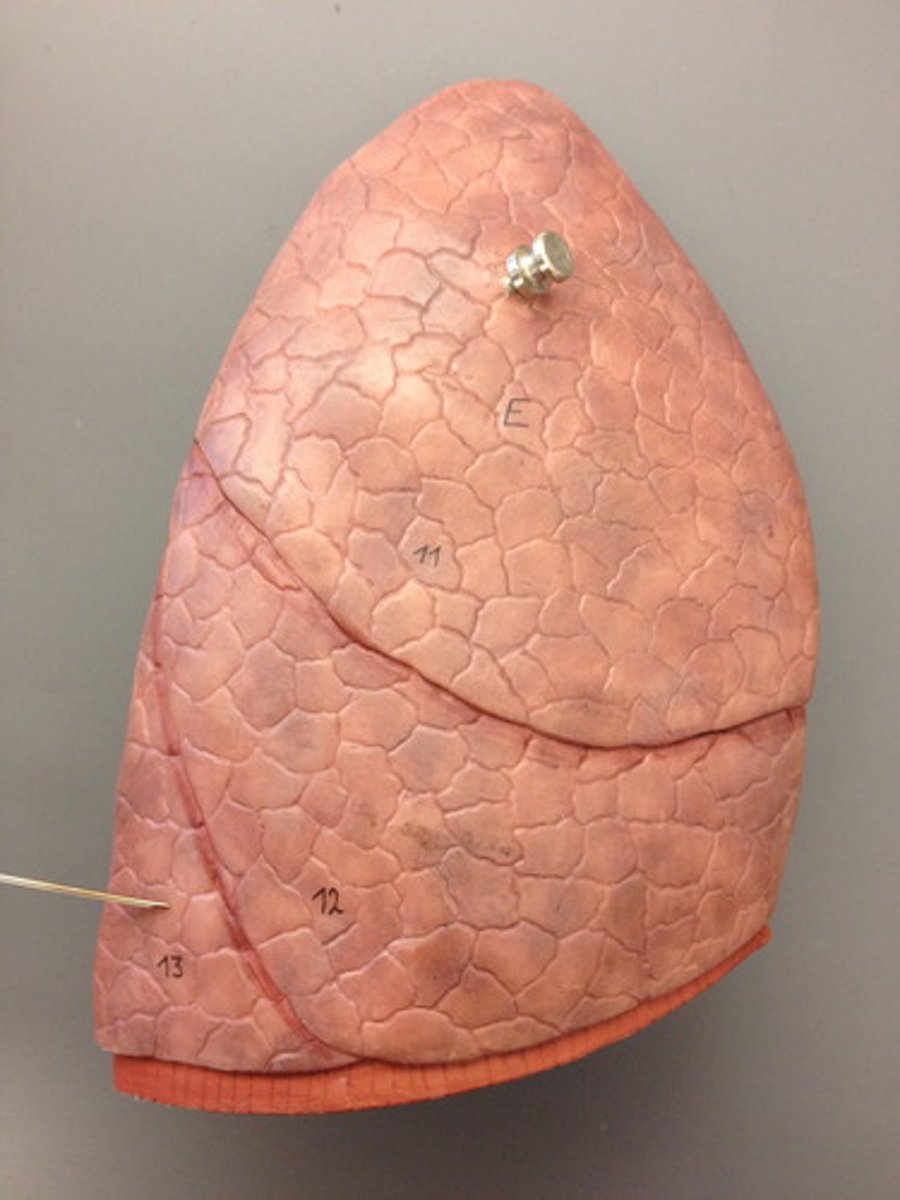
inferior lobe of right lung
primary bronchus (right and left)
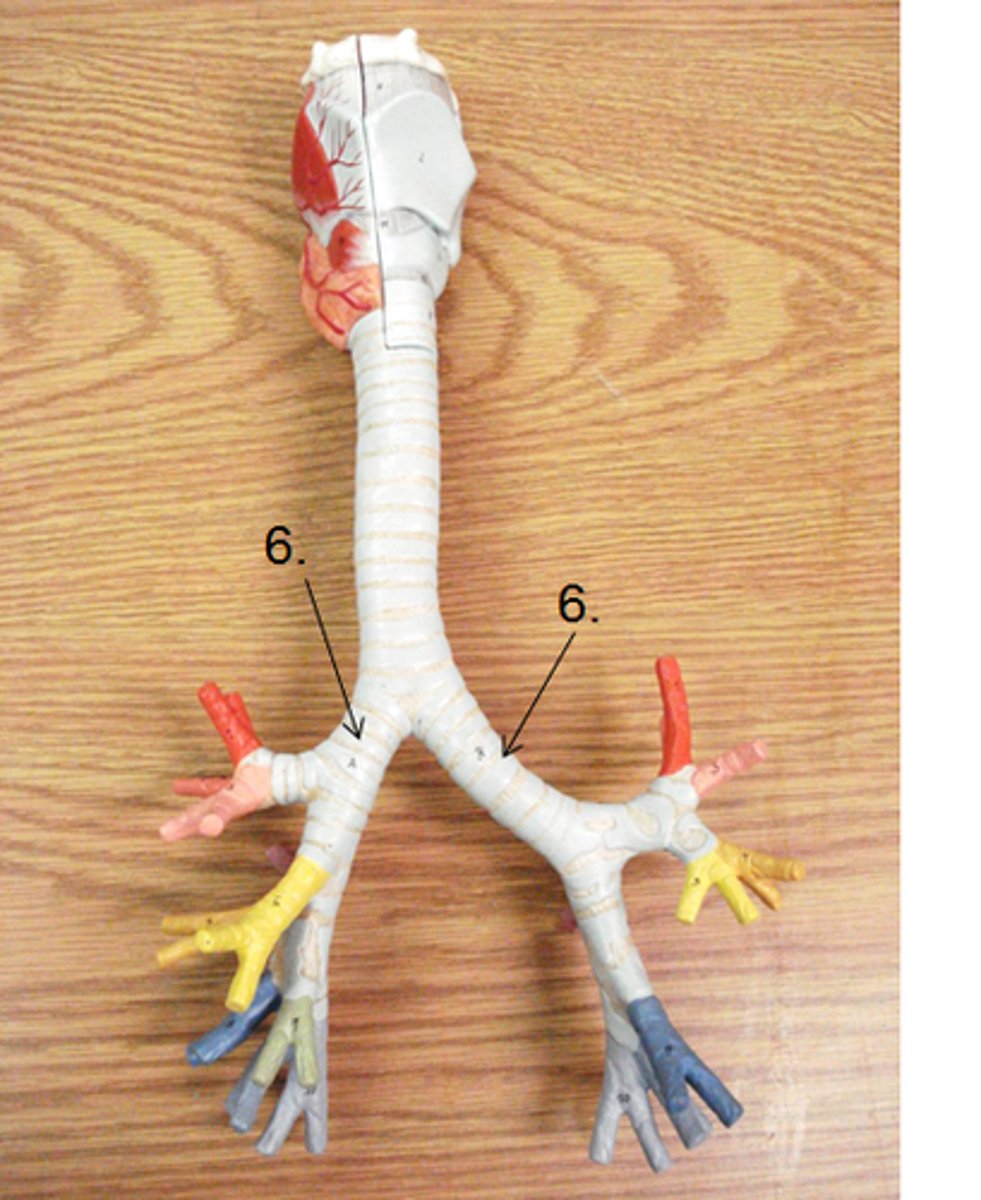
secondary bronchi

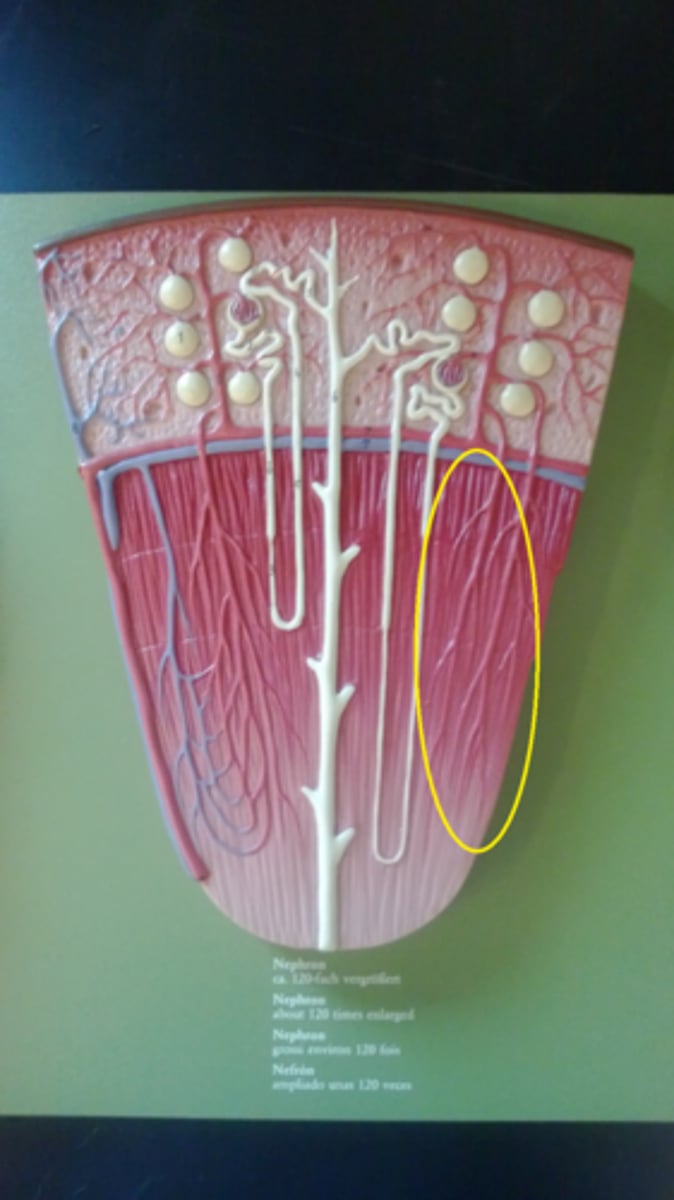
cortex

medulla pyramids
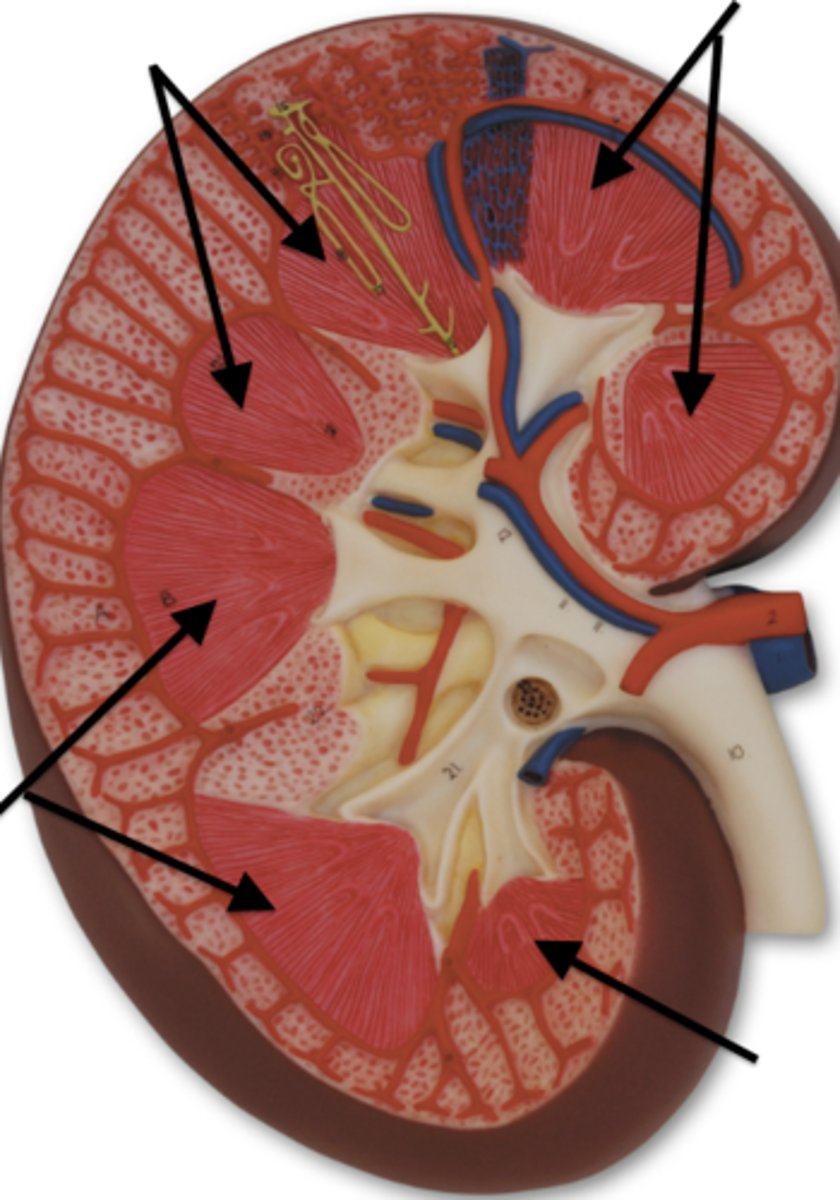
renal capsule
renal pelvis
renal artery
renal vein
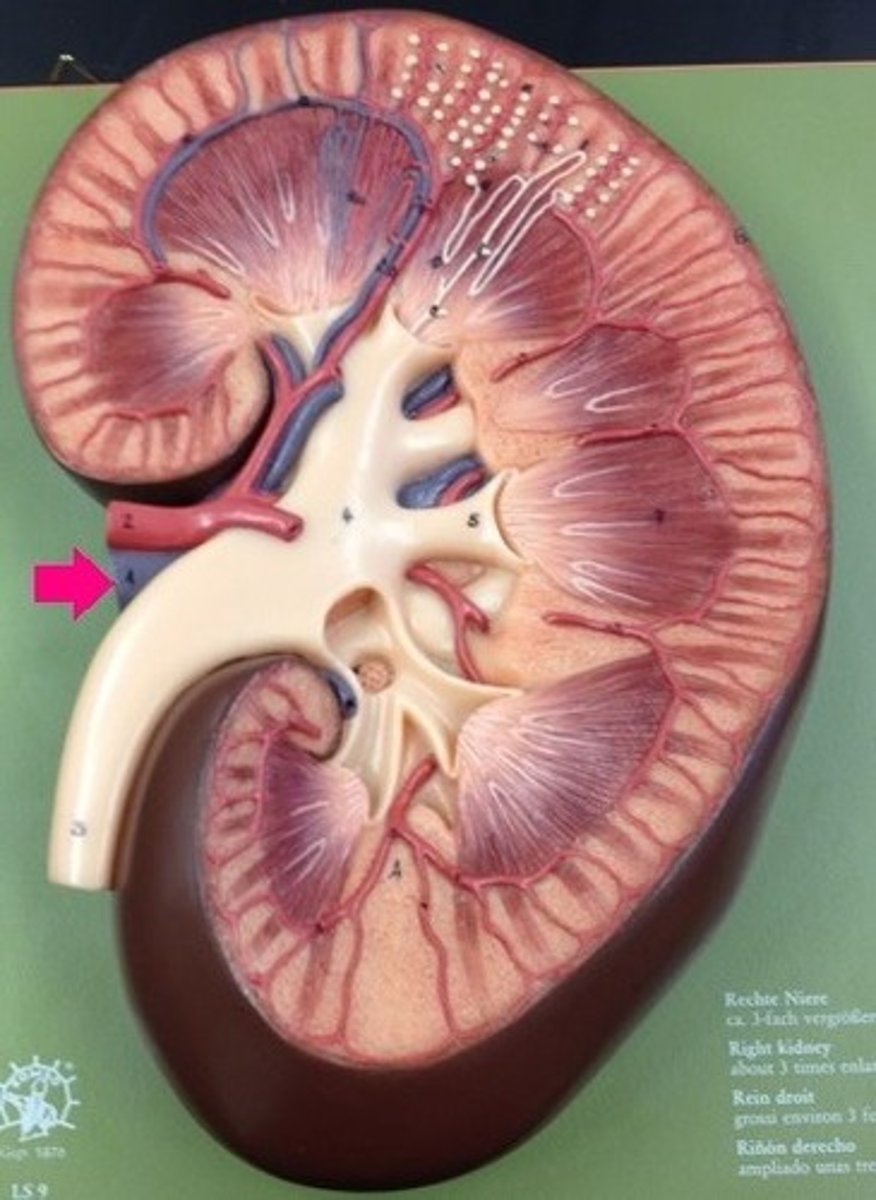
ureter
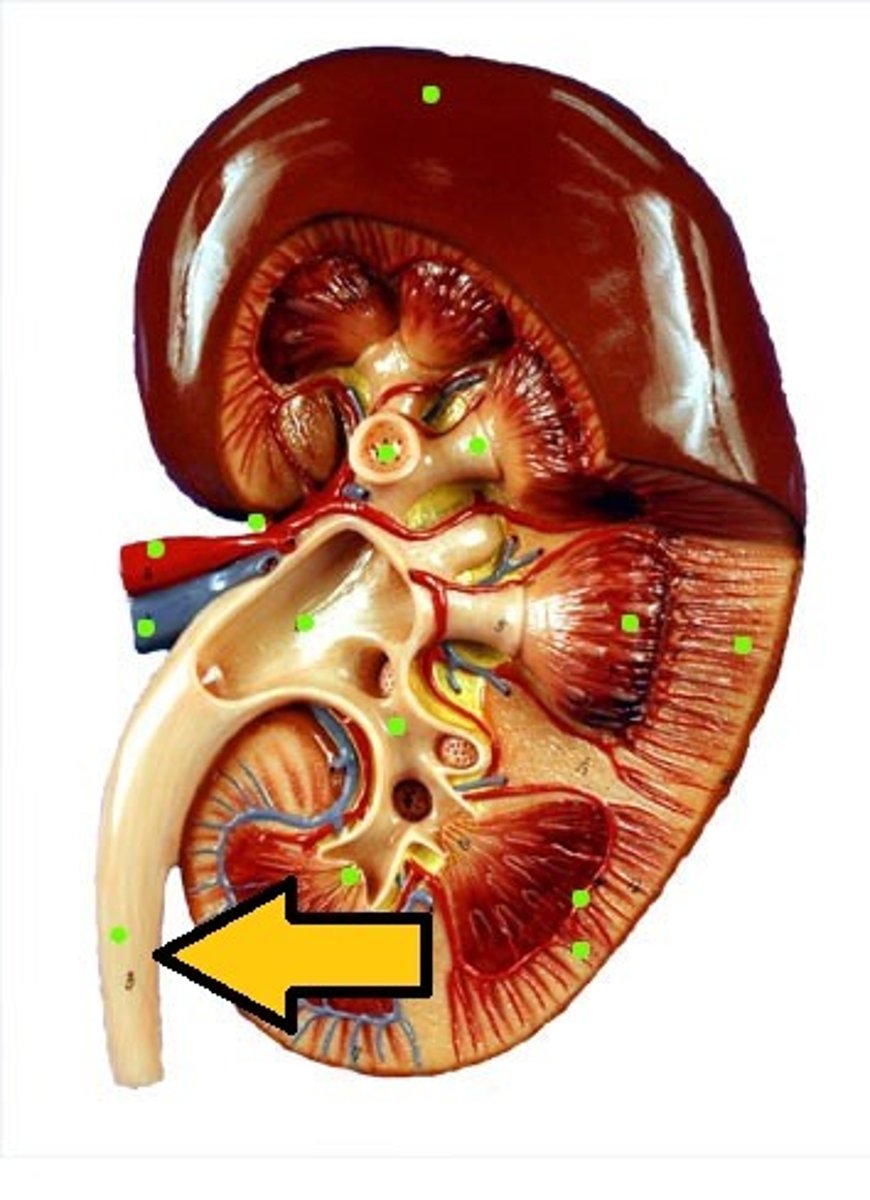
calyx

renal papilla

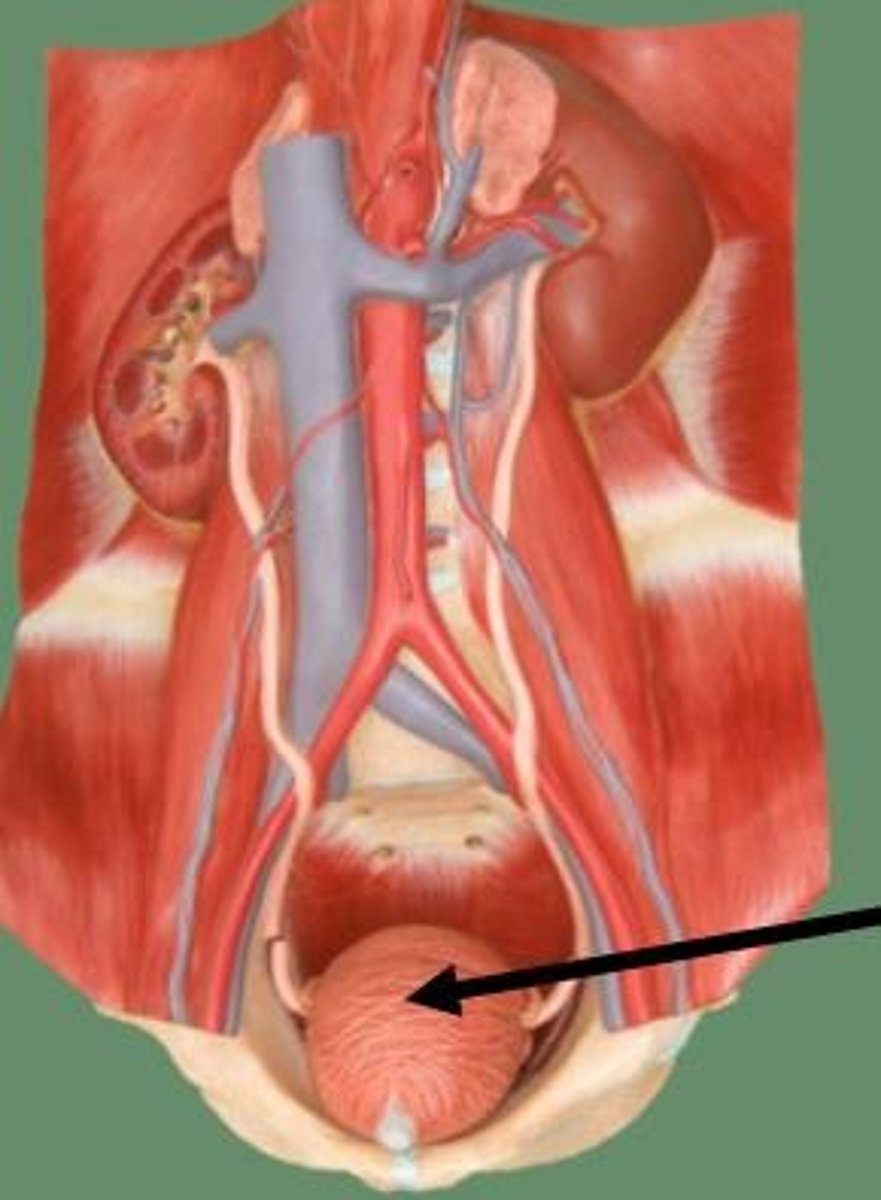
urinary bladder
adrenal gland

renal corpuscle
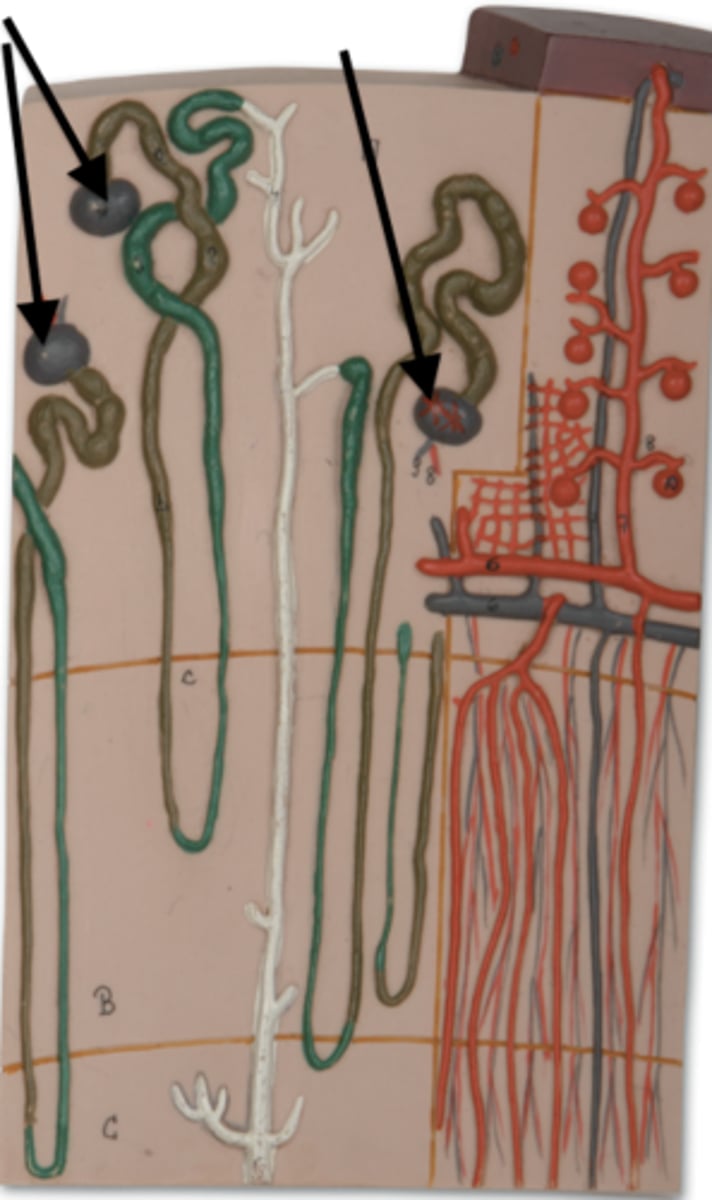
afferent arteriole

efferent arteriole

glomerulus
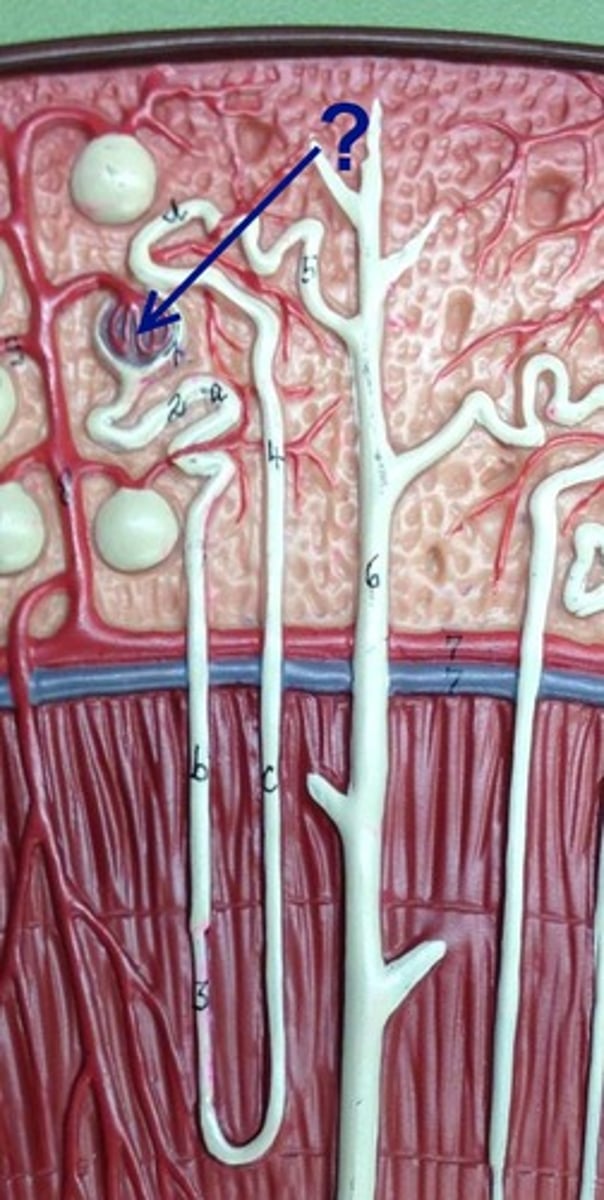
podocyte
proximal convoluted tubule
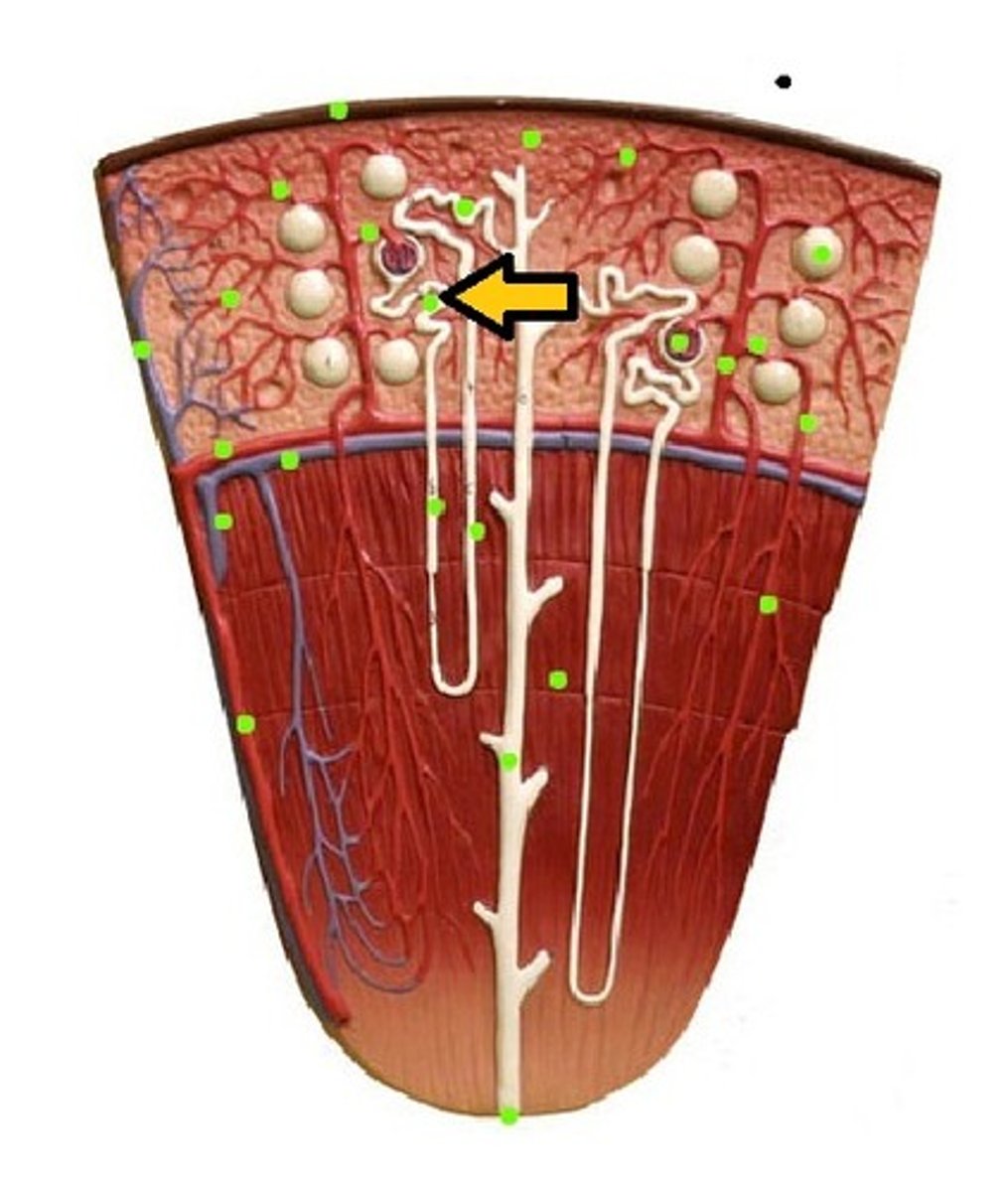
Loop of Henle (ascending)
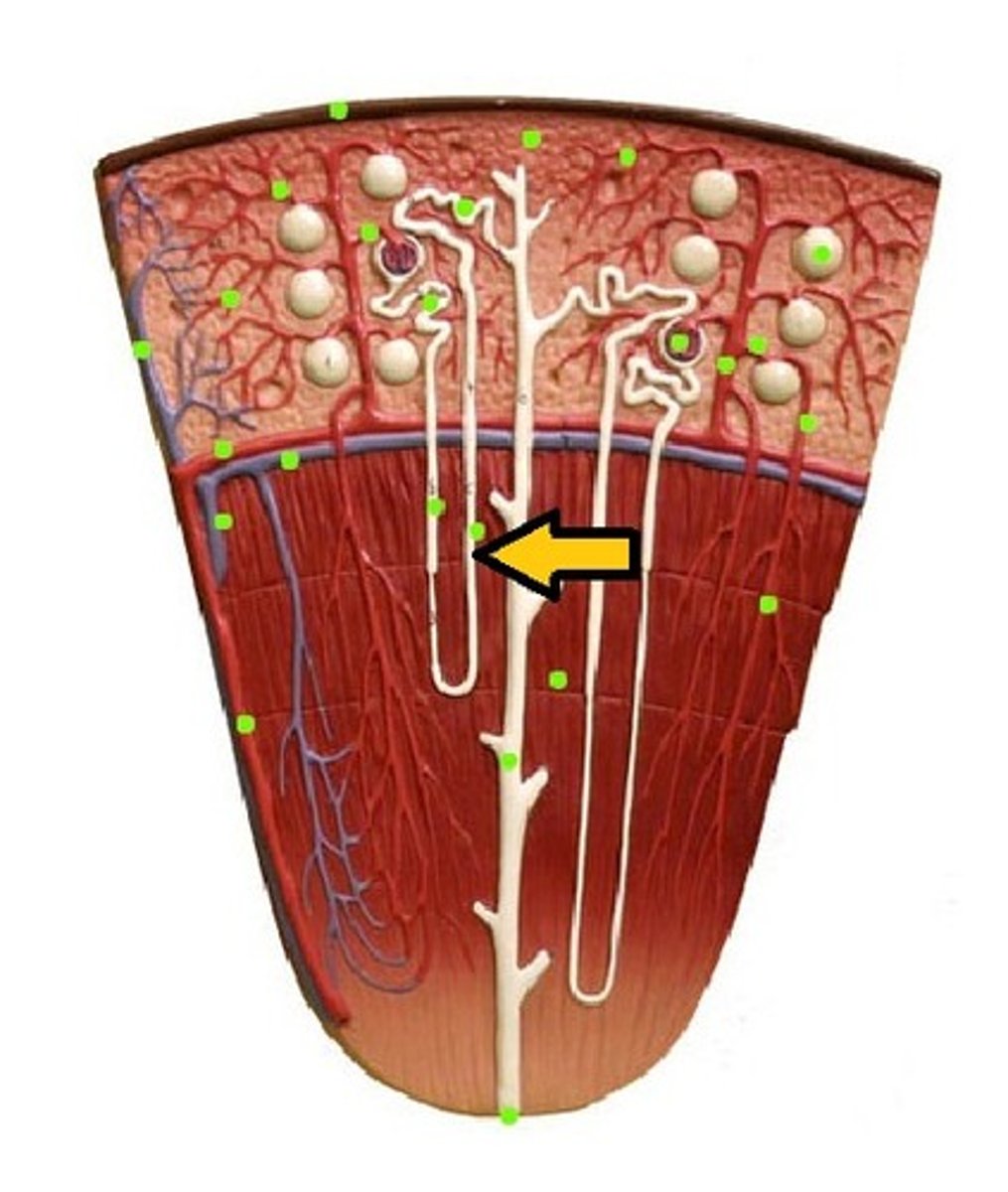
loop of henle (descending)
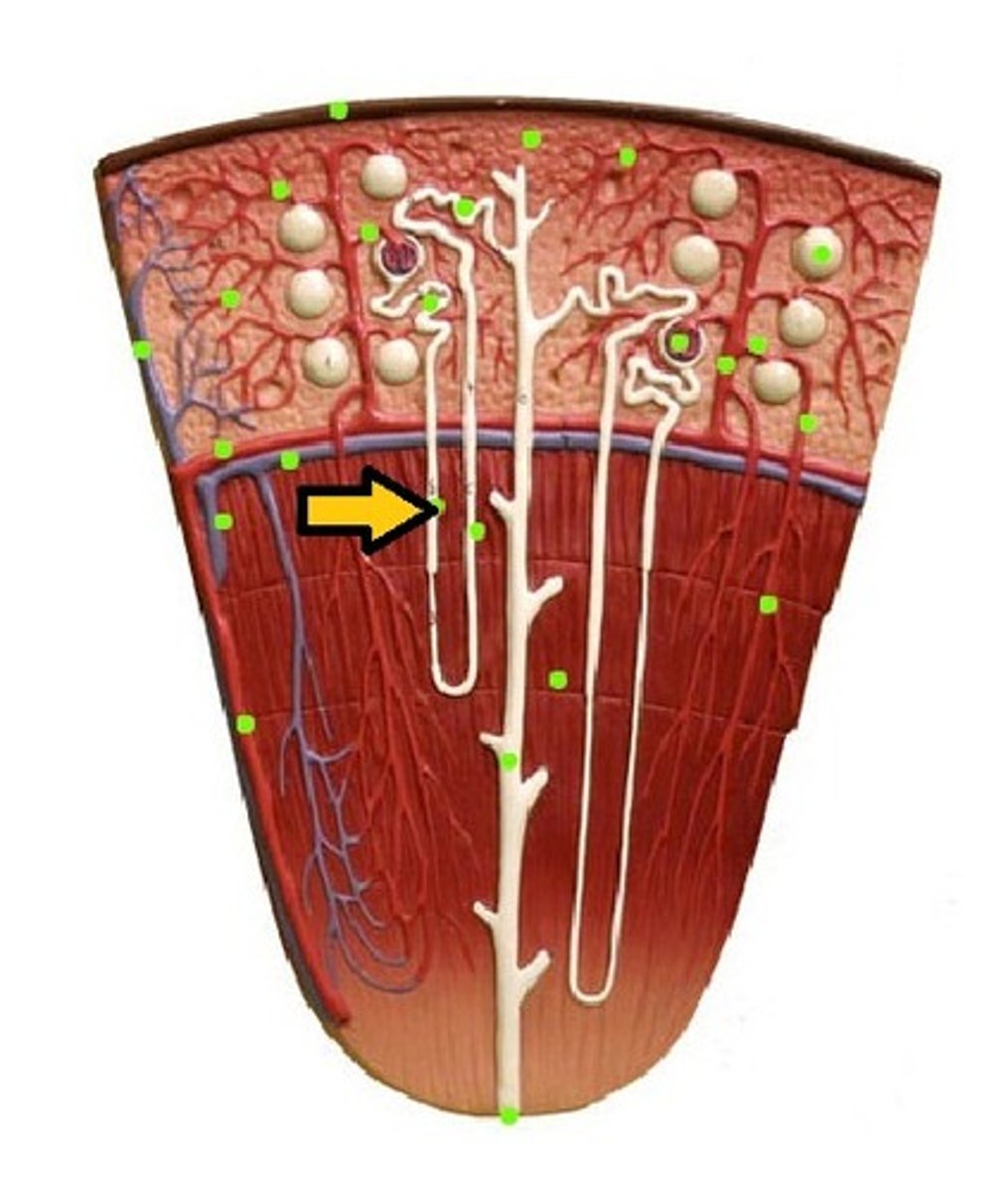
Loop of Henle (thin segment)
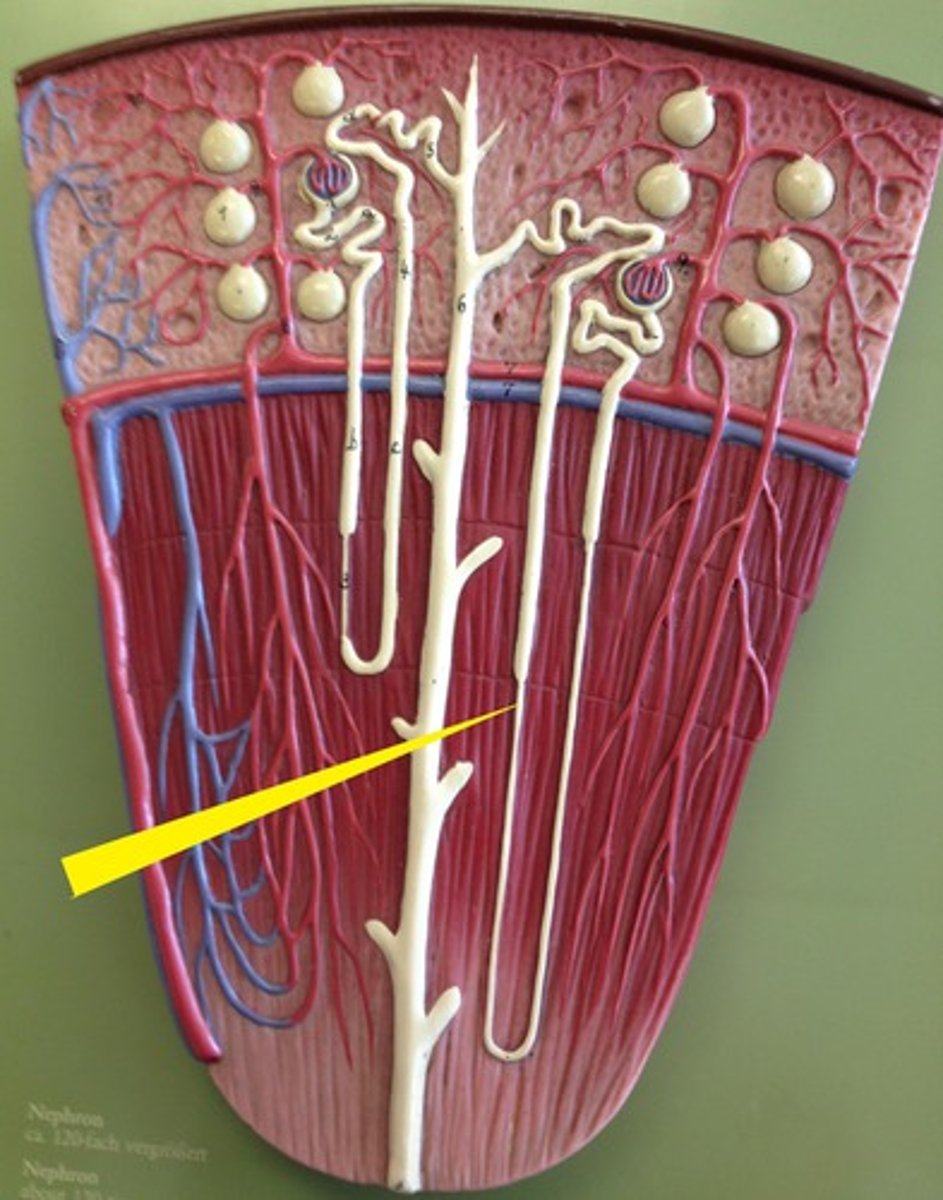
Loop of Henle: thick ascending limb
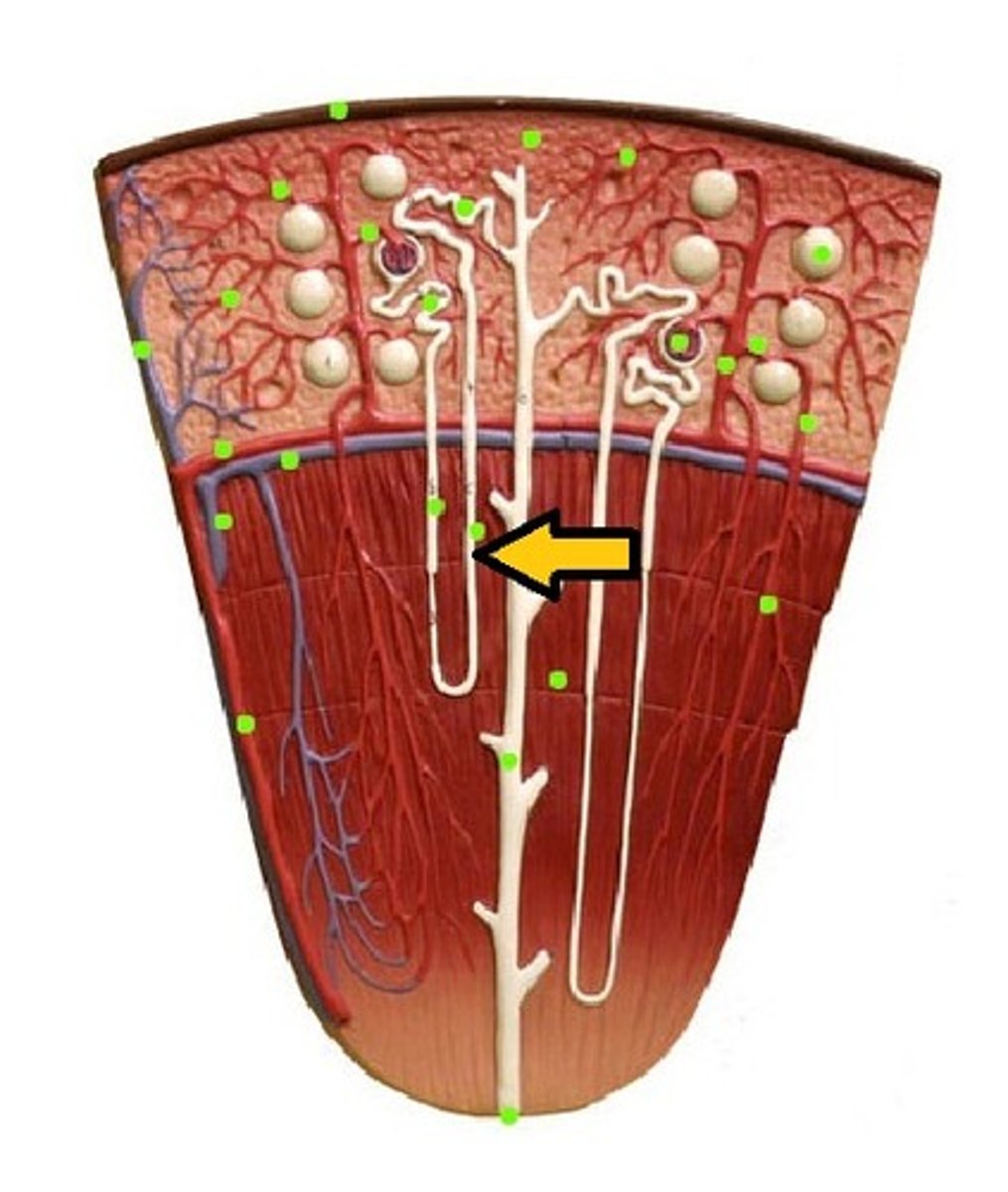
distal convoluted tubule
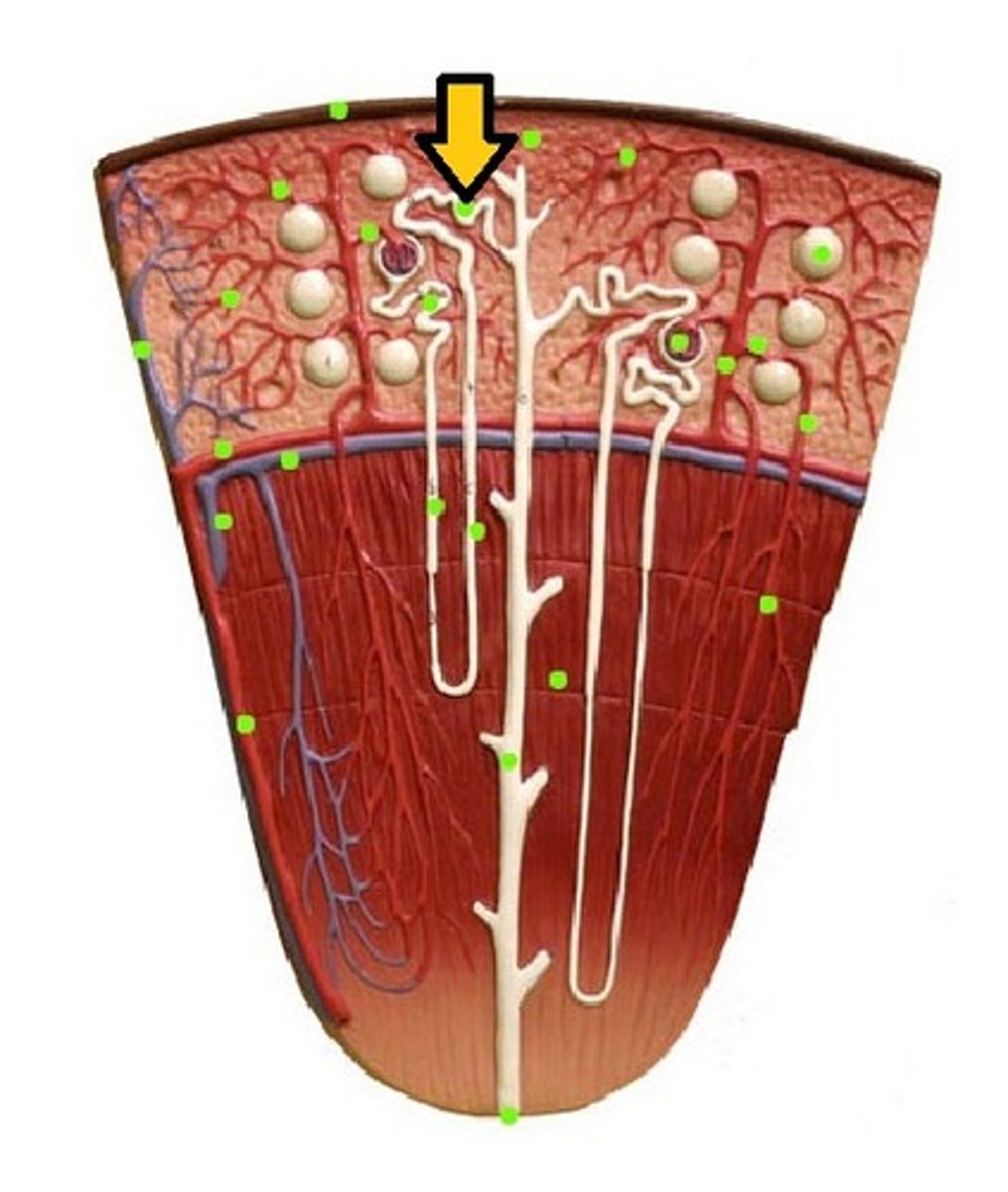
macula densa

collecting tubule/duct
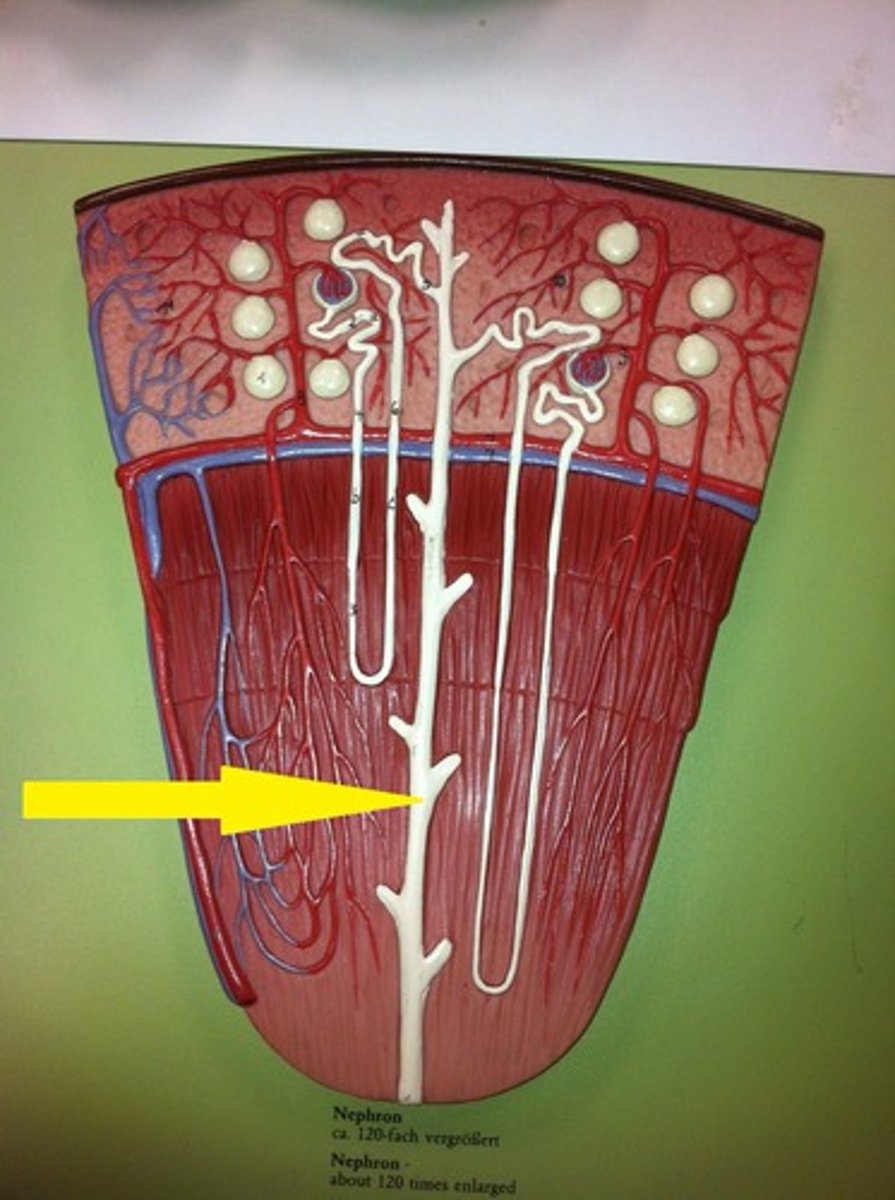
peritubular capillaries

vasa recta
tidal volume
Amount of air that moves in and out of the lungs during a normal breath
vt
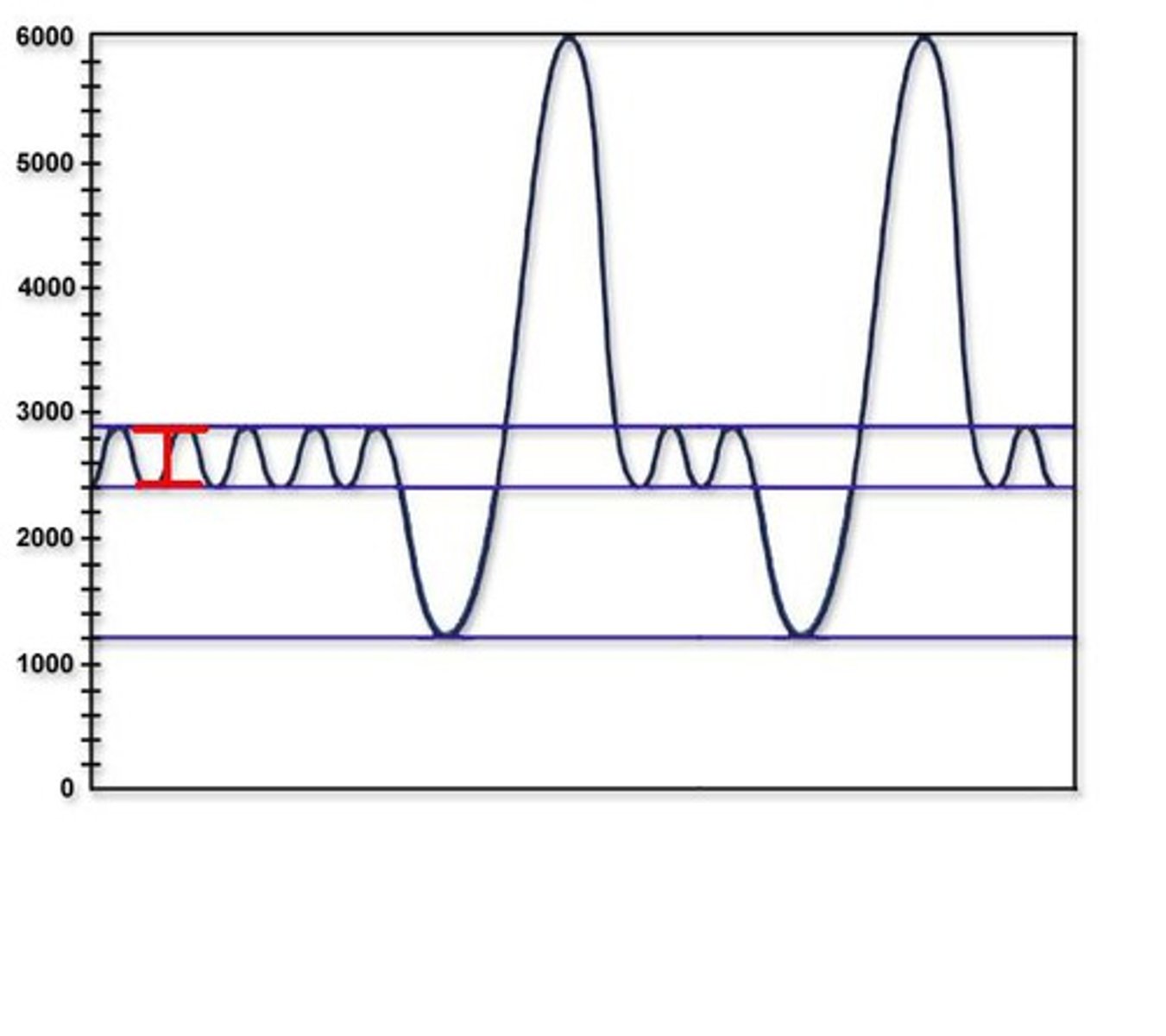
expiratory reserve volume
Amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal tidal volume exhalation

inspiratory reserve volume
Amount of air that can be forcefully inhaled after a normal tidal volume inhalation

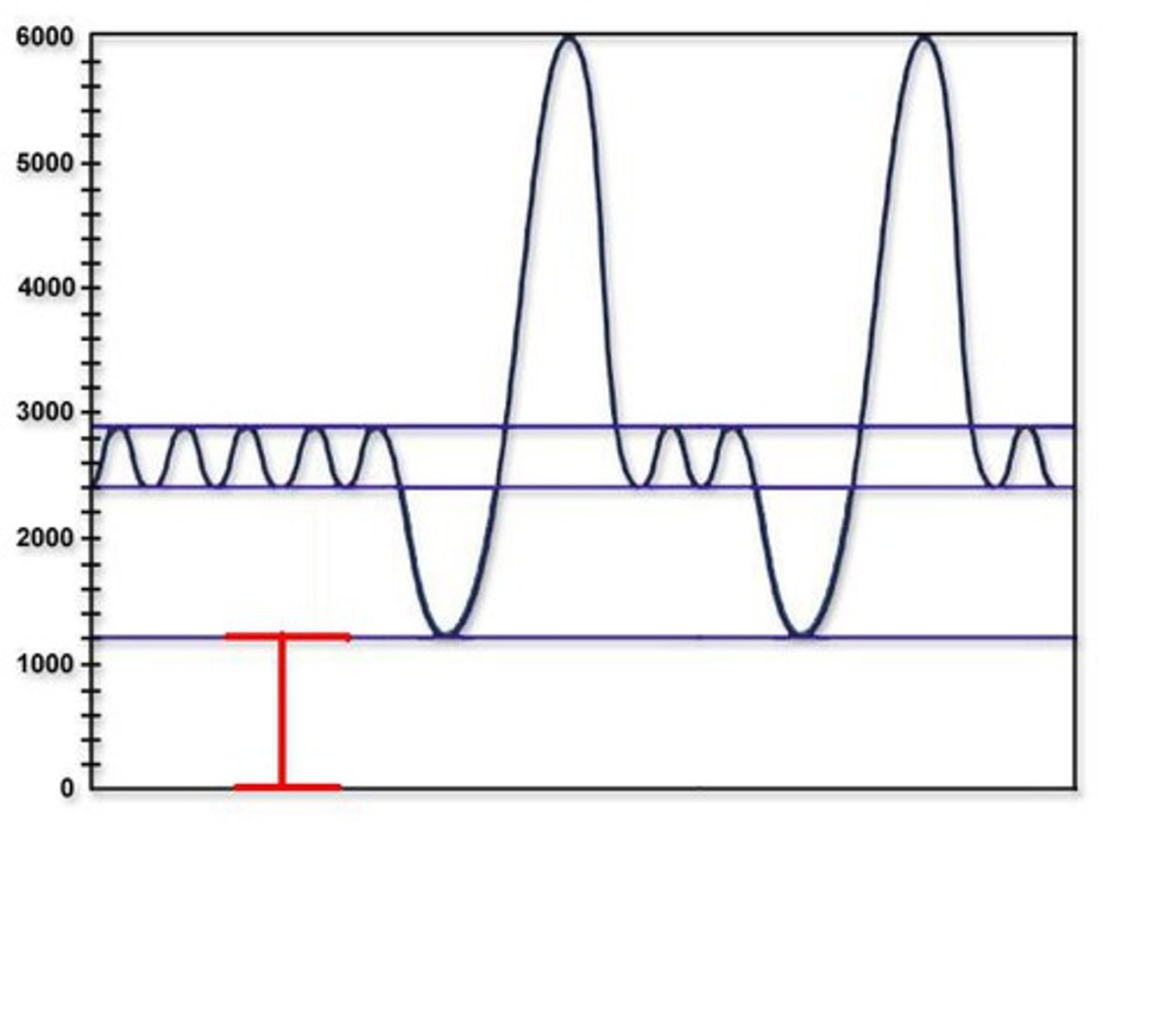
residual volume
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation
vc x .25
vital capacity
The total volume of air that can be exhaled after maximal inhalation.
irv + erv+ vt
total lung capacity
sum total of air the lungs can contain
vital capacity + residual volume
forced vital capacity
the maximum amount of air that can be removed from the lungs during forced expiration
Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV)
amount of gas expelled during specific time intervals of FVC
healthy lungs can exhale about 80%
FEV1 / FVC
Respiration Minute Volume (RMV)
the volume of air inhaled or exhaled from a person's lungs in one minute, TV x BPM (breaths per minute)
During normal quiet breathing its about 6 l/min
500 ml of breath multiplied by 12 breaths per minute
expired minute volume
the amount of air exhaled in one minute of breathing
f x Vt
what happens to respiration volumes when the bronchi constrict?
the volumes decreases, as less air can get into the lungs
what happens to respiration volume when the bronchi dilate?
the volumes increase, as more air can get into the lungs
75-80%
average FEV1/FVC in humans is
Spirometry
a measurement of breathing (or lung volumes)
allows many components of pulmonary function (Fig. 1) to be visualized, measured and calculated.
chest movement measurements
pump air in and out of lungs
allows o2 and co2 exchange
increase, increase, increase, decrease
when there is an increase in pco2, there is ____ hco3 ____ H+ (ph), ______ H2co2, ______ 02
o2 and co2
breathe in and hold your breath, you have plenty of ____- and little of _____
o2 and co2
over time after breathing in and holding your breathe, you run out of _____ and there is an increase in blood
breathe
when co2 levels are too high you ______
decrease in lung volume, co2 of lungs is higher than blood
exhale and force co2 out. why is breathing here harder?
increase
decrease
co2
lungs are full of breath, you have an _____ in o2 concentration and a ____ in co2 than your blood
o2 flows into your blood and co2 out
lungs and blood are equal of co2
___ does not leave your blood but builds up until the next breath
increase
athletes have __ in lung compliance, lungs are used to having to take in more air
decrease
older people and babies have a ____ in lung compliance
hyperventilation
the condition of taking abnormally fast, deep breaths
not allowing deep breaths
hypoventilation
decreased rate or depth of air movement into the lungs
increase in pco2
glucosuria
Nonpathological: excessive intake of sugary foods. Pathological: diabetes mellitus.
glucose in the urine
nonpath and path
proteinuria
Nonpathological: excessive physical exertion, pregnancy, high protein diet. Pathological: heart failure, severe hypertension, damage to glomerular filtration membrane - glomerulonephritis
the presence of an abnormal amount of protein in the urine
nonpath and path
hematuria
Nonpathological: menstruation. Pathological: bleeding urinary tract, urinary tract infection, kidney stones
presence of blood in the urine
nonpath and path
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
increases water reabsorption, decreases urine production, urine is more concentrated
decrease in osmolality when there was an increase due to hydration
causes an increases in plasma volume
occurs in collecting duct
Aldosterone
"salt-retaining hormone" which promotes the retention of Na+ by the kidneys. na+ retention promotes water retention, which promotes a higher blood volume and pressure
increases K+ secretion
in kidney tubules and collecting duct
increase the interstitial concentration
If you _____ the interstitial concentration, water will flow into the nephron to try to equal the solute concentrations therefore urine will not be concentrated.
decrease interstitial fluid
water will flow out of nephron into the interstitial fluid and it will make concentrated urine.
higher number
water flows to the ___________ ______
sweating and become dehydrated increase in adh, aldosterone and reabsorption of na from dct
urine concentration will increase
You are on a 2 day hiking trip to the mountains. You pack adequate provisions including plenty of water because you know that no water is available on the trail. About 4 hrs into the hike you fall on loose rock and your backpack falls, breaking the water bottles which soaks the ground. You decide to go back due to the lack of water. Explain what will happen to your urine concentration and why? Mention the specific events that occur along different parts of the nephron.
water will follow salt--- pulls h2o out and will dehydrate you
challenge for kidneys and is worse for you
If you are shipwrecked on an island with no access to fresh water, should you drink seawater? Explain your answer.
decrease in adh
collecting duct is impermeable
stay with dilute urine
increase in aldosterone, to keep Na and balance osmolality
You like drinking water, all day and everyday. Explain the events in the nephron (and the related hormones) that enable you to remain in osmotic equilibrium.
athletes has the higher fev, muscles are more efficient to breathe air out than a nonathlete
An athlete and non-athlete both take a pulmonary function test to measure their Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV). Which person do you think would have the higher FEV and WHY?
after inspiration: deep breath, air into lungs, o2 ro alveoli
after expiration: metabolism builds up co2 and makes you breathe again
During which phase of respiration can the breath be held the longest? Why?
recover
athletes have a deepr breath to
higher
if you have a deeper breath, you have a _________ amplitude
closer together
if you are breathing fast, it is
50 - 750 mg/dL. High values indicate a high salt diet
Normal chloride content in humans ranges from
1.001 to 1.035. Low values indicate a dilute urine and high values a concentrated urine
The normal range of urine specific gravity in humans is
4.5 - 8.0. Normally you should not find blood, glucose or protein in human urine (
Normal pH range for human urine is