Comprehensive Nursing and Public Health Concepts: Chapters 1, 2, 6-8, and 25
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are the three levels of health care promotion?
Primary health promotions, secondary focus on early detection, and tertiary care for restoration and rehabilitation.
What is an example of primary health promotion?
Vaccines and education.
What is the focus of secondary health care?
Early detection of diseases, such as colon cancer screening and blood pressure checks.
What does tertiary care aim to achieve?
Restoration and rehabilitation, minimizing long-term effects of diseases, such as cardiac rehab.
What are the six stages of change in health promotion?
Pre-contemplative, contemplative, preparation, action, maintenance, and relapse.
What does the clinical model of health emphasize?
Absence of disease, with prevention not emphasized.
What is the adaptive model of health?
The ability to adapt positively to changes in social, mental, and physiological aspects.
How is health defined in the role performance model?
Health is based on whether a person can perform societal roles.
What does the eudemonistic model of health encompass?
Optimal health defined broadly, indicating exuberant well-being.
What is the ecological/systems model of health?
Promotes health on multiple levels, focusing on the interconnection between people and their environment.
What is epidemiology?
The study of health and disease from a societal perspective.
What are the nursing roles in health care?
Advocate, care manager, consultant, delivery of services, healer, and researcher.
What is evidence-based practice in nursing?
Using research to make informed decisions in clinical practice.
What are the two types of research mentioned in the notes?
Quantitative (numbers) and qualitative (history, culture).
What is transcultural nursing?
Developing cultural awareness to adapt healthcare to individual needs.
What are the four goals of Healthy People 2020?
Attain high-quality longer lives, achieve health equity, create environments that promote health, and promote quality of life.
What is the difference between race and ethnicity?
Race is a fixed social construct associated with power, while ethnicity is fluid, encompassing meanings, values, and ways of life.
What is the definition of homelessness?
Lacking a fixed, regular nighttime residence or imminent loss of primary nighttime residence.
What are the main differences between HIV and Ebola?
HIV is spread via body fluids and slowly destroys the immune system, while Ebola is transmitted via blood or body fluids and can cause fatal hemorrhaging.
What are the symptoms of Dengue?
Fever, myalgia, and rash.
What are the main types of noncommunicable diseases?
Cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes.
What is antimicrobial resistance?
When pathogens mutate and antibiotics become ineffective.
What are the four main systems in the systems theory?
Micro, meso, exo, and macro systems.
What does the micro system focus on?
Individual factors such as home, parents, school, and peer group.
What are Gordon's Functional Patterns?
Patterns that assess health and dysfunction in individuals and families.
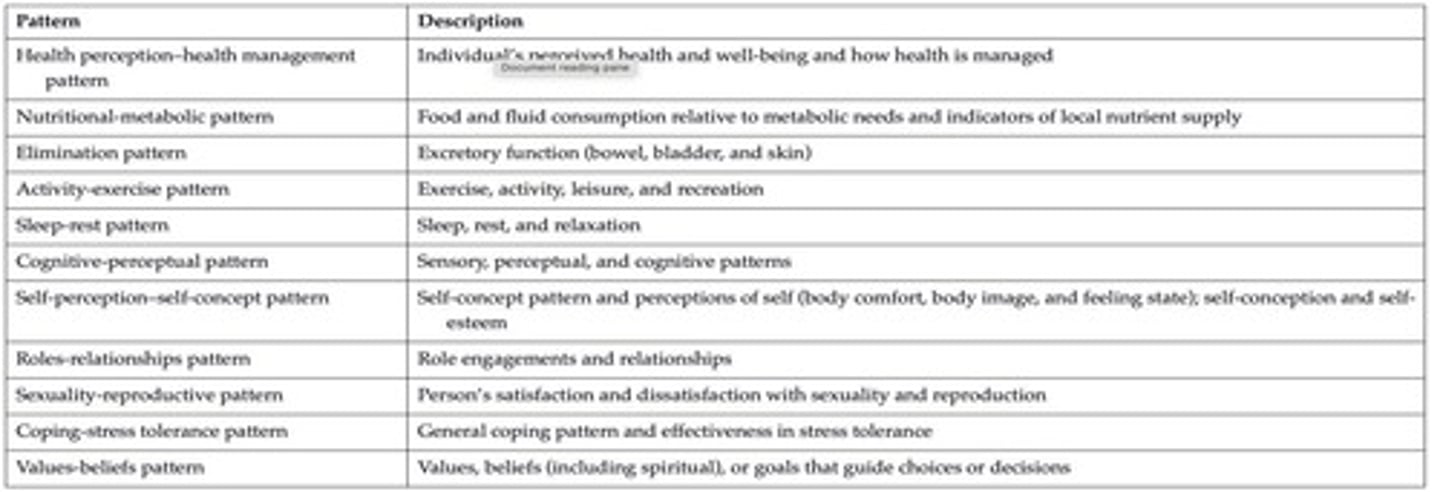
What does dysfunction in health management look like?
Conflict, poor communication, tension, emotional neglect, abuse, and instability.
What is the role of a community nurse?
Collecting data to address family problems and creating, implementing, and evaluating care plans.
What is the purpose of ecomaps and genograms?
Ecomaps show functional relationships, while genograms highlight family membership and structure.
What is the Clinical Reasoning Model in nursing?
A model used to identify problems and follow through with the nursing process.