Skull/Spine Imaging
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Why is taking rads of the head complicated?
Lots of superimpositions
Need gen anesthesia
Will need multiple obliques to see thing
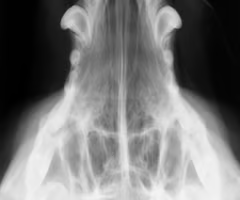
What view do we use to valuate the nasal cavity and maxilla?
Ventrodorsal open mouth
It is important to _____ the nose when taking a radiograph of the nasal cavity?
Prop so it is level
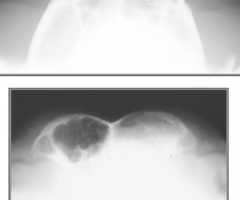
What view is used to look at the frontal sinus?
Rostral caudal
What view can you use to look at the tympanic bulla?
Rostral caudal open mouth - usually easy to see b/c gas filled structures prevent superimposition
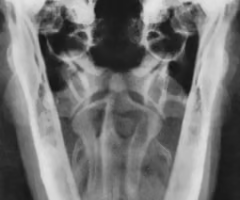
When suspecting Otitis media we should take ___ views?
Multiple views to evaluate each tympanic bulla
What modality of imaging is more commonly used to view the tympanic bulla?
CT
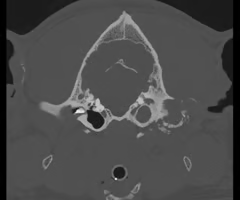
Which side is abnormal?
R - Mineralization and fluid in canal/ bulla
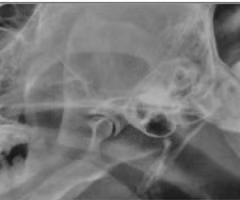
What is best viewed by a lateral oblique?
Temporomandibular joint
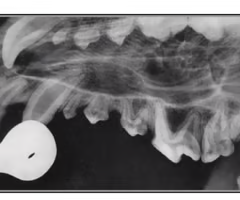
How do you view teeth on radiograph?
Lateral oblique
Why is it difficult to take equine skull rads?
Can't open mouth as wide
Must be done standing
More superimposition
How are most radiographs of the equine skull taken?
Intraoral dorsal ventral - can be ventral dorsal if plate turned
What animal is dental dz more of a problem in that rads play a large role in?
horses
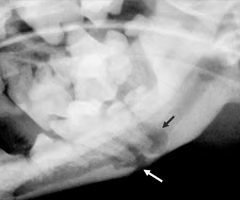
What view is this and what is the pathology?
Oblique - tooth route abscess
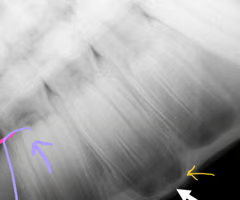
Is the yellow arrow a pathology?
No- common in young horses w/ teeth still growing
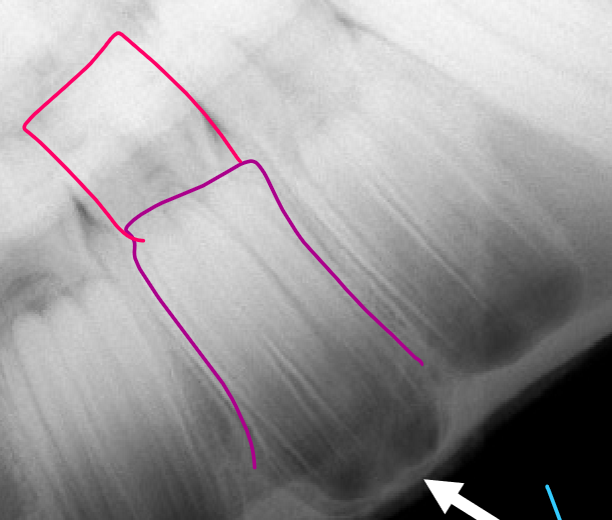
What is the pink structure?
Dental cap/ baby tooth
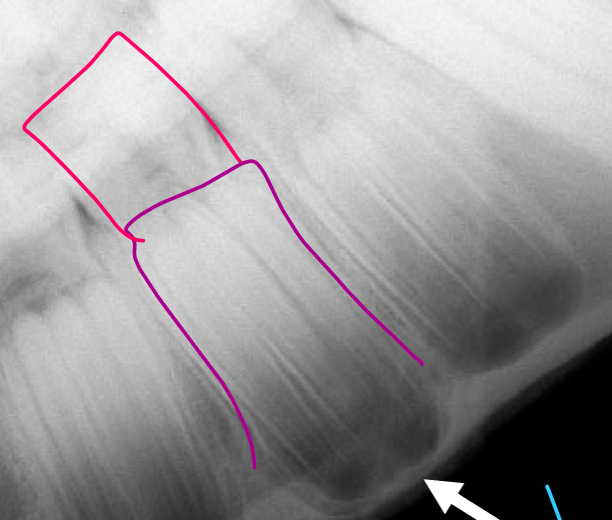
What is the purple structure?
Adult tooth
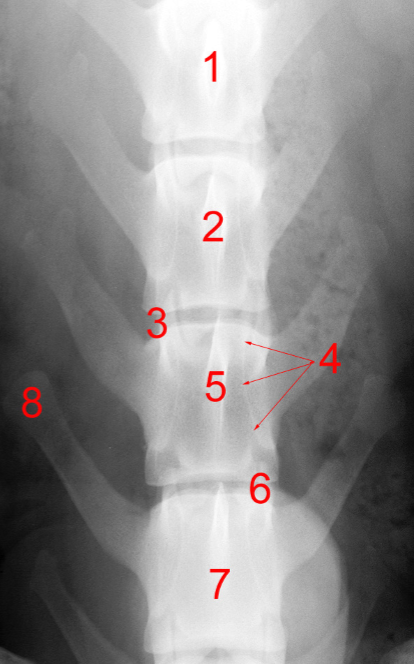
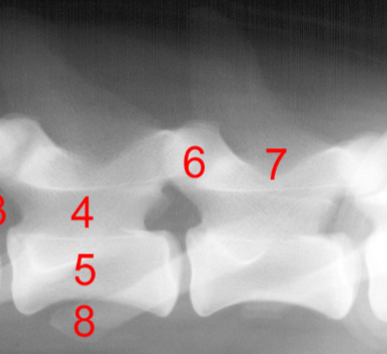
Identify structure 1, 2, 5, 7:
Spinous process
Vertebral body
Vertebral canal
Dorsal laminae
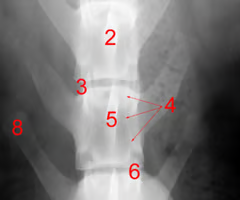
Identify structure 3:
Intervertebral foramen
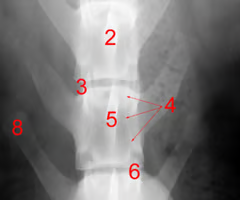
Identify structure 4:
Pedicle
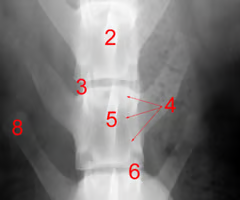
Identify structure 6:
Articular process
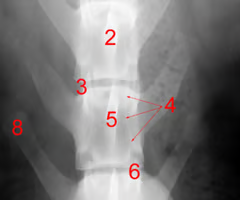
Identify structure 8:
Transvers process
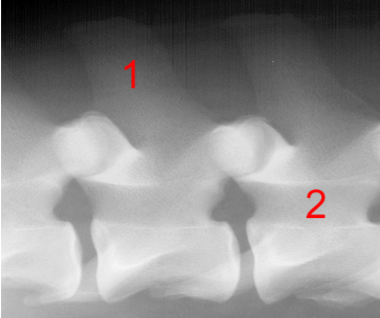
Identify structure 1:
Spinous process

Identify structure 2 and 4:
Vertebral canal
Pedicle

Identify structure 3:
Intervertebral foramen

Identify structure 5:
Vertebral body

Identify structure 6:
Articular process
Identify structure 7:
Dorsal laminae

Identify structure 8:
Transverse process
Name the number of vertebrae in most species:
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Cervical 7
Thoracic 13
Lumbar 7
Sacral 3-fused

Identify the species?
Feline
-ribs thin
-vertebrae long/rectangular

Identify the species?
Canine
-Thick blocky vertebrae
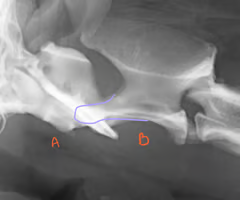
Identify the structures?
A: Atlas C1
B: Axis C2
Purple: dens
What does the dens allow for?
rotation of head
What is spondylosis?
Osteophytes of the spine to stabilize the joint
What may need to be done to see the Dens if it is superimposed w/ the atlas wings ?
Rotate the head
Why might we only take one lateral view of the spine?
Trauma/ discspondylitis
You can only evaluate disk spaces in the ____ of a rad b/c radiographs radiate out?
Center - periphery can't be accurately evaluated
What are risks of a myelogram?
Invasive
Seizures
-CT/MRI replaced
Where do we give contrast medium?
Subarachnoid space at L5-L6 b/c spinal cord has ended here
An extradural mass and intramedullary mass will look the same on ___ but different on ___?
VD
Lat
What are possible pathologies of extradural masses?
Abscess
disc extrusion
Tumor
Hemorrhage
What are possible pathologies for an intramedulary mass?
Edema
Tumor
What is the only dx for an intradural extra medullary mass?
Tumor
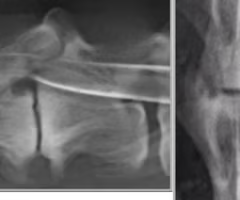
Identify the pathology?
Extradural

Identify the pathology?
Intramedullary
What are two signs of intradural extra medullary?
Golf tee sign -widening subarachnoid
Filling defect
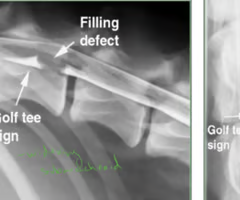
Identify the pathology?
Intradural extra medullary