Chapter 5 - Emotional Intelligence: Physiology of Emotions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Central Nervous System
The nervous system at the brain and spinal cord
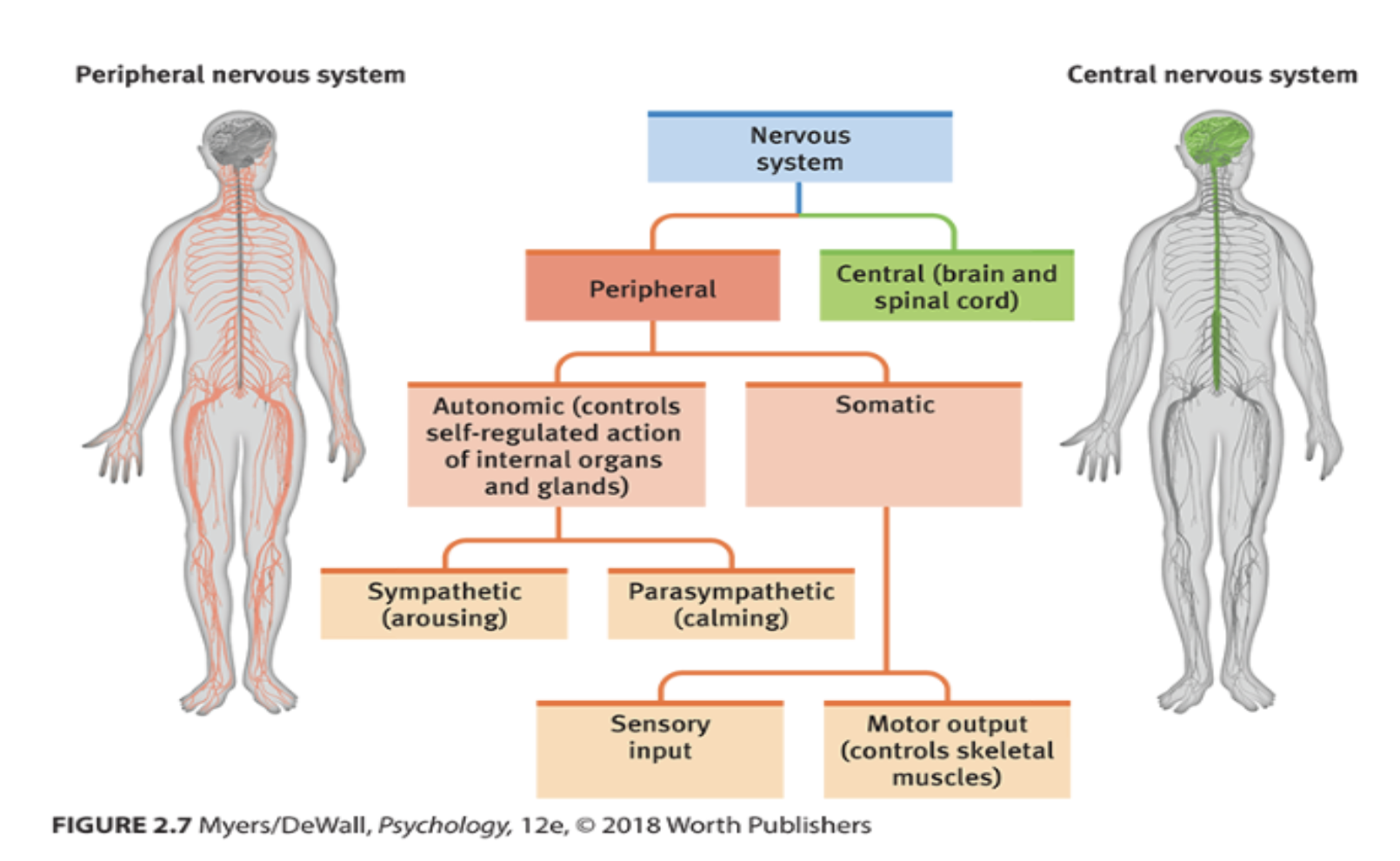
Peripheral Nervous System
The nervous system that isn’t the brain and spinal cord
Contains the autonomic nervous system
regulates physiological responses and therefore automatic
Within, has the sympathetic nervous system that controls “fight or flight” and handles arousing reactions
Within, also has the parasympathetic nervous system that allows the body to relax and “rest and digest”
Contains the somatic nervous system
delivers information to the brain under everything the body can control
The Limbic System
The structures in the brain that are most important for memory
Hippocampus: responsible for processing factual memories
Amygdala: process emotional responses, especially fear and anger
Memories with those emotions are easiest to remember
Cingulate Gyrus: regulates emotions and learns from mistakes
Hypothalamus: controls the release of hormones
Pituitary Gland: releases the hormones
Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex: connects limbic systems and interprets physiological responses
Periaqueductal Gray: responsible for fight or flight response
Hippocampus
The structure in the limbic system that processes your memory’s facts and events that took place
Amygdala
The structure in the limbic system that processes emotional events
Most significantly anger and fear
Reason why we remember memories attached to those the most
Cingulate Gyrus
The structure in the limbic system that helps learn from mistakes and unpleasant experiences via processing the emotions
Hypothalamus
The structure in the limbic system that controls with homeostasis and the release of hormones
Pituitary Gland
The structure in the limbic system that releases the hormones
Examples: Dopamine, Serotonin, Estrogen, Testosterone
Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex
The structure in the limbic system helps make decisions by interpreting the physiological responses that are connected by all the structures
Periaqueductal Gray
The structure in the limbic system that is responsible for triggering fight-or-flight responses
Comes hand in hand with compassion as it gives one the ability to act against one’s suffering
Ventral PAG: freezes one in place
Dorsolateral PAG: if the stressor gets too close, it will trigger fight or flight
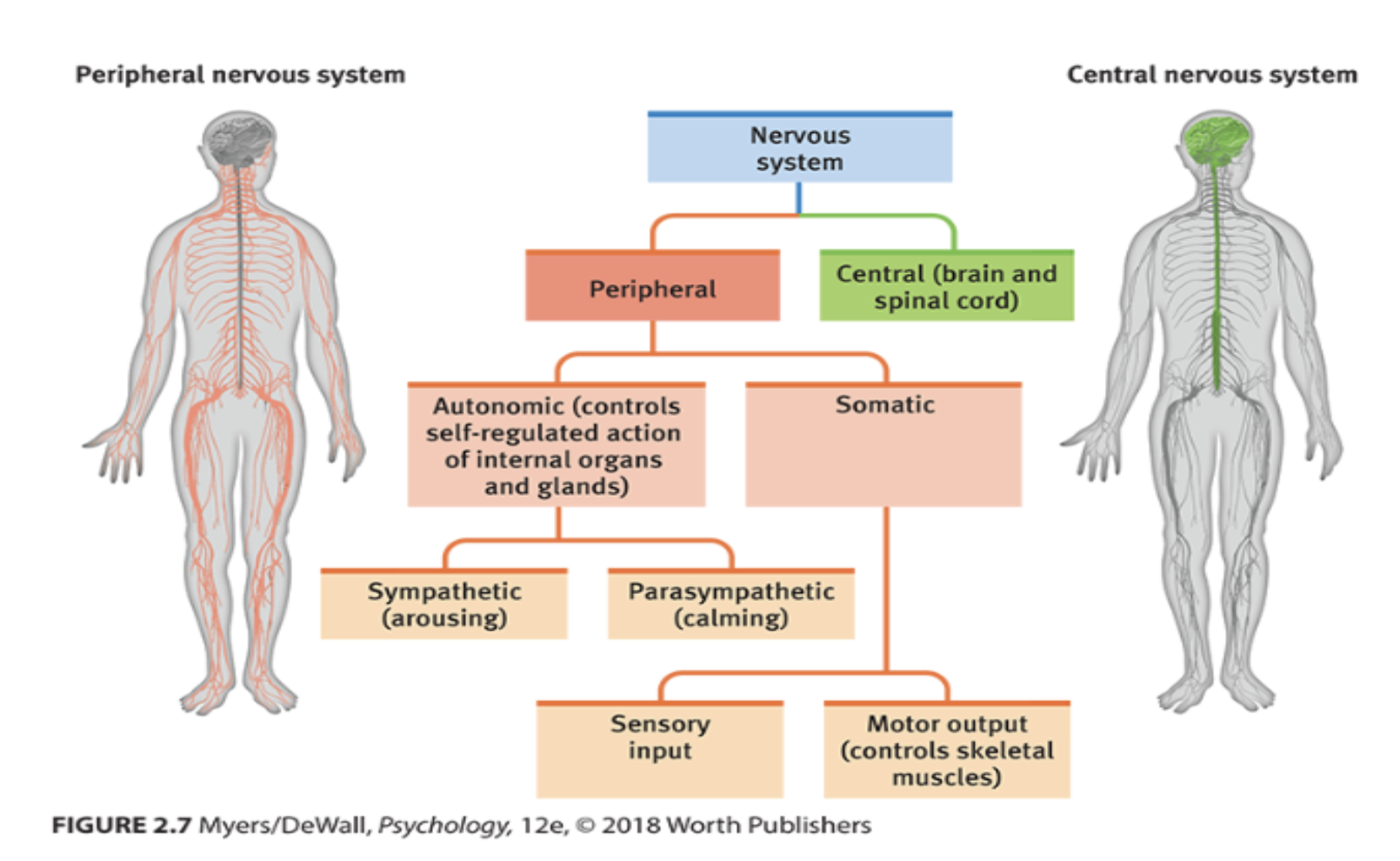
Neural Pathway of Fear
The pathway in which the brain processes fear
Example of how it works for fear:
The Lateral Nucleus receives an external stimulus
The Basal Nucleus processes the context of it by the hippocampus
Information goes to the Striatum, which influences action
Also goes to the central nucleus to send information to the Brain stem to make the body produce a physiological response
Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex will place the label on the emotion
Levenson et al Study
A study on facial movements on autonomic physiology
Results: Showed that each emotion has their distinct physiological activation
It went against the core affect theory with the belief that there were too many overlapping physiological reactions
Autonomic Responses for Positive Emotions
Physiological responses to positive emotions tend to overlap the most
The body doesn’t feel the need to change
greater activation of vagus nerve is strongly connected with positive emotions
Blushing
The most noticeable autonomic response
Happens when one feels shame or embarrassment
Increased blood volume in the face
Culturally universal, most common in western cultures
Chills
A nonverbal behavior that can be either positive or negative emotion
Goosebumps: Positive Chills
Cold Shivers: Negative Chills
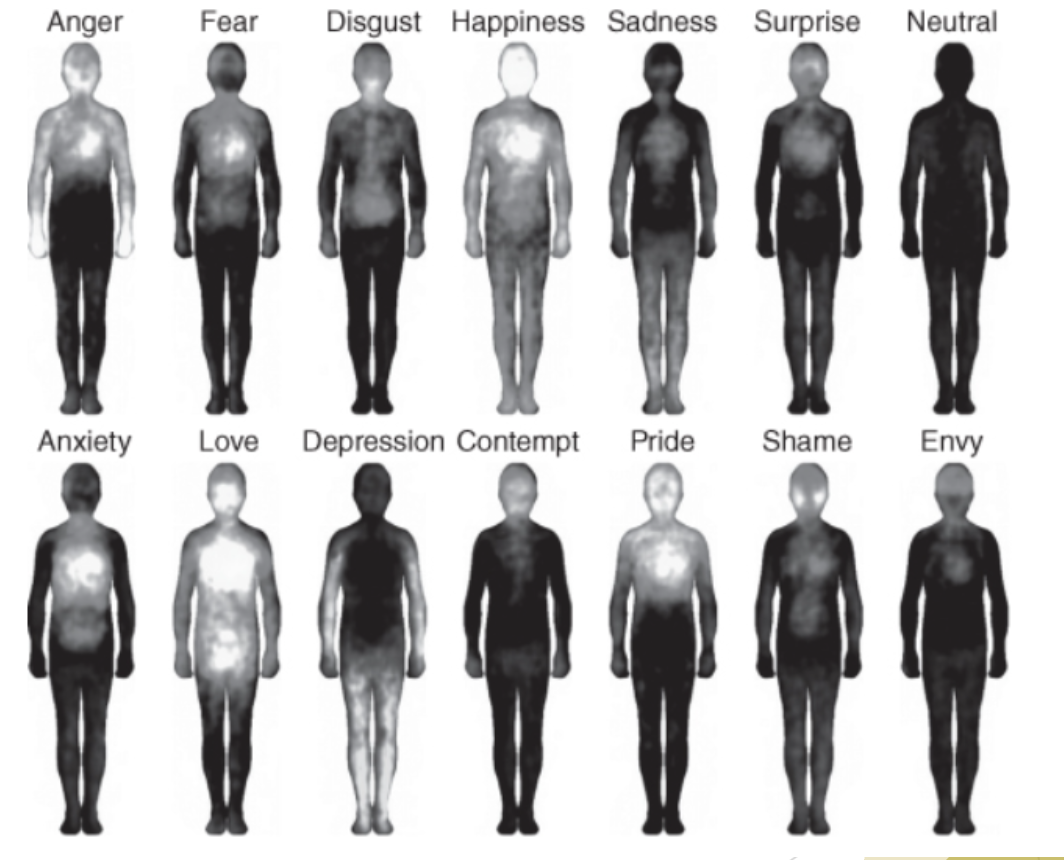
Nummenmaa et al Study (2014)
A study conducted where participants colored parts of the body where they felt the most of emotion
Lighter colors mean the stronger the emotion is in that certain area
Supports physiology
Results: Mostly universal across several cultures
Sympathoedullary Pathway (SAM)
The pathway in the body’s quick response to a stressor
The fight or flight response
Heart rate increases
Alpha-amylase (breaks down sugars) activity increases
Blood pressure increase
Breathing increases
HPA Axis
The pathway in the brain that processes the slow responses to stress
Releases cortisol (stress hormone)
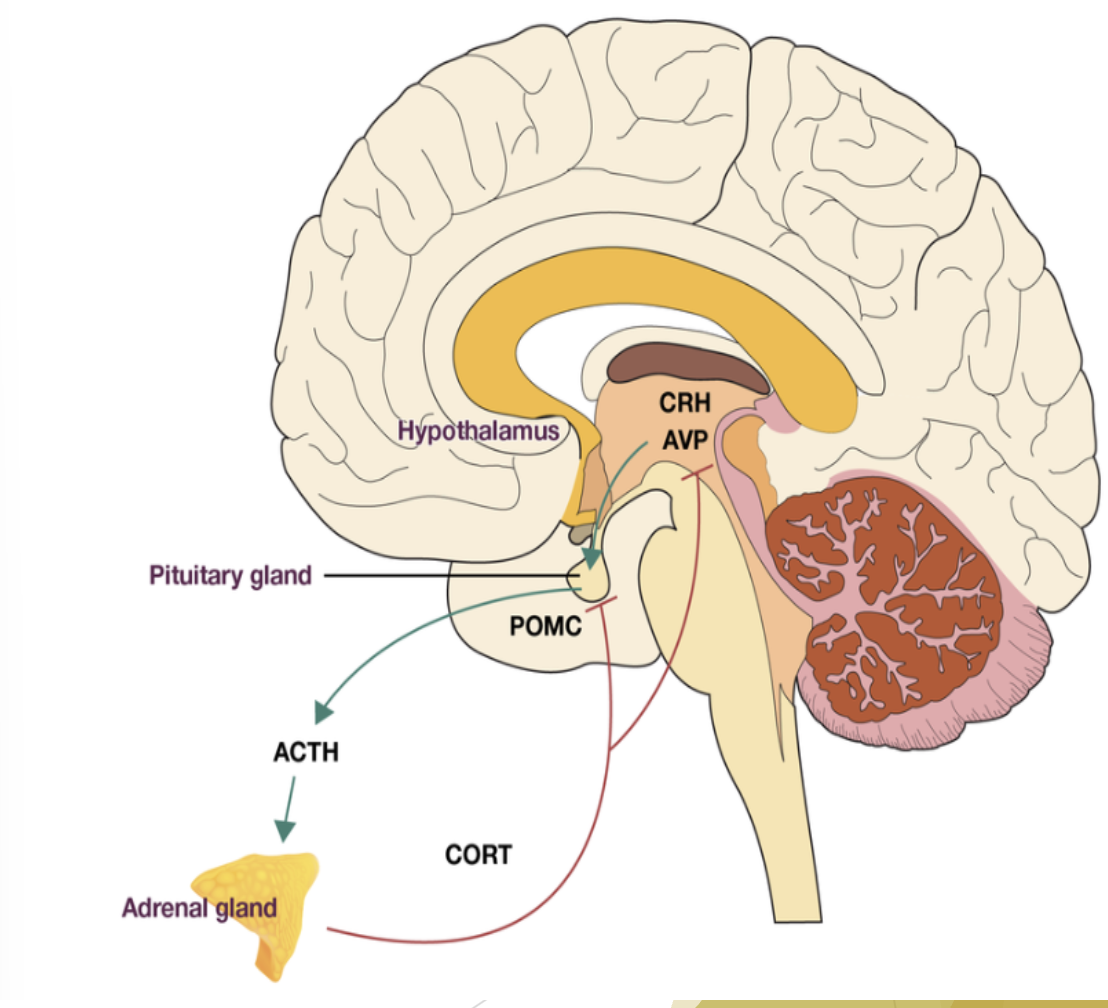
Cortisol
The hormone released in stressful situations
Mineralocorticoids (MR) like cortisol and will bind to it
Activation will improve memory
Glucocorticoids (GR) do not like cortisol as much
Cortisol won’t bind here unless MR is too full
Will impair memory
Stress & Memory
A little bit of stress is good for the body, but excessive stress will be damaging to the memory
Hippocampus will shrink as a result
The cortisol receptor GR will be damaging, as they don’t accept cortisol too well
Activation will impair memory as well
Trier Social Stress Test
A stress test that invokes stress in humans
Stress can be measured using heart rate, blood pressure, cortisol, alpha-amylase, and heart rate variability (amount of time between heartbeat)
Cytokines
Proteins for cell signaling
Elevated stress causes pro-inflammatory cytokines to be released
Induces immune response and fights bacteria and viruses
Can lead to sicknesses
Often correlated with embarrassment and shame