Abnormal Findings and Disorders (CNS)- VERY IMPORTANT
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
Autoimmune destruction of myelin sheath in CNS
What are the symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis?
Progressive weakness
Gait instability
Bladder dysfunction
Sensory loss
Vision changes (optic neuritis)
What is Meningitis?
Bacterial or viral infection → inflammation of the meninges
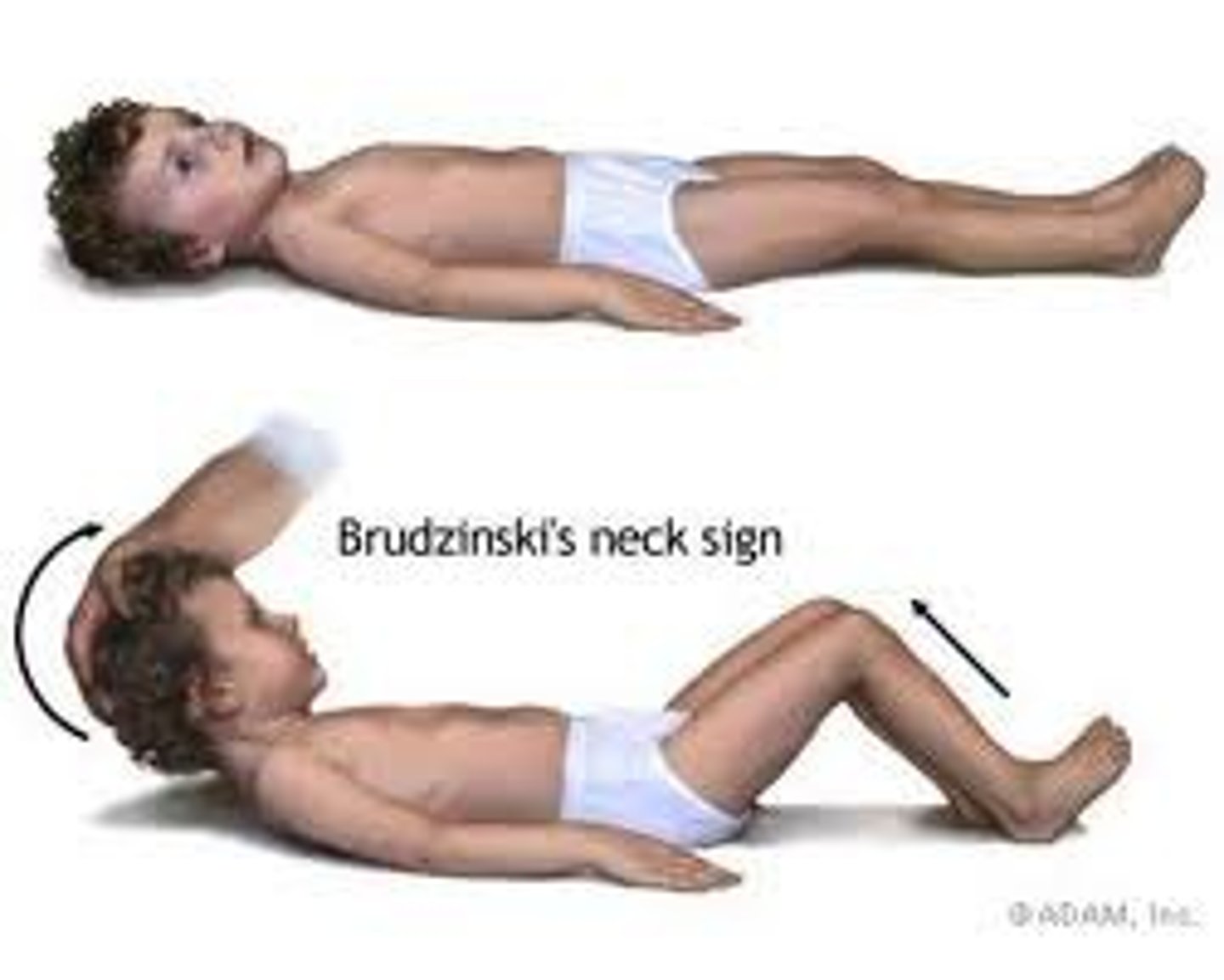
What are the key signs of meningitis?
Kernig's sign and Brudzinski's sign
Brudzinski's sign
Flexion of hips/knees when neck is flexed → indicates meningeal irritation.
Kernig's sign
Pain with extension of knee when hip is flexed.

What is Generalized seizure disorder?
Episodic, sudden, involuntary contractions of a group of muscles caused by excessive discharge of cerebral neurons.
What causes Generalized seizure disorder?
Systemic disease, head trauma, toxin, stroke, hypoxic syndromes
What are some Symptoms of Generalized seizure disorder?
Disturbances in consciousness, behavior, sensation, and autonomic functioning. Urinary and fecal incontinence can occur.
What is stage 1 of Lyme disease?
Bulls eye rash
What is stage 2 of Lyme disease?
Cardiac/neuro symptoms
What is stage 3 of lyme disease?
Chronic arthritis, worsening neuro involvement.
What is a Space-Occupying Lesion?
It can be a primary tumor or a metastatic mass.
What is cerebral palsy?
A non-progressive disorder of muscle tone, posture, & movement.
Often associated with:
- Cognitive problems
- Sensory impairments
= Speech issues
What is Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH)?
Increased CSF in the ventricles - enlarged ventricles, but the CSF pressure is normal on the lumbar puncture
Signs of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH)?
Gait disturbance (magnetic gait)
Urinary incontinence
Cognitive changes
Treatment of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH)?
Ventriculoperitoneal (V-P) shunt.
What is Spina Bifida?
A Neural tube defect → incomplete development of the brain, spinal cord, or coverings.
What is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)?
Progressive degeneration of motor neurons.
Muscle weakness
Atrophy
Fasciculations
Eventual respiratory failure
What is a Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)?
Brain Attack or Stroke- sudden focal neurologic deficit resulting from impaired circulation to/within the brain
What CVA's caused by?
Thrombosis (most common)
Embolism
Hemorrhage
- Most occur in anterior circulation.
What are some Stroke Warning Signs?
Sudden weakness/numbness
Sudden vision problems:
Sudden confusion, difficulty speaking (aphasia) or articulating (dysarthria)
Sudden severe headache
Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, coordination problems
Remember: Right brain → left body, and vice versa.
What is Diplopia and its types?
(Double vision) perception of two images of the same object that may be side by side, on top of each other, or diagonal.
Monocular diplopia
Binocular diplopia
Monocular Diplopia
Double vision persists when one eye is covered.
Usually due to problems within the eye itself, such as: Corneal irregularities (e.g., keratoconus, scar)
Lens problems (e.g., cataract)
Refractive error or astigmatism
Binocular diplopia
Double vision occurs only when both eyes are open; it disappears if either eye is covered.
Caused by misalignment of the eyes — the two eyes are not pointing at the same target.
What causes Binocular diplopia?
Cranial nerve palsies (III, IV, VI)
Extraocular muscle disorders (e.g., myasthenia gravis)
Orbital trauma or tumors
What is BE FAST?
Balance - watch for sudden loss of balance
Eyes - Check for vision loss
Face - Look for uneven smile
Arm - Check if one arm is weak
Speech - Listen for slurred speech
Time - Call 911 right away