receptive fields
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:22 PM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
how many ganglion cells are there?
1 million
2
New cards
what do ganglion cells do?
condense raw info from photorecepetors
* aims to extract important info from the retinal image
* aims to extract important info from the retinal image
3
New cards
what is single cell recording?
an electrode is inserted into a neuron which measures electrical activity of a SINGLE neuron
* electrode measures the spike in voltage during action potential
* electrode measures the spike in voltage during action potential
4
New cards
how do you use single cell recording to measure the activity of the ganglion cell?
* as the ganglion cell is always active experimenters try to find a stimulus that changes the activity of that ganglion cell
5
New cards
what is a receptive field?
its the area on the retina which, when stimulated by light, elicits a change in the firing rate of a cell
6
New cards
what is an excitatory responce?
increase in cell’s response rate
7
New cards
what is an inhibitory responce?
decrease in cell’s response rate
8
New cards
why are ganglion cells influenced by a region on the retina?
convergence
* multiple neurons in the retina send signals to a single neuron in the brain
* allows the brain to recieve input from a larger area of the visual field, which can improve the sensitivity and resolution of visual info
* can also reduce the amount of detail that is transmitted to the brain
* multiple neurons in the retina send signals to a single neuron in the brain
* allows the brain to recieve input from a larger area of the visual field, which can improve the sensitivity and resolution of visual info
* can also reduce the amount of detail that is transmitted to the brain
9
New cards
what is lateral inhibition?
inhibition that is transmitted across the retina by horizontal and amacrine cells
* the inhibition creates a contrast between the stimulated photoreceptor and its neighbours, which enhances the perception of edges and boundaries in the visual field
* the inhibition creates a contrast between the stimulated photoreceptor and its neighbours, which enhances the perception of edges and boundaries in the visual field
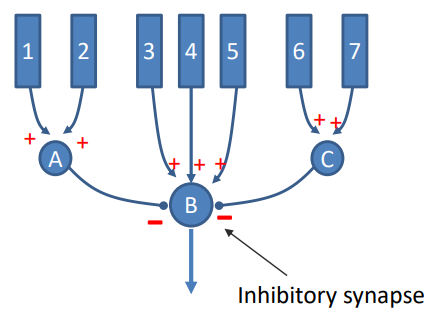
10
New cards
what are horizontal cells?
specialized cells in the retina that connect photoreceptor cells to bipolar cells
* responsible for lateral inhibition - inhibits surrounding photoreceptors
* responsible for lateral inhibition - inhibits surrounding photoreceptors
11
New cards
what are the 2 centre-surround antagonism?
* on-centre off-surround
* off-centre on-surround
* off-centre on-surround
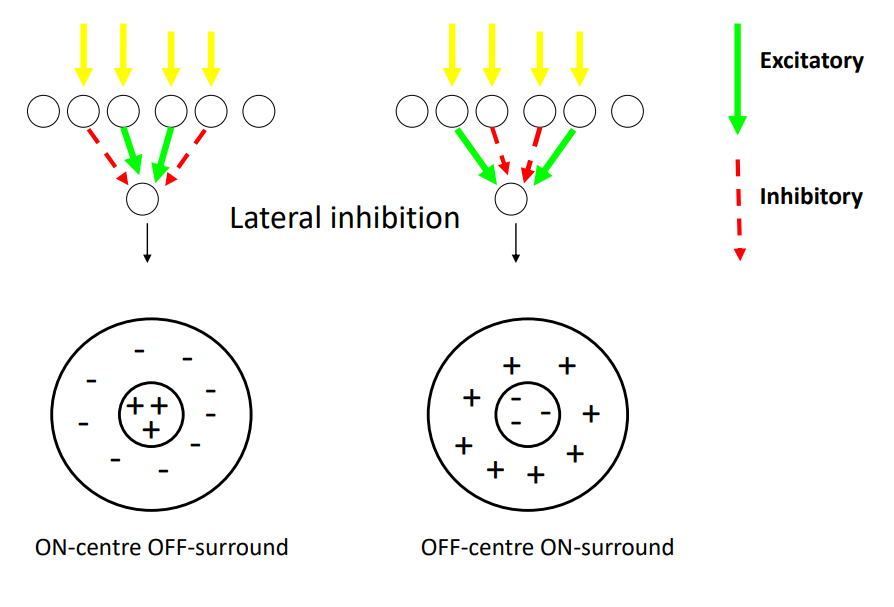
12
New cards
what does an on-centre off-surround cell look like with different light?
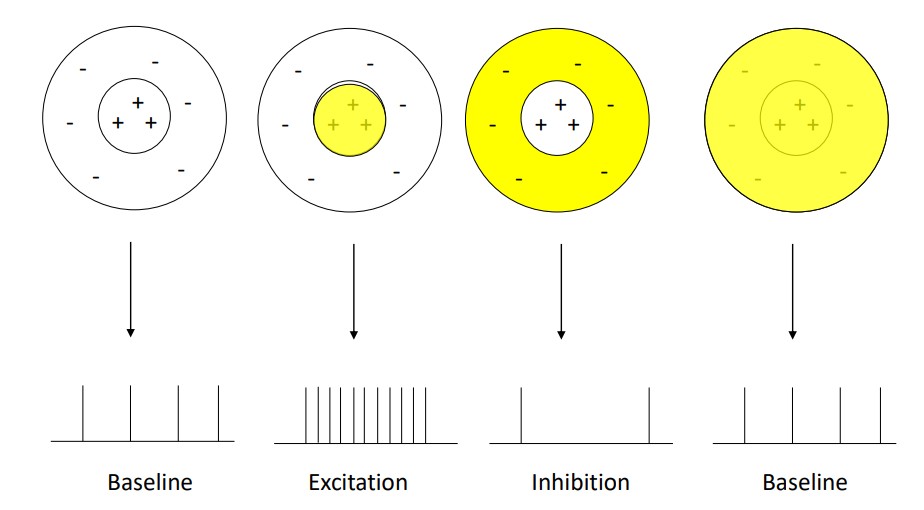
13
New cards
what does an off-centre on-surround cell look like with different light?
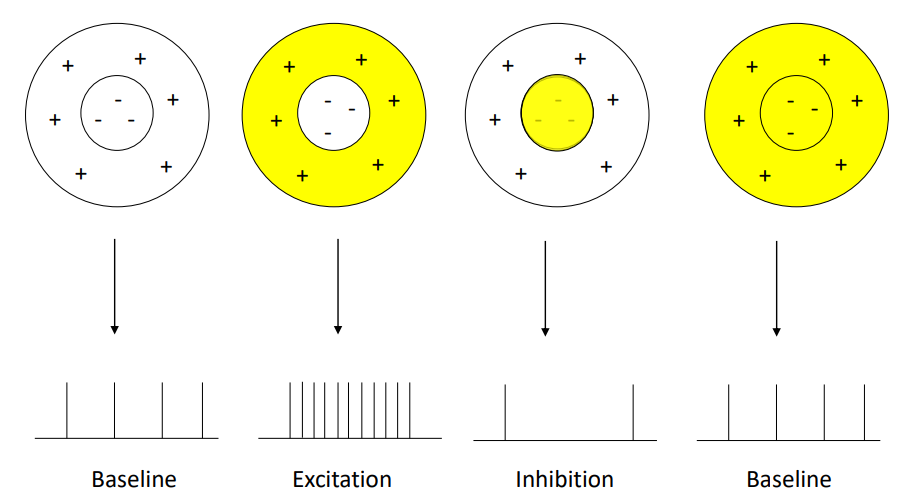
14
New cards
why do we have this organisation of ganglion cells on the receptive field?
ganglion cells respond to changes in light falling in the receptive field
15
New cards
what are ganglion cells not able to detect?
* orientation of bars
* no response to change in overall level of illumination
* no response to change in overall level of illumination
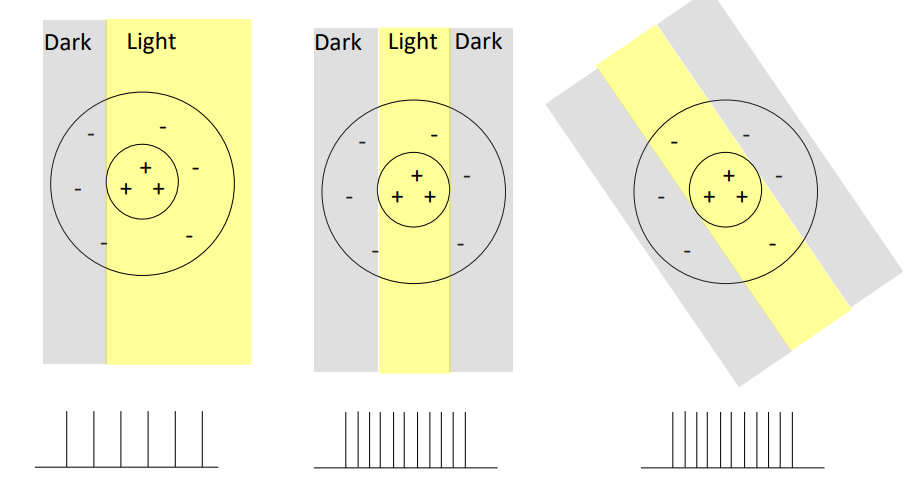
16
New cards
why do ganglion cells respond to changes in patterns of light?
changes carry out the most important info
* boundaries between areas of light & dark that carry the most important
* they have to condense down the amount of info the photoreceptors are providing (too much info)
* boundaries between areas of light & dark that carry the most important
* they have to condense down the amount of info the photoreceptors are providing (too much info)
17
New cards
how do ganglion cells reduce the amount of info from photoreceptors?
by selectively responding to certain types of info and ignoring others
* they do this by integrating signals from multiple bipolar cells and comparing the relative levels of extinction and inhibition they recieve
* allows for the detection of edges, motion, and colour
* they do this by integrating signals from multiple bipolar cells and comparing the relative levels of extinction and inhibition they recieve
* allows for the detection of edges, motion, and colour

18
New cards
how can receptive fields explain the hermann grid?
* two on-centre cells centred on light regions of the grid
* when RF at intersection - more light falls on the surround (OFF region) so receives more inhibition and cells fire less
* less firing interpreted as less bright so we perceive a dark spot
* when RF at intersection - more light falls on the surround (OFF region) so receives more inhibition and cells fire less
* less firing interpreted as less bright so we perceive a dark spot
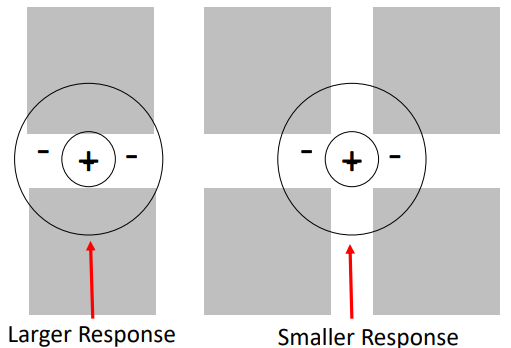
19
New cards
how is the hermann grid typically explained?
1. centre-surround antagonism
2. varying receptive field sizes
20
New cards
how can simultaneous contrast illusions be explained?
* when light falls on the photoreceptors, it generates an electrical signal that is transmitted to the brain
* lateral inhibition occurs when photoreceptors send signals to each other through horizontal cells, which sends signals to bipolar cells and ganglion cells
* the on-centre ganglion cell in the grey objects RF are inhibited by the horizontal cells because the photoreceptors in the grey object receives less light than those in the white object
* lateral inhibition occurs when photoreceptors send signals to each other through horizontal cells, which sends signals to bipolar cells and ganglion cells
* the on-centre ganglion cell in the grey objects RF are inhibited by the horizontal cells because the photoreceptors in the grey object receives less light than those in the white object
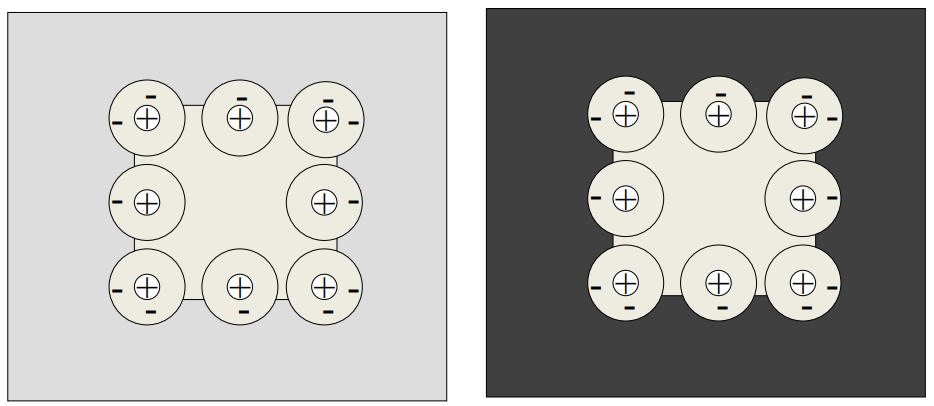
21
New cards
what is the simultaneous contrast illusion?
it occurs when the brain perceives the colour of an object to be different based on the colours of the surrounding objects