Unit 7-- Lymphatic & Immune Systems:
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Epidemiologist
Investigates the cause of disease + works to control the spread
Functions of blood:
oxygenate body tissues
remove waste
defend against infection and disease
blood clotting
Red blood cell functions:
Manufactured in the bone marrow
Carry oxygen to body cells
Remove carbon dioxide
Contain hemoglobin
White blood cells:
Defend against infection and disease
Manufactured mainly in the bone marrow
Systems within the immune system:
integumentary system
respiratory system
digestive system
lymphatic system
Bone Marrow Biopsy-
Needle inserted into bone marrow cavity.
Small amount is aspirated.
Needle Biopsy-
Needle inserted
Tissue removed for examination
Autoimmune Disease-
The immune system attacks its own cells
Functions of immune system:
Defends against pathogens
Recognizes self vs. non-self
Destroys infected/abnormal cells
Produces inflammation
Makes antibodies
Creates immune memory
Removes dead/damaged cells
Natural Immunity-
Type that you are born with.
Acquired Immunity-
the body’s ability to protect itself against specific bacterium
Acquired Active-
when body is exposed to and learns to defend itself against one type of pathogen.
Antibodies-
Blood protein produced in response to a specific antigen. Combine chemically with substances that the body recognizes as alien.
Debilitating-
a weakening or fatiguing effect
Hypersensitivity-
condition in which the body reacts with an exaggerated immune response to an allergen
Iatrogenic-
diseases or conditions that arise as a complication of medical or surgical intervention
Immunological-
Pertaining to a reaction between an antigen and an antibody
Ischemic-
conditions or diseases that are caused by a temporary deficiency in blood flow to an organ or tissue
Metabolic-
disorders that interfere with the chemical processes involved in converting food to energy
Nutritional-
Pertaining to chemical processes in the body that occur after ingesting (eating) food
Opportunistic-
term for diseases or conditions that do not take hold unless the immune system is in a weakened state
Definition of immune system:
system of cells, tissues, organs, and vessels that work together to defend your body against infection and disease.
Lymphocytes:
Detect antigens and destroy them
Tonsils:
lymphatic tissues that trap pathogens entering the mouth and nose
Lymph nodes:
Small structures located throughout the body. Filter foreign substances from the lymph before it is returned to the blood.
Hemolysis:
process by which worn-out erythrocytes are destroyed
Liver:
converts glycogen into glucose when the body’s cells need energy,
filters the blood, serves as storehouse for healthy erythrocytes
Immunity definition:
ability to resist pathogens and toxins that cause infection or disease
How is lymph different from blood:
Lymph= no platelets or RBCs
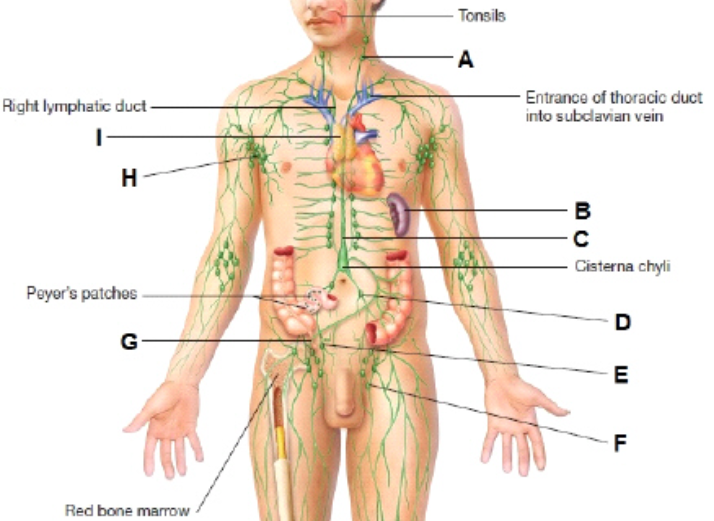
What is A?
cervical lymph node
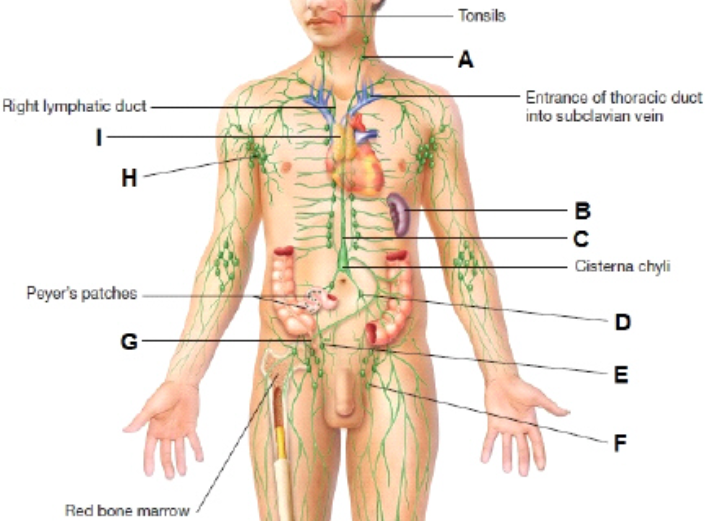
What is I?
thymus
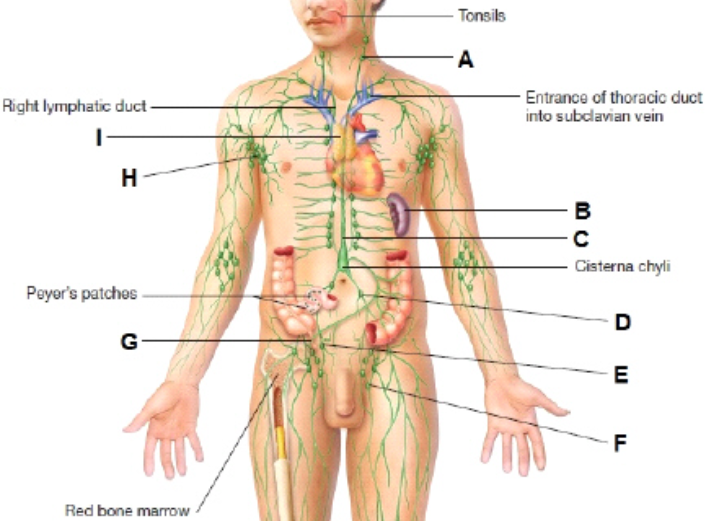
What is H?
Axillary lymph node
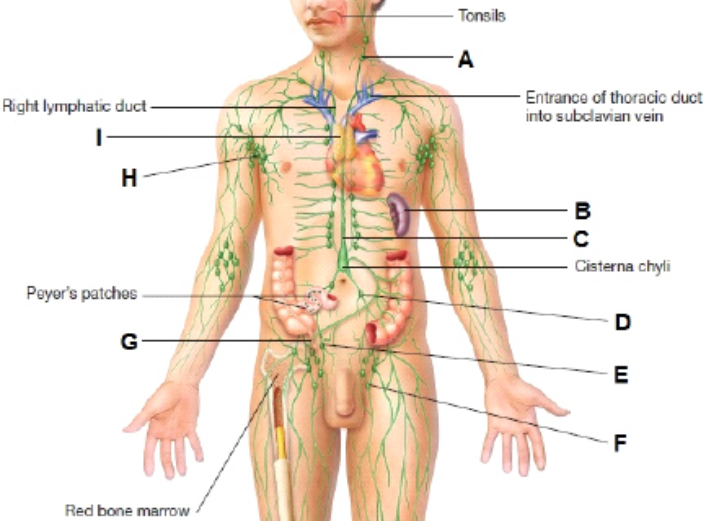
What is B?
Spleen
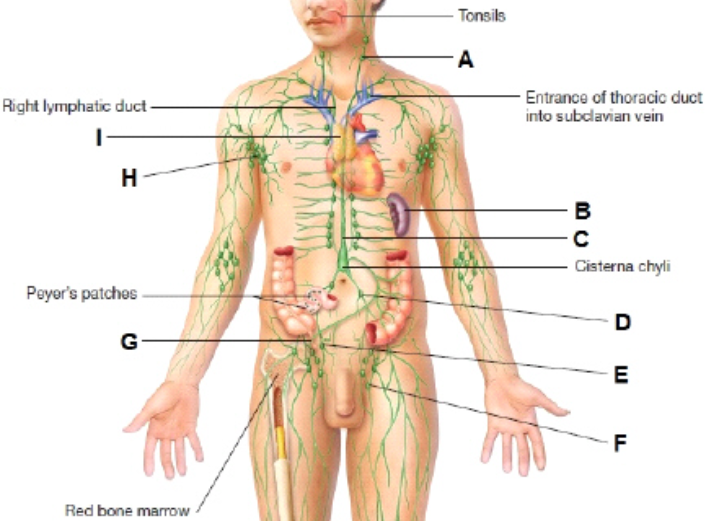
What is G?
Appendix
How can a person live without a spleen:
The liver and bone marrow help remove old red blood cells
Lymph nodes and white blood cells still fight infections
Spleen:
Thymus:
Organ where T cells mature and learn to recognize self vs. non-self
Lymphatic vessels:
Tubes that carry lymph fluid back to the bloodstream
Lymphatic capillaries:
Microscopic vessels where lymph first forms from tissue fluid
IgD
immunoglobulin D
IgA
immunoglobulin A
Hx, hx
history
HIV
human immunodeficiency virus
HIB
Haemophilus influenzae bacteria
HBV
hepatitis B virus
g/dL
grams per deciliter
eos
eosinophils
EBV
Epstein-Barr virus
Dx
diagnosis
diff
differential
cu mm
cubic millimeters
CT
computed tomography; computerized tomography
CC, c/c
chief complaint
CBC
Complete blood count
baso
basophils
bands
immature white blood cells (granulocytes)
AIDS
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
IgD
immunoglobulin D
T-cells
White blood cells that directly attack infected or abnormal cells
Bronchodilators –
Drugs that open airways in the lungs
Corticosteroids –
Drugs that reduce inflammation and immune activity
Epinephrine –
Hormone/drug used to treat severe allergic reactions
Vasoconstrictor –
Substance that narrows blood vessels
Bone marrow transplant –
Replacement of damaged bone marrow with healthy cells
Immunotherapy –
Treatment that uses the immune system to fight disease
Immunosuppressant –
Drug that weakens immune responses
Antibiotic –
Drug that kills or slows bacteria
Antifungal –
Drug that treats fungal infections
Antiviral –
Drug that treats viral infections
Antihistamine –
Drug that reduces allergy symptoms
Antineoplastic –
Drug used to treat cancer
Antitoxin –
Substance that neutralizes toxins
Biologic –
Drug made from living cells to target immune processes
Cytotoxic drug –
Drug that kills rapidly dividing cells