lab exam 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:26 AM on 4/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
what is a sarcomere
the fundamental repeating unit of a muscle causing the contraction
2
New cards
what are the parts of a sarcomere
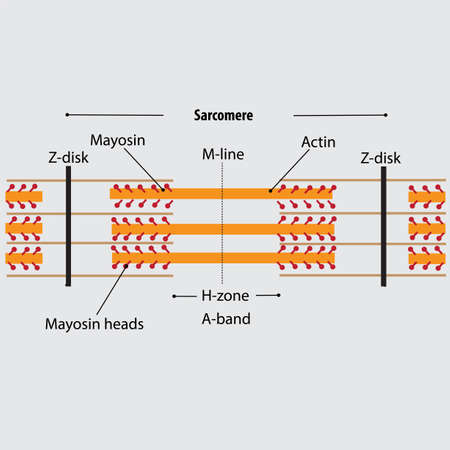
3
New cards
what are the component parts of a muscle fiber
the myofilaments actin and myosin along with the dark a band and the light i band making up the sarcomeres and the transverse tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum
4
New cards
what is occurring at a neuromuscular junction
the space between the nerve and the muscle and is responsible for transmission of electrical impulse from a nerve to the muscle
5
New cards
what are the parts of a neuromuscular junction
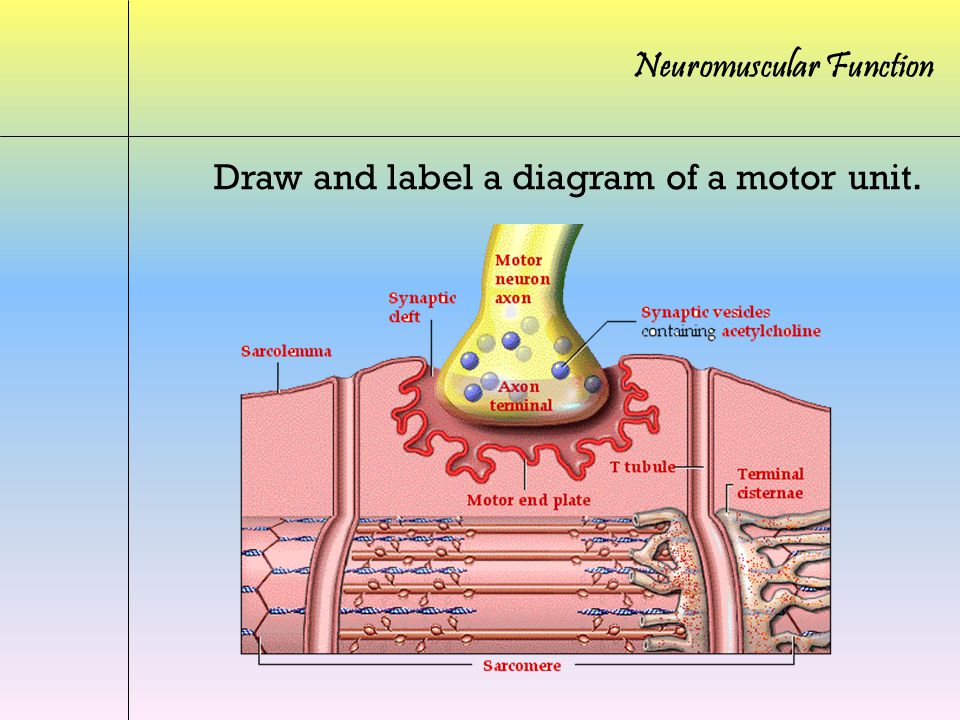
6
New cards
what are the three phases of a muscle twitch
lag phase, contraction phase, relaxation phase
7
New cards
what is the lag phase
the time when the electrical impulse travels across the muscle cell membrane and calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
8
New cards
what is the contraction phase
the myofilaments slide across one another and the muscle fiber shortens causing a contraction
9
New cards
what is the relaxation phase
the phase in which the fiber returns to a resting state
10
New cards
what are the parts of the sliding filament model
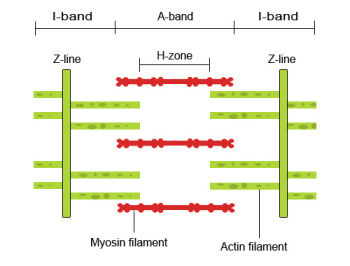
11
New cards
what types of filaments are present at the a band
actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments
12
New cards
what types of filaments are present at the i band
actin (thin) filaments
13
New cards
what types of filaments are present at the h zone
myosin (thick) filaments
14
New cards
what happens at the neuron axon during a skeletal contraction
the action potential reaches the end of the axon and acetylcholine is released
15
New cards
what happens when a neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane
channels are opened and sodium ions enter the cell
16
New cards
how is action potential delivered to the interior of a muscle cell
the t tubules carry the action potential into the interior of a cell
17
New cards
what ion is released in skeletal muscle contraction
calcium
18
New cards
what is a motor unit
a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers innervating it
19
New cards
what are the parts of a motor unit
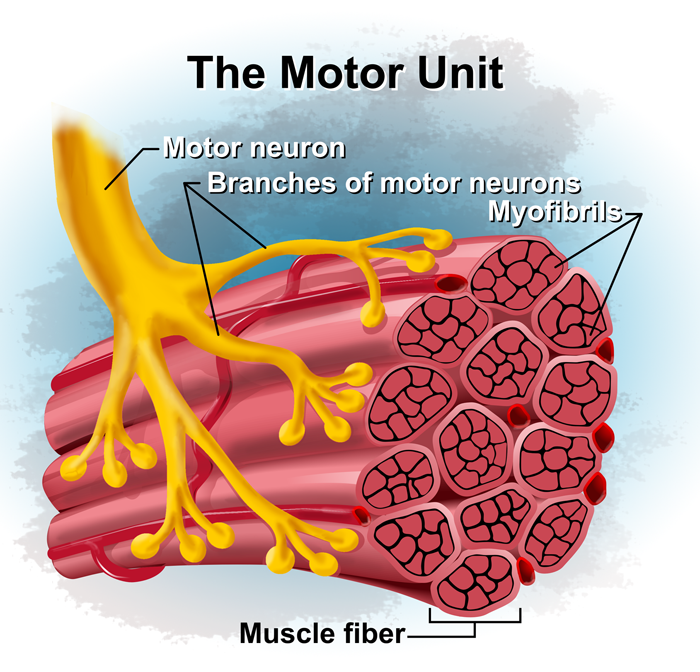
20
New cards
what is a graded response
the amount of action potentials necessary for a muscle contraction
21
New cards
what is temporal summation
changing the frequency of simulation
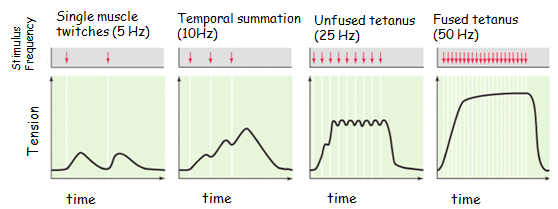
22
New cards
what is multiple unit summation or recruitment
changing the strength of a stimulation
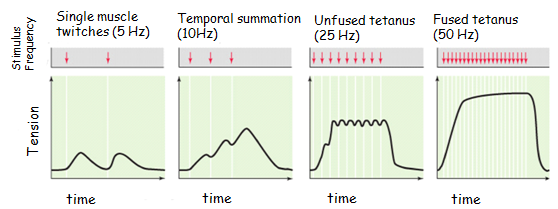
23
New cards
what is fused tetanus
no relaxation between contractions
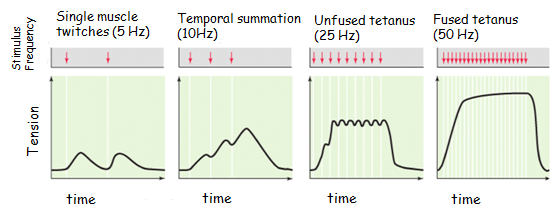
24
New cards
what is unfused tetanus
the muscle fibers do not completely relax
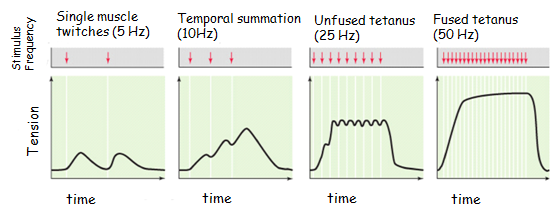
25
New cards
what is an all or nothing response
the muscle fiber either contracts or it doesn’t
26
New cards
epimysium
dense irregular elastic tissue covering the entire muscle
27
New cards
perimysium
dense irregular elastic tissue covering muscle fascicles
28
New cards
endomysium
areolar connective tissue covering the individual muscle fibers
29
New cards
what are the structures of a skeletal muscle fiber
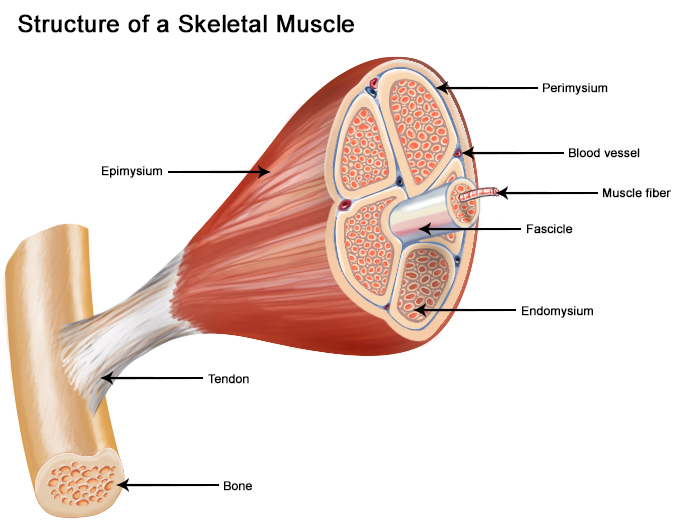
30
New cards
origin
the stationary part of a muscle end
31
New cards
insertion
the more mobile part of a muscle end
32
New cards
muscle function or action
the effects the muscle has on a part of the body
33
New cards
innervation
the name of the nerve that controls the muscle
34
New cards
what are the 8 criteria used to name muscles
shape, location, size, orientation, origin and insertion, number of heads, action and length
35
New cards
what is an example of a muscle named for its location
the tibialis or the frontalis
36
New cards
what is an example of a muscle named for its size
the adductor magnus or gluteus minimus
37
New cards
what is an example of a muscle named for its shape
the deltoid
38
New cards
what is an example of a muscle named for its orientation
the transversus
39
New cards
what is an example of a muscle named for its origin and insertion
the infraspinatus or hallucis
40
New cards
what is an example of a muscle named for its number of heads
the triceps or biceps
41
New cards
what is an example of a muscle named for its action
the extensor
42
New cards
what is an example of a muscle named for its length
the longus or brevis
43
New cards
what are the four muscles of the rotator cuff
subscapularis, infraspinatus, teres minor and supraspinatus
44
New cards
what are the four muscles that make up the quadriceps femoris group
vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, rectus femoris and vastus intermedius
45
New cards
what three muscles make up the hamstring group
biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranous
46
New cards
what three muscles make up the achilles
gastrocnemius, soleus, and the plantaris
47
New cards
what is a a function of the deltoid
arm abduction (raising over ones head)
48
New cards
what is a function of the triceps brachii
extension of the elbow joint
49
New cards
what is a function of the subscapularis
internal rotation of the head of the humerus
50
New cards
what is a function of the infraspinatus
provides glenohumeral stability
51
New cards
what is a function of the biceps brachii
flexion and supination of the forearm
52
New cards
what is a function of the pectoralis major
adduction of the arm
53
New cards
what is a function of the supraspinatus
stabilizes the humerus head on the glenoid fossa
54
New cards
what is a function of the teres major
extend, adduct, and internally rotate the humerus
55
New cards
what is a function of the brachialis
provides flexion of the elbow
56
New cards
what is a function of the supinator
to supinate the forearm
57
New cards
what is a function of the pronator teres
pronates the forearm
58
New cards
what is a function of the latissimus dorsi
adduct and extend the arm at the glenohumeral joint
59
New cards
what is a function of the brachioradialis
flexes the forearm at the elbow
60
New cards
what is a function of the flexor retinaculum
serves as a pulley for the carpal flexor muscles
61
New cards
what is a function of the teres minor
stabilizes the glenohumeral joint by helping hold the humeral head
62
New cards
what is a function of the trapezius
helps to stabilize and move the scapula
63
New cards
what is a function of the tensor faciae latae
assist in movement and stabilization of the hip and knee
64
New cards
what is the function of the vastus medialis
extends the knee and assists in stabilization of the patella
65
New cards
what is the function of the biceps femoris
thigh extension, knee flexion and external rotation
66
New cards
what is the function of the adductor magnus
flexes and extends the thigh
67
New cards
what is the function of the pectineus
flexes and adducts the thigh at the hip joint
68
New cards
what is the function of the gracilis
assists in hip adduction and knee flexion
69
New cards
what is a function of the vastus lateralis
extend the knee
70
New cards
what is a function of the tibialis anterior
dorsiflexion
71
New cards
what is the function of the semimembranous
knee flexion and internal rotation
72
New cards
what is the function of the illiotibial tract
overall important structure involved in lower extremity motion
73
New cards
what is the function of the extensor retinaculum
connect the tibia and the fibula
74
New cards
what is the function of the sartorius
helps in rotating the thigh laterally
75
New cards
what is the function of the rectus femoris
extend the knee
76
New cards
what is the function of the extensor digitorum longus
to extend the lateral four tarsals
77
New cards
what is the function of the gluteus medius
assist in flexion and medial rotation of the hip
78
New cards
what is the function of the achilles (calcaneal) tendon
causes plantar flexion of the foot allowing in locomotion
79
New cards
what is the function of the gastrocnemius
helps in walking and posture
80
New cards
what is the function of the vastus intermedius
knee extension
81
New cards
what is the function of the semitendinosus
extend at the hip and flex at the knee
82
New cards
what is the function of the gluteus maximus
extend the hip
83
New cards
what is the function of the adductor longus
adduct the thigh at the hip joint
84
New cards
what is the function of the soleus
provide plantar flexion and posture
85
New cards
what is the function of the linea alba
to maintain the abdominal muscles at a certain proximity to each other
86
New cards
what is the function of the transverse abdominus
to maintain abdominal tension and support abdominal viscera
87
New cards
what is the function of the rectus abdominis
to move the body between the ribcage and the pelvis
88
New cards
what is the function of the diaphragm
to assist in breathing
89
New cards
what is the function of the external abdominal oblique
to help rotate the trunk
90
New cards
what is the function of the internal abdominal oblique
movement of the trunk
91
New cards
what is the function of the serratus anterior
to lift the rib cage and assist in breathing
92
New cards
what is the function of the sternocleidomastoid
rotation of the head
93
New cards
what is the function of the occipitofrontalis
to move the scalp forwards
94
New cards
what is the function of the orbicularis oris
allows in movement of the lips
95
New cards
what is the function of the orbicularis oculi
closes the eyelids
96
New cards
what is the function of the sternohyoid
depresses the hyoid bone during speech and swallowing
97
New cards
what is the function of the temporalis
to produce movements of the mandible
98
New cards
what is the function of the buccinator
to assist in swallowing, sucking, etc.
99
New cards
what is the function of the digastric
swallowing, chewing, and speech
100
New cards
what is the function of the masseter
responsible for chewing