Electron bonding and structure
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Define electron pair repulsion theory ?
The shape of the molecule is determined by the electron pair surrounding the central atom
This is based on the fact that pairs of electrons repel each other
What is the effect of lone pairs on the shape of molecule?
Lone pairs reduce the bonding angle by 2.5
Lone pairs repel more strongly
What happens when electron repel each other ?
-They move further away
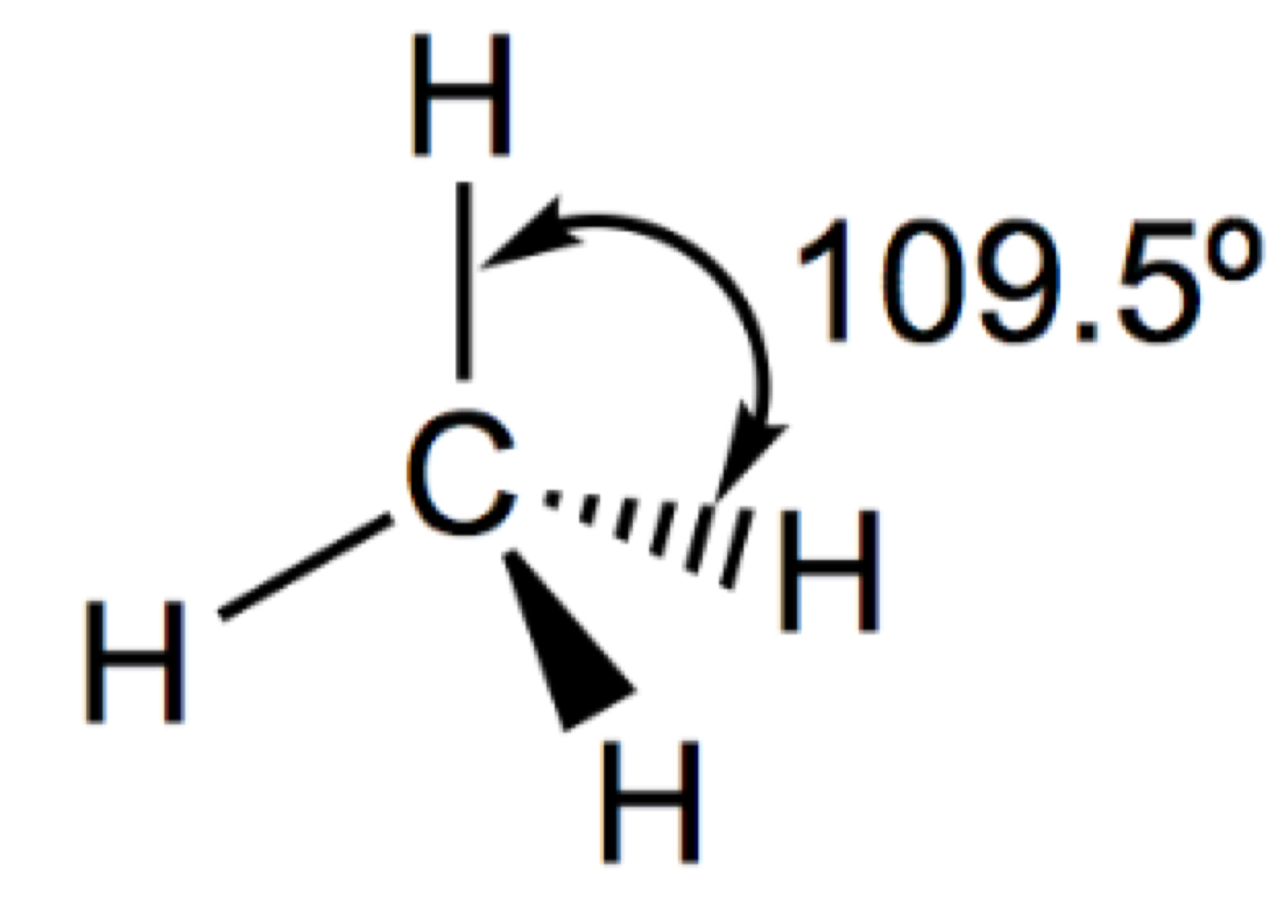
Describe and draw a linear molecule
2 Bonding pairs
180
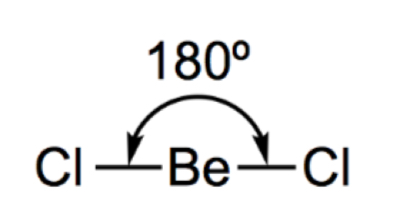
Describe and draw a trigonal planar
3 bonded pairs
120
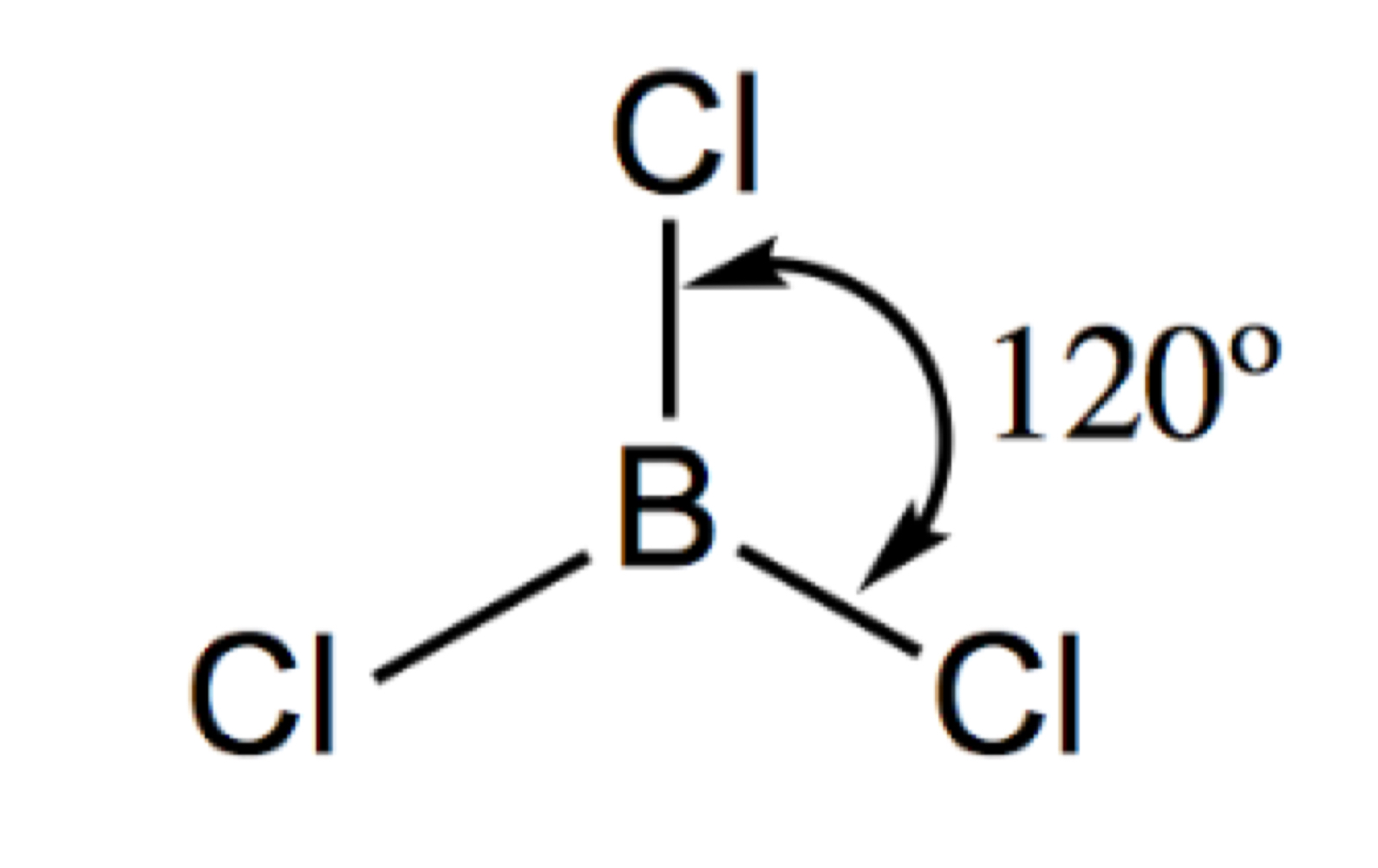
Describe and draw a octahedral
6 Bonding pairs
90
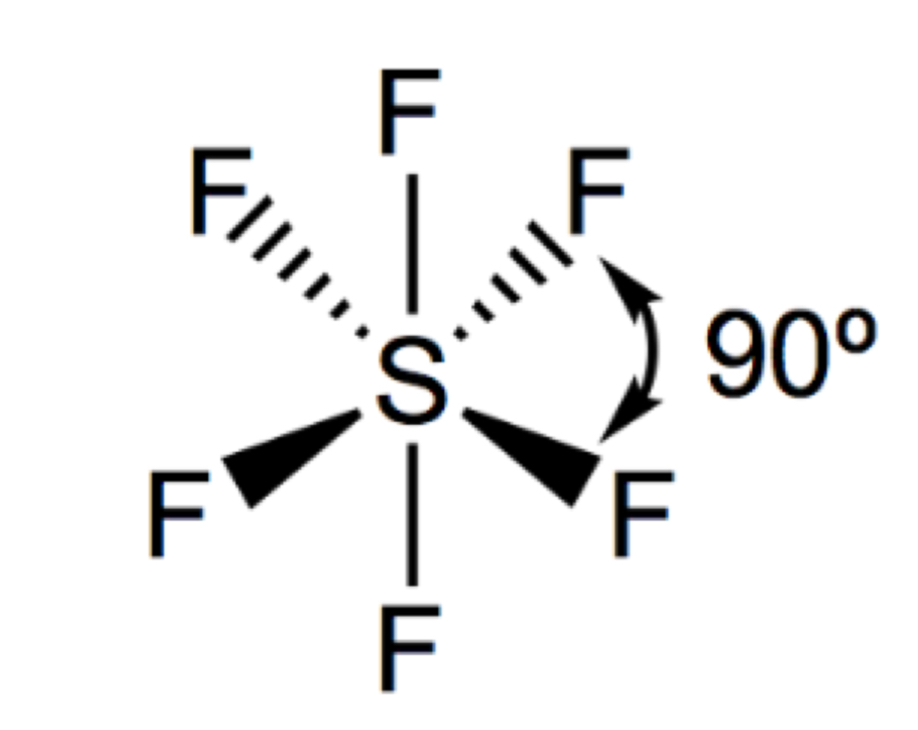
Describe and draw a tetrahedron
4 bonding pairs
109.5
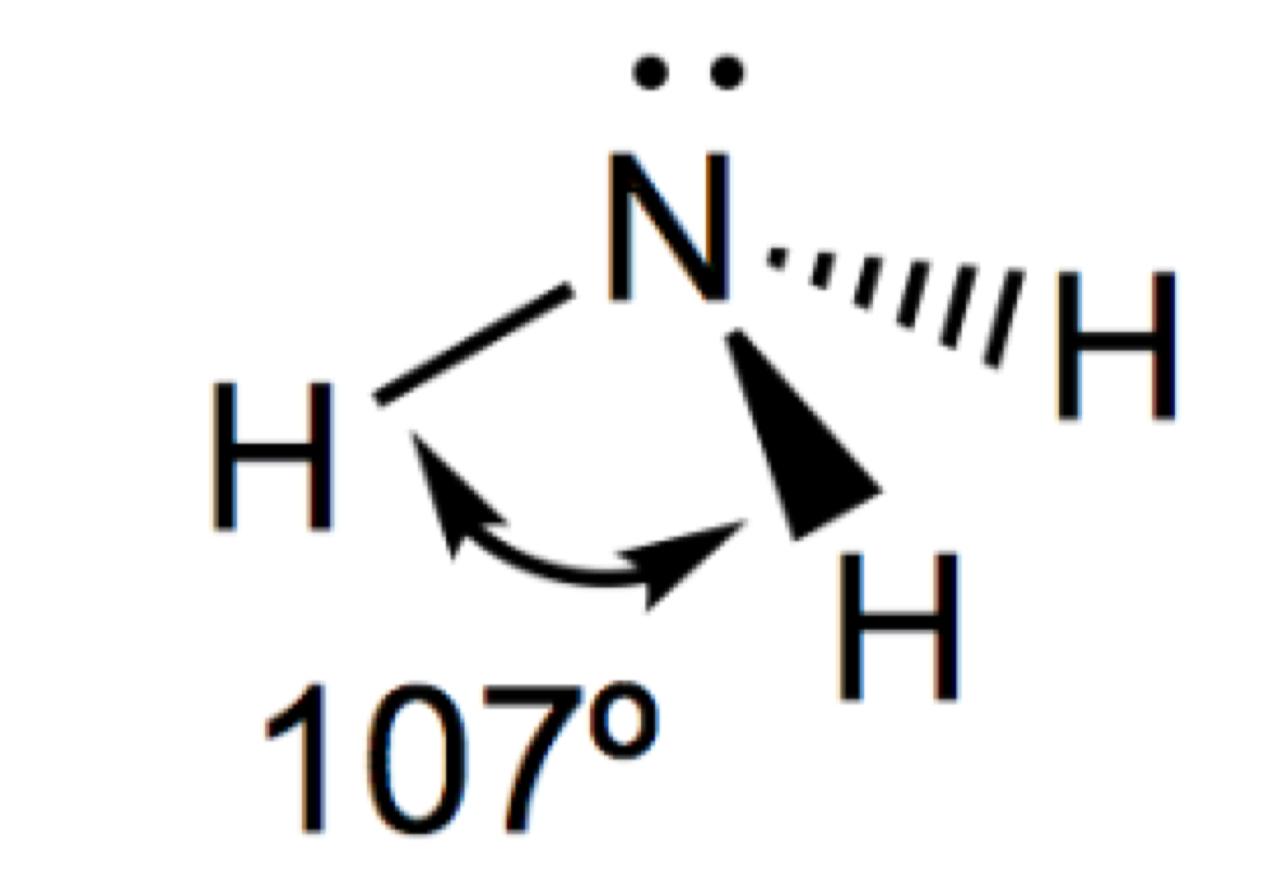
Describe and draw a triangular pyramid
3 bonded pairs
1 lone pair
107
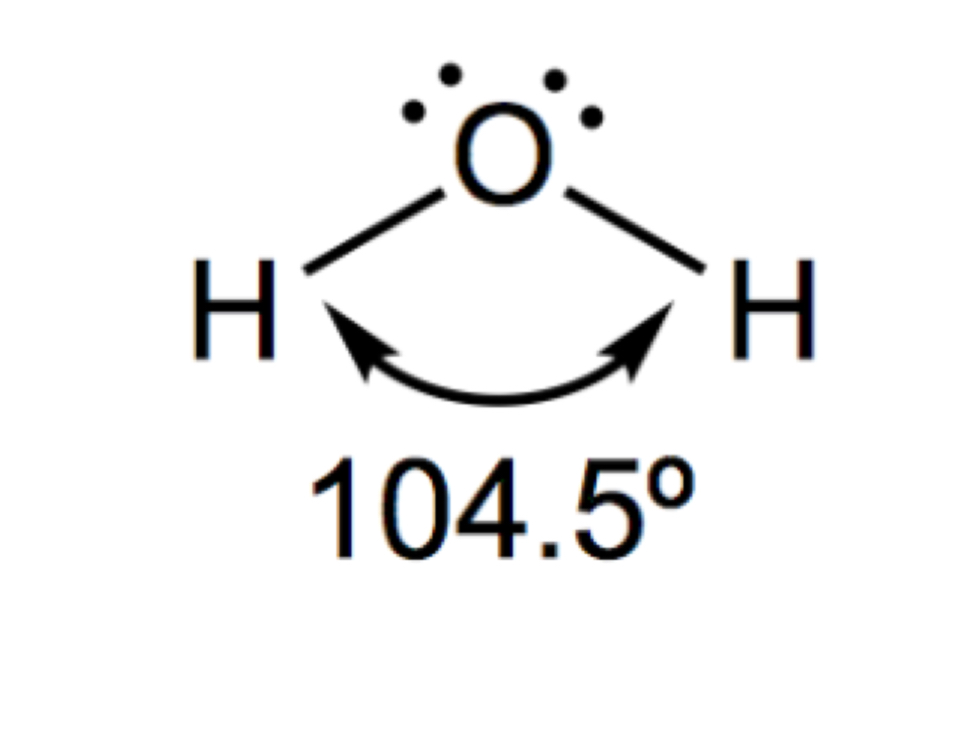
Describe and draw a non-linear
2 Bonded pairs
2 lone pairs
104.5
Define ionic bonding
The electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charge ions
Describe the structure of sodium chloride
Ions are packed closely together forming a lattice
Each ion is electrostatically attracted in all directions to ions of opposite charge
What are the properties of ionic compounds?
They conduct electricity when they are molten or dissolved
They have high melting and boiling point
Why do ionic compounds dissolve ?
Water molecules are polar so interact with the ionic compound
The ions are pulled away from the lattice
What is a molecule?
A group of atoms bonded together held by covalent bonds
What is a covalent bond?
Is the electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms?
State the three main rules for electron configurations
A single energy orbital is filled fast
For orbitals with the same energy electrons occupy orbitals singly with the same spin before pairing begins
Why is the 4S orbital filled in first than the 3d orbital?
4S has a lower energy level than 3d
What is an orbital ?
A region of space and electron moves in
Describe and state the three orbitals ?
S orbitals are spherical
P orbitals are a dumbbell shaped
D orbitals
Define an intermolecular force?
They are forces between molecules
What is the strongest type of intermolecular force?
Hydrogen bonds
How does a hydrogen bond form?
When hydrogen is covalent bonded to fluorine nitrogen and oxygen
Weak bonds form between the hydrogen atom of one molecule and a loan pair of electrons on the other molecule.
Why is water less dense in ice form?
Ice has hydrogen bonds then liquid
Hydrogen bonds are relatively long
Resulting in the molecules being further apart
State the two properties of hydrogen bonds
They are soluble in water
They have high melting and boiling points
What are the two properties of simple covalent bonds?
Have low melting and boiling points
They don’t conduct electricity
Describe in disciple dipole interactions
Dipoles can cause another induced dipole the two dipoles holeare then attracted to each other
What causes an induced dipole dipole interaction?
Electrons in charge clouds travel quickly
What causes a stronger induced dipole dipole?
Larger molecules because they have larger electron clouds
Molecules with greater surface areas because they have a bigger exposed
What are the properties with molecules with stronger induced dipole dip?
High boiling point
Describe a permanent dipole?
Form on polar molecules
They cause electrostatic forces of attraction between molecules
It’s cause in addition to induced dipole dipole interactions
Define electronegativity ?
A atoms ability to attract the electron pair in a covalent bond
What the trends in electronegativity in the periodic table ?
Electronegativity increases across
Electronegativity decreases down groups
Define ionic bonding
The electrostatic force of attraction between positively charged ions and negatively charged ions