Chapter 2 organic and inorganic compounds
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/52
Last updated 3:44 PM on 10/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
organic compound
must contain C - usually covalently bonded to H
2
New cards
hydrolysis
a chemical reaction that breaks chemical bonds by the addition of water molecules
3
New cards
dehydration synthesis
a chemical reaction creating chemical bonds by the removal of water molecules
4
New cards
polymers of glucose
starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
5
New cards
buffers
resist sudden/abrupt changes in pH
6
New cards
normal blood pH range
7.35-7.45
7
New cards
lipid
ratio of H to O is not 2:1 - lots more H than O
8
New cards
carbohydrate
H:O ratio is 2:1 (it can be an approximate ratio of C to H to O of 1:2:1)
9
New cards
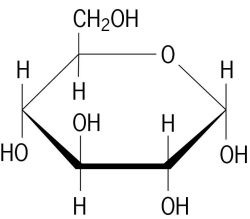
carbohydrate
10
New cards
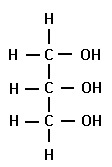
glycerol
11
New cards
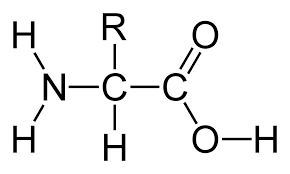
amino acid
12
New cards
lipid
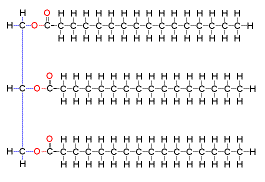
13
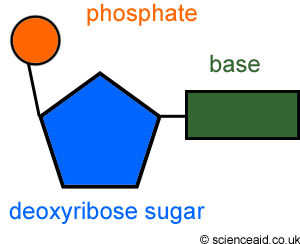
New cards
nucleotide
14
New cards
purine
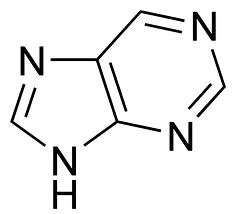
15
New cards
pyrimidine
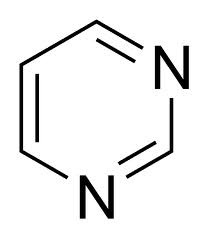
16
New cards
carboxyl group (organic acid group)
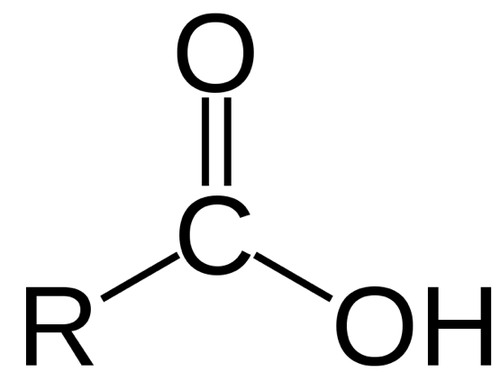
17
New cards
amine group (amino group)
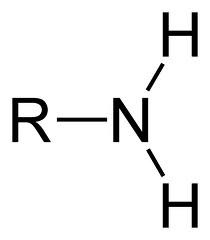
18
New cards
high heat vaporization
this property of water helps keep us cool
19
New cards
water
most abundant/important inorganic cpd in living matter
20
New cards
water
universal solvent
21
New cards
Monosaccharides
building blocks (monomers) of carbohydrates
22
New cards
glucose, fructose, galactose
monosaccharide examples
23
New cards
disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
24
New cards
polysaccharides
cellulose, starch, glycogen, chitin
25
New cards
glycogen
how animals store carbs in liver and muscles
26
New cards
weak hydrogen bonds
what bonds water molecules to other water molecules
27
New cards
blood plasma and cerebrospinal fluid
examples of colloids in the body
28
New cards
ATP
energy storing molecule - fuels all life's processes - no life without it
29
New cards
carbohydrates
major source of fuel for our bodies/cells
30
New cards
polysaccharide
long chain of monosaccharides (simple sugars)
31
New cards
collagen
single most abundant protein in body
32
New cards
acid
sour/can react with metal/proton donor
33
New cards
base
bitter/slippery feel/proton acceptor
34
New cards
double helix
another name for DNA
35
New cards
cholesterol
used to make vitamin D, sex hormones, bile salts, aldosterone, cortisol
36
New cards
functional proteins
are globular, water soluble, chemically active, mobile, unstable, tertiary/quaternary level proteins
37
New cards
structural proteins
are fibrous, long, skinny, insoluble in water, stable, primary/secondary level proteins
38
New cards
-ase
suffix typical of enzymes
39
New cards
enzyme/substrate complex
when an enzyme bonds to its substrate at the active site
40
New cards
nucleotides
building blocks of nucleic acids
41
New cards
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acid chains
building blocks of lipids
42
New cards
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
43
New cards
peptide bond
chemical bond that forms between the carbon of a carboxyl group of one amino acid and the nitrogen of the amino group of another amino acid - links amino acids together in a protein
44
New cards
nucleotide
made of phosphate group, 5 Carbon sugar, and nitrogen base
45
New cards
RNA
carries out order for protein synthesis issued by DNA
46
New cards
DNA
carrier of genetic code, determines nucleotide coding in RNA, determines types of proteins cell can produce
47
New cards
unsaturated fat
has one or more double/triple covalent bonds in the fatty acid chain(s)
48
New cards
water
Biochemical reactions in the body must occur in this
49
New cards
A, T, C, G
four nitrogen bases in DNA
50
New cards
A, U, C, G
The four nitrogen bases found in RNA
51
New cards
-ose
suffix associated with a sugar
52
New cards
backbone structure of DNA
alternating sugars and phosphates
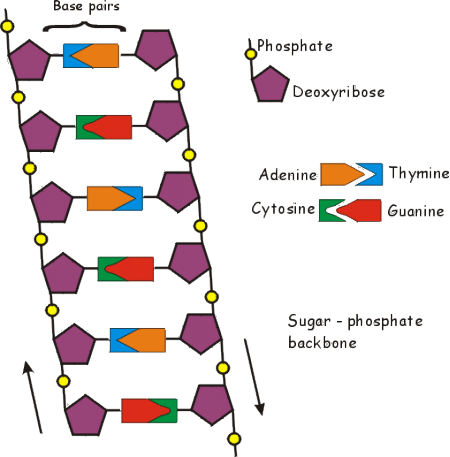
53
New cards
For DNA and RNA , the nitrogen bases are always attached to the _______________ on the backbone of DNA or RNA
5 Carbon sugar