1.6 Cell Division
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
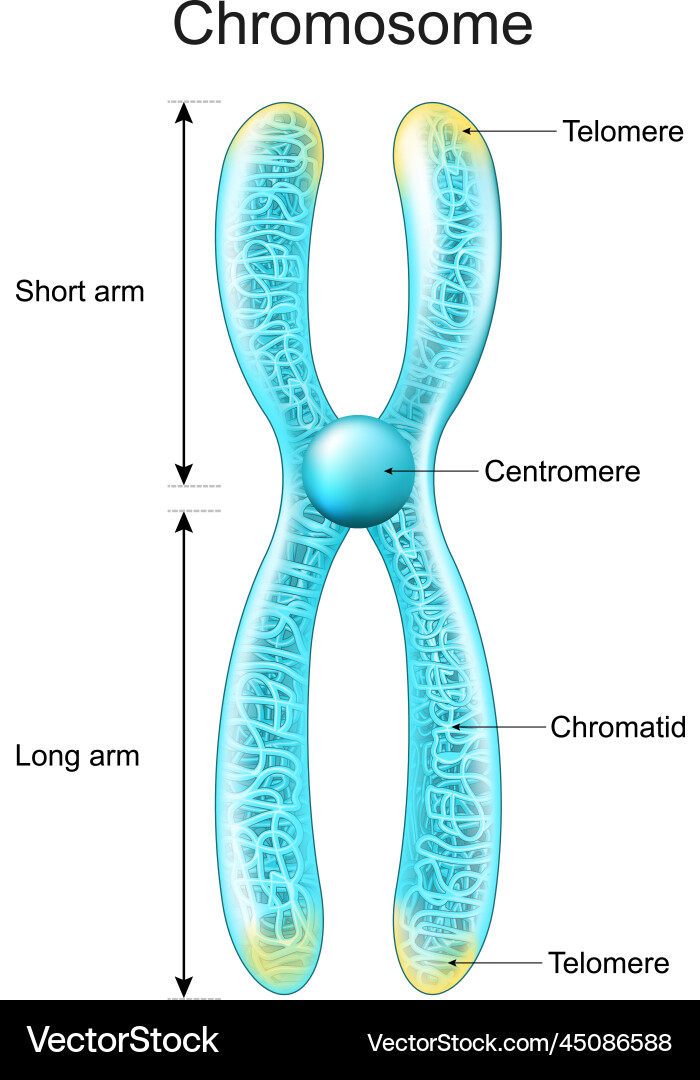
Structure of a chromosome
How many pairs of homologous chromosomes do humans have?
23
Main features of mitosis
produces two identical daughter cells
maintains chromosome number throughout
allows growth and repair
asexual reproduction
What can uncontrolled mitosis lead to?
Growth of cancerous cells
What are the 6 main stages of mitosis?
Interphase
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
What happens when a cell is in interphase?
forms new organelles e.g. centrioles
DNA replication
builds an energy store
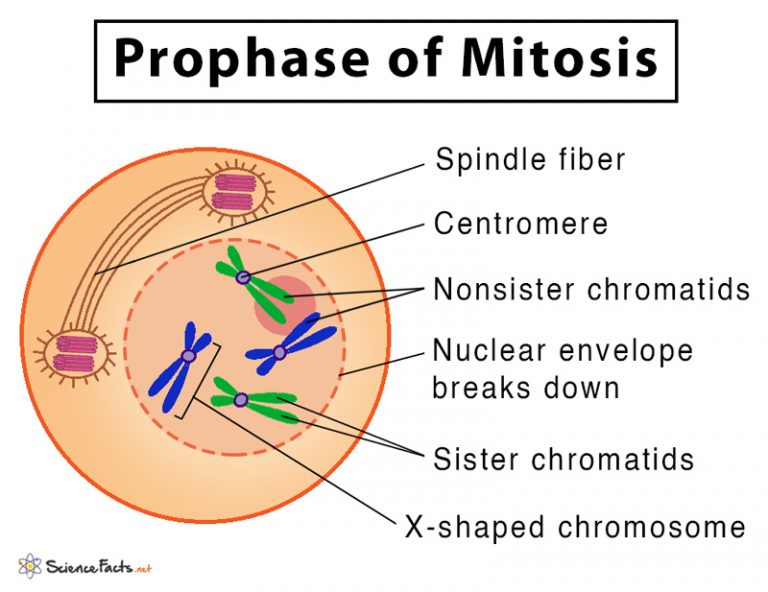
What happens in prophase? - mitosis
chromosomes condense and become visible
centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell
spindle fibres develop from centrioles
nuclear membrane breaks down and nucleolus disappears
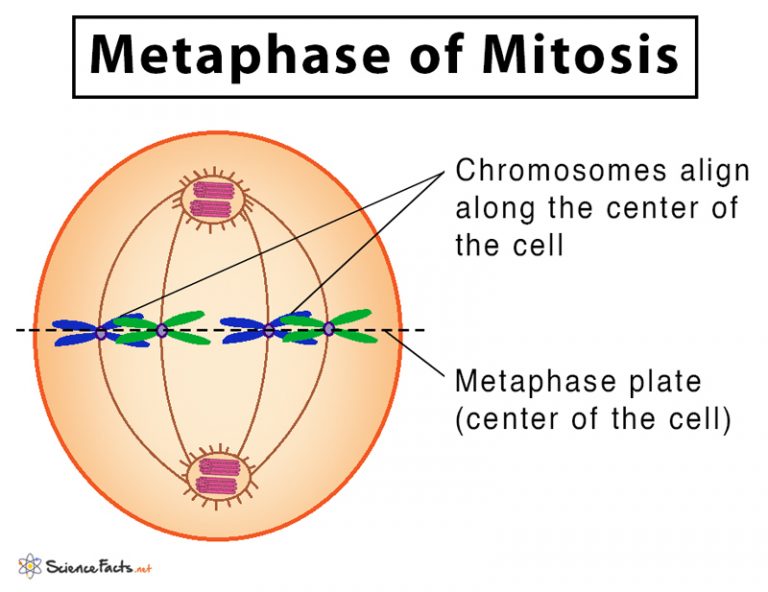
What happens in metaphase? - mitosis
chromosomes line up at centre of cell
spindle fibres attach to the individual chromtids by the centromere
What happens in anaphase? - mitosis
spindle fibres contract and pull chromatids apart to opposite poles of the cell
mitrochondria gather to provide energy
What happens in telophase? - mitosis
spindle fibres break down
chromatids become indistinct
nuclear membrane surrounds both sets of chromatids
nucleolus reforms
What happens in cytokinesis? - mitosis
forms the two daughter cells
organelles and cytoplasm equally divide
Main features of meiosis
sexual reproduction
genetic variation
2 divisions
chromosomes half in each daughter cell
What are the main stages of meiosis?
interphase
prophase 1
metaphase 1
anaphase 1
telophase 1
cytokinesis
prophase 2
metaphase 2
anaphase 2
telophase 2
cytokinesis
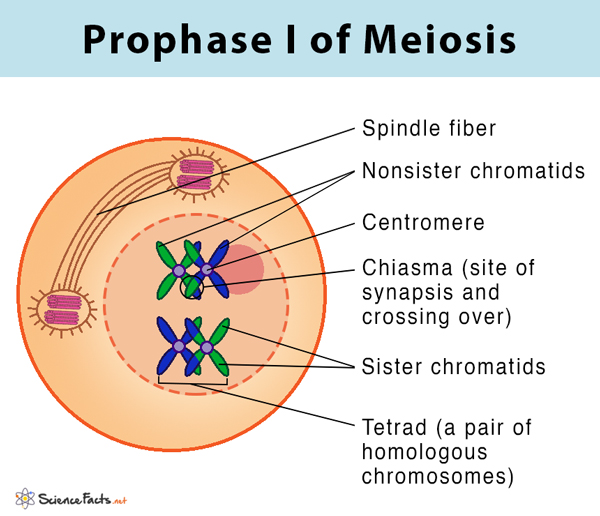
What happens in prophase 1? - meiosis
chromosomes condense and become visible
centrioles move to opposite poles of cell and spindle fibres develop
paternal and maternal chromosomes associate in their homelogous pairs (bivalents)
chromosomes wrap around each other and join at the chiasmata in a process called synapsis
nuclear membrane breaks down and nucleolus disappears
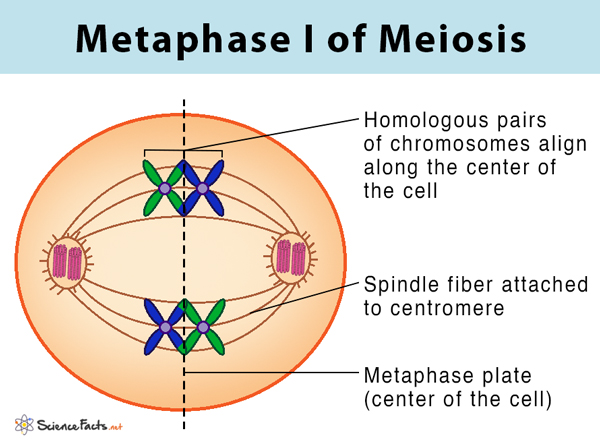
What happens in metaphase 1? - meiosis
bivalents arrange themselves at centre of cell
the maternal and paternal chromosomes are arranged randomly allowing new genetic combinations (random arrangement)
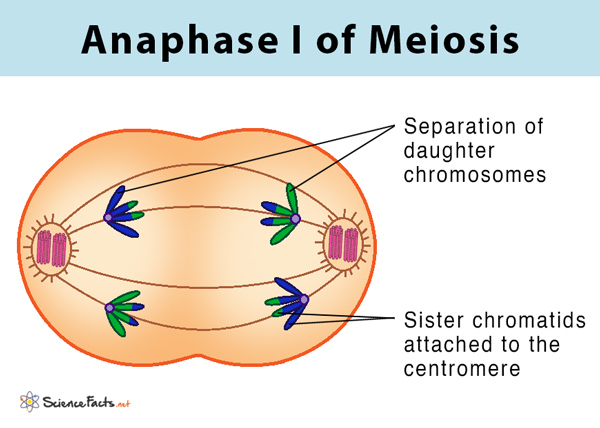
What happens in anaphase 1? - meiosis
chromosomes in each bivalent separate and spindle fibres pull them to opposite poles of cell
each pole receive one chromosome from a homologous pair
it will be a random mixture of maternal and paternal chromosomes (independent assortment)
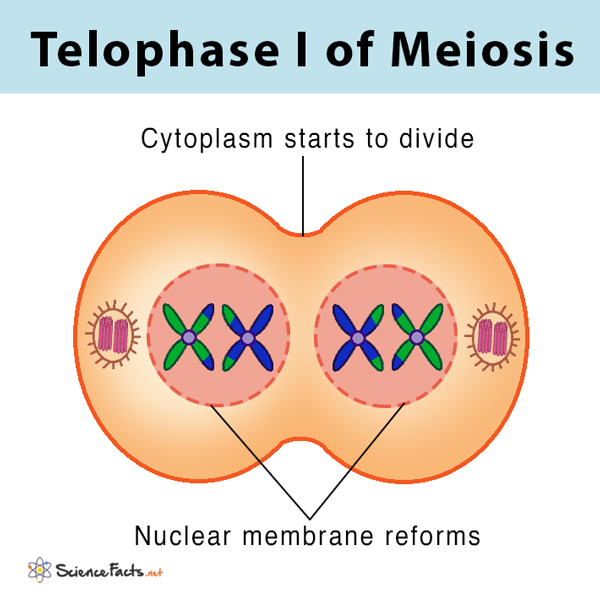
What happens in telophase 1? - meiosis
nuclear membrane surrounds both sets of chromosomes
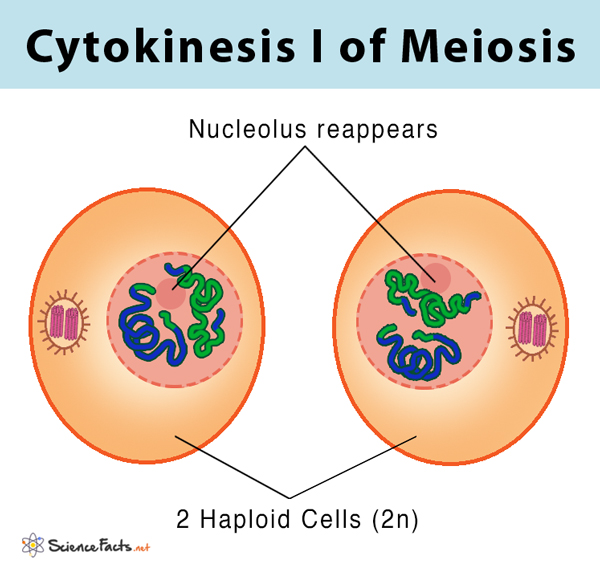
What happens in cytokinesis 1? - meiosis
2 haploid cells formed
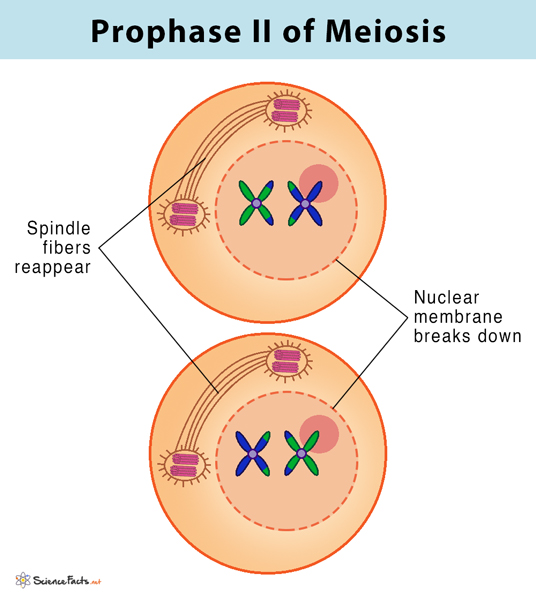
What happens in prophase 2? - meiosis
new spindle fibres develop at right angles to old
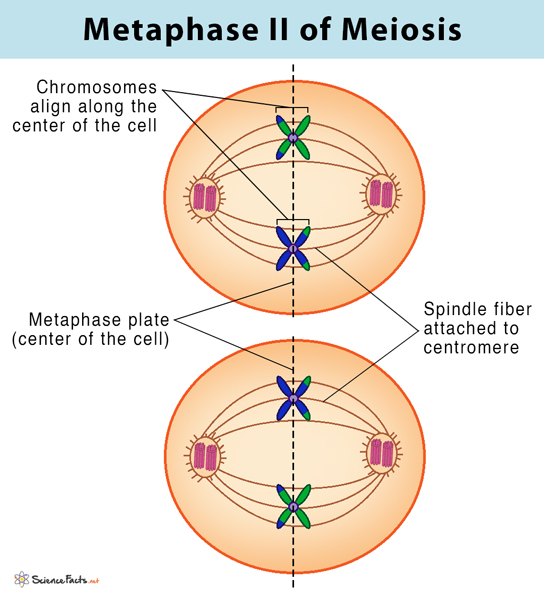
What happens in metaphase 2? - meiosis
chromosomes line up separately in middle and spindle fibres attach
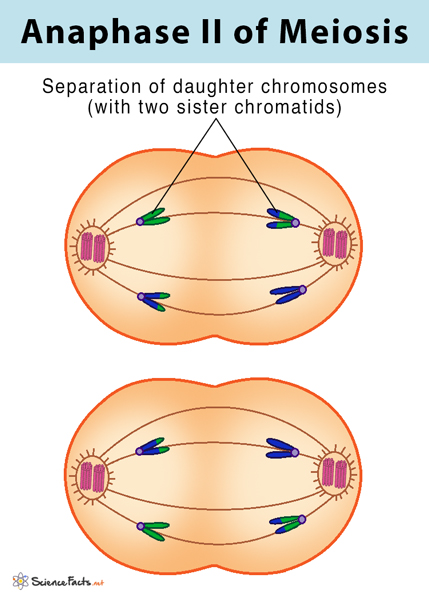
What happens in anaphase 2? - meiosis
chromatids pulled to opposite poles of cell
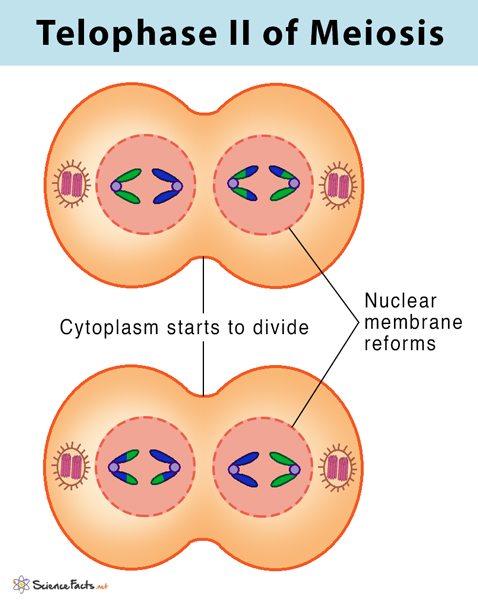
What happens in telophase 2? - meiosis
chromatids become indistinct
spindle fibres disappears
nuclear membrane and nucleolus reform
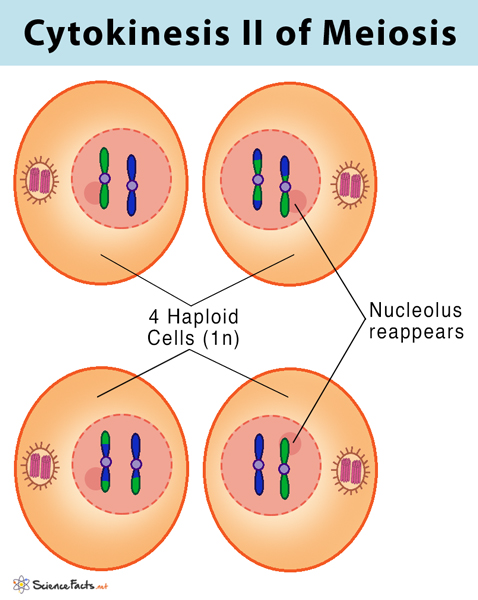
What happens in cytokinesis 2? - meiosis
4 haploid cells formed