D651: Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology I Exam 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Hint: Most common collagen vascular immune mediated condition in the US
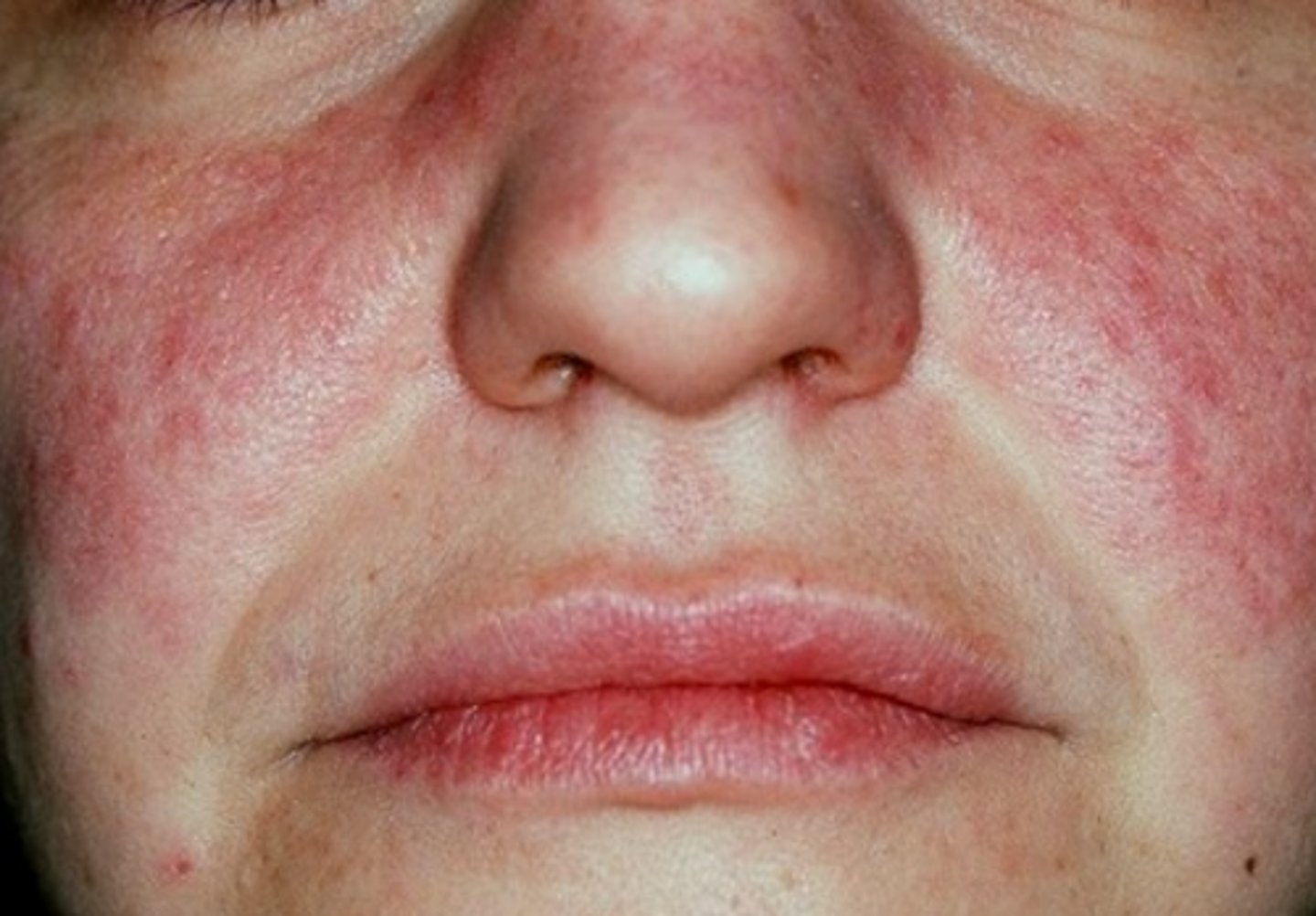
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Hint: Most common collagen vascular immune mediated condition in the US; oral manifestations may appear as lichenoid areas
Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
Hint: skin lesions present as discoid lupus erythematous
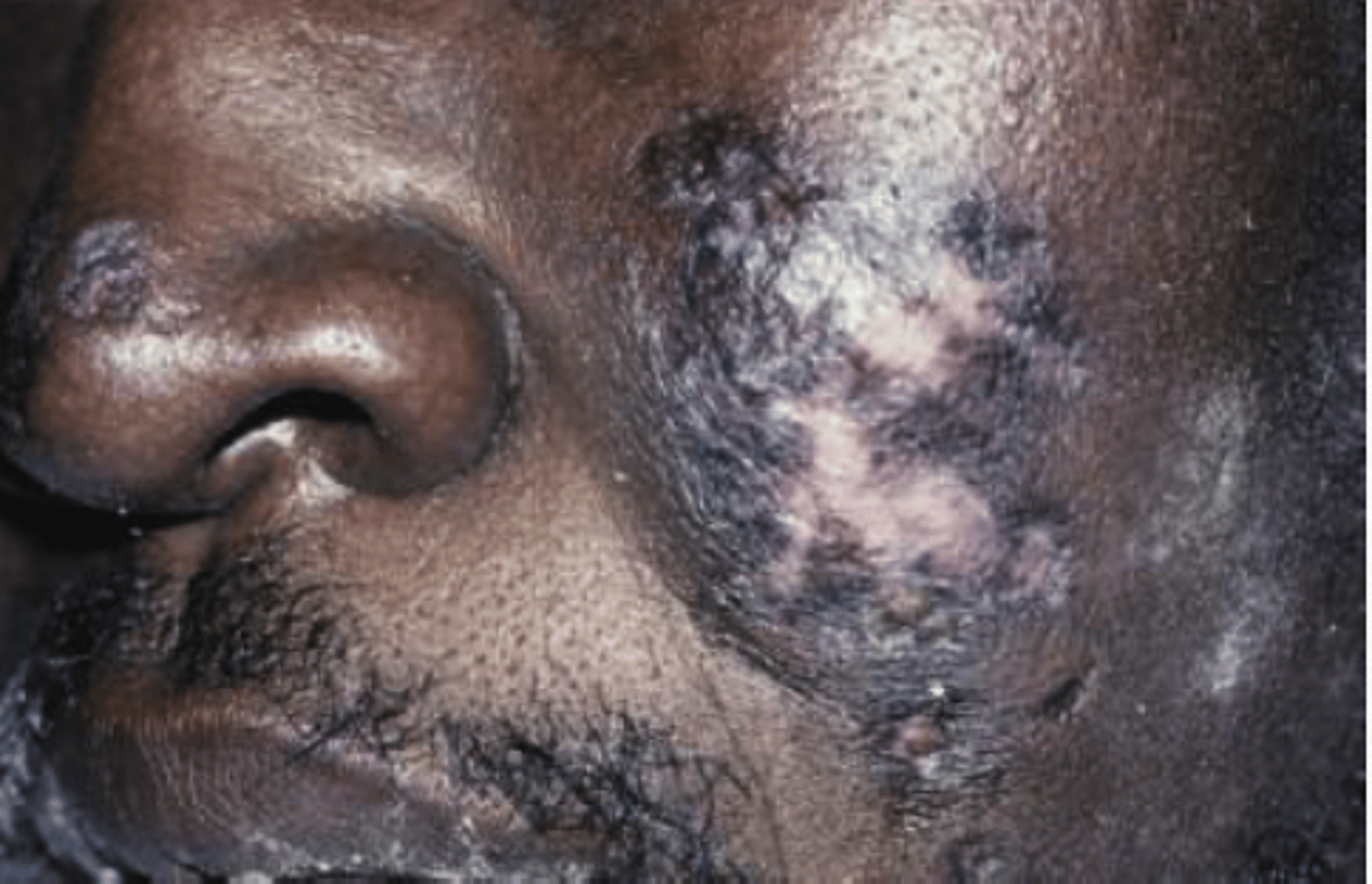
Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
Hint: Oral lesions identical to erosive lichen planus
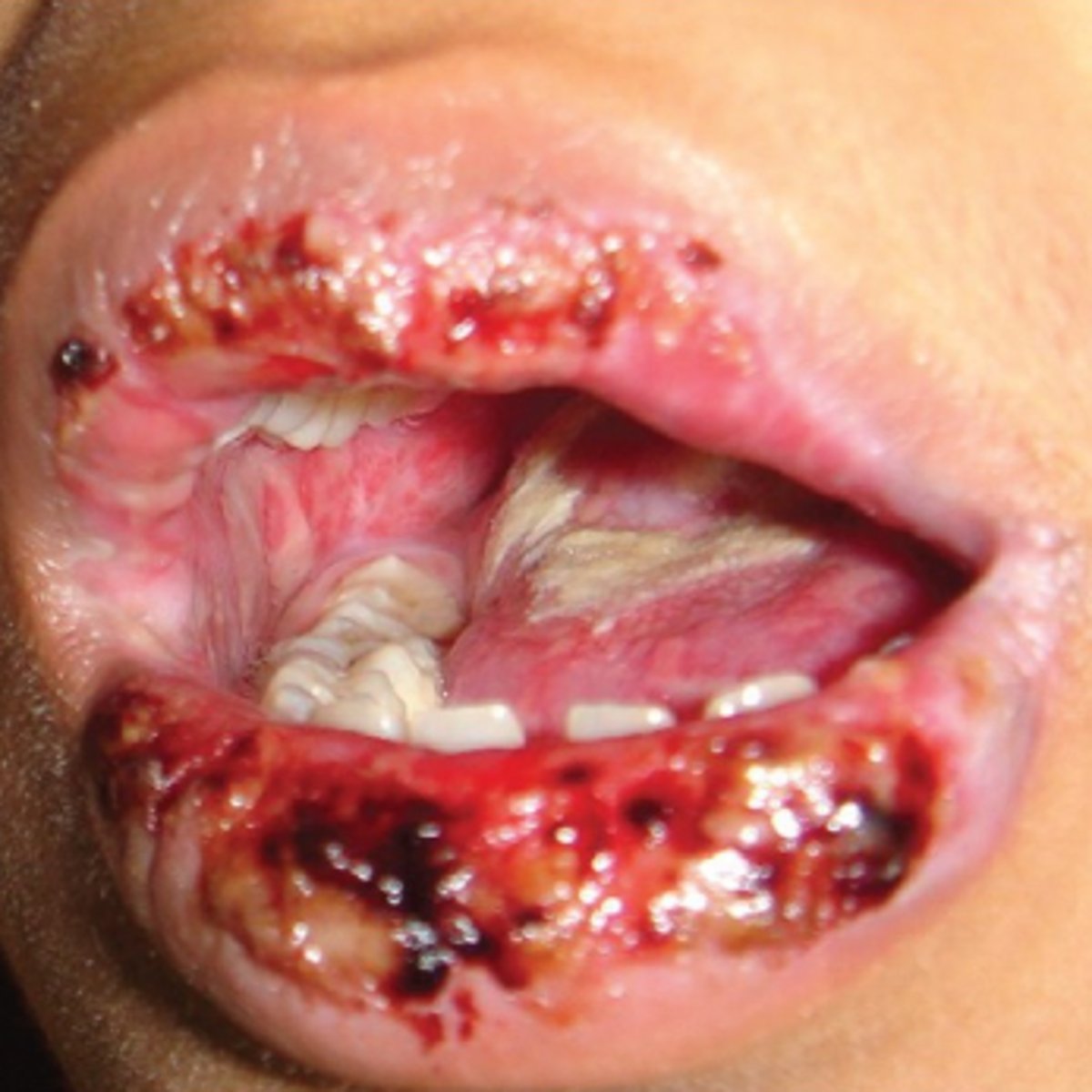
Erythema Multiforme
Hint: Hemorrhagic crusting of lips
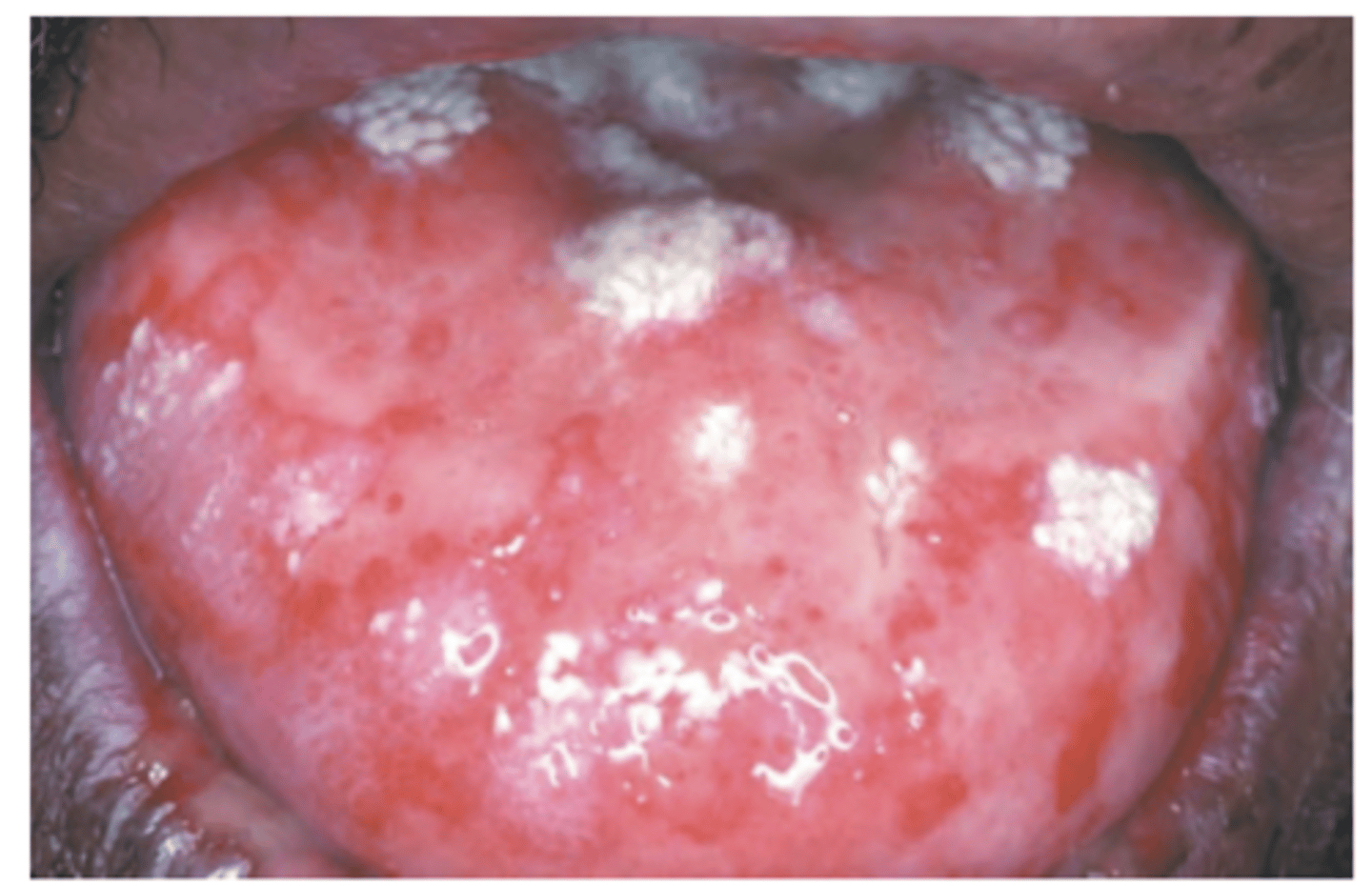
Erythema Multiforme
Hint: Begins with target lesions on extremities
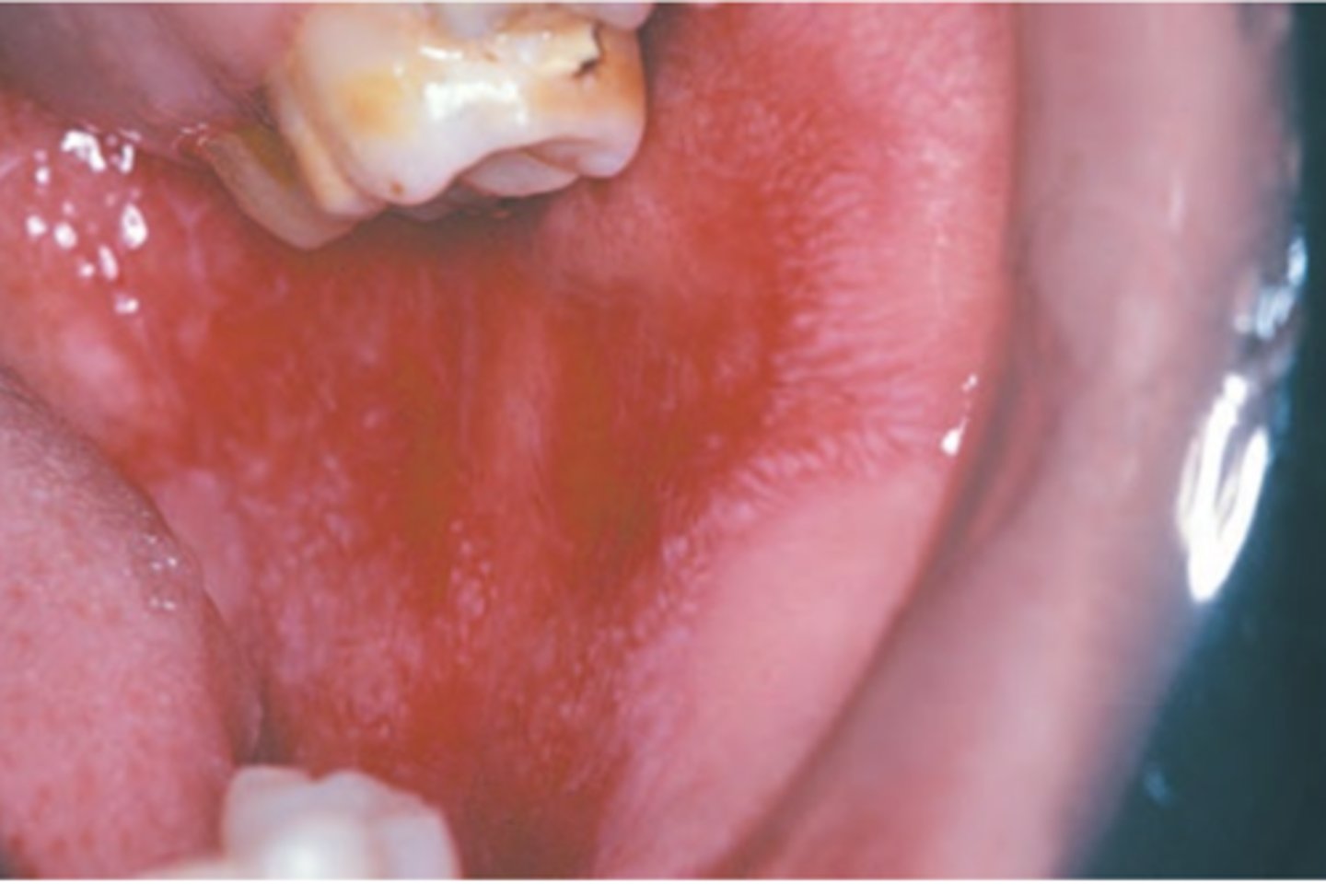
Erythema Multiforme
Hint: Begins with target lesions on extremities
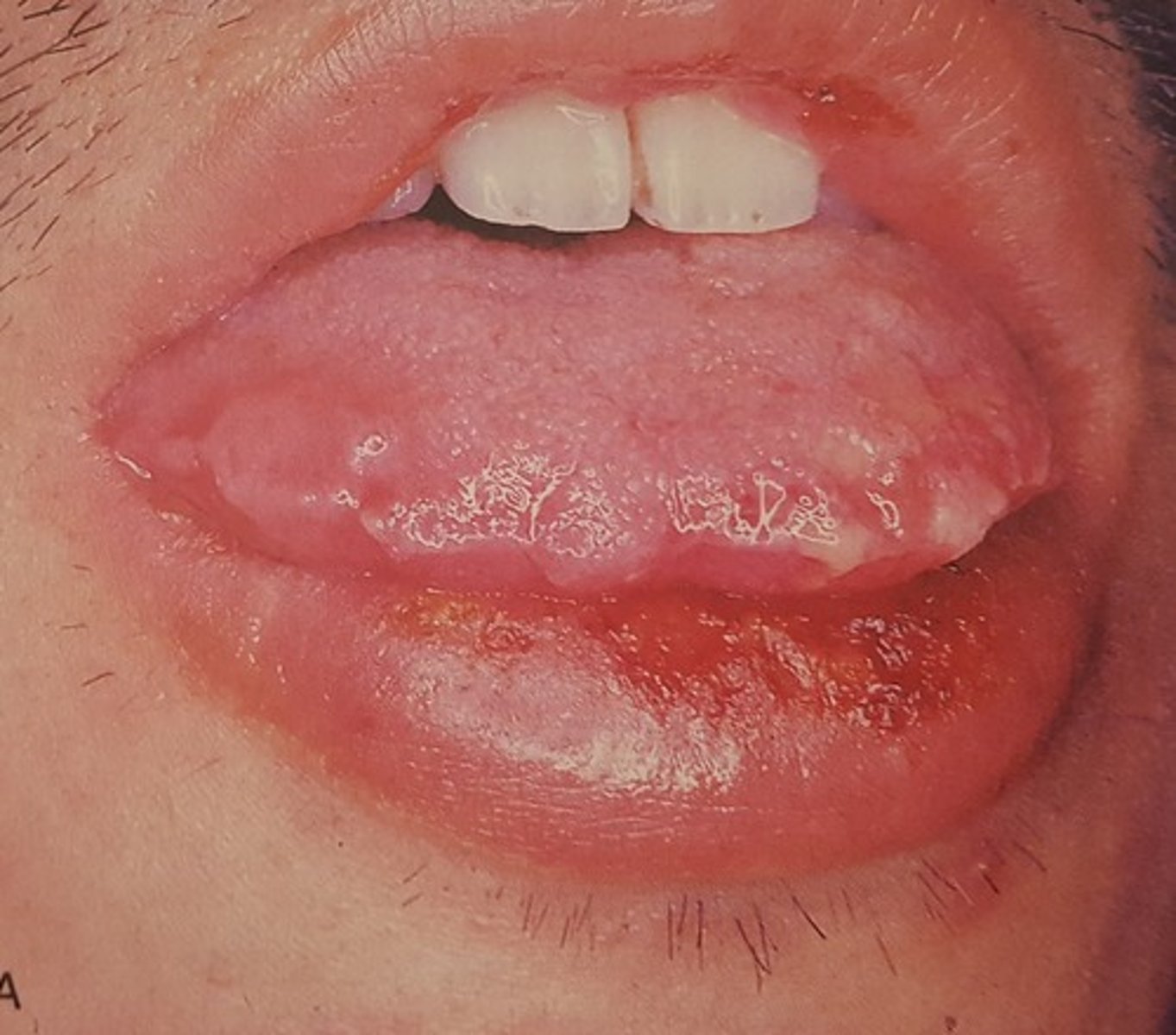
Erythema Multiforme
Hint: target lesions
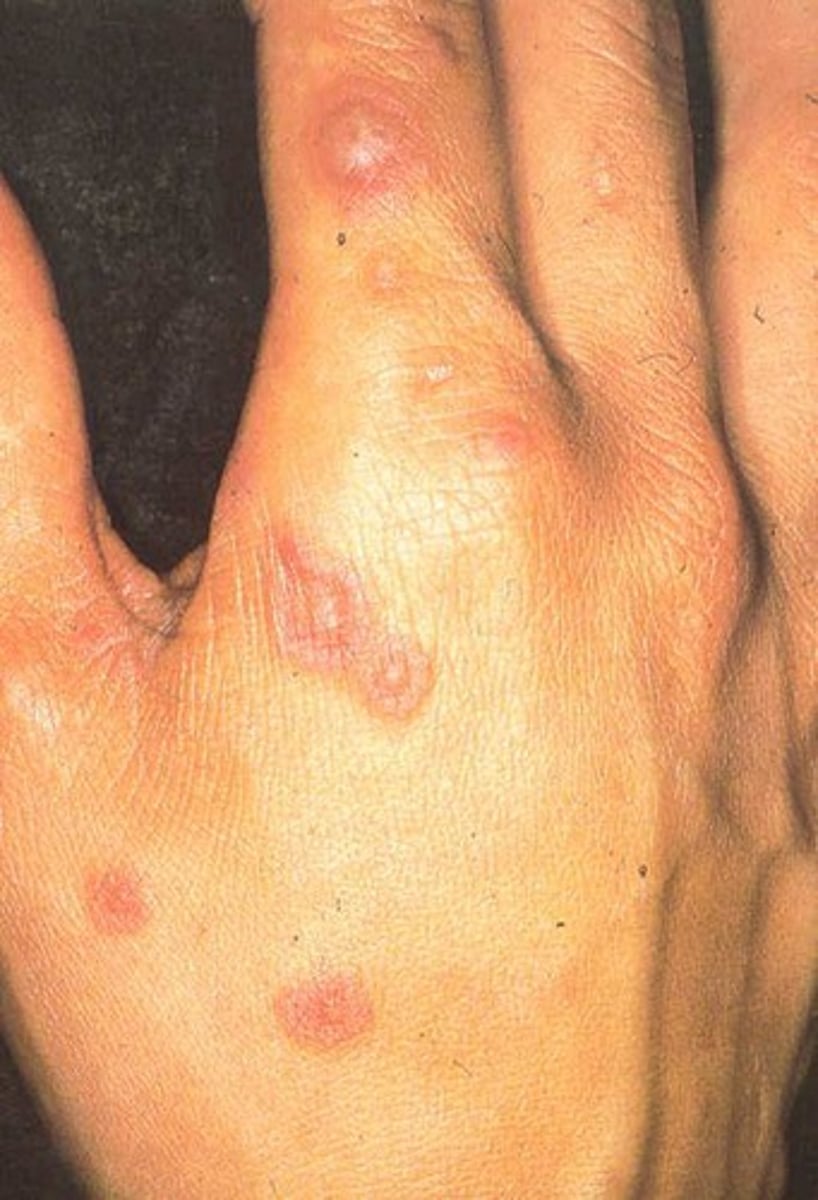
Erythema Multiforme
Hint: target lesions
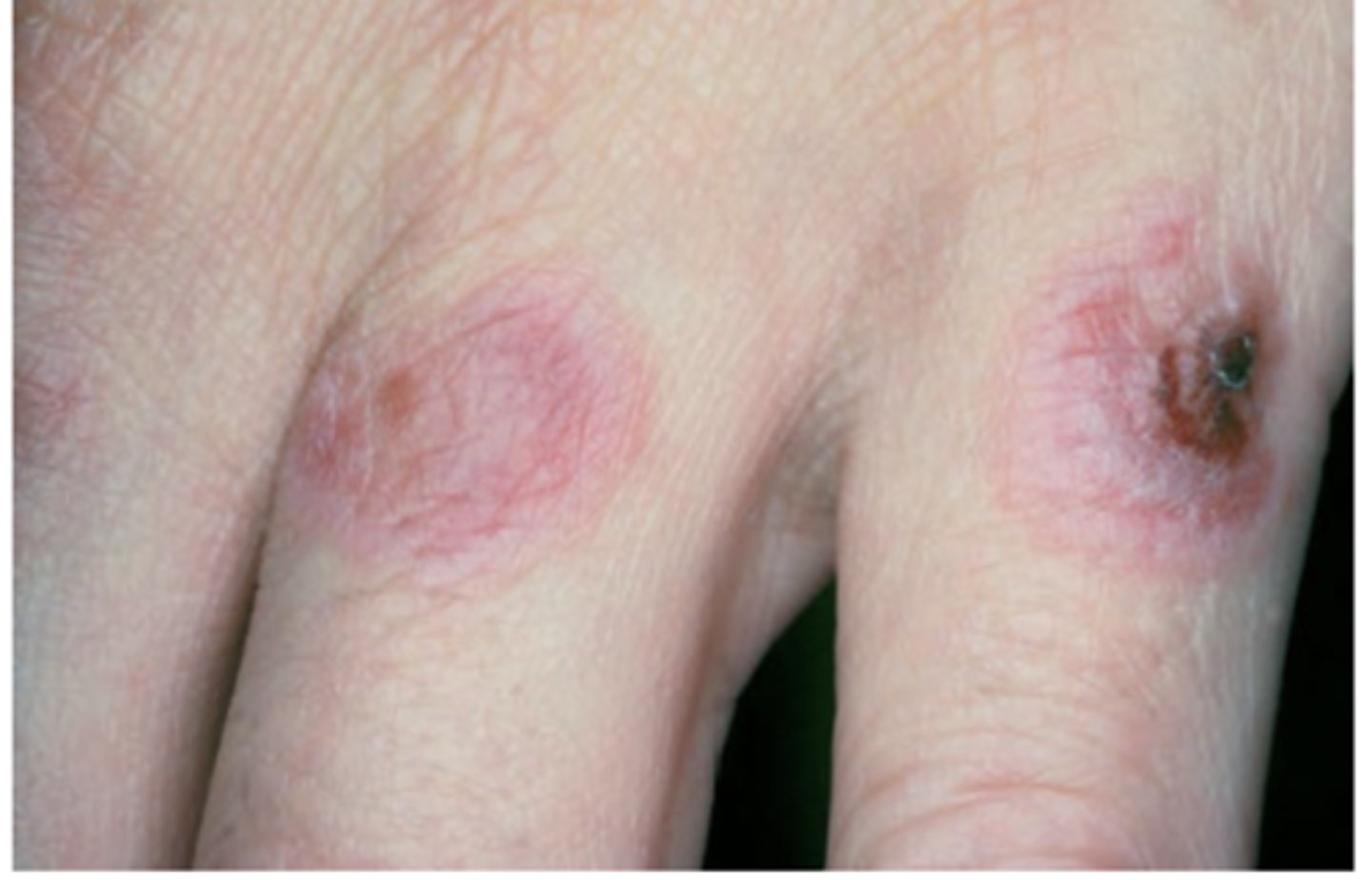
Stevens-Johnson syndrome/Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Hint: Previously considered most severe form of erythema multiforme
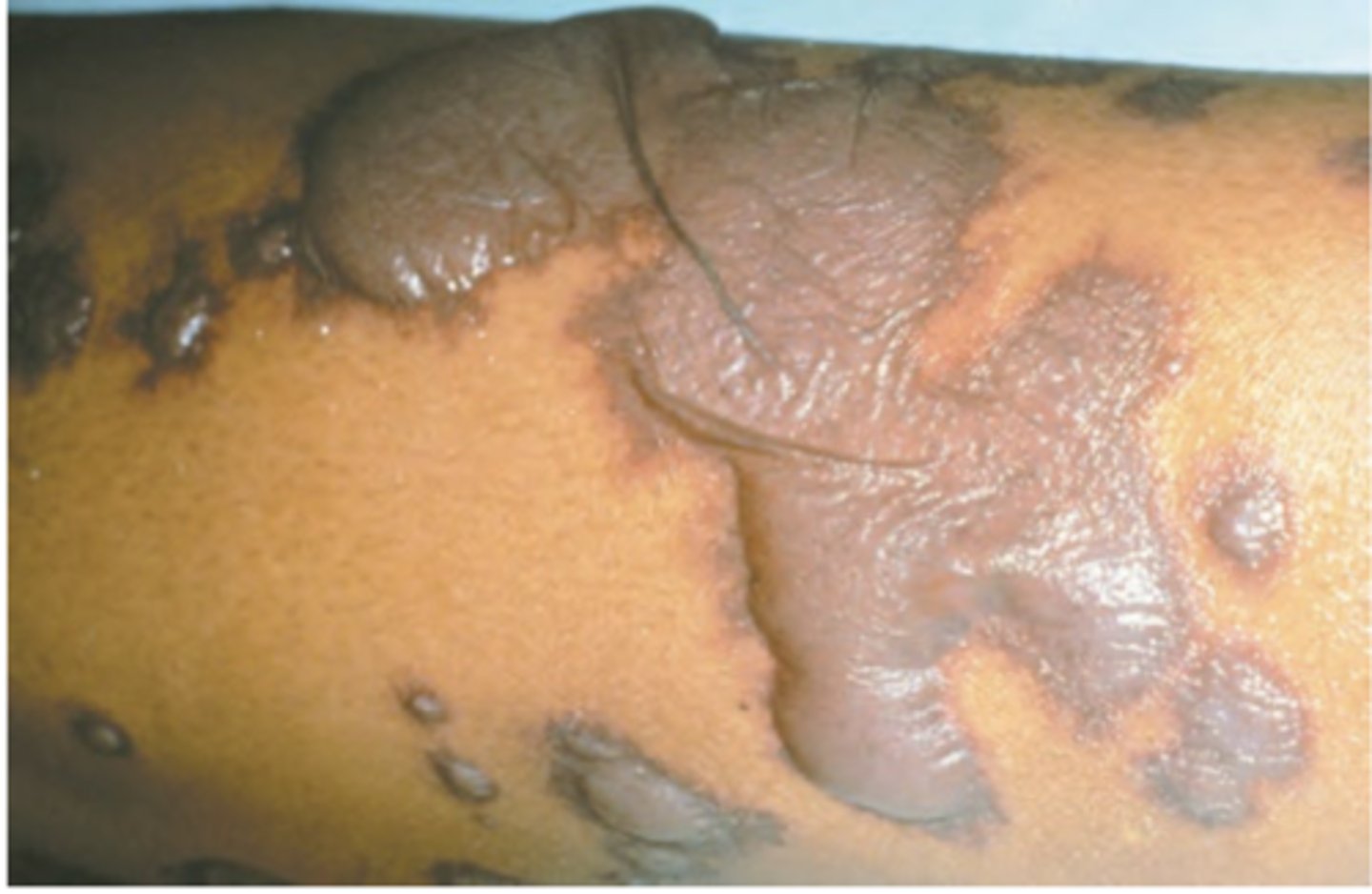
Stevens-Johnson syndrome/Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Hint: Previously considered most severe form of erythema multiforme
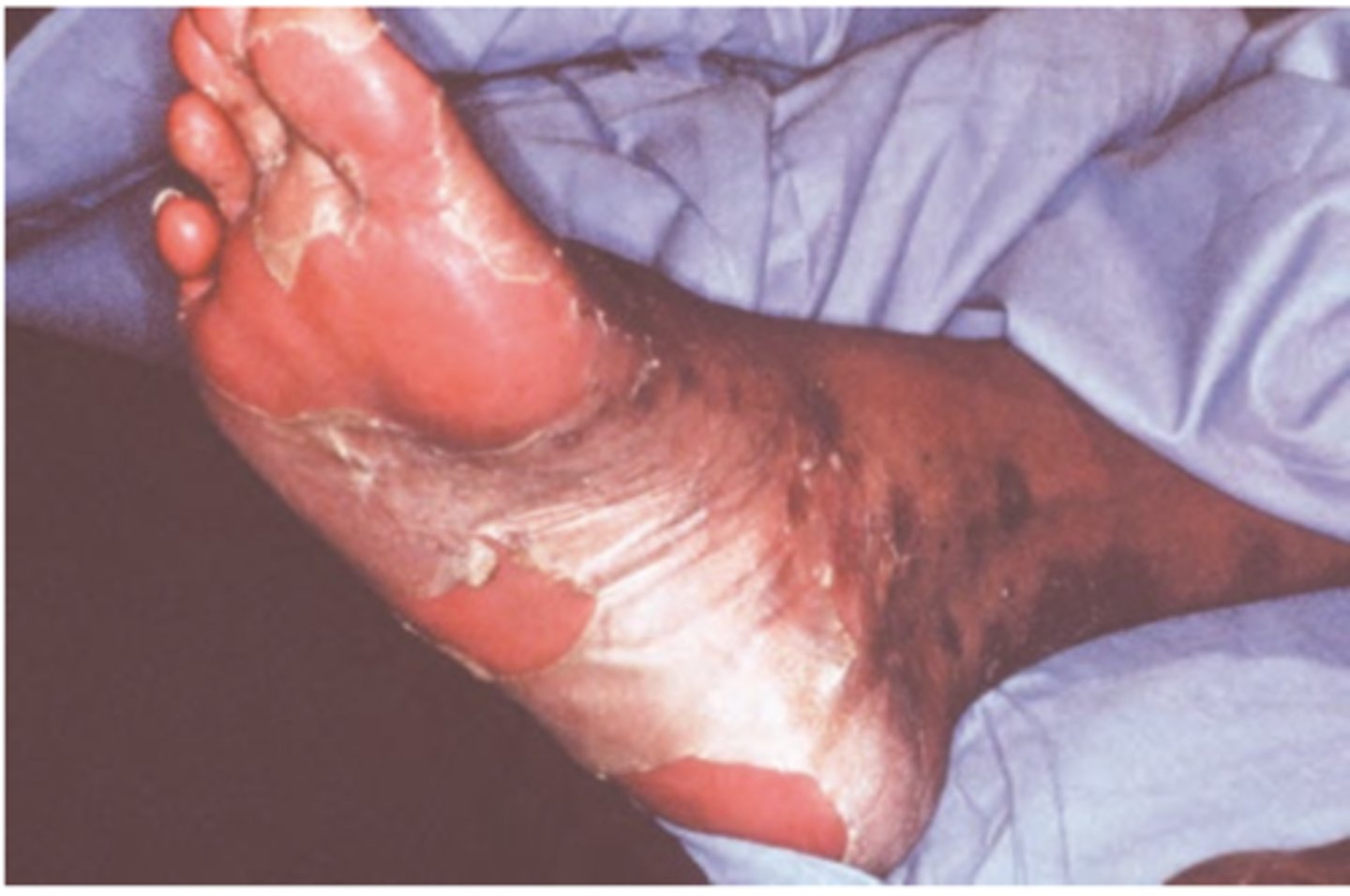
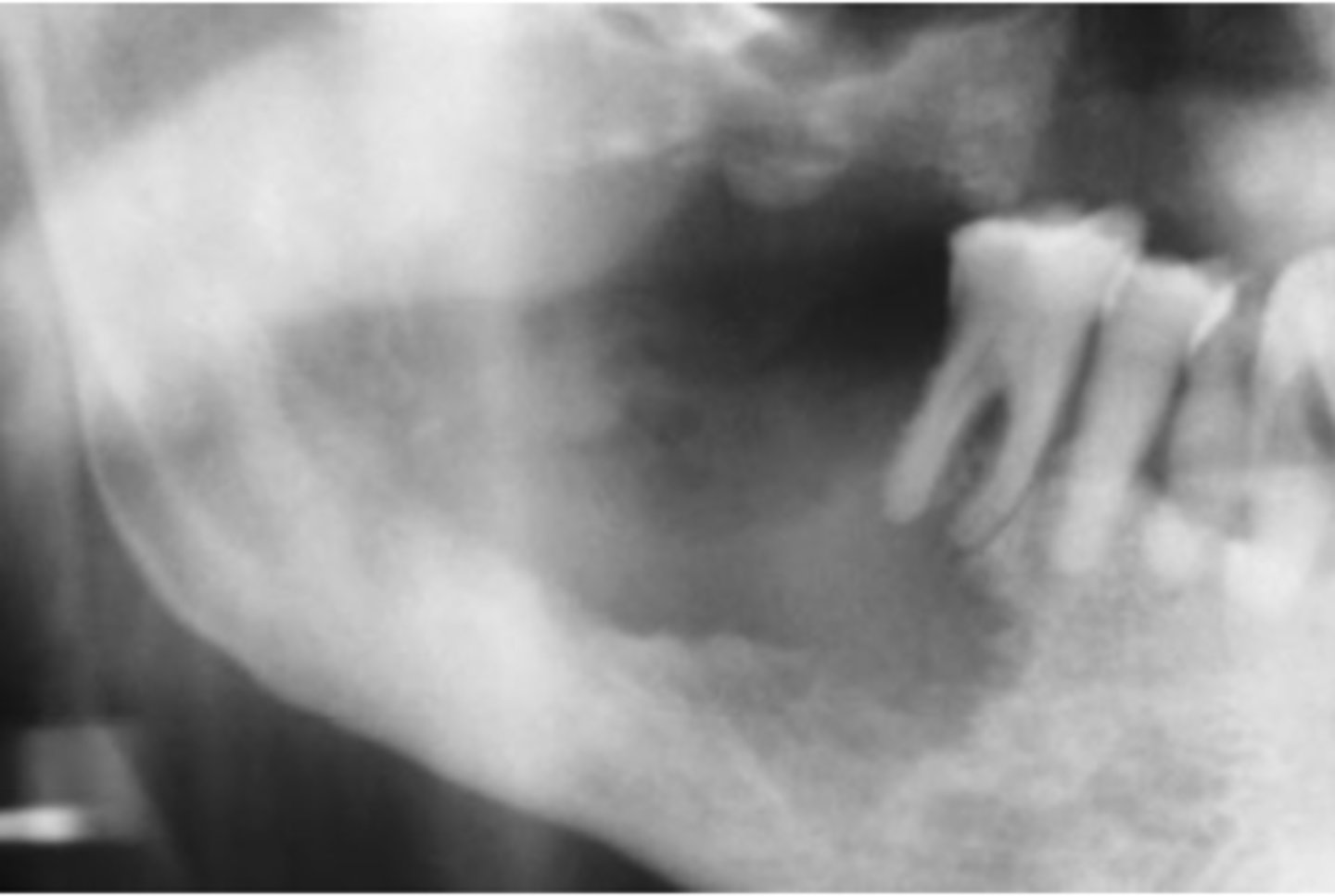
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Hint: Varied clinical presentation
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Hint: Varied clinical presentation
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Hint: Varied clinical presentation
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Hint: Varied clinical presentation
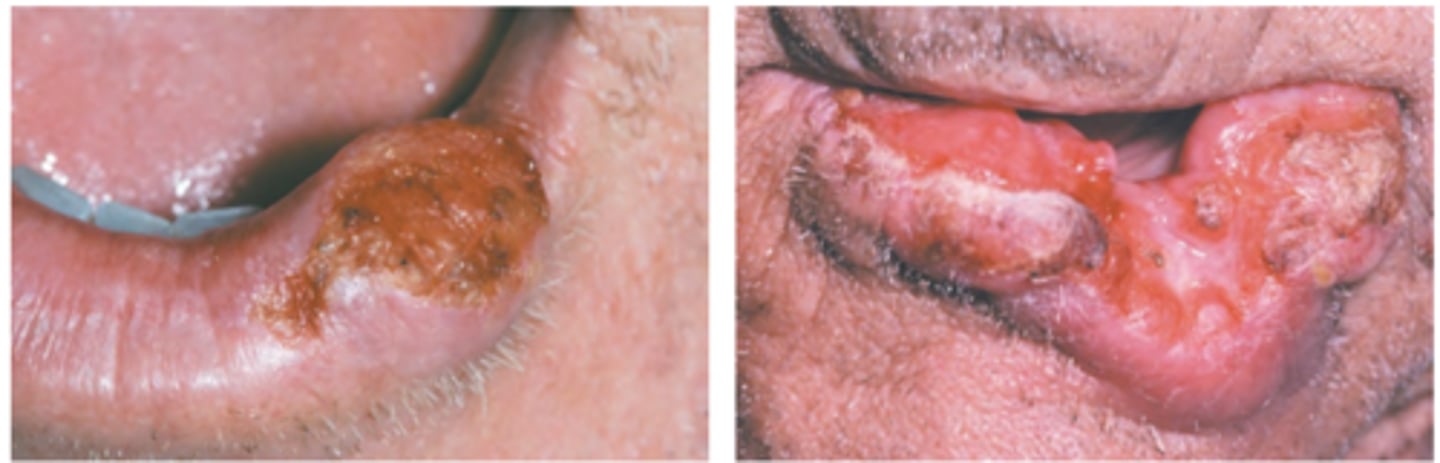
Lip Vermillion Carcinoma (SCC)
Hint: Usually associated with actinic cheilosis
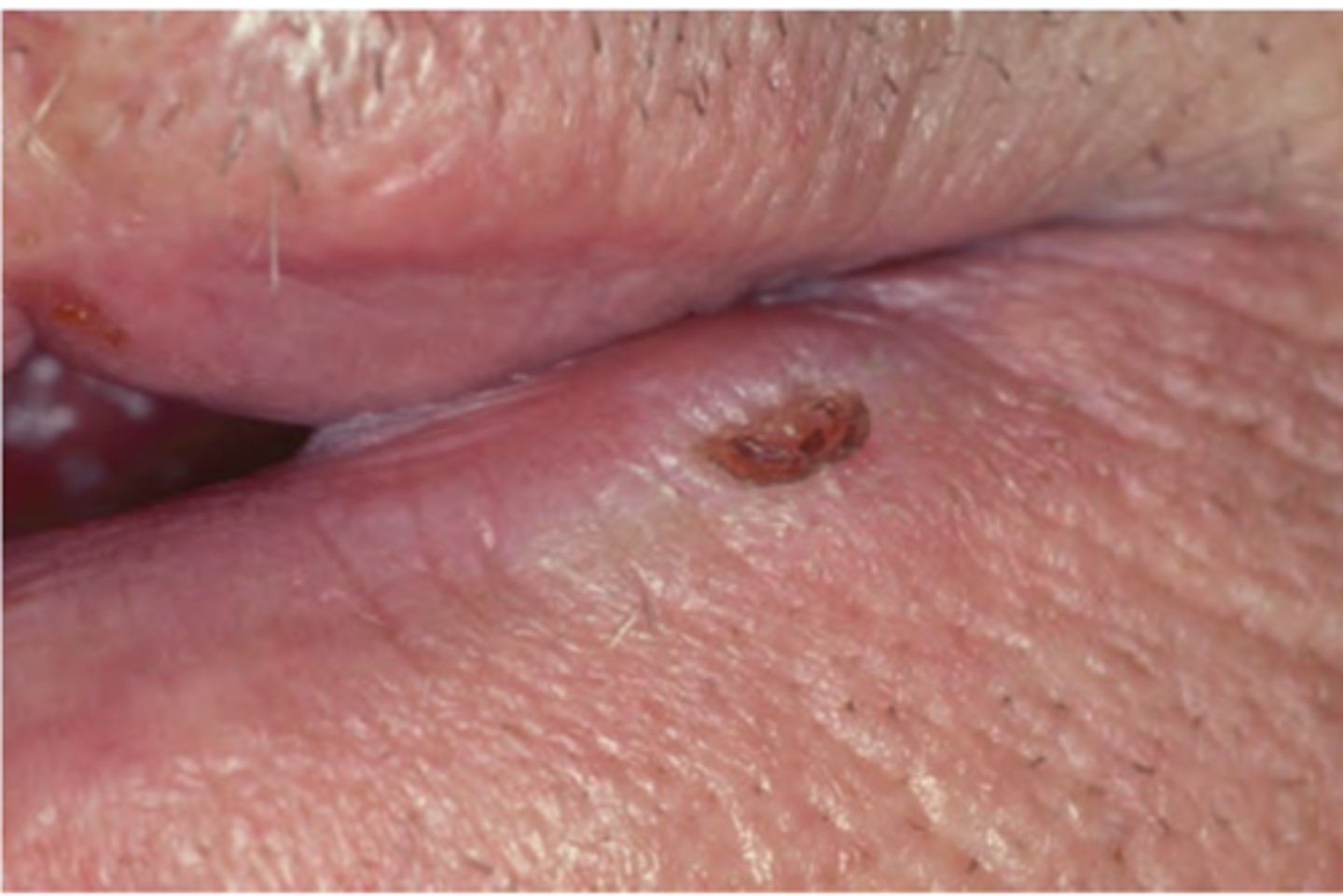
Lip Vermillion Carcinoma (SCC)
Hint: 90% occurrences on lower lip - best prognosis
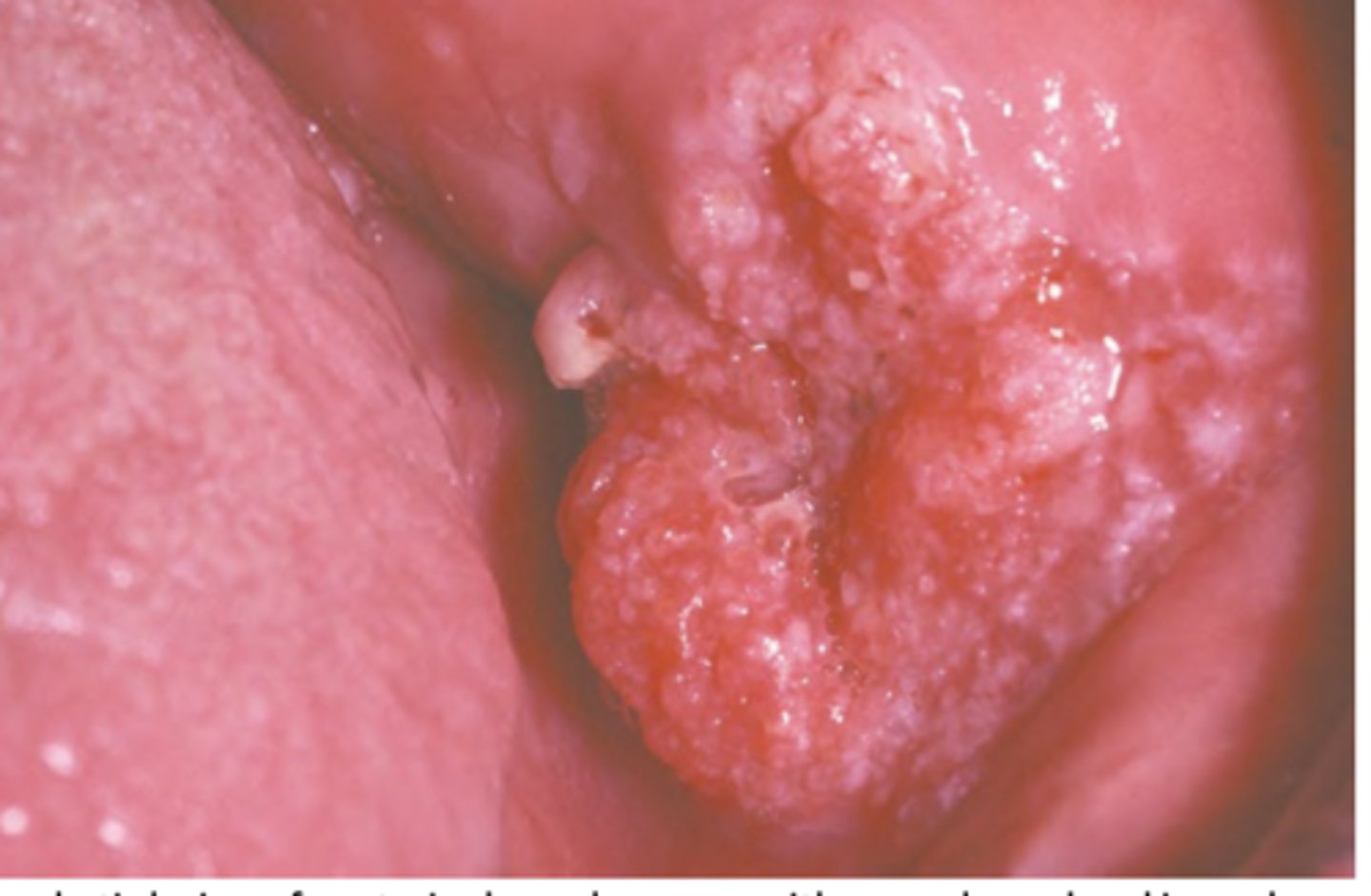
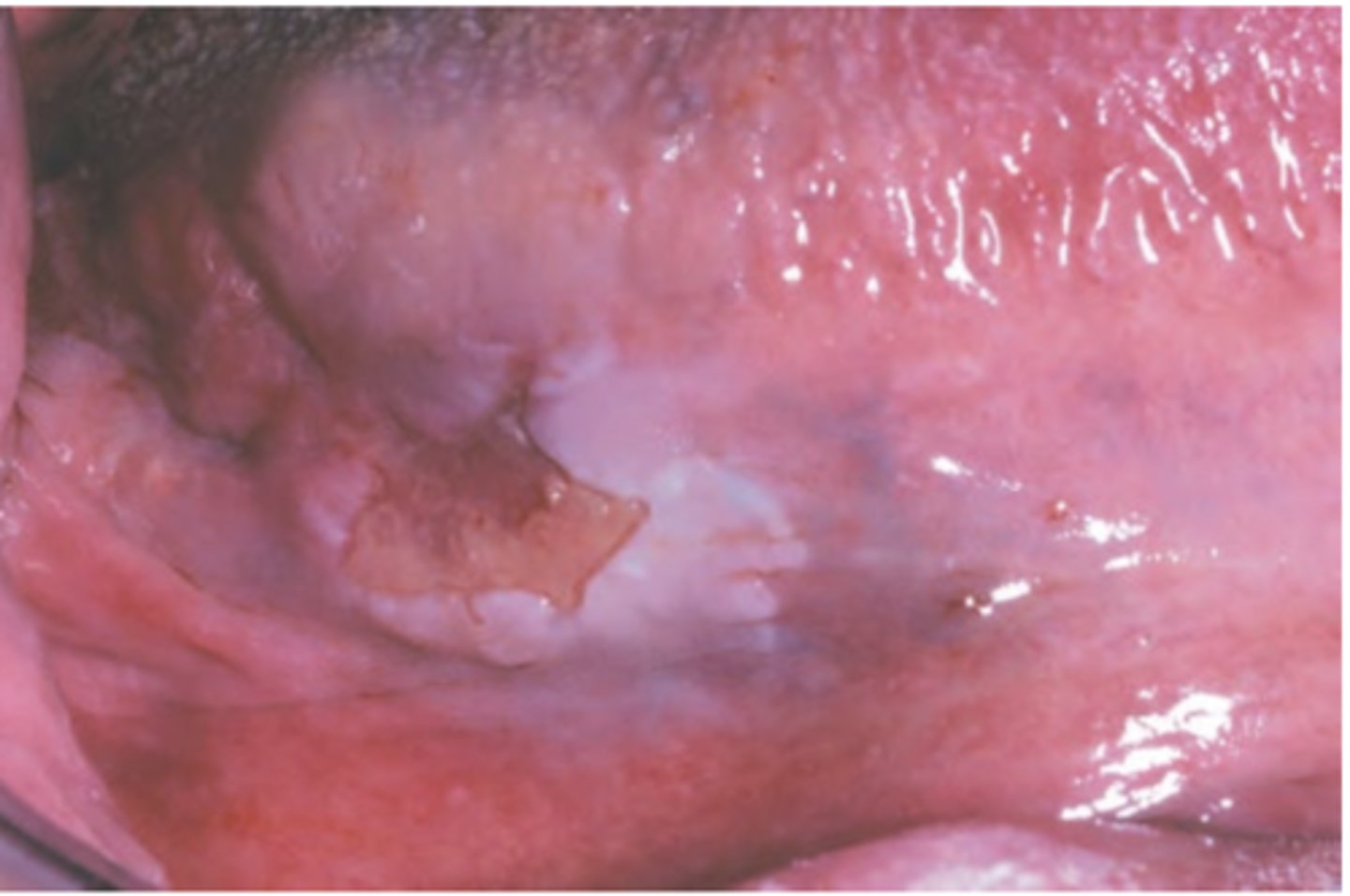
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (intraoral)
Hint: most common sites of this pathology are tongue (posterior lateral and ventral) and floor of mouth
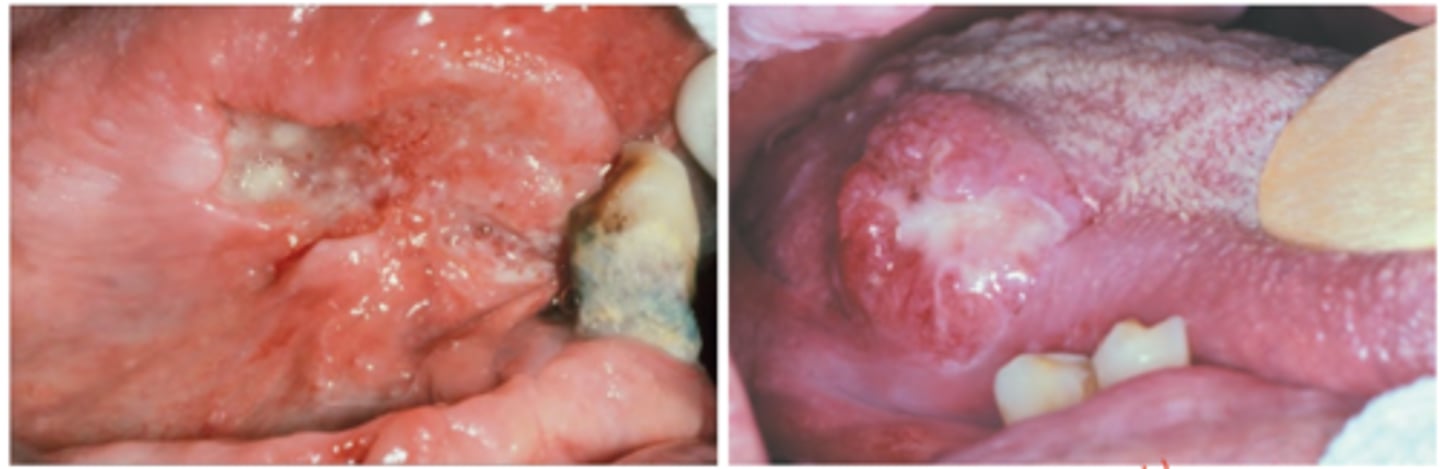
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (intraoral)
Hint: most common sites of this pathology are tongue (posterior lateral and ventral) and floor of mouth
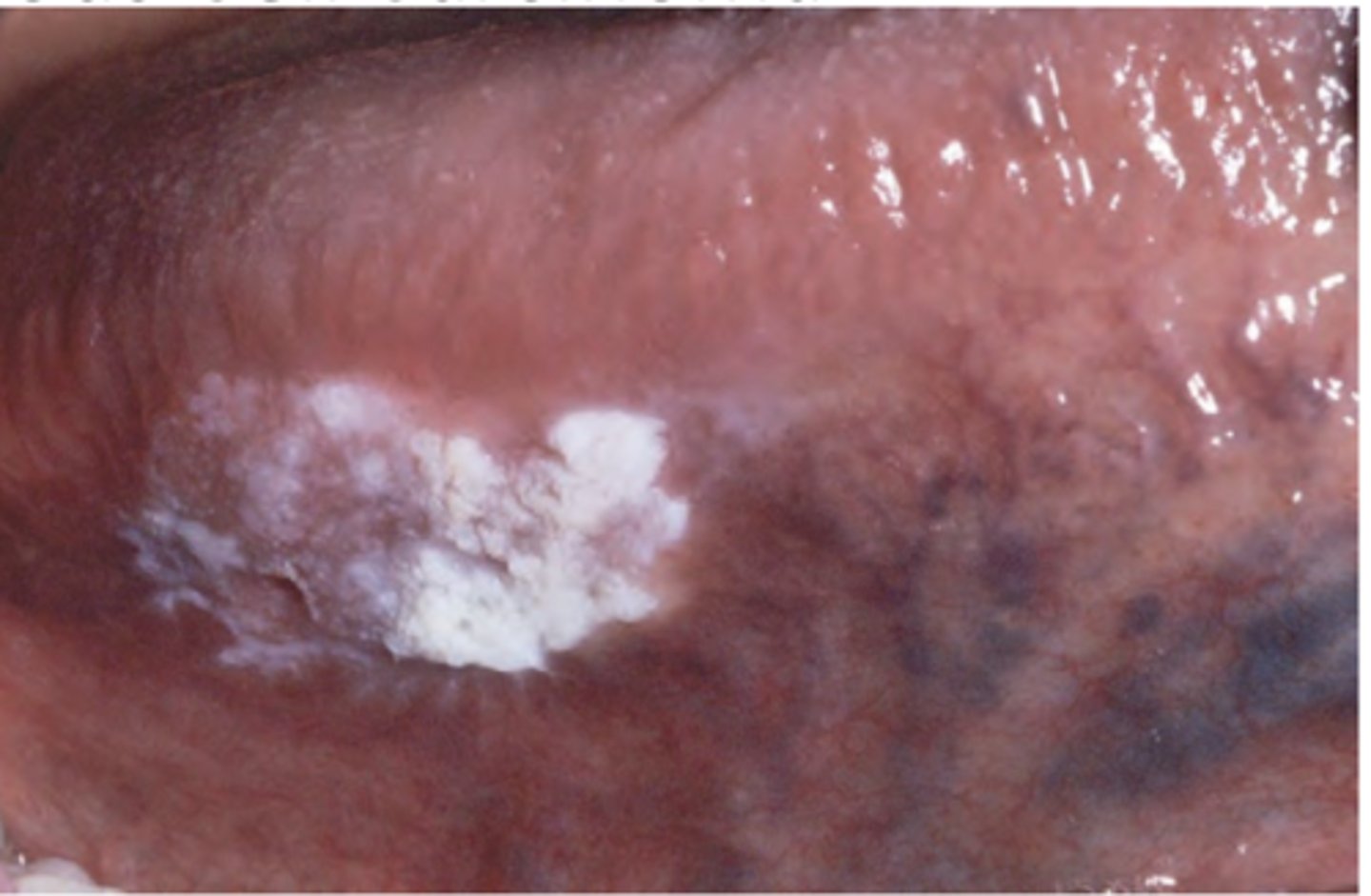
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (floor of mouth)
Diffuse erythematous speckled plaque on floor of mouth; most likely to arise from existing leukoplakia
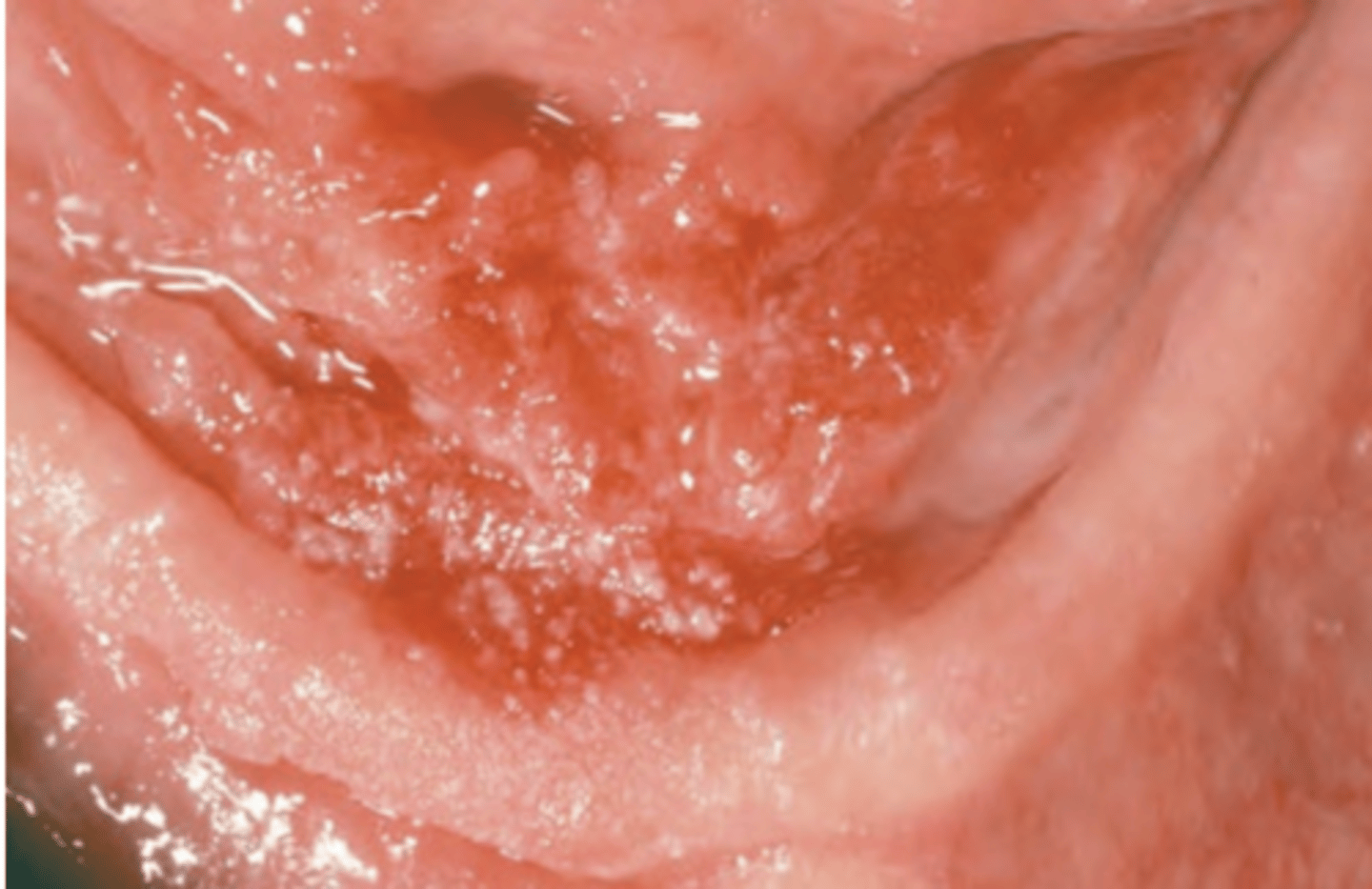
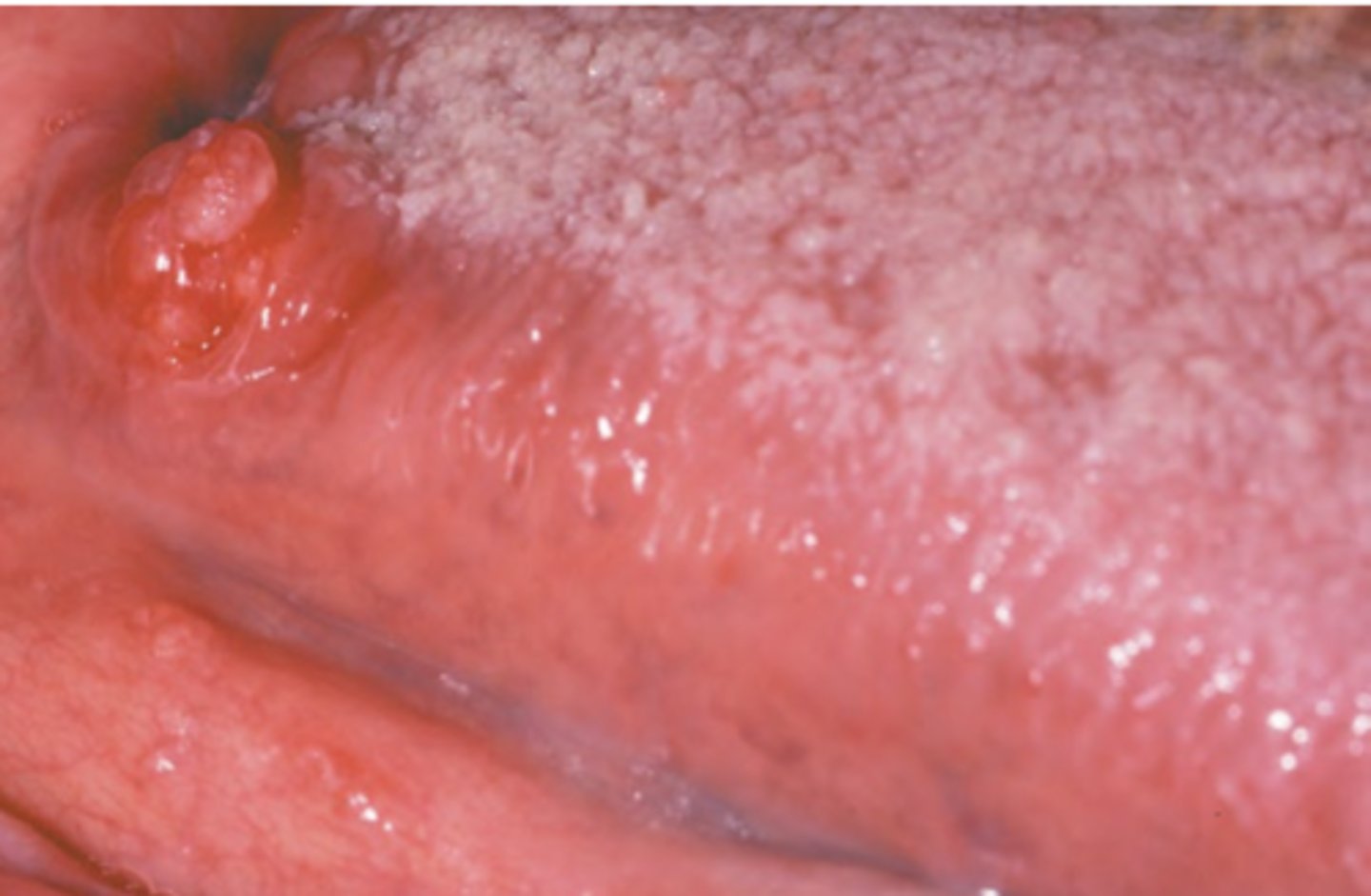
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (gingival and alveolar)
Hint: mimics common, benign inflammatory and reactive lesions (pyogenic granuloma)
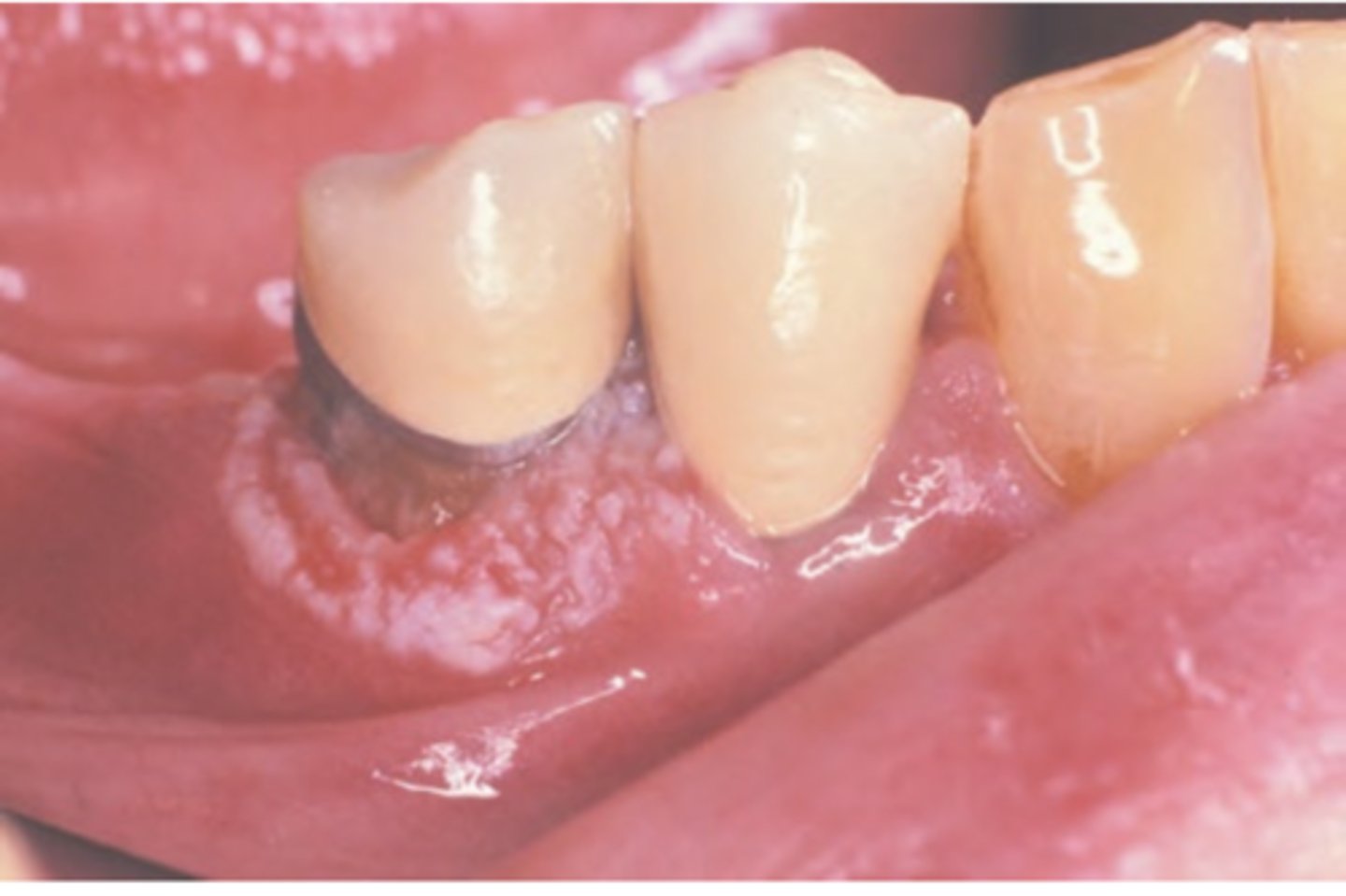
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (gingival and alveolar)
Hint: mimics common, benign inflammatory and reactive lesions (pyogenic granuloma)
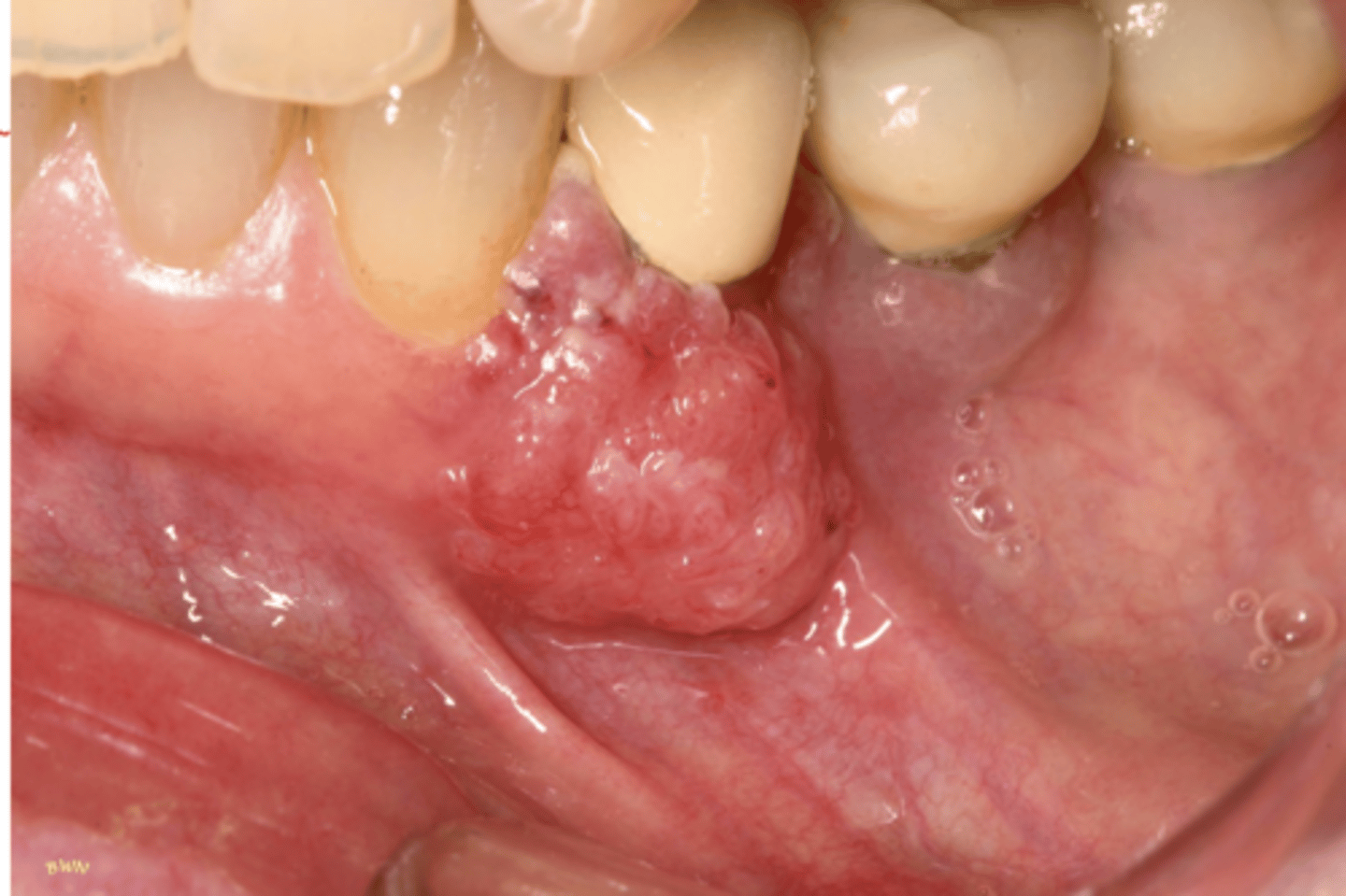
Oropharyngeal Carcinoma (SCC)
Hint: Favored site for HPV-associated carcinomas
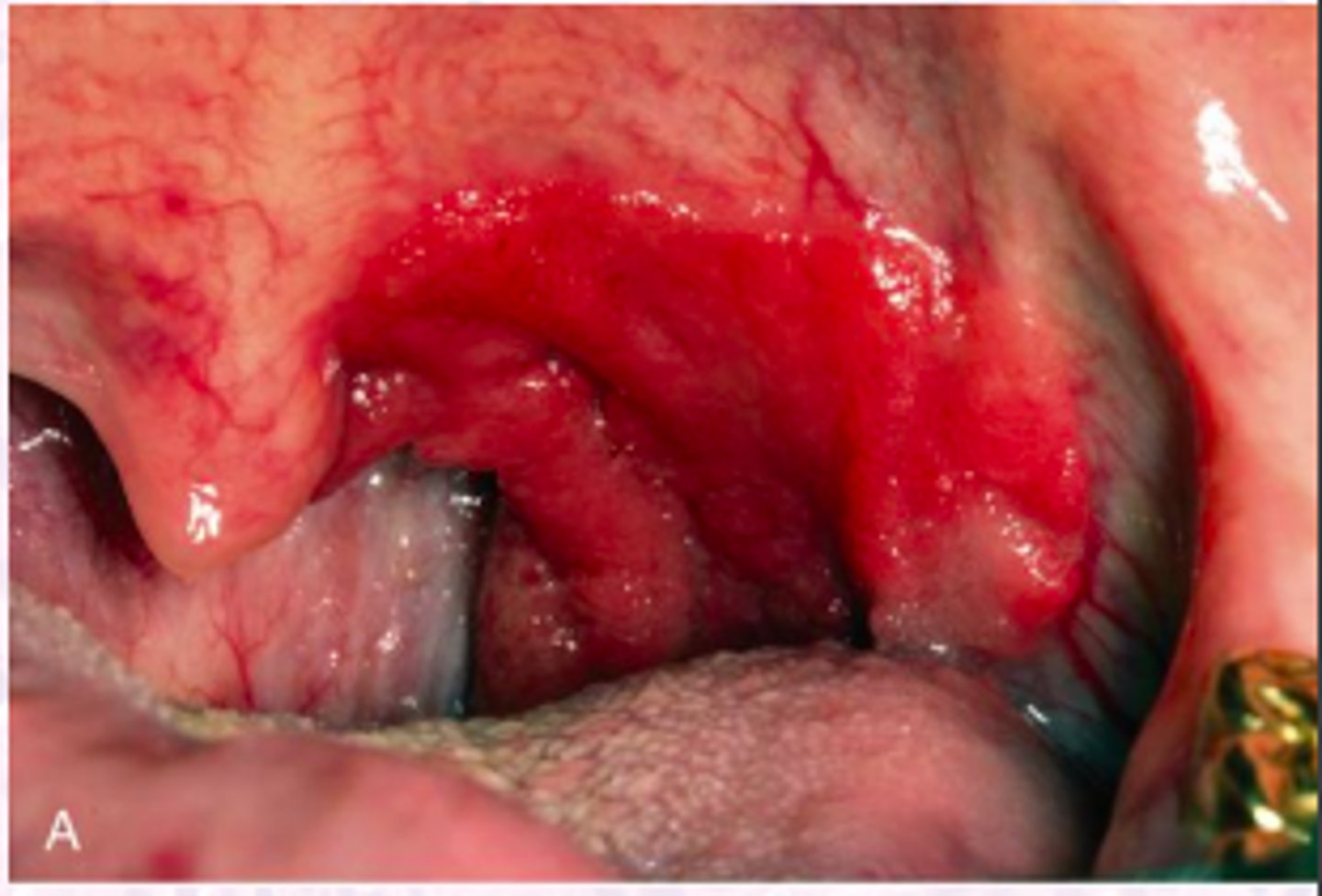
Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal type
Hint: midline swelling of soft palate may precede deep, necrotic ulcer
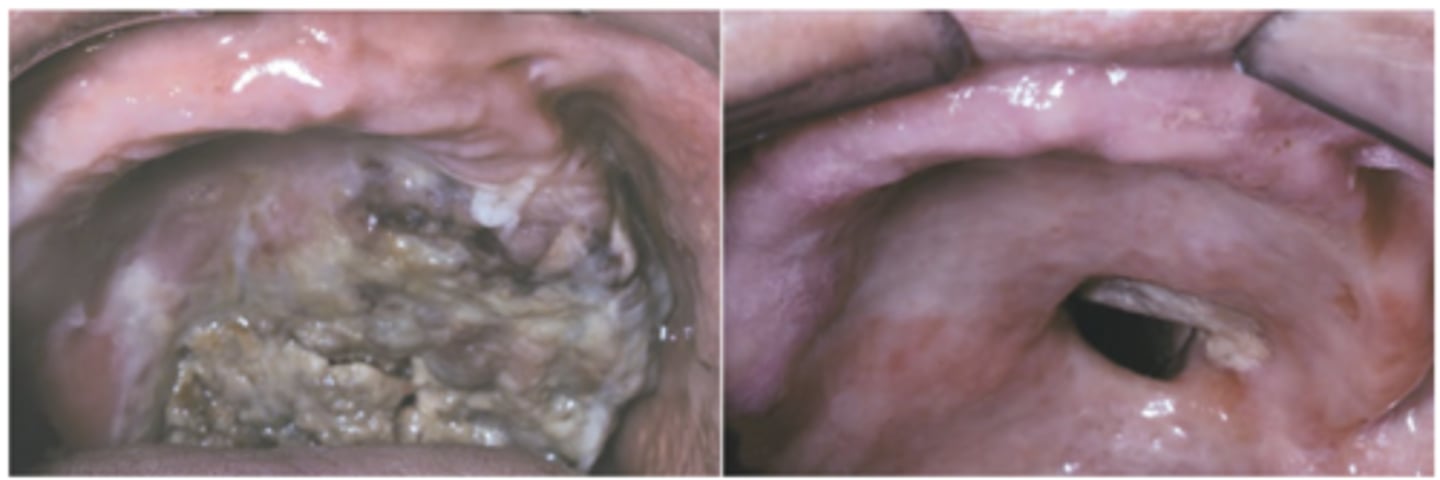
Primary Herpes Simplex Virus
Hint: occurs in young children on mouth/lips
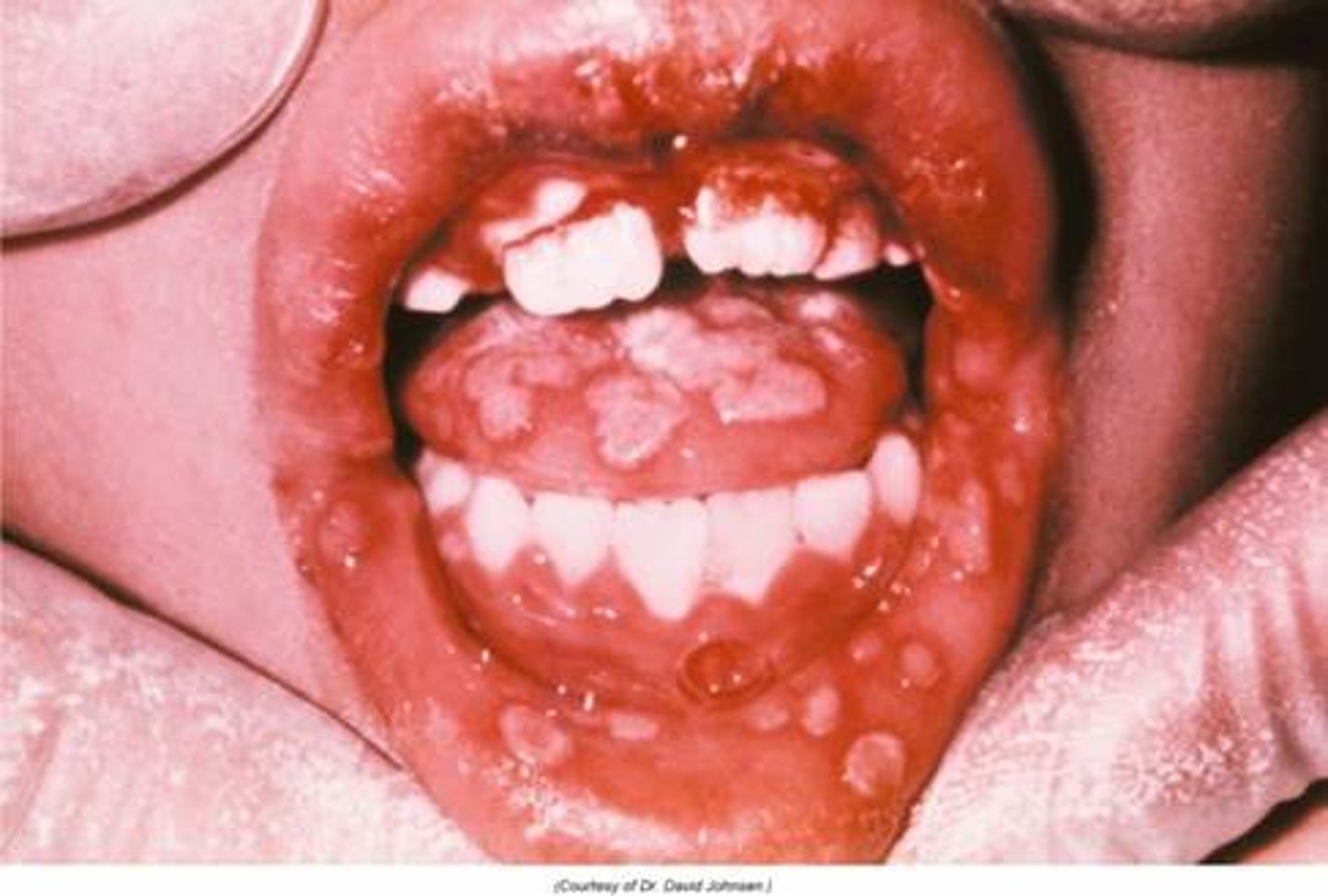
Primary Herpes Simplex Virus
Hint: occurs in young children on mouth/lips
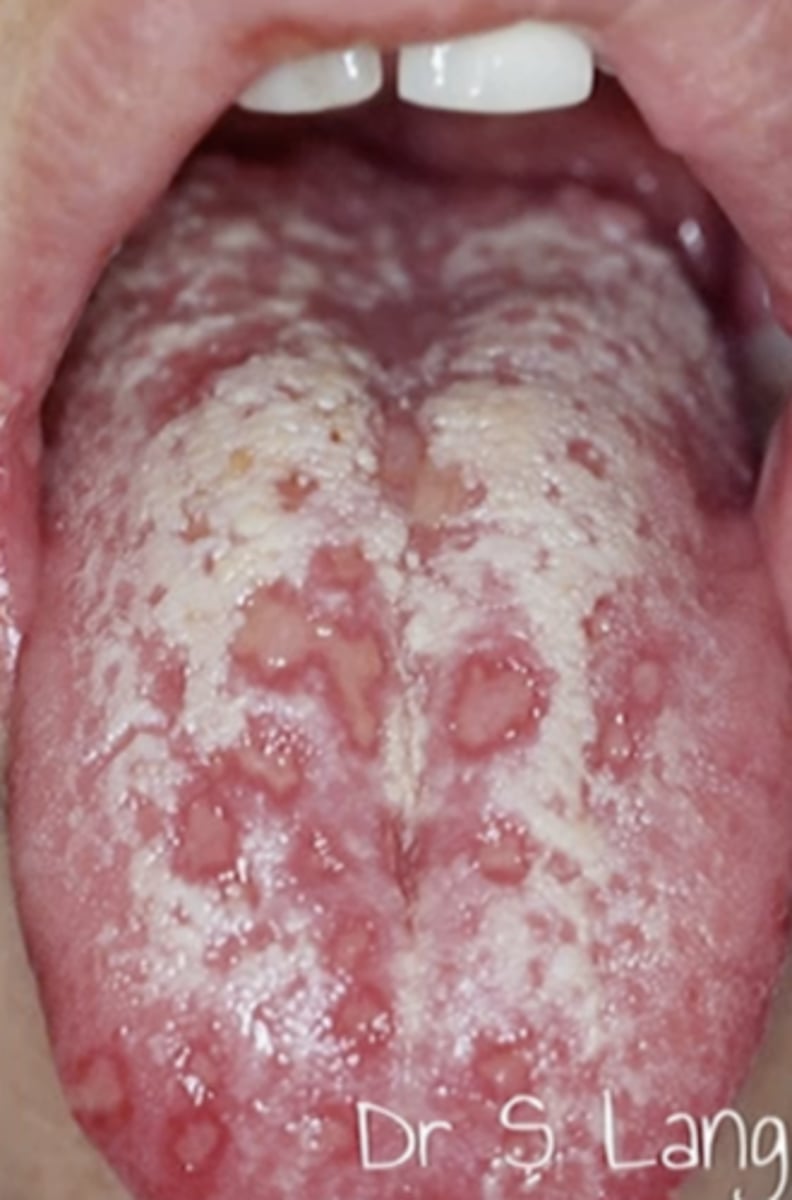
Primary Herpes Simplex Virus
Hint: occurs in young children on mouth/lips; painful enlarged erythematous palatal gingiva
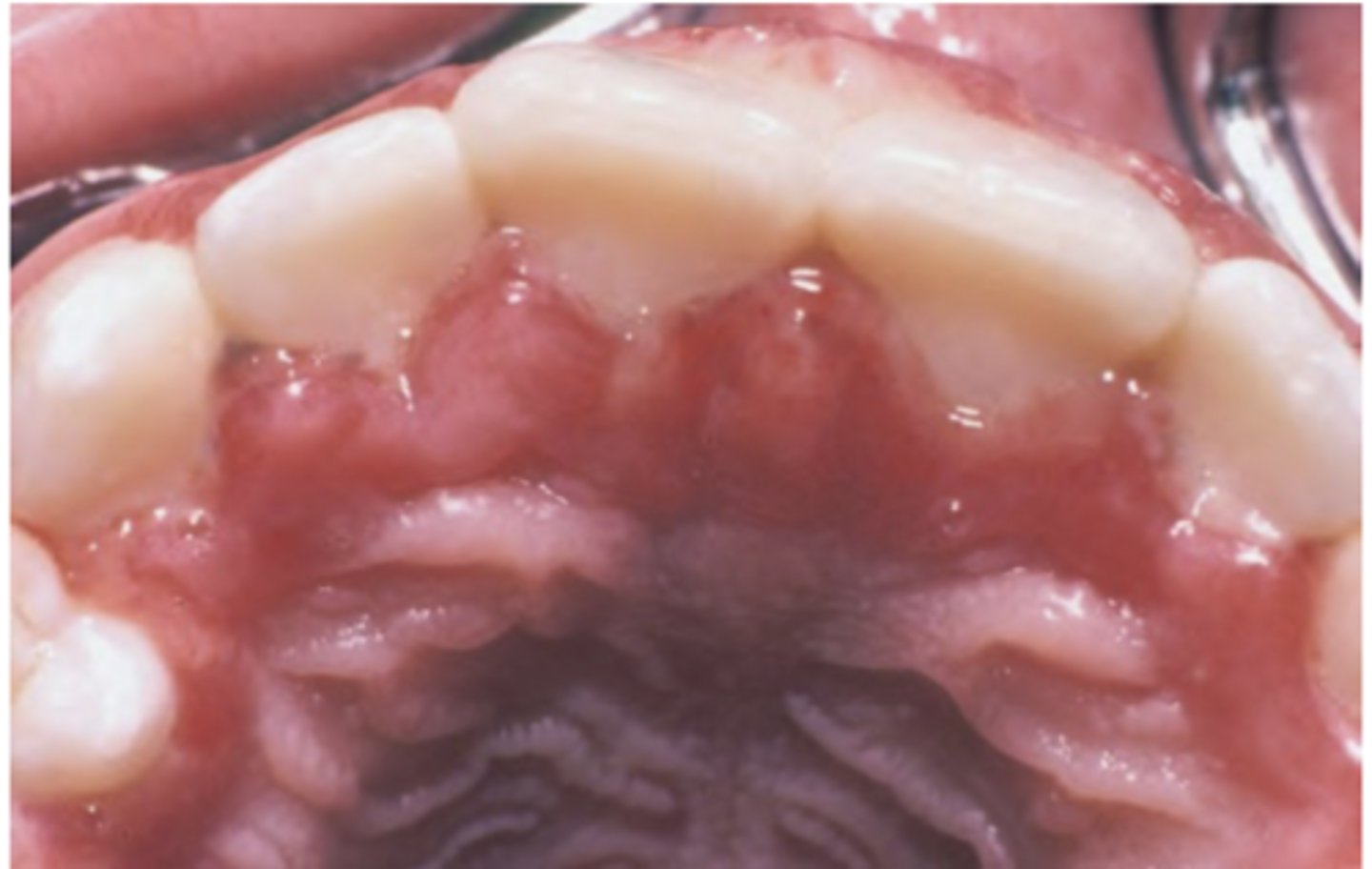
Primary Herpes Simplex Virus
Hint: Primary infection in adults - pharyngotonsillitis
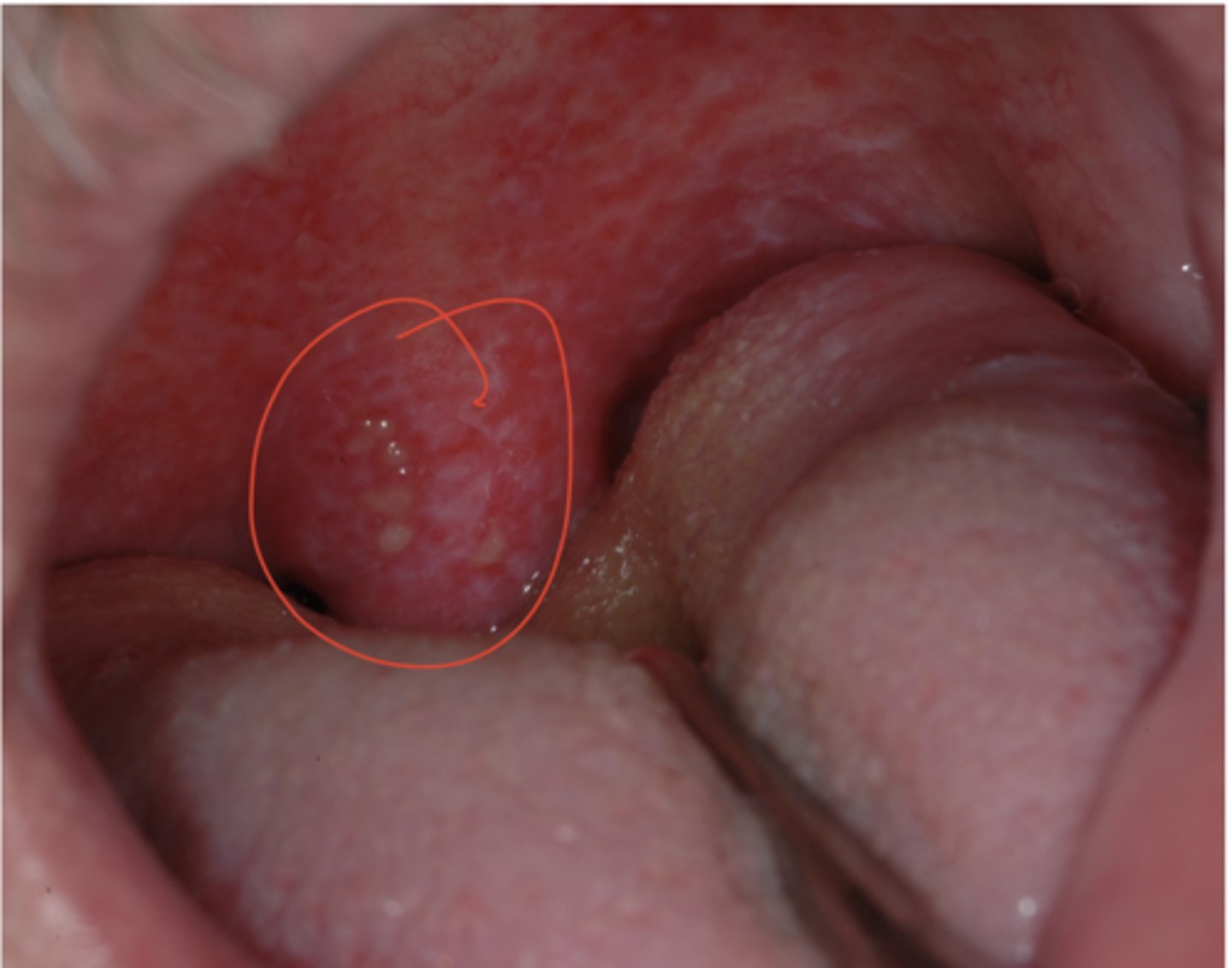
Recurrent Herpes Simplex Virus
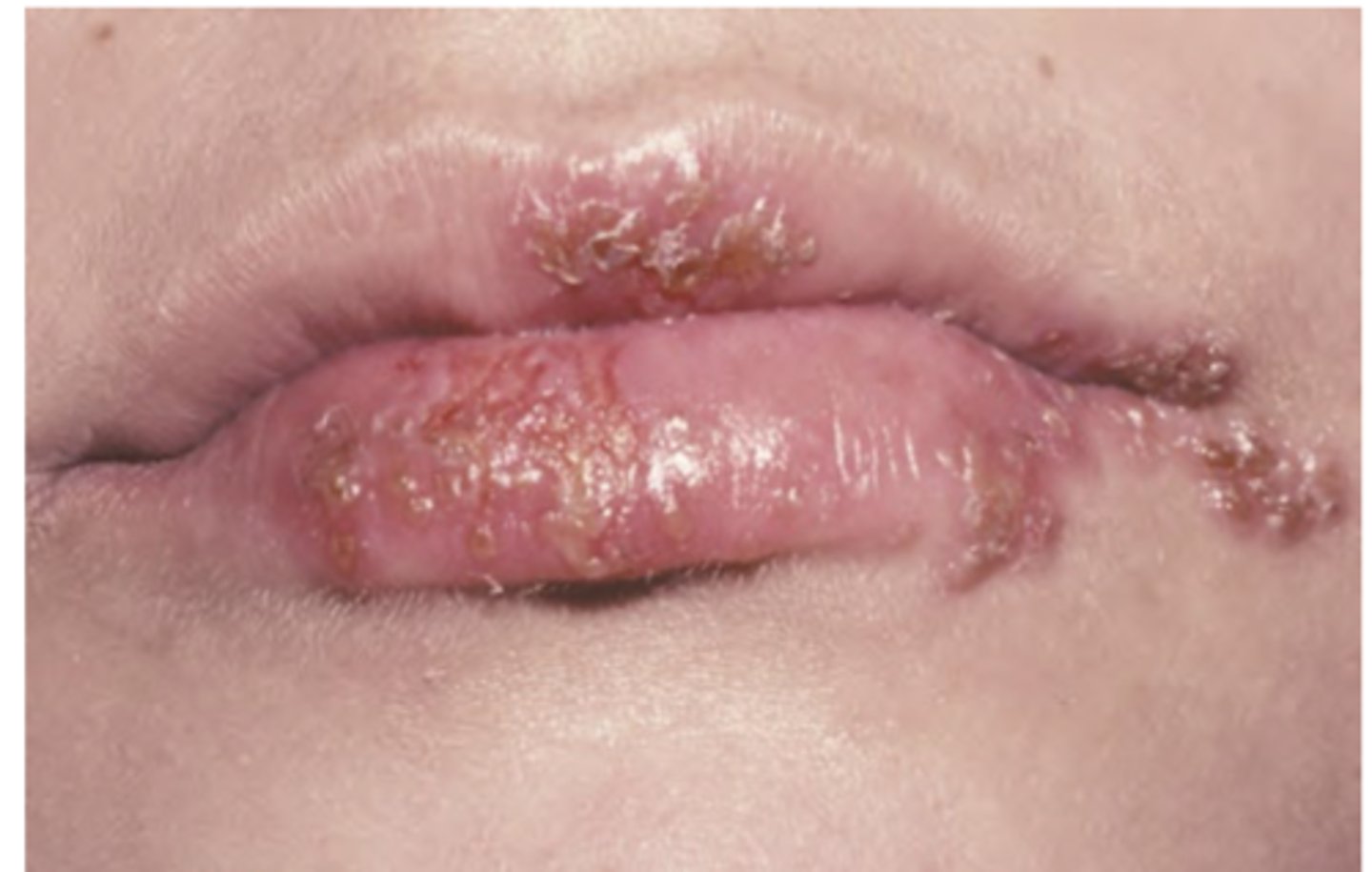
Recurrent Herpes Simplex Virus
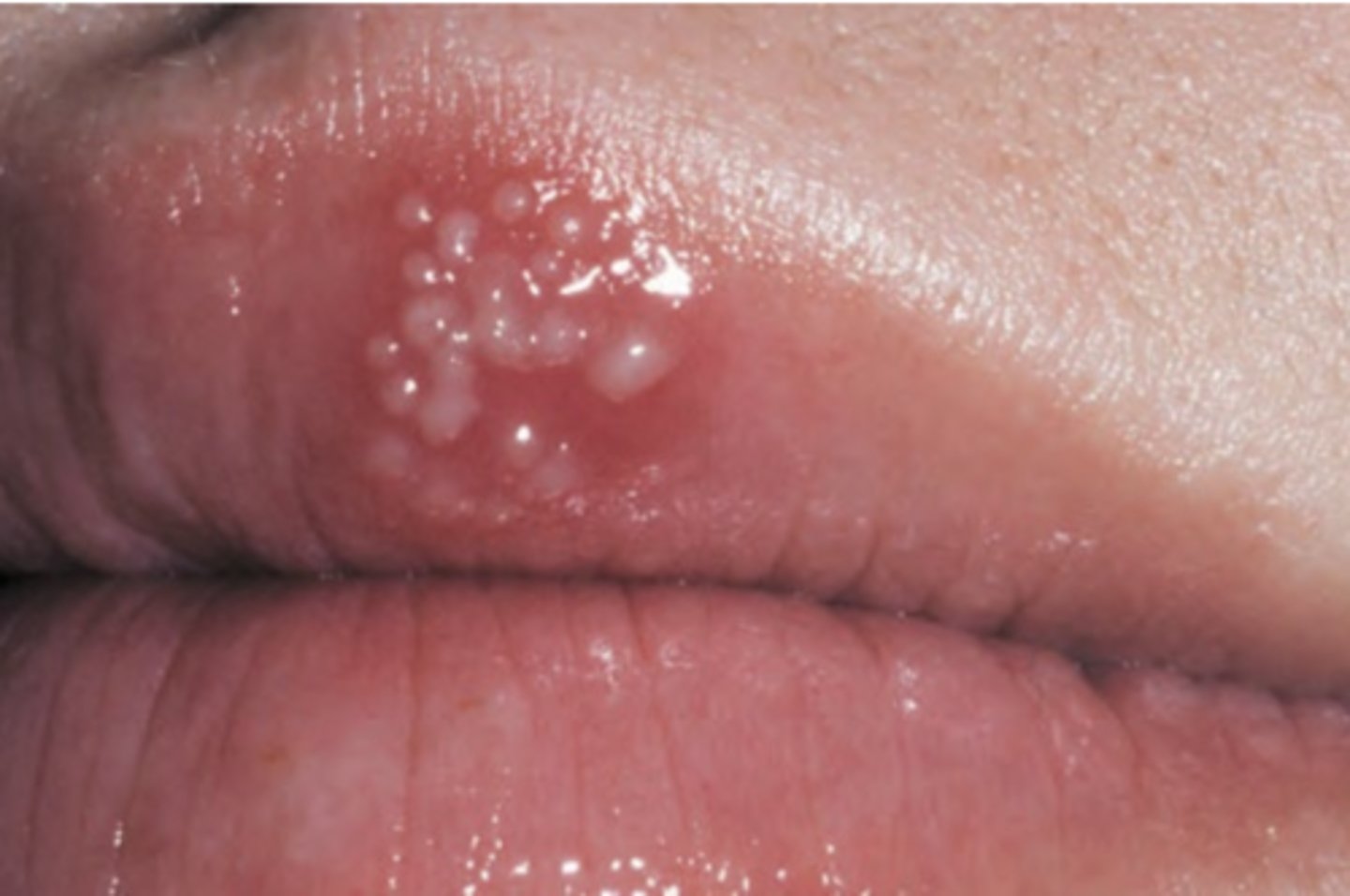
Recurrent Herpes Simplex Virus
Hint: occurs on keratinized mucosa bound to bone (attached gingiva and hard palate)
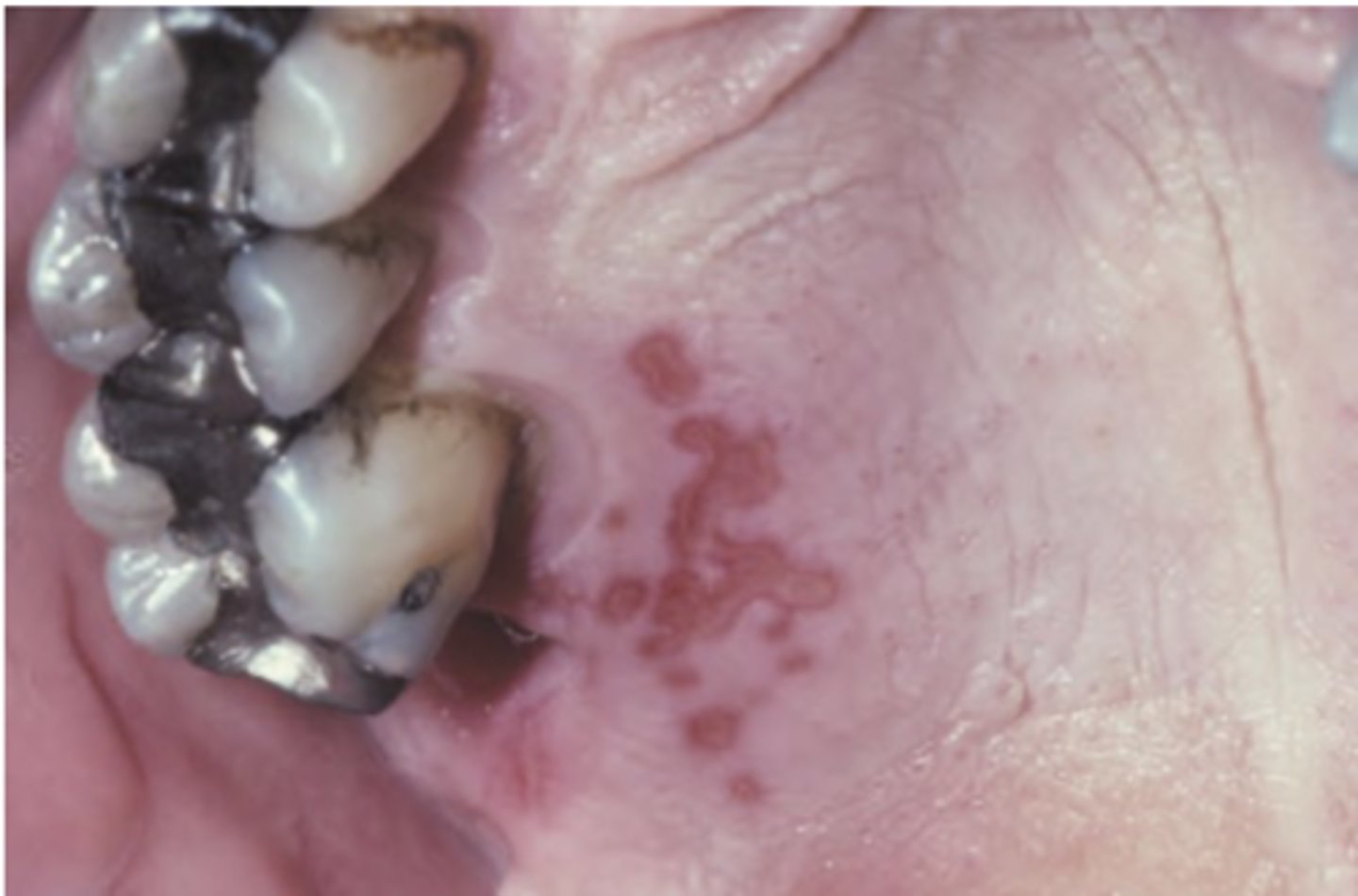
Herpetic Whitlow (HSV)
Hint: Primary or recurrent infection of the fingers
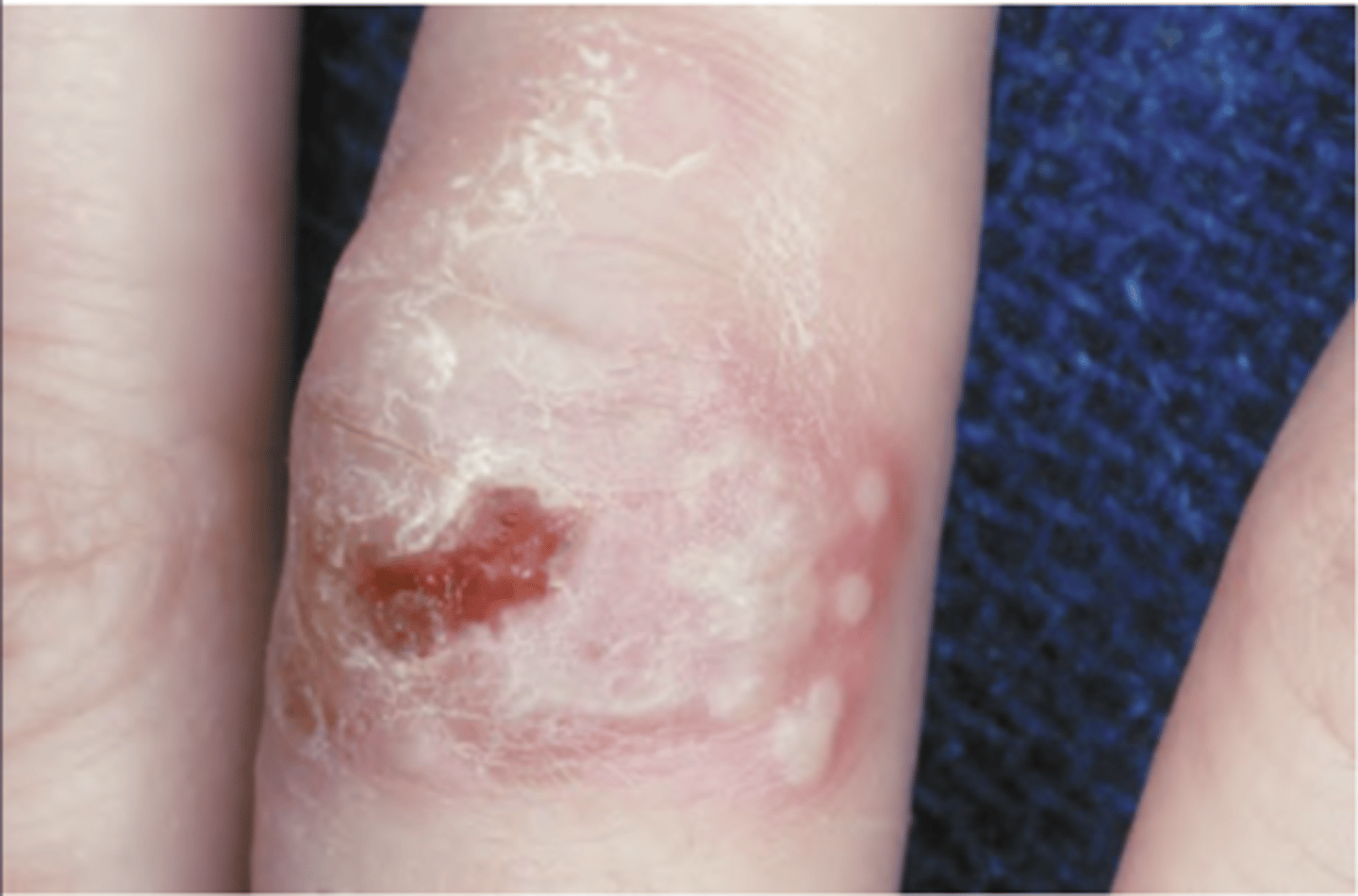
Chronic herpetic infection (HSV)
Hint: host is immunocompromised; begins on mucosa bound to bone but often spreads to unbound mucosa
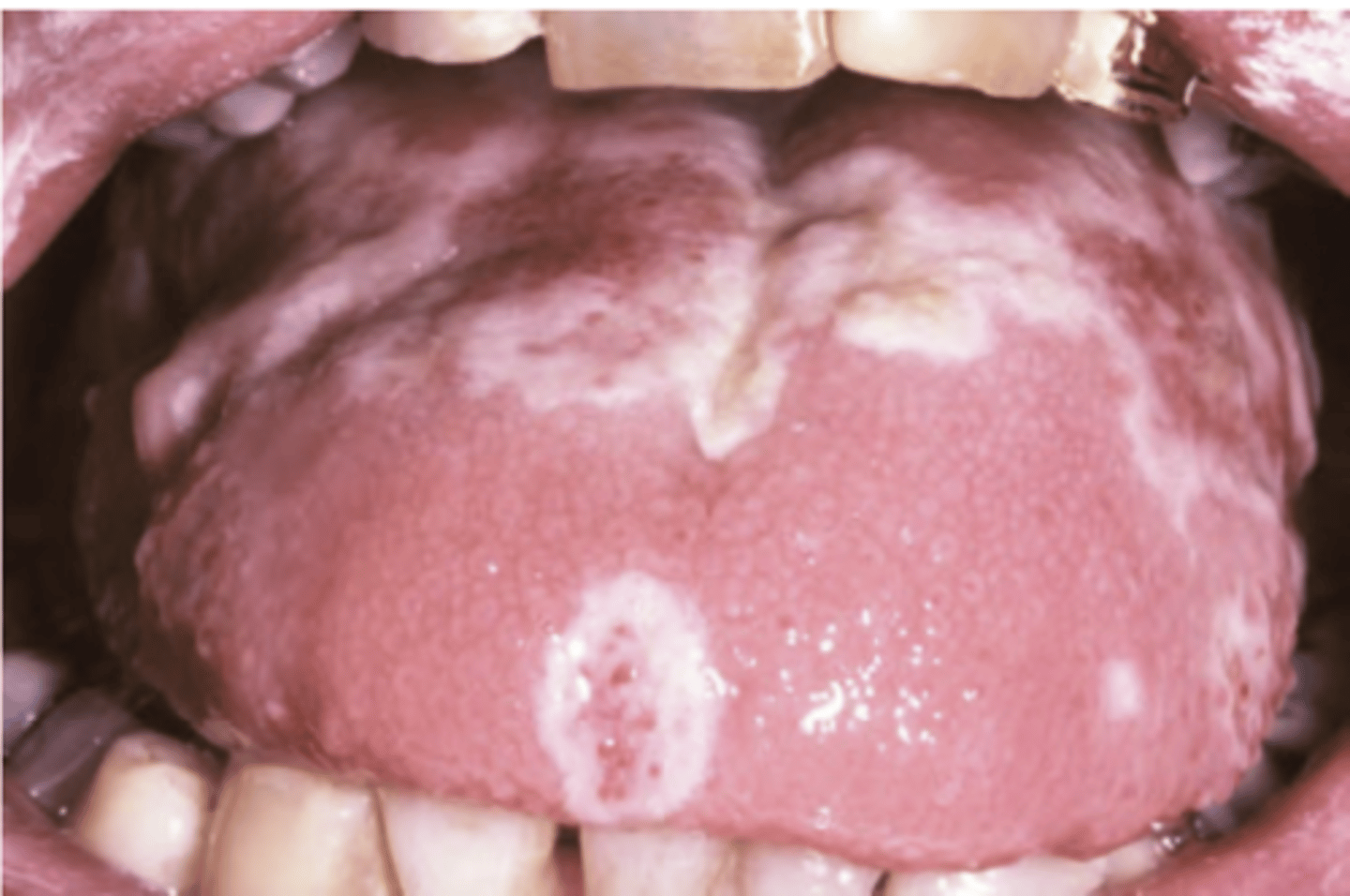
Varicella
Hint: lesions usually painless, common and may precede skin lesions; White opaque vesicles on hard palate
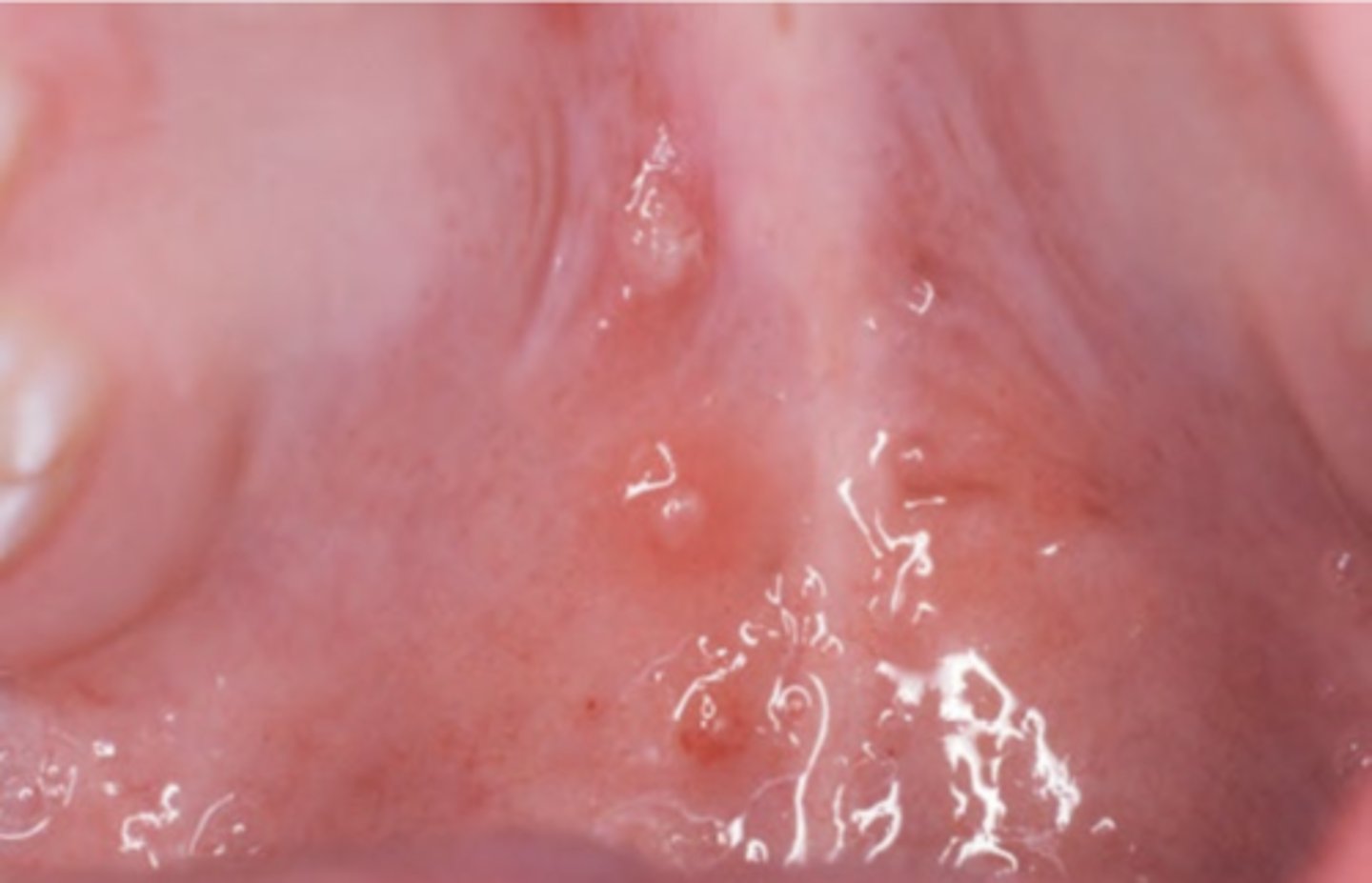
Herpes Zoster
Hint: involve moveable and bound mucosa; teeth may develop pulpitis; bone necrosis with tooth loss
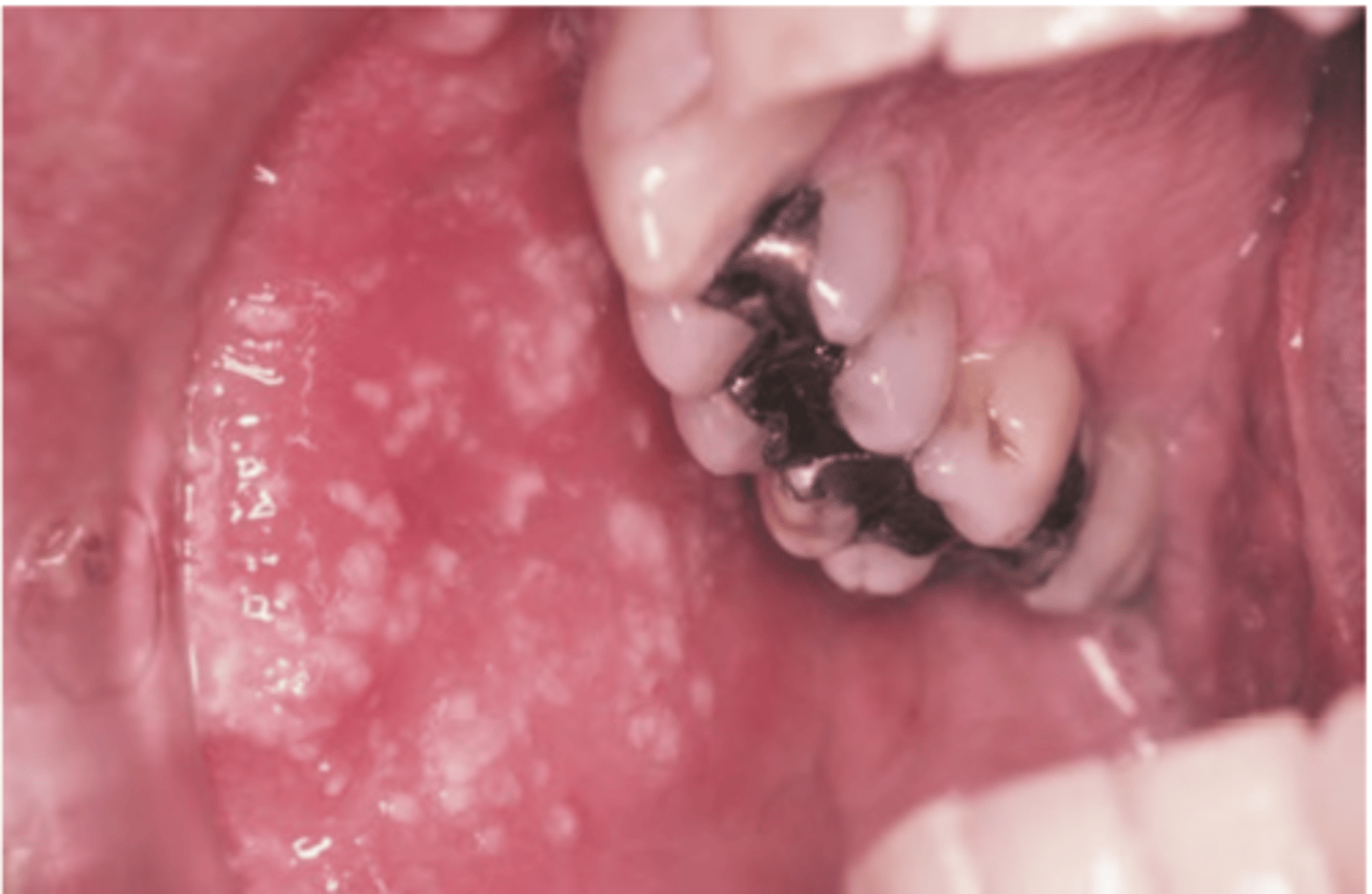
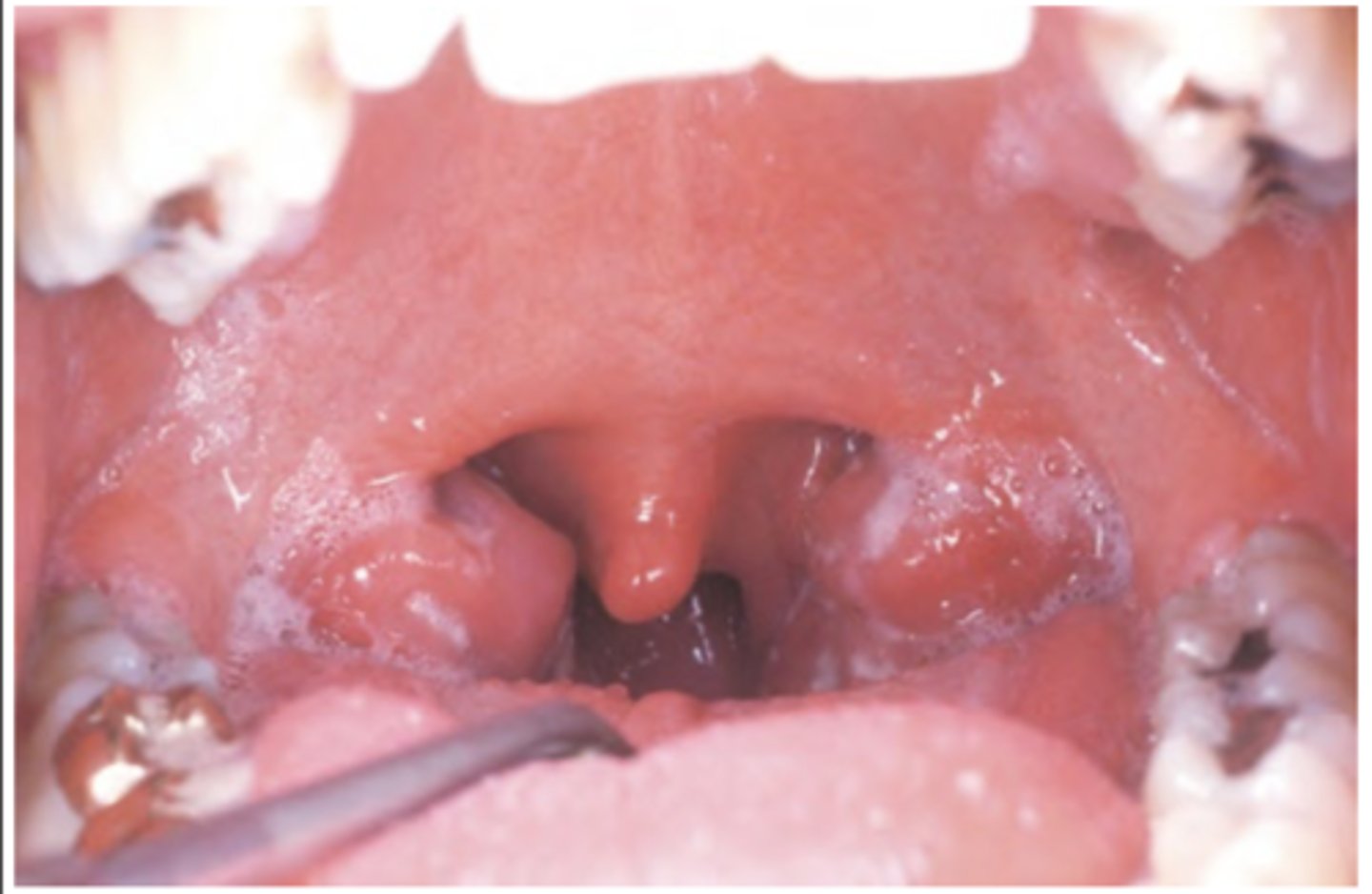
Infectious Mononucleosis
Hint: oropharyngeal tonsillar enlargement and lymphoid hyperplasia
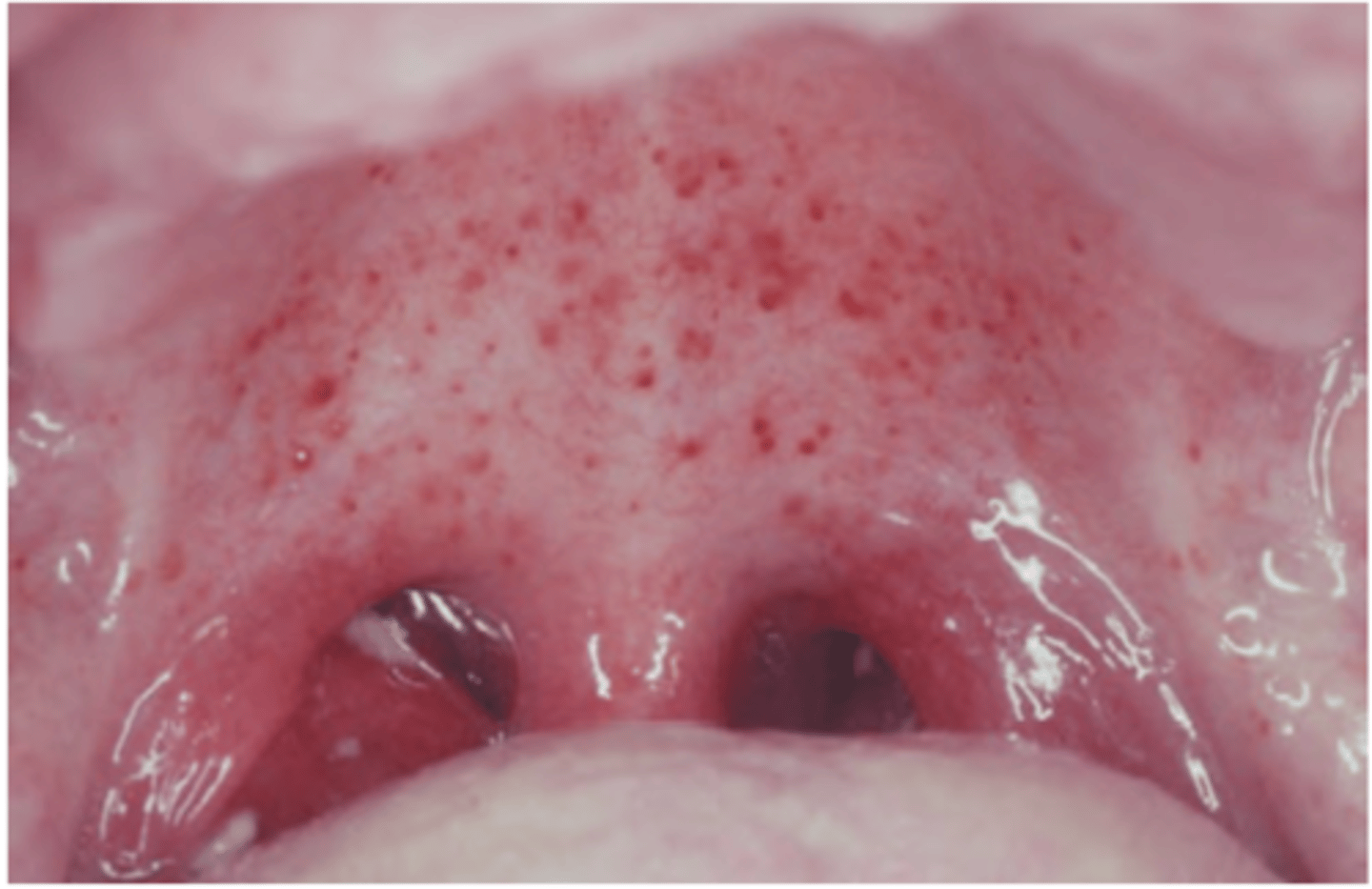
Infectious Mononucleosis
Hint: Petechiae on hard or soft palate
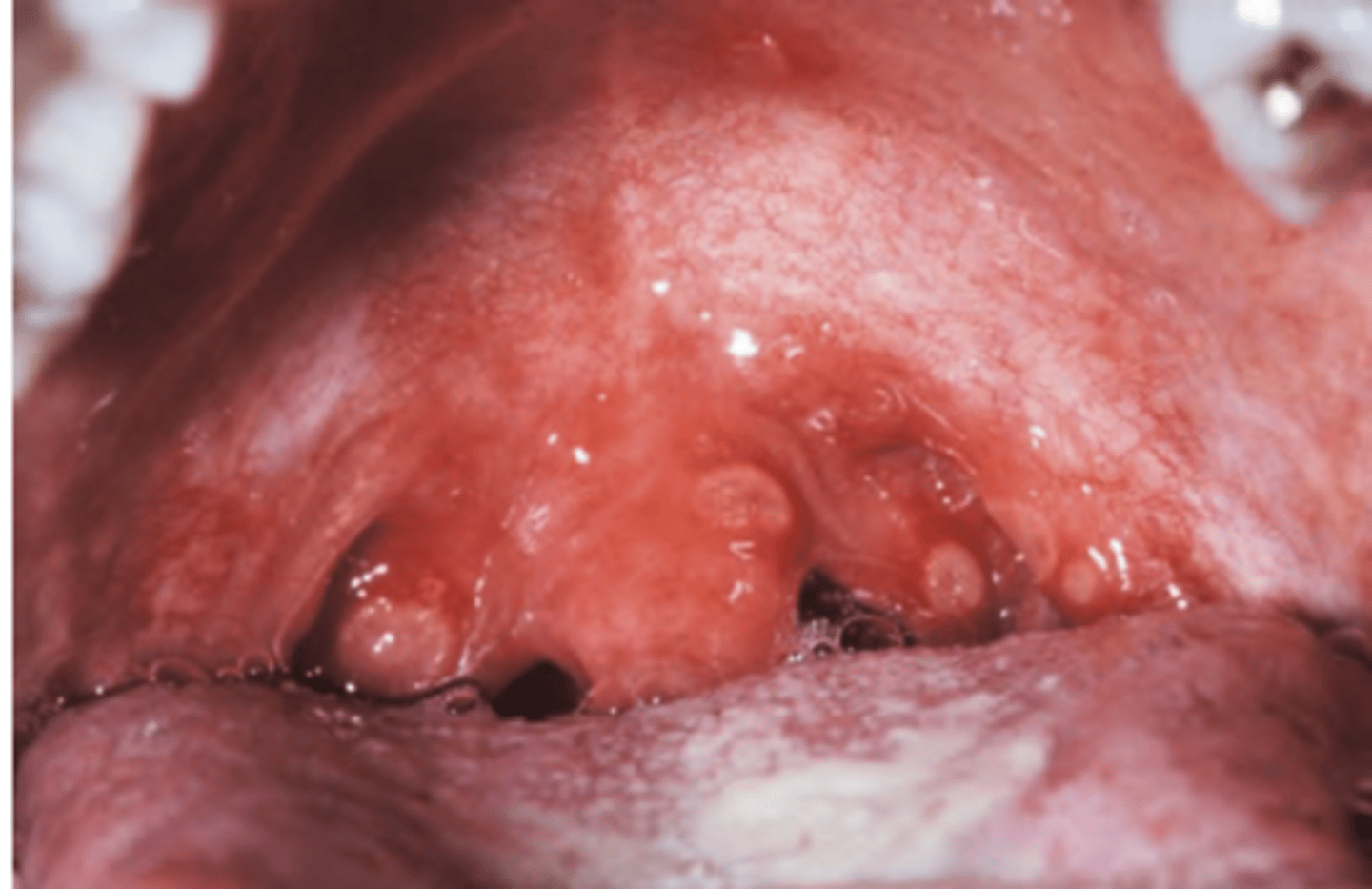
Enterovirus (Herpangina)
Hint: Lesions typically develop on soft palate or tonsillar pillars
Enterovirus (Hand foot and Mouth)
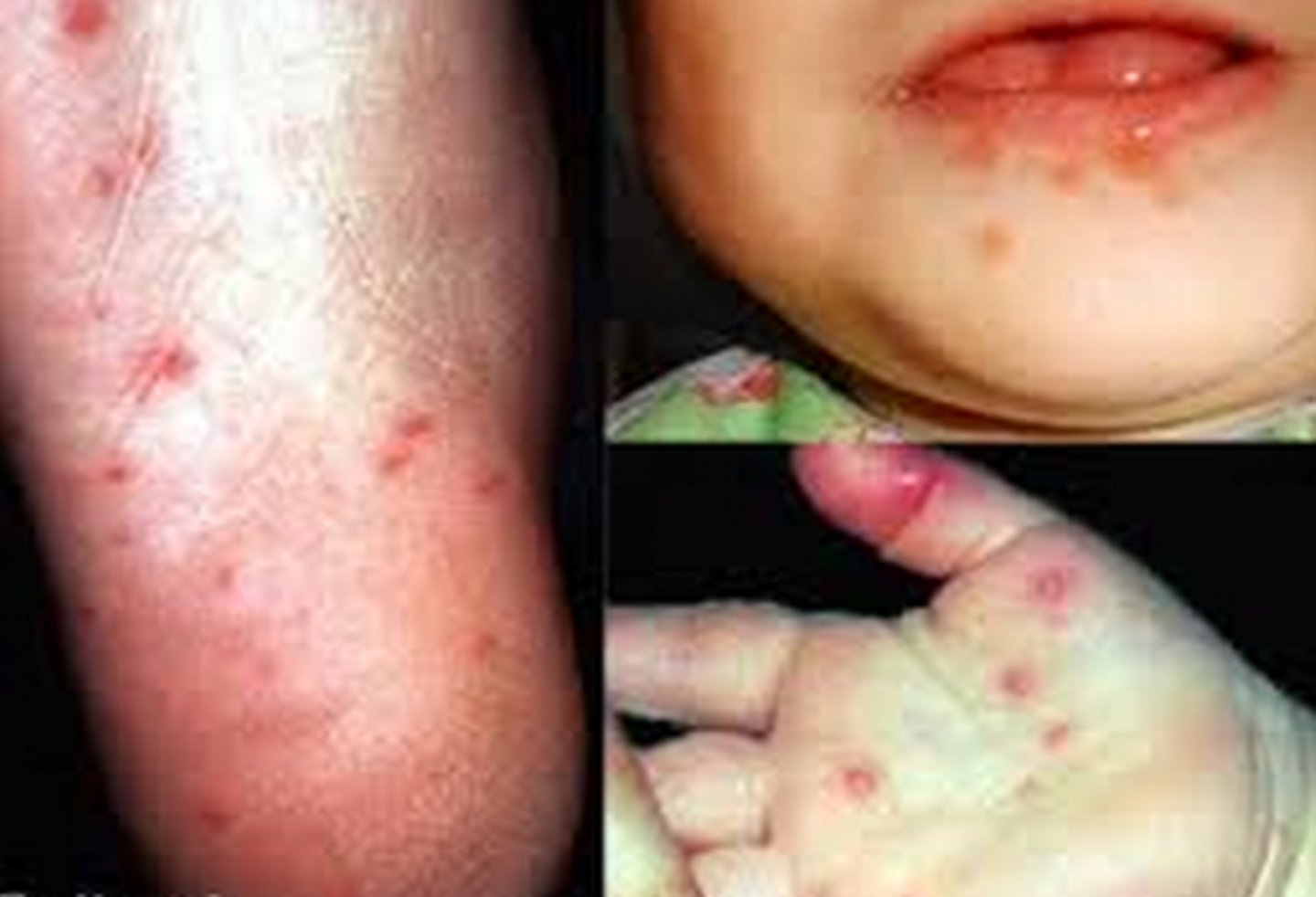
Enterovirus (Hand foot and Mouth)
Hint: Resembles herpangina but more numerous and involve anterior regions of mouth; buccal & labial mucosa & tongue are most common
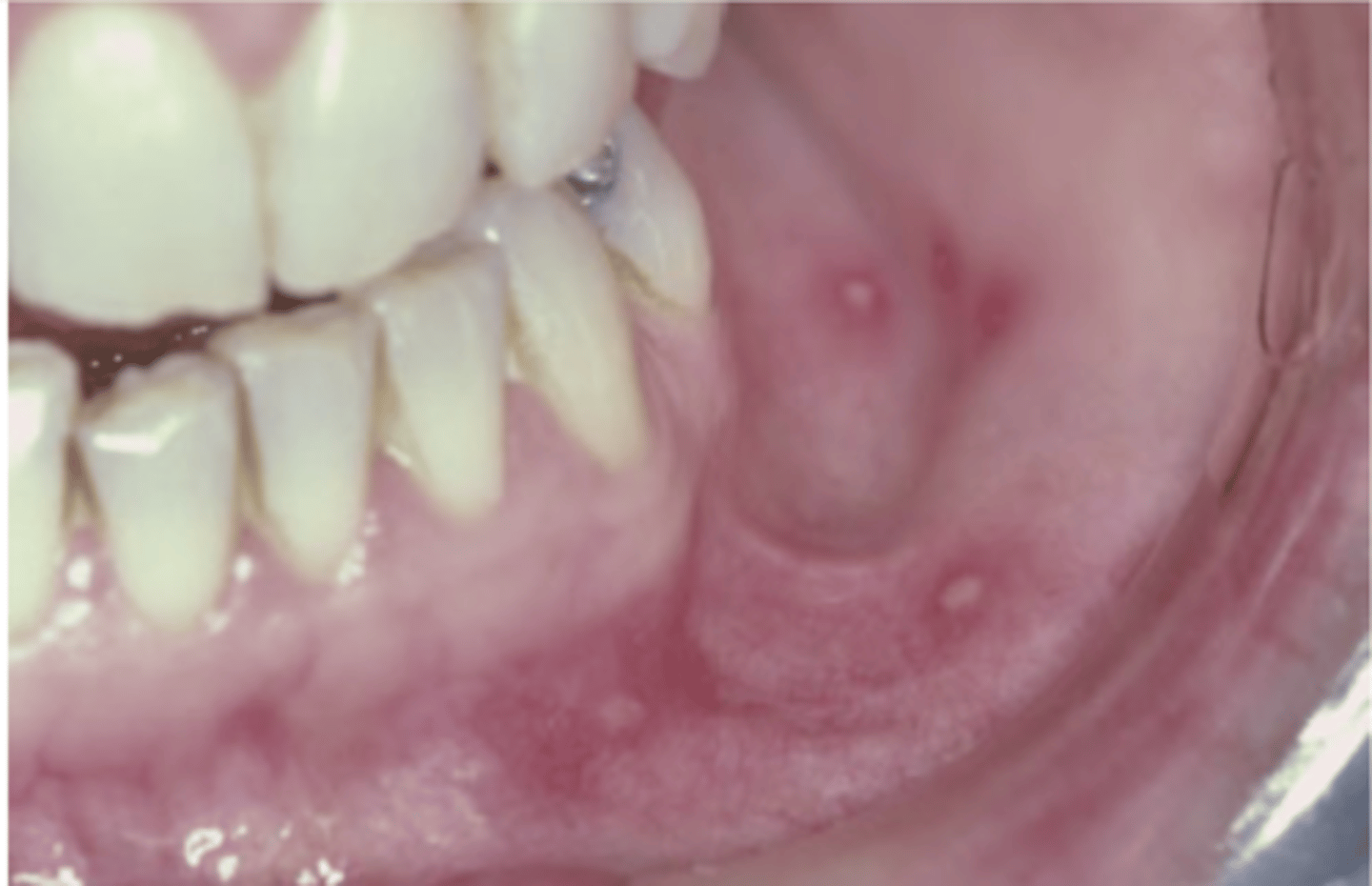
Enterovirus (Acute lymphonodular Pharyngitis)
Hint: few (1-5) yellow to dark-pink nodules develop on soft palate or tonsillar pillars that resolve within 10 days
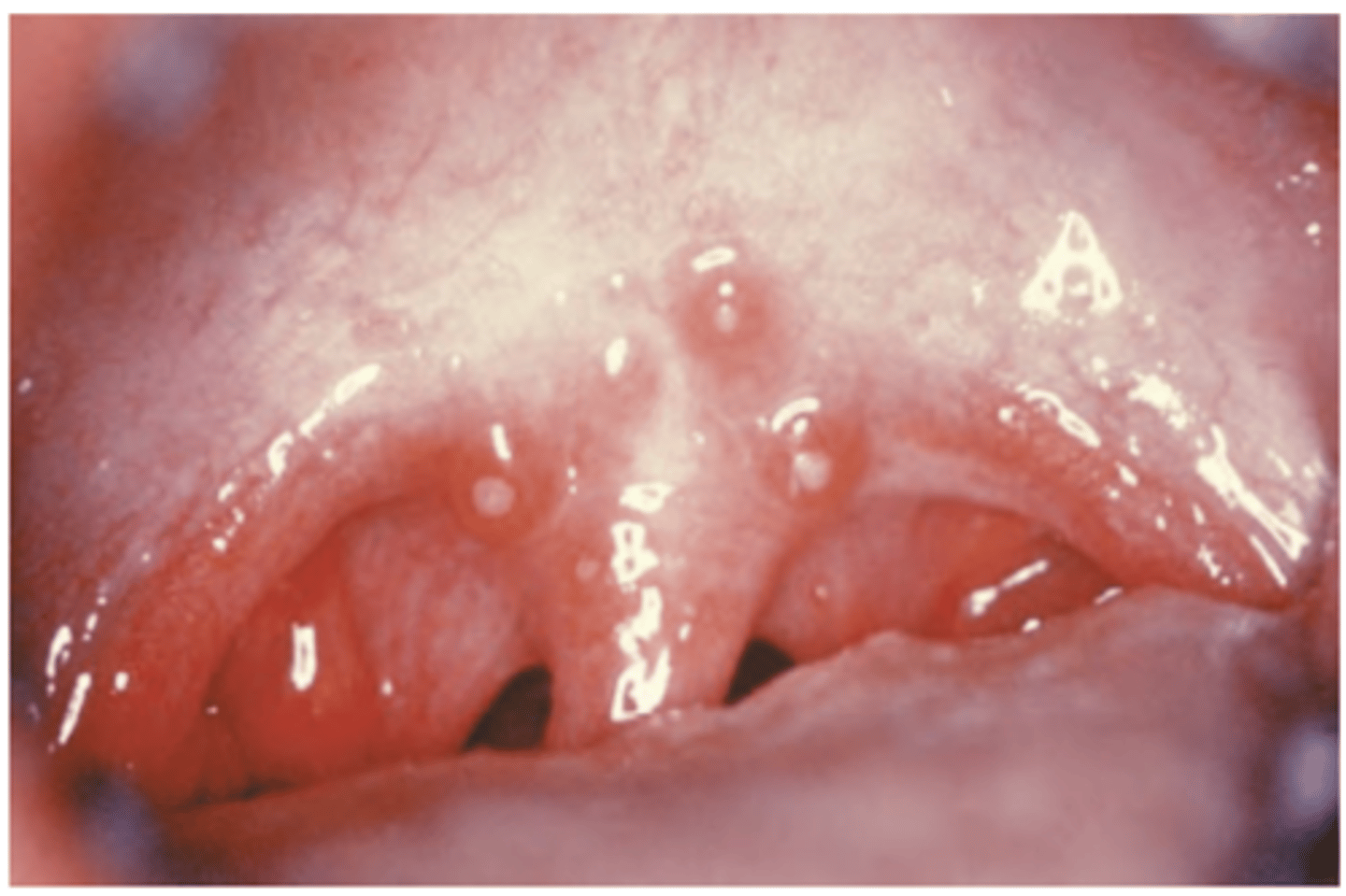
Measles
Hint: Koplik spots
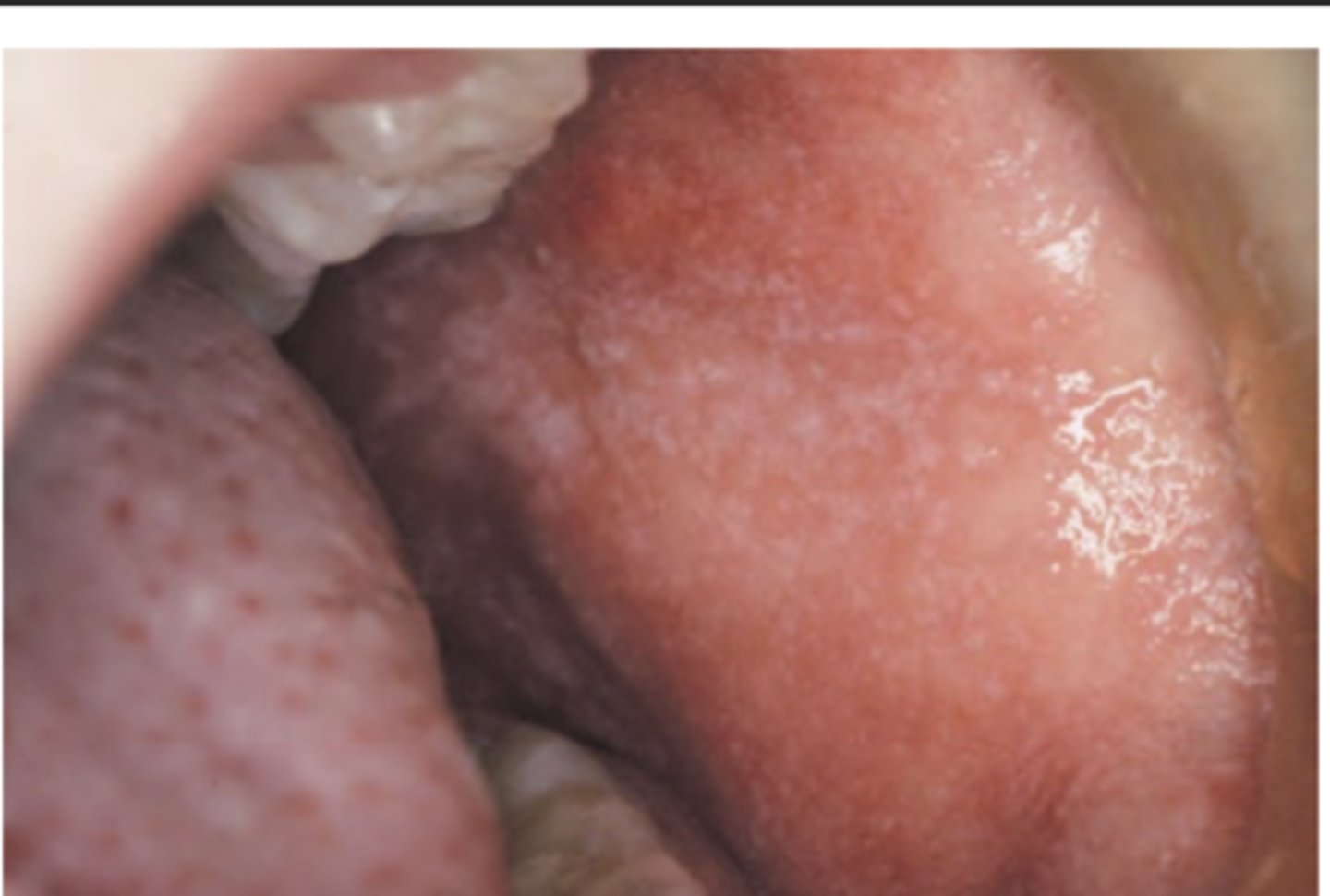
Measles
Hint: maculopapular rash that blanches with pressure 1st affecting face with downward spread to trunk and extremities
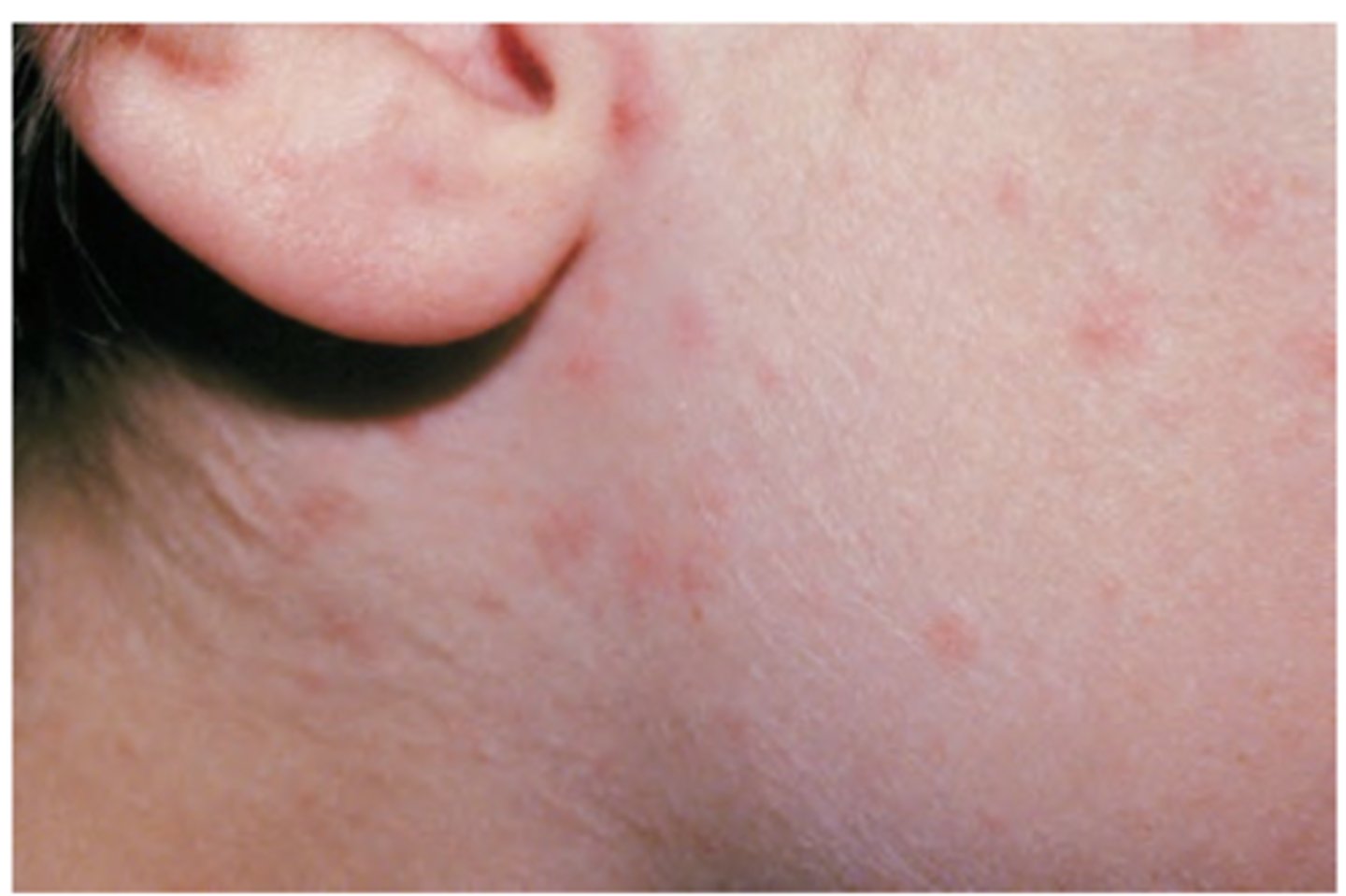
Molluscum Contagiosum
Hint: children & young adults; predominantly on skin of neck, face, trunk, & genitalia (Mucosa rare)
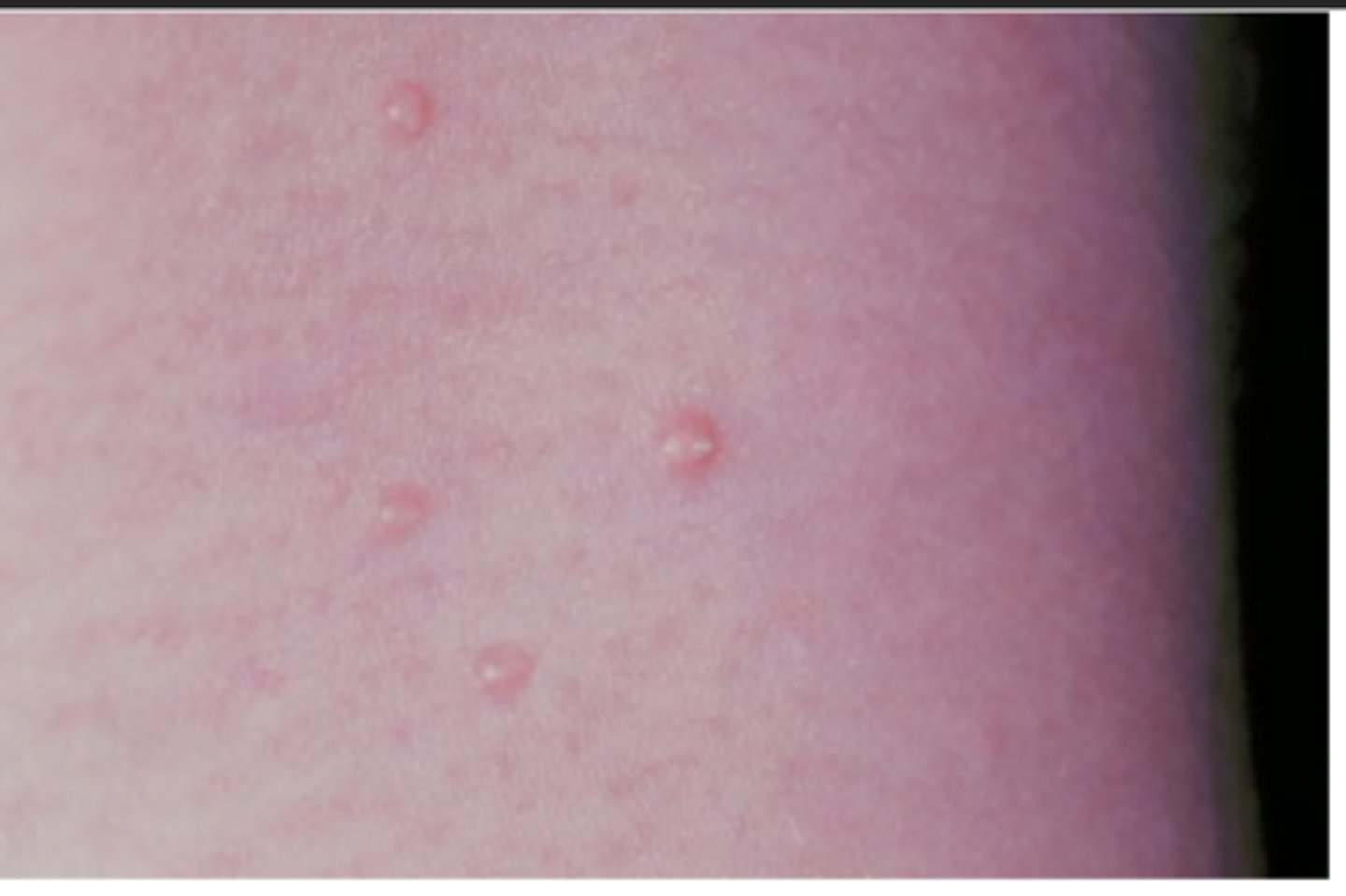
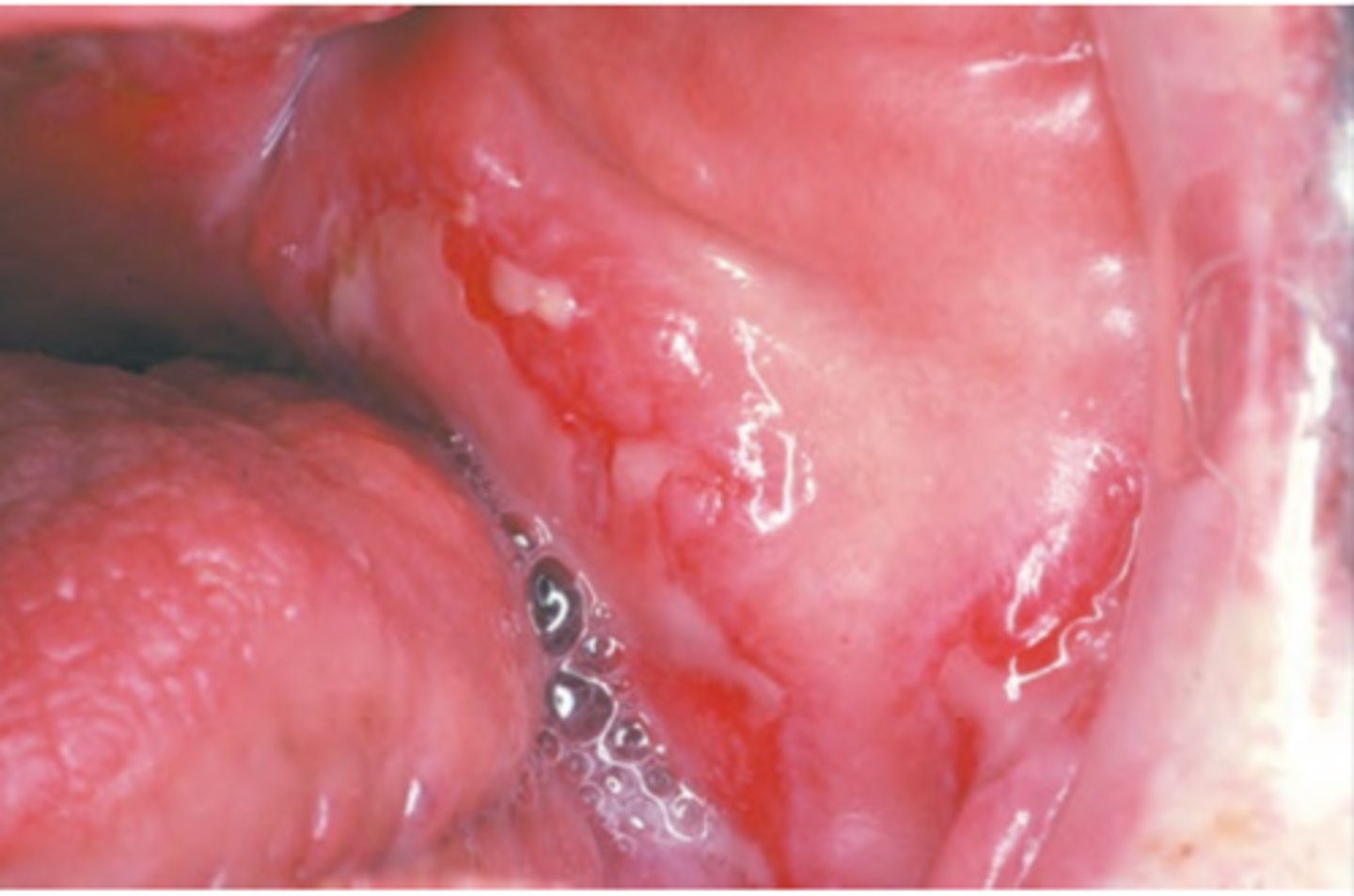
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Hint: Painful and long persisting superficial and ragged erosions affecting mucosal surfaces
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Hint: Oral lesions are "First to show, last to go"
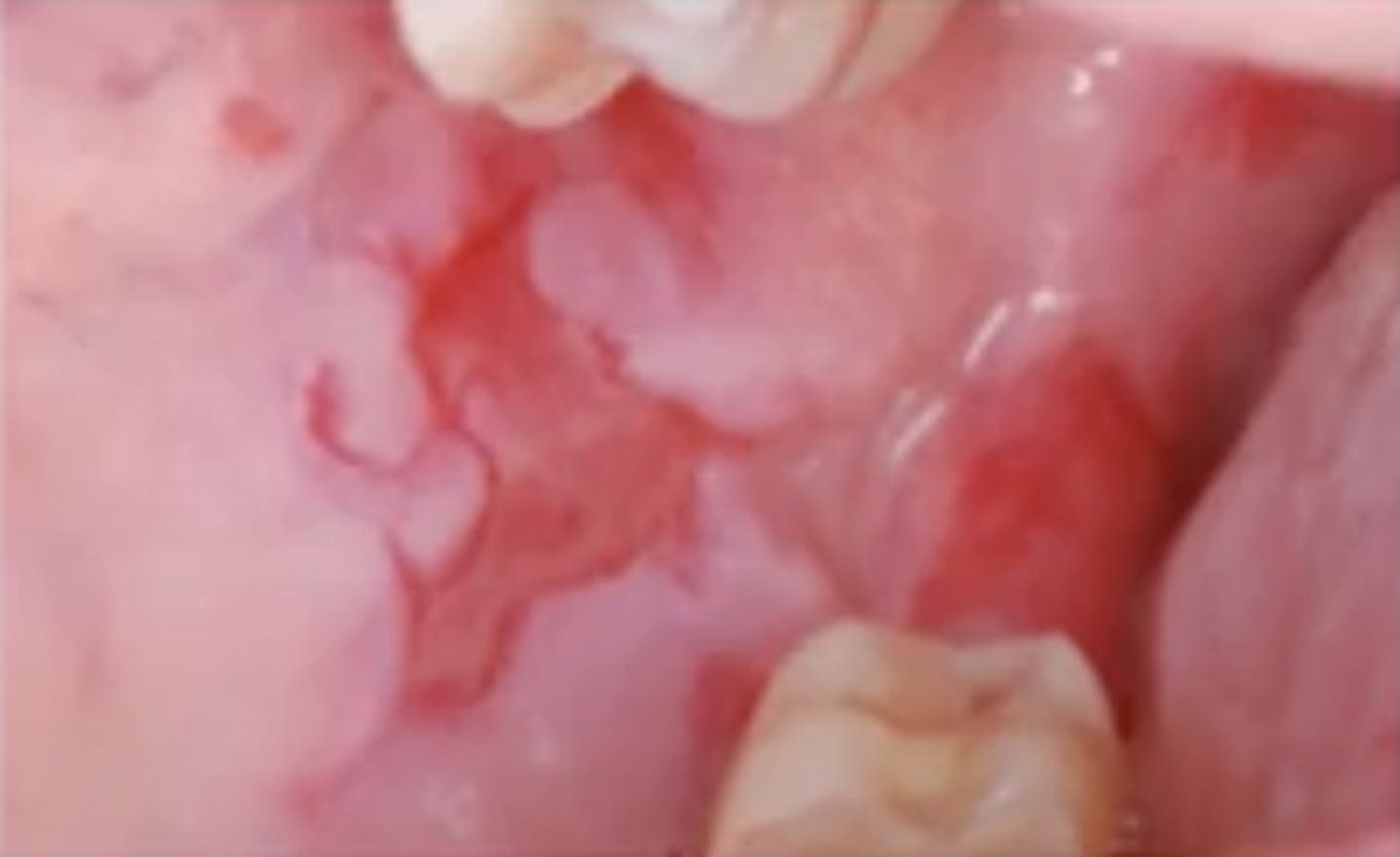
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Hint: Flaccid vesicles & bullae that rupture quickly
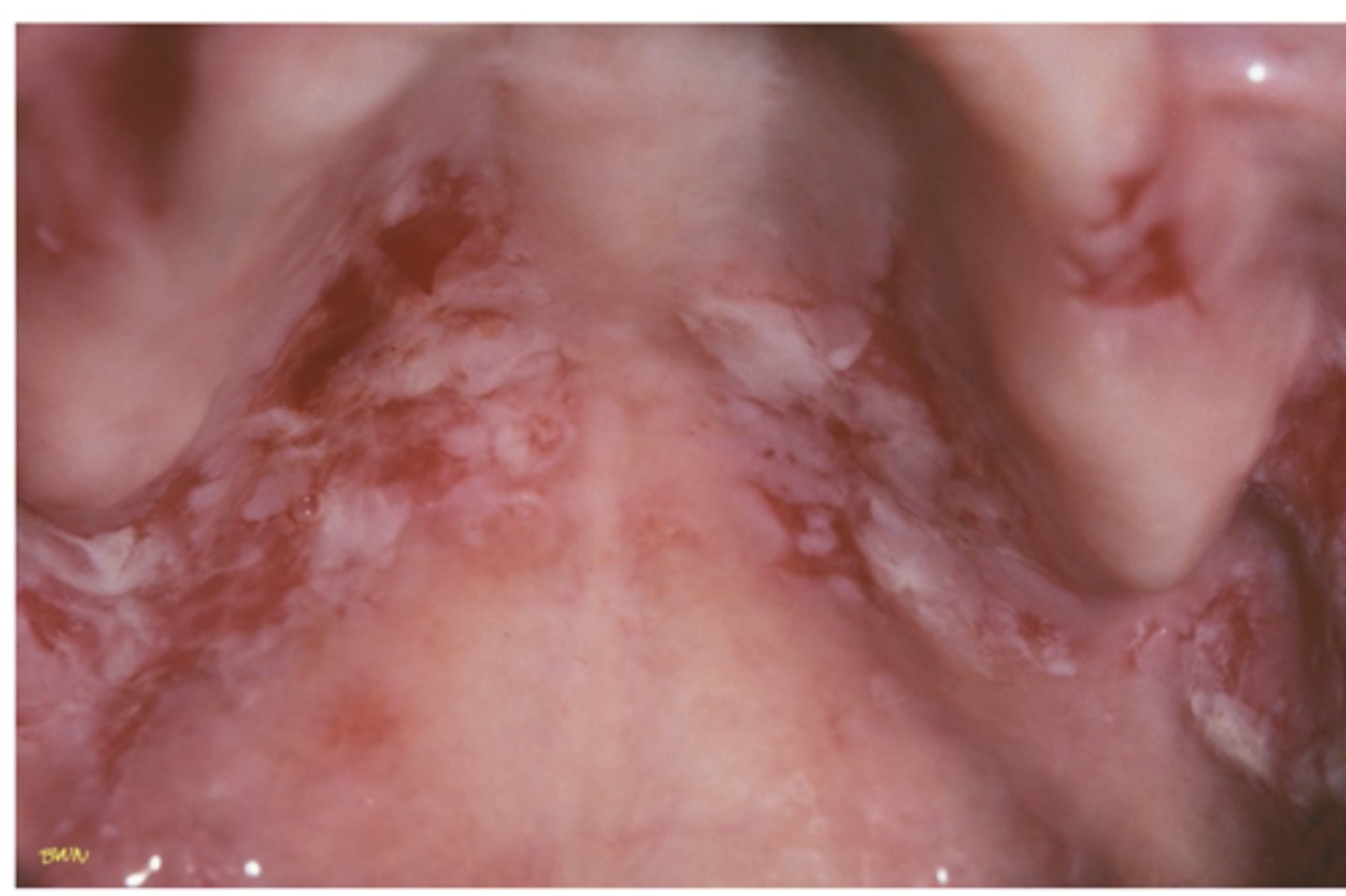
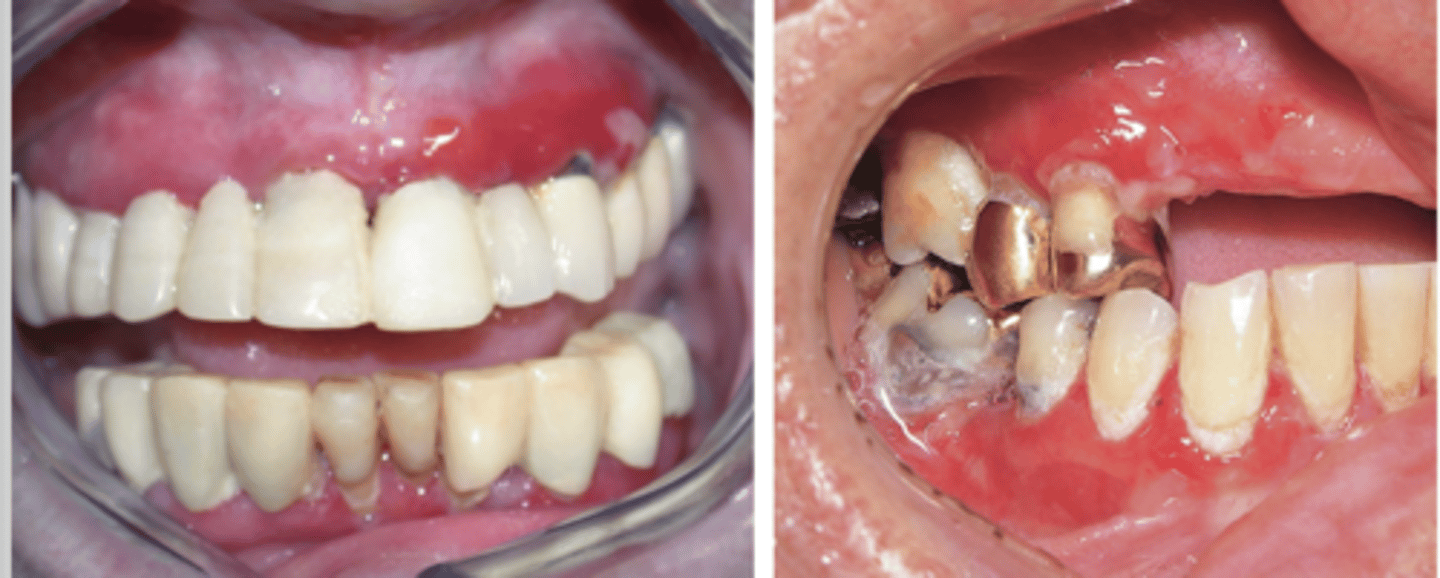
Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
Hint: in tact bullae
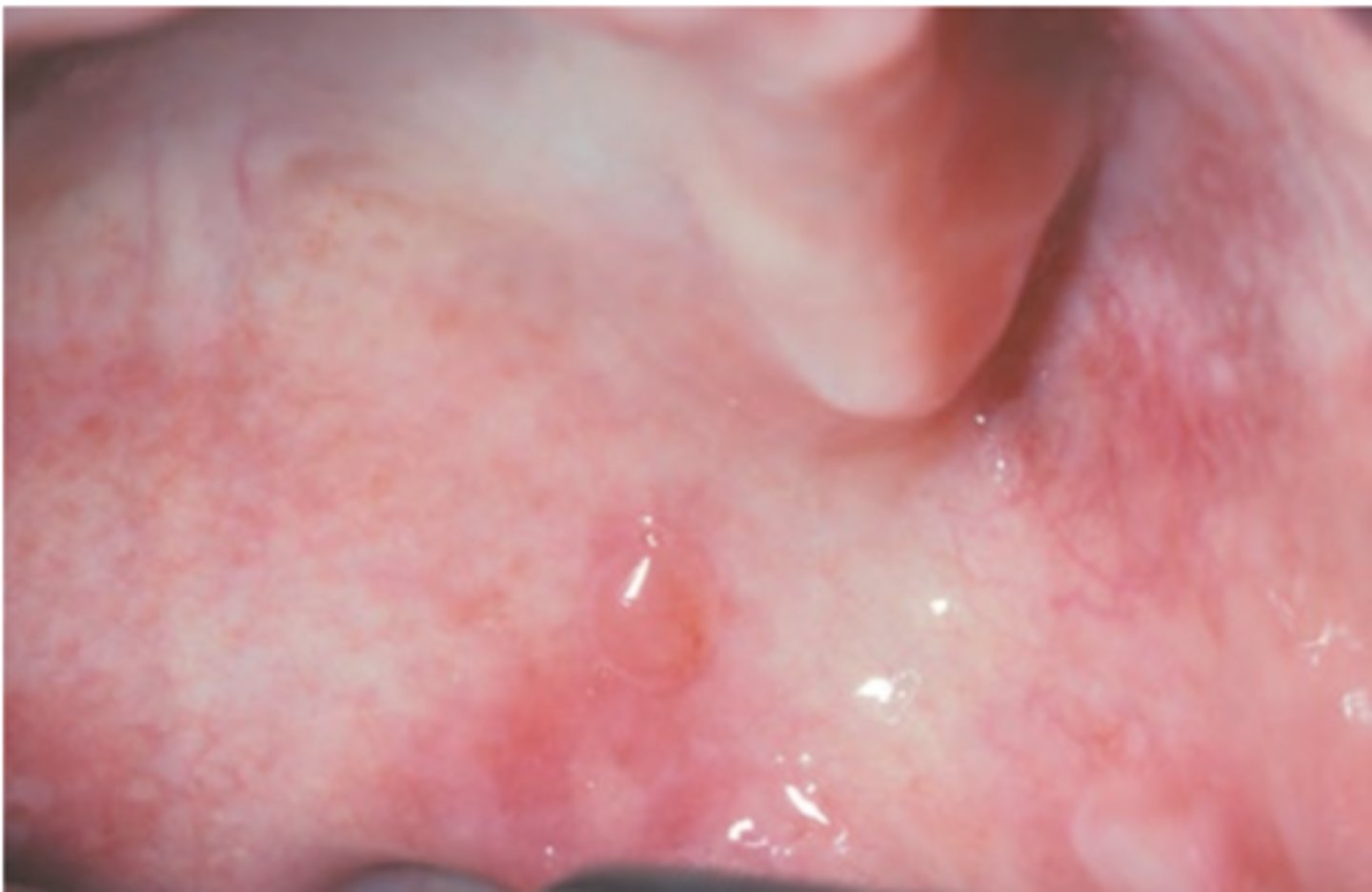
Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
Hint: in this disease antibodies are directed against components of the basement membrane
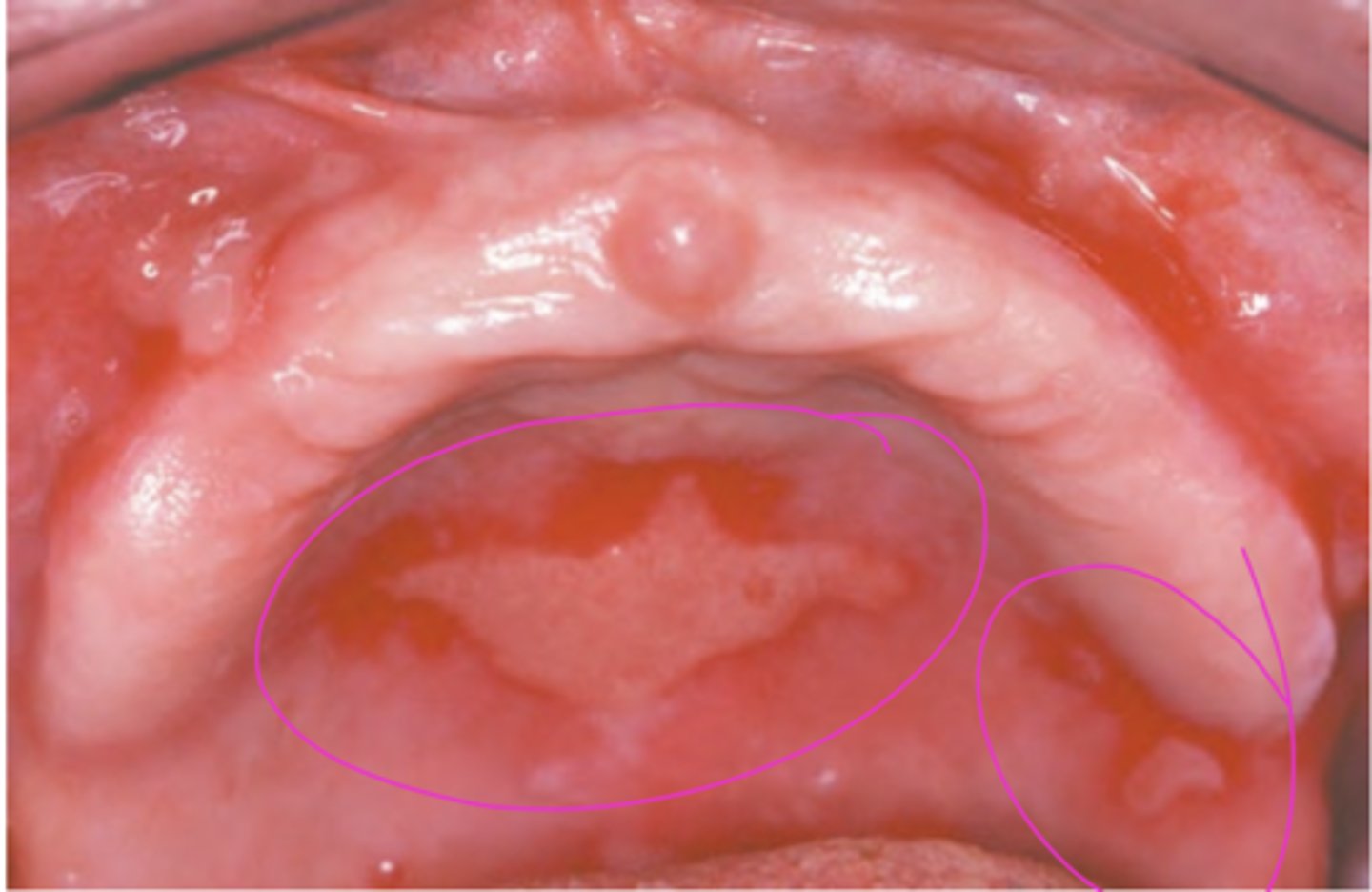
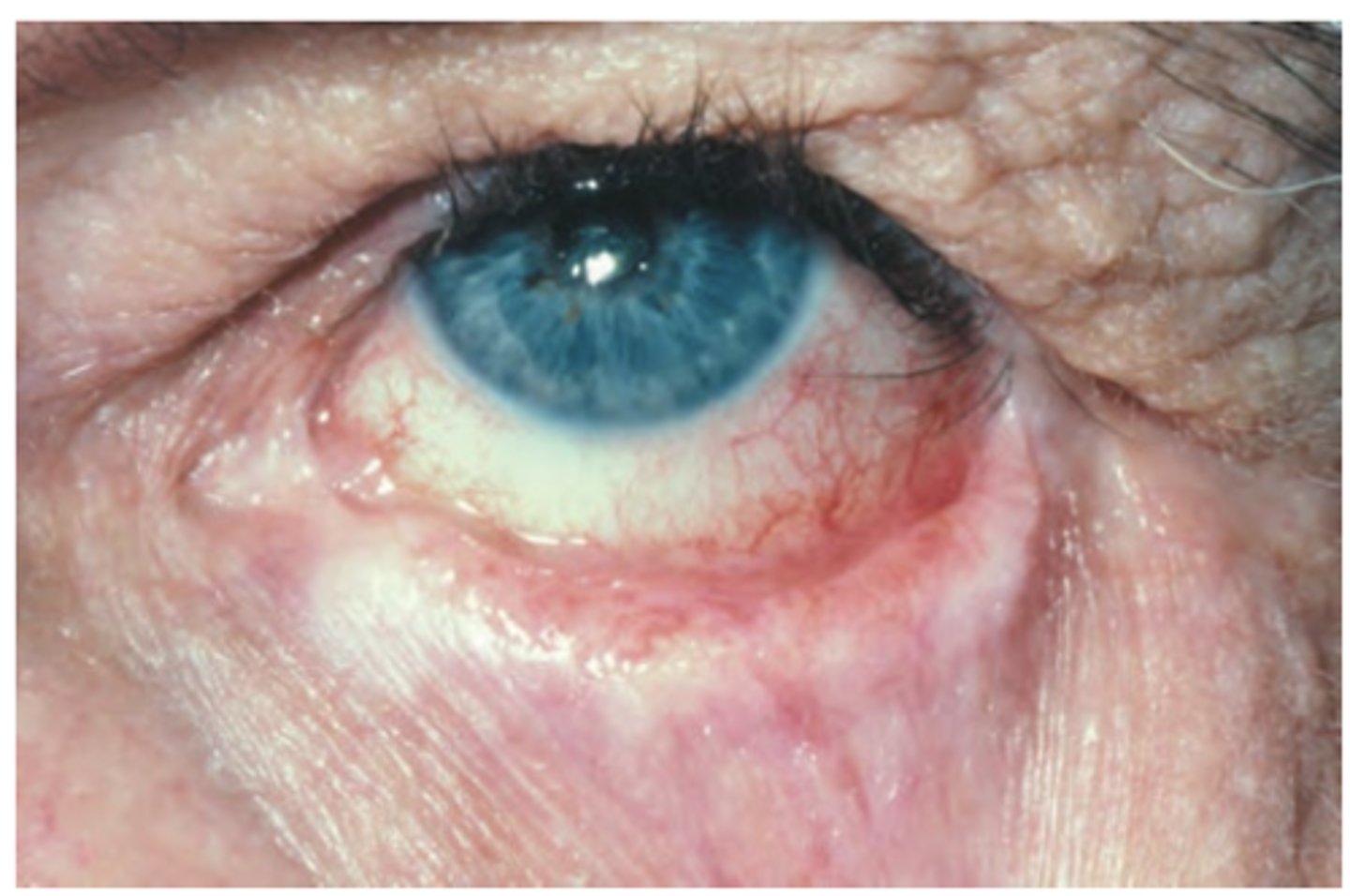
Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid
Hint: there is ocular involvement with this patient
Symblepharon
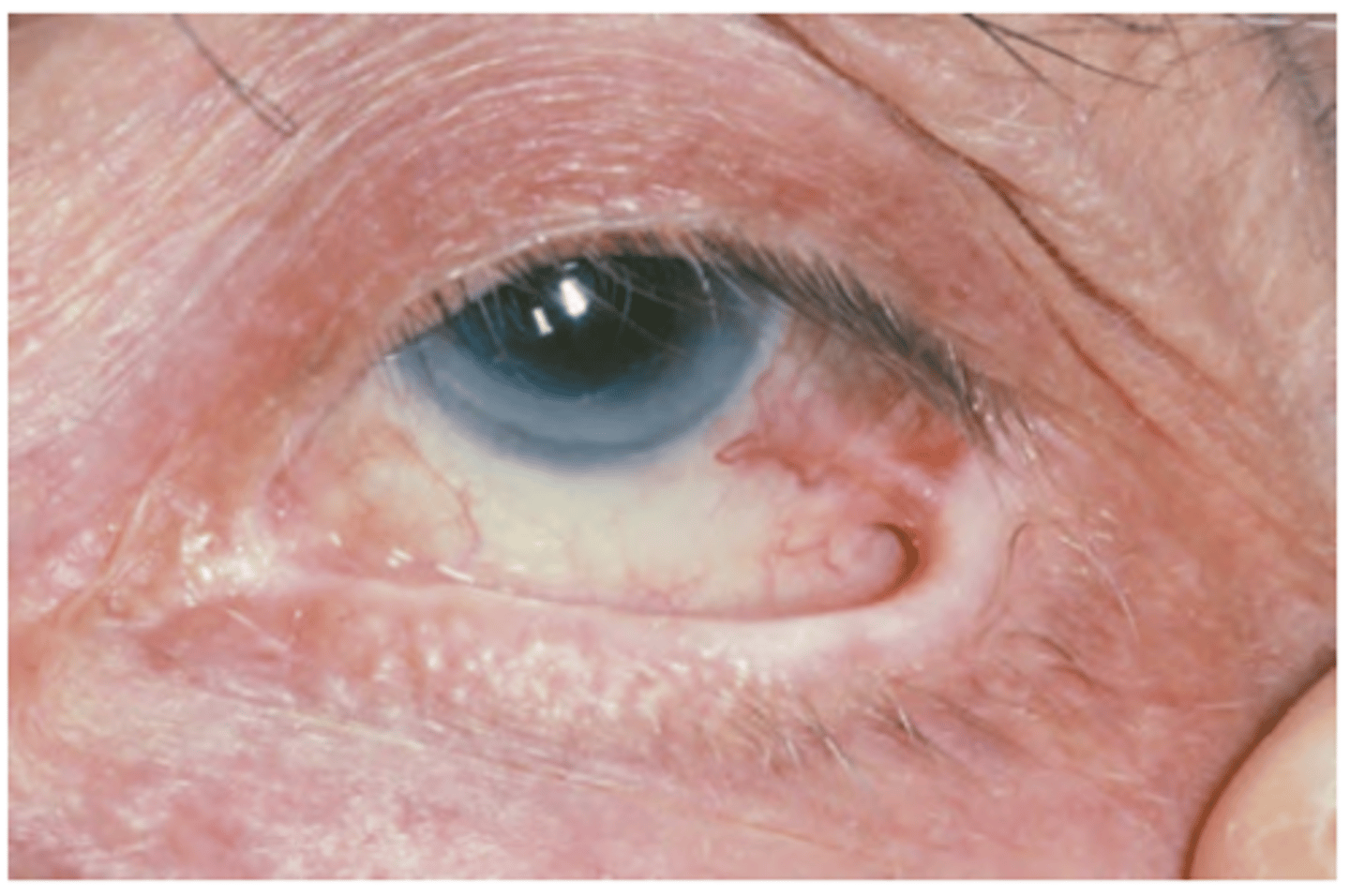
Entropion & trichiasis
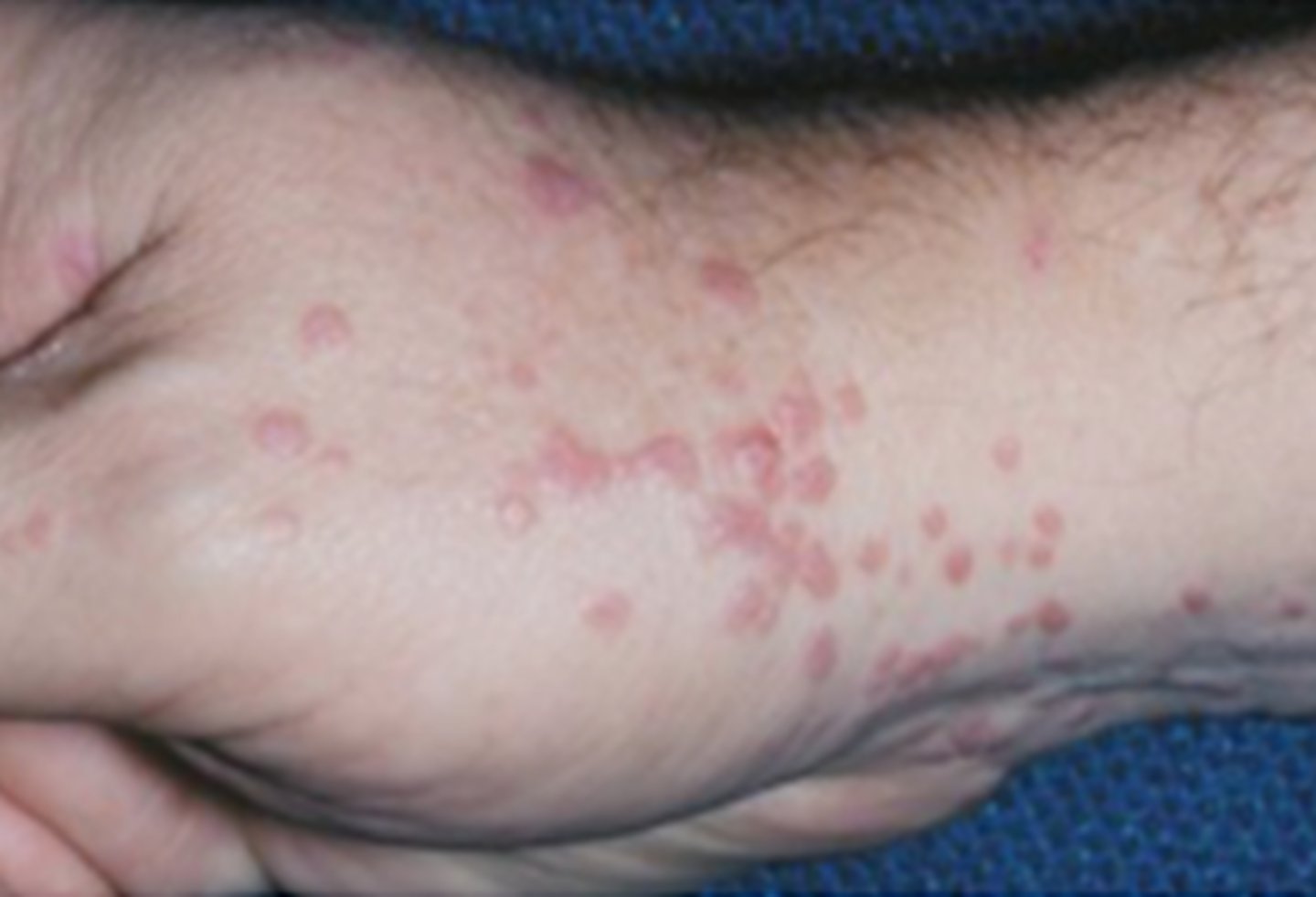
Lichen Planus
Hint: purple, pruritic, polygonal papules
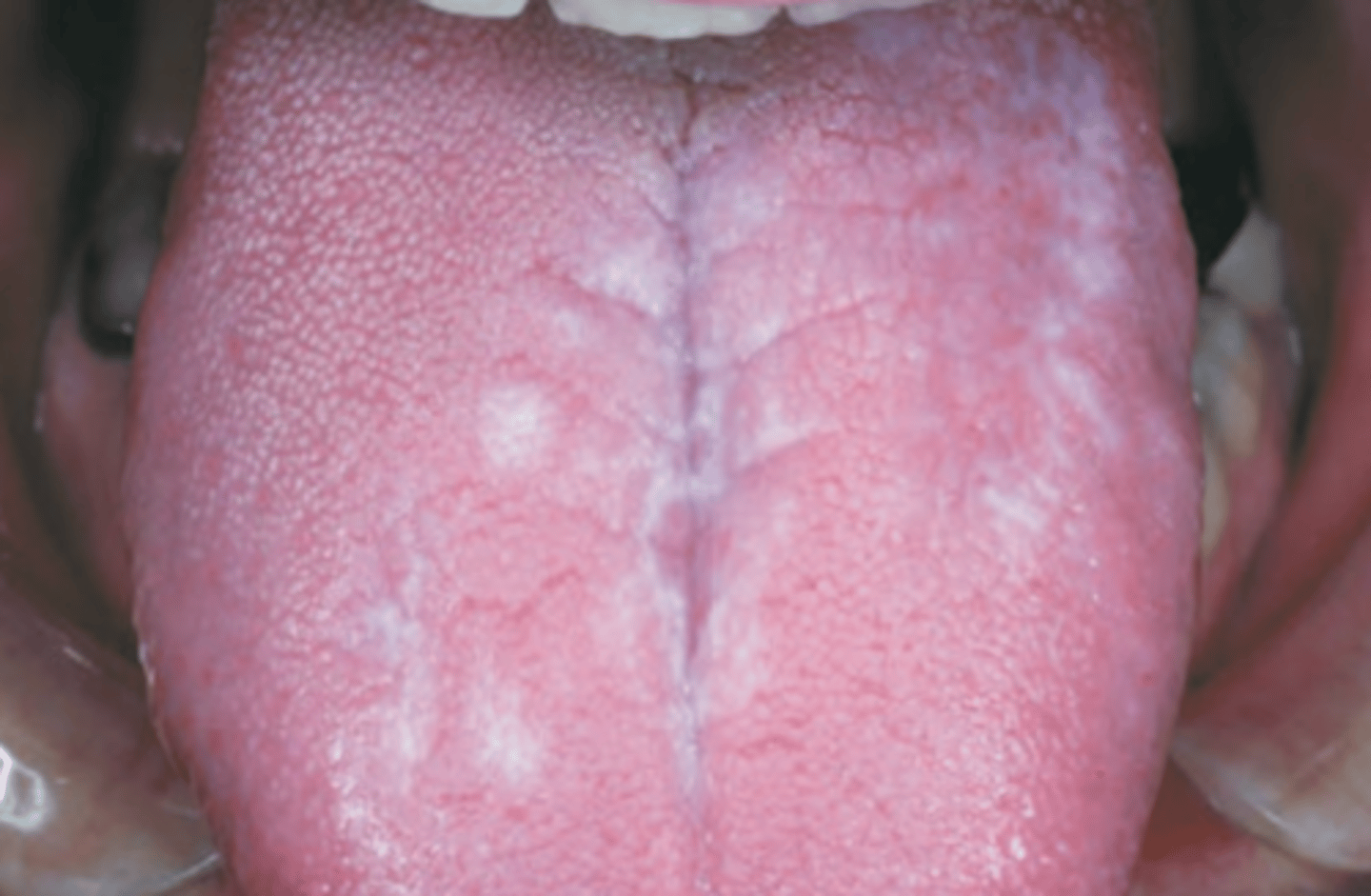
Reticular Lichen Planus
Hint: most frequent affects posterior buccal mucosa bilaterally
Reticular Lichen Planus
Hint: Lesions wax and wane
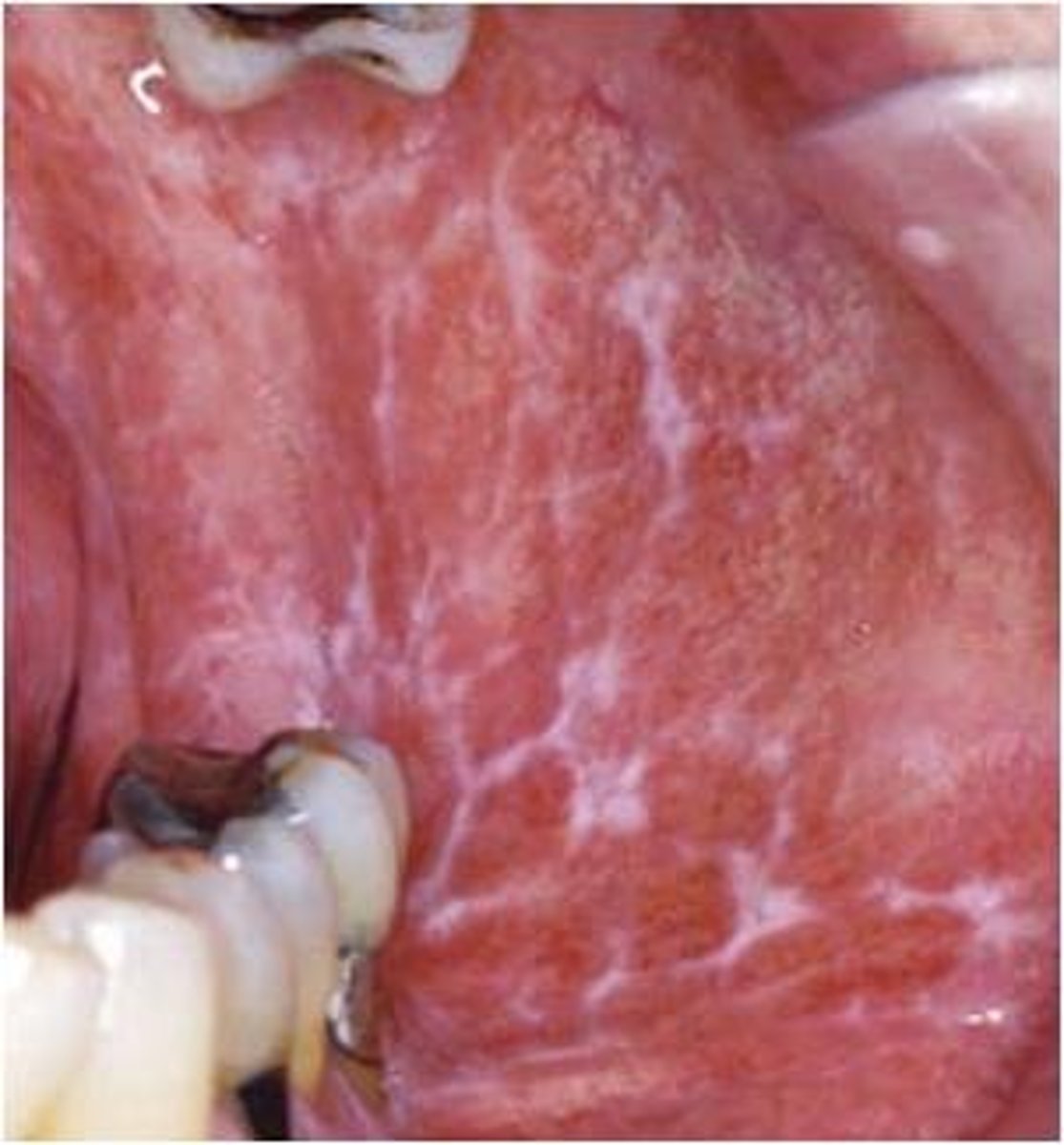
Erosive Lichen Planus
Hint: ulceration with bordered periphery of white radiating striae
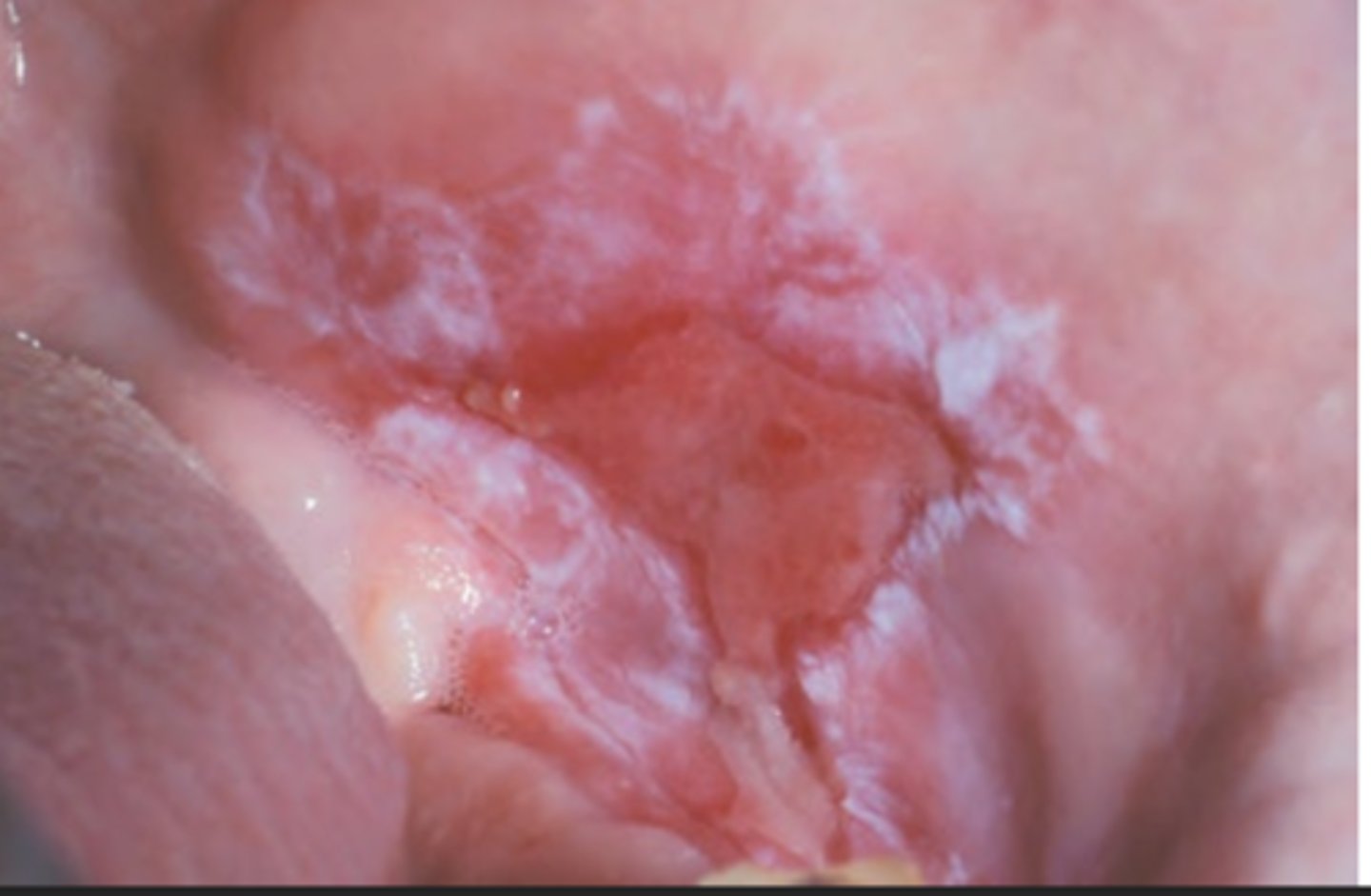
Erosive Lichen Planus
Hint: type of lichen planus
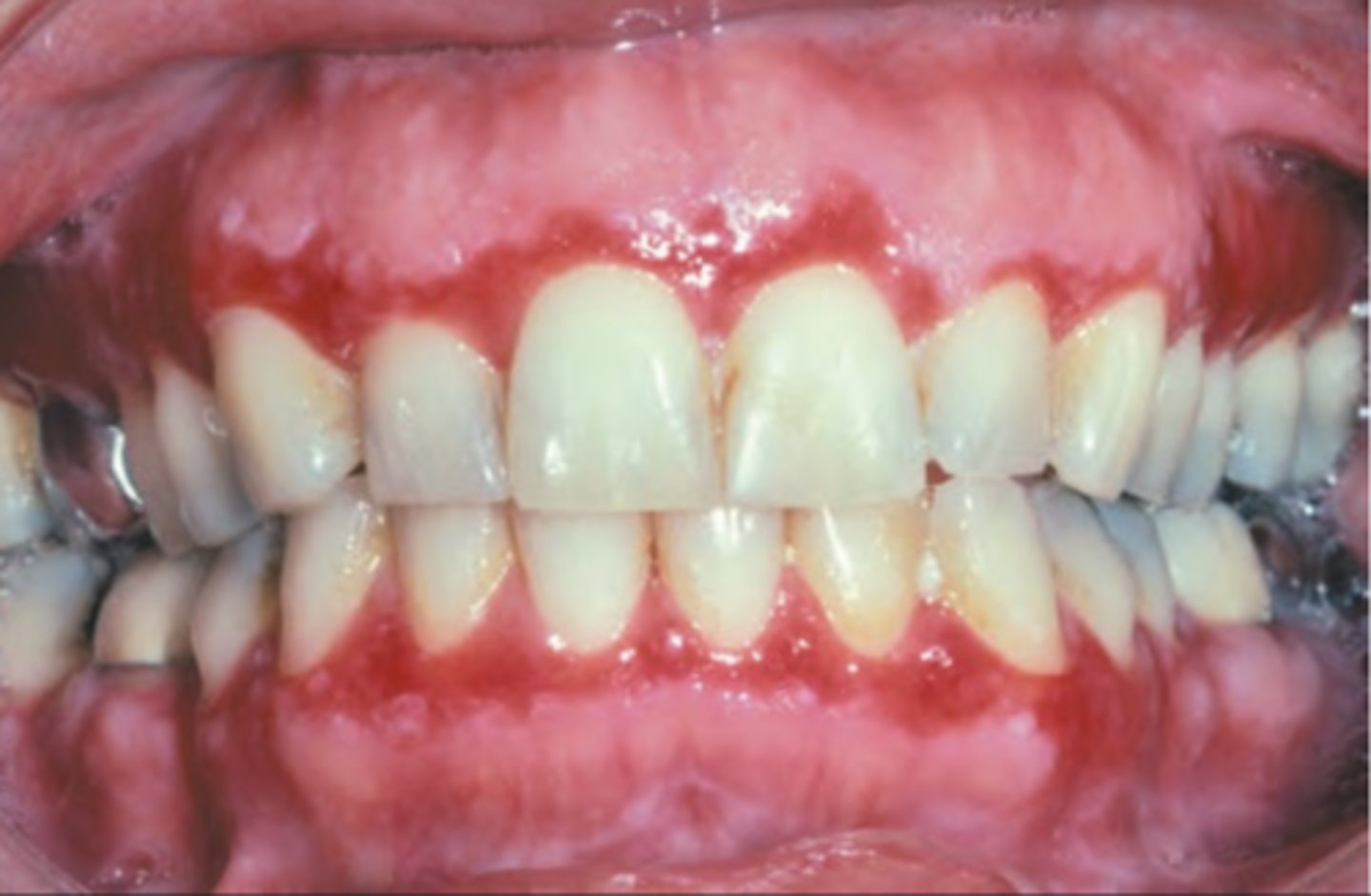
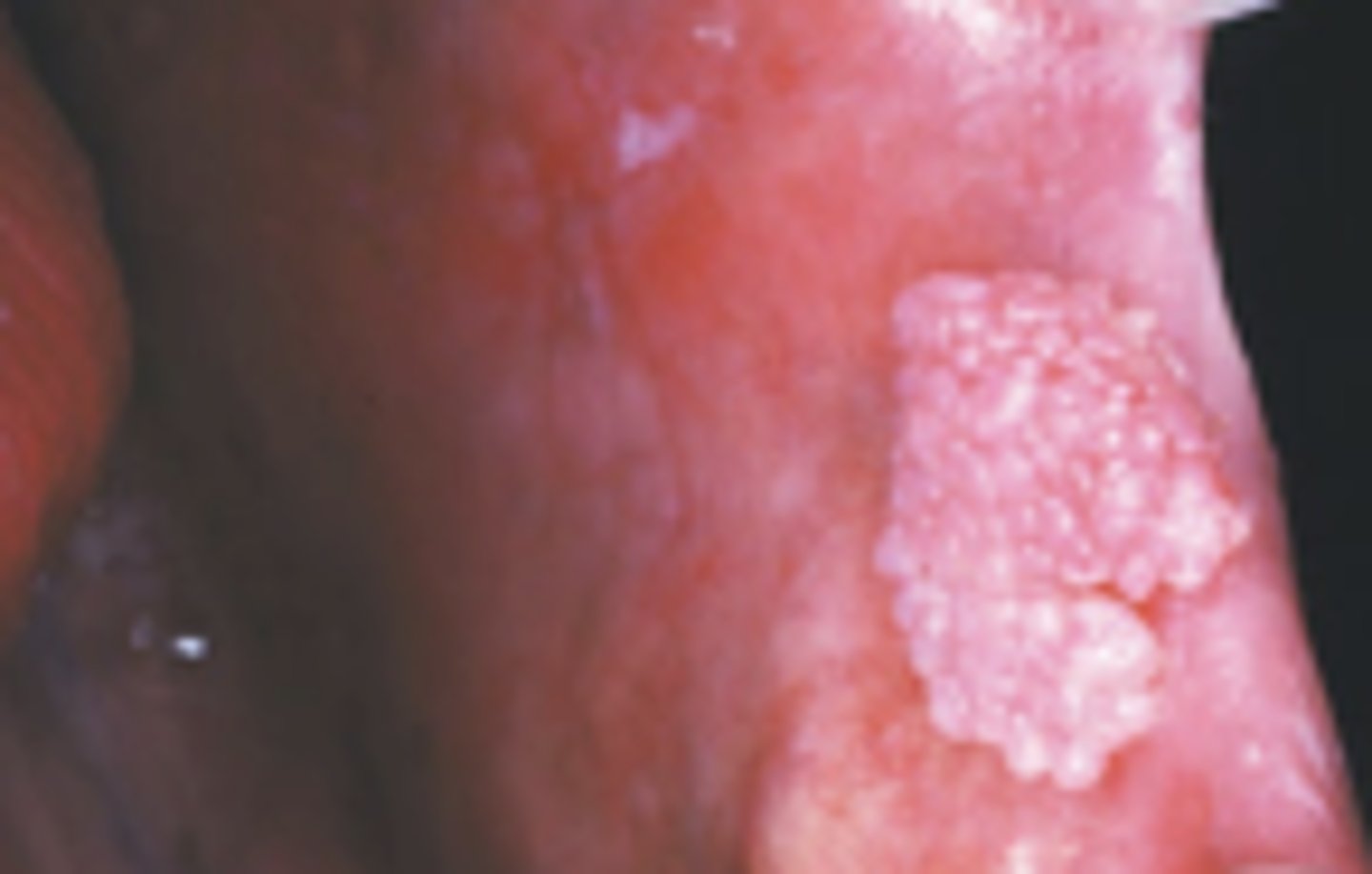
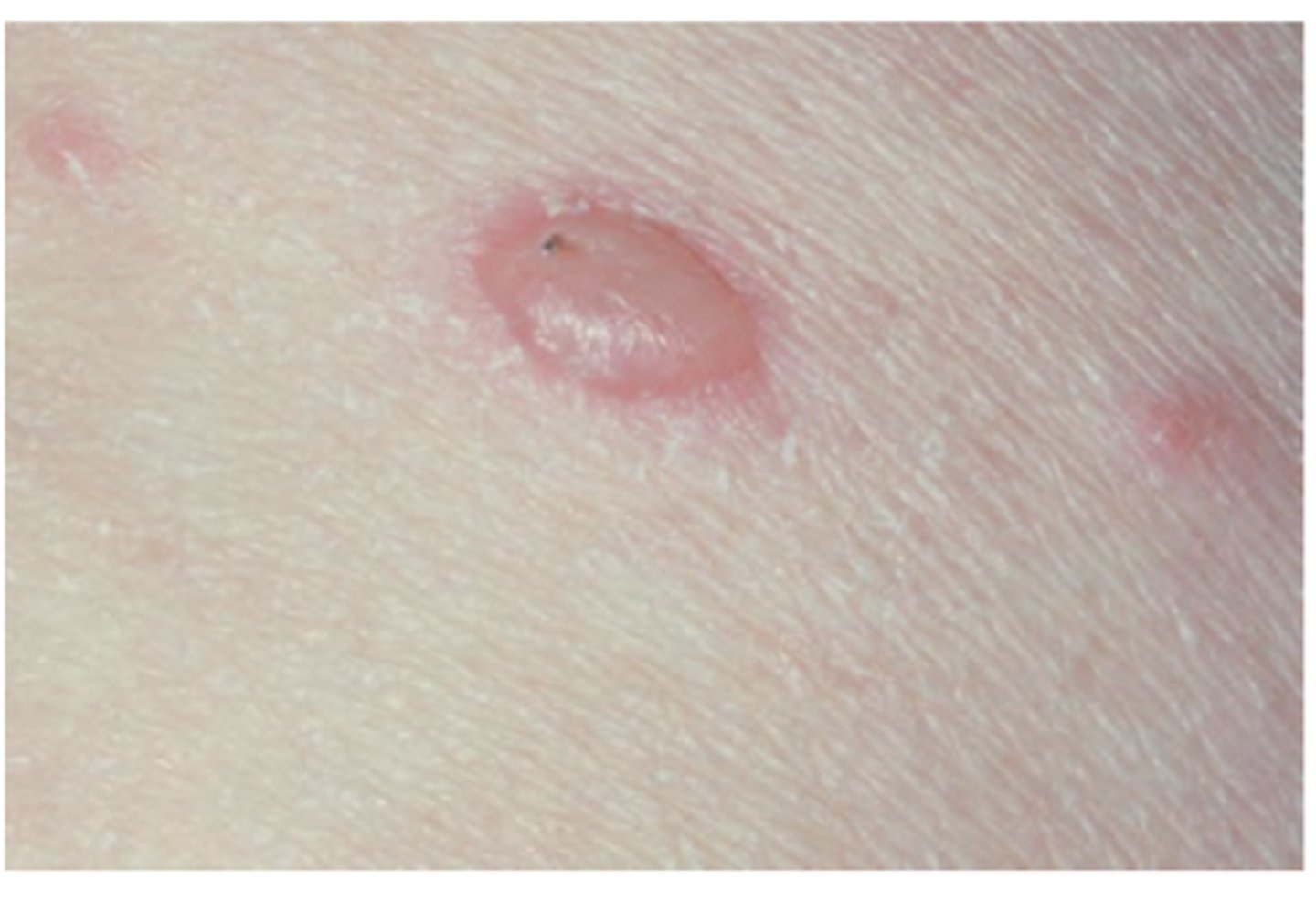
Verruca Vulgaris
Hint: focal, benign, HPV-induced proliferation of stratified squamous epithelium
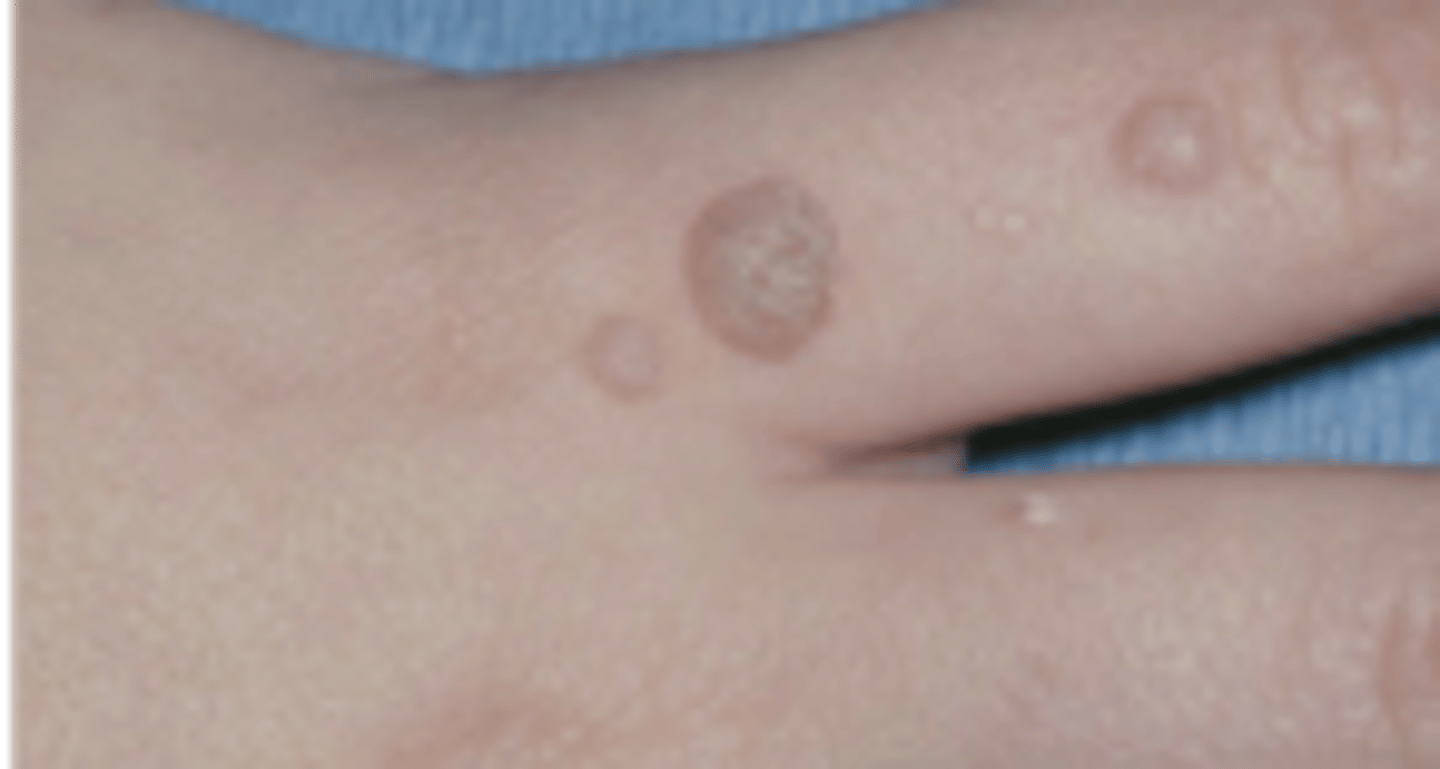
Verruca Vulgaris
Hint: painful nodule with rough, pebbly surface
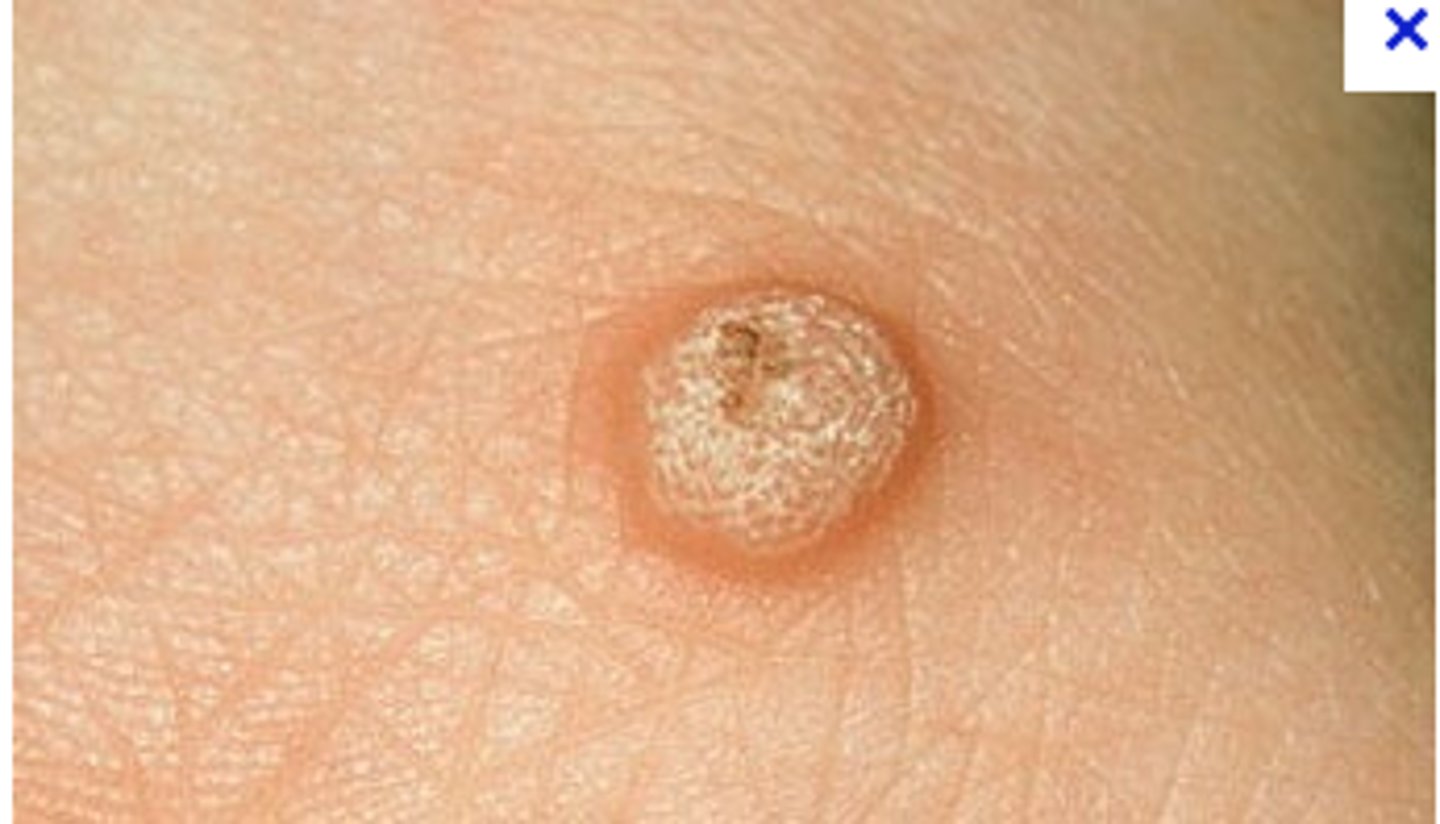
Condyloma Acuminatum
Hint: clustered, sessile, pink, well-demarcated exophytic mass with blunted surface projections
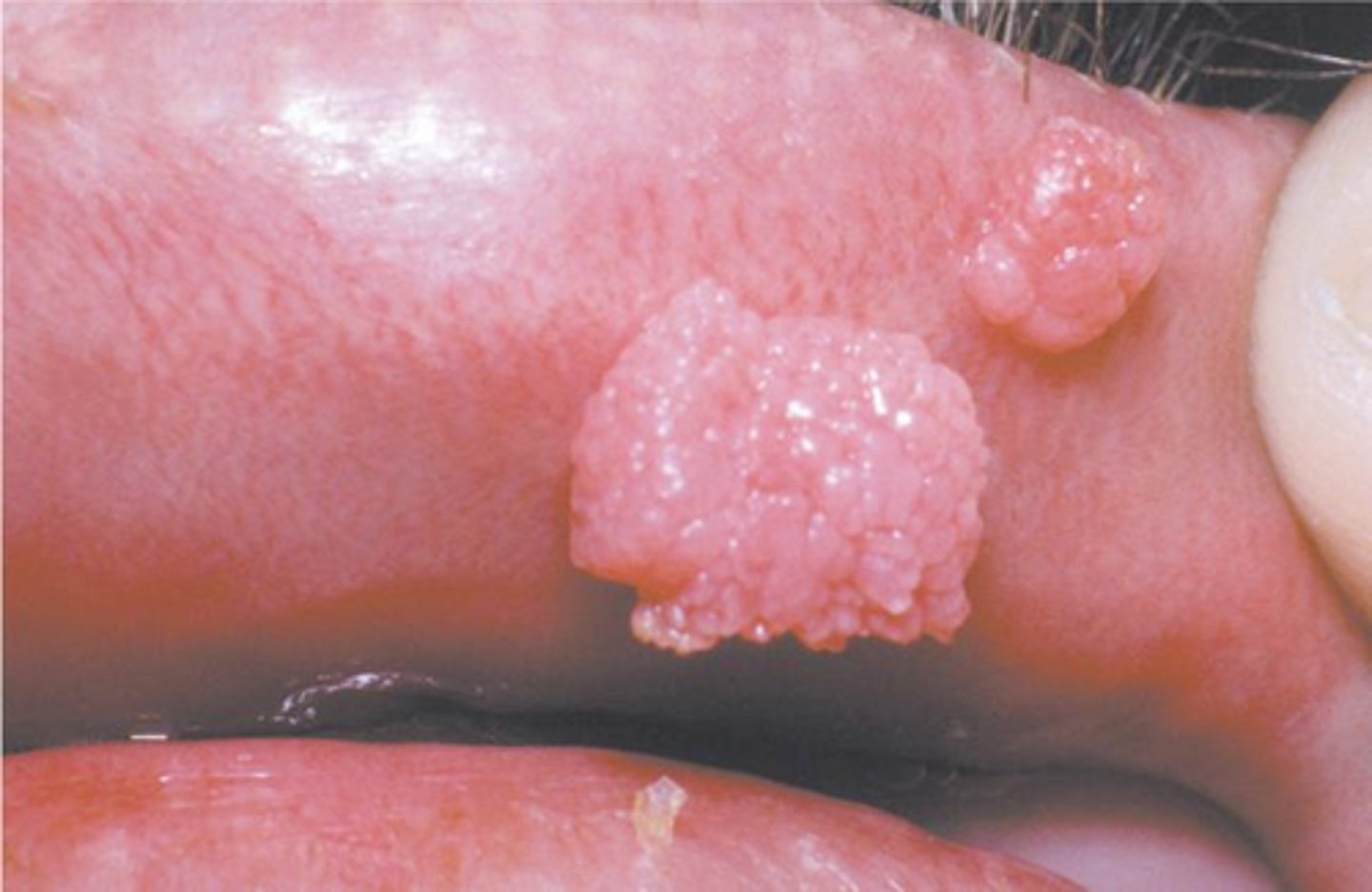
Multifocal Epithelial Hyperplasia
Hint: HPV 13 and 32
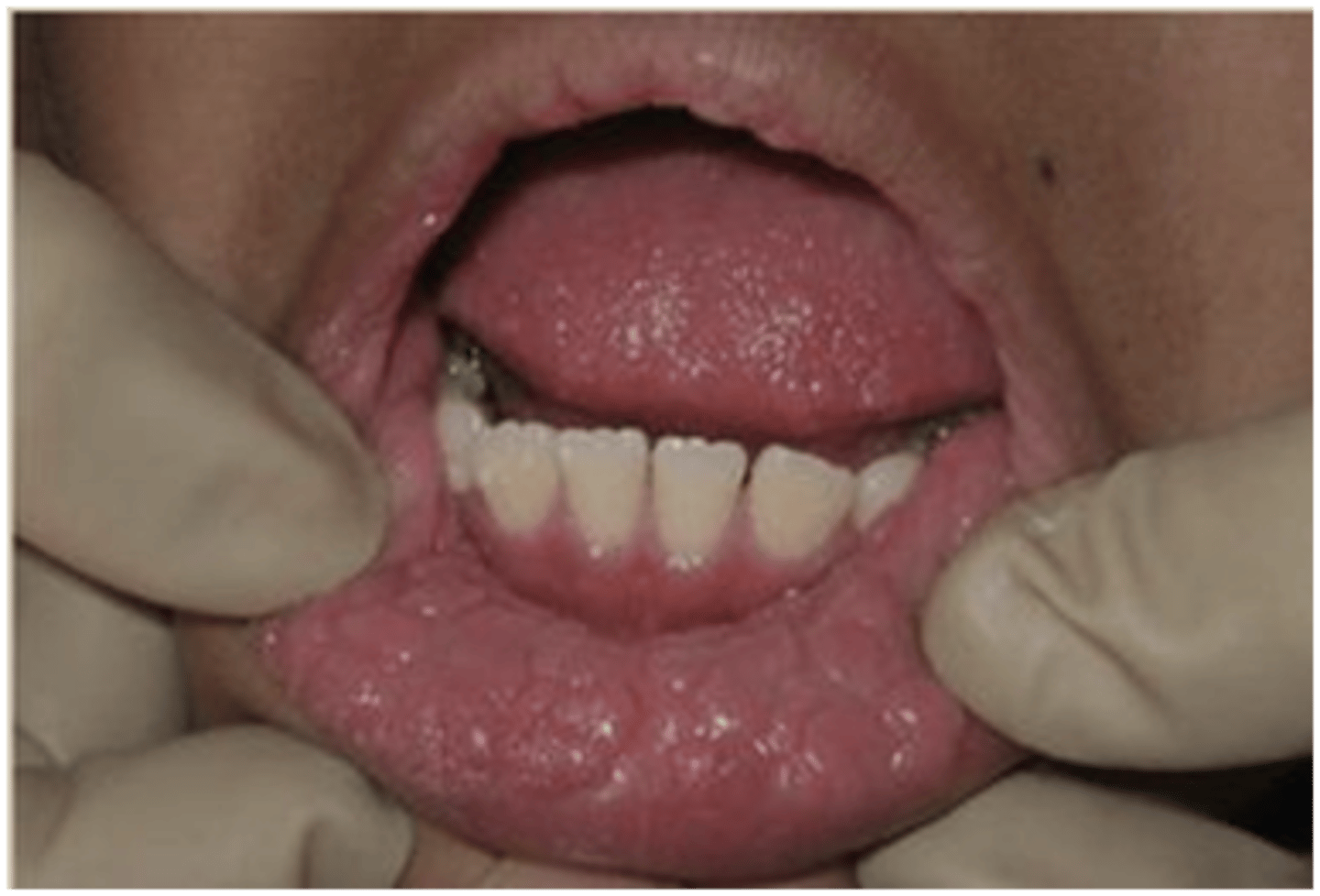
Multifocal Epithelial Hyperplasia
Hint: Mitosoid cell
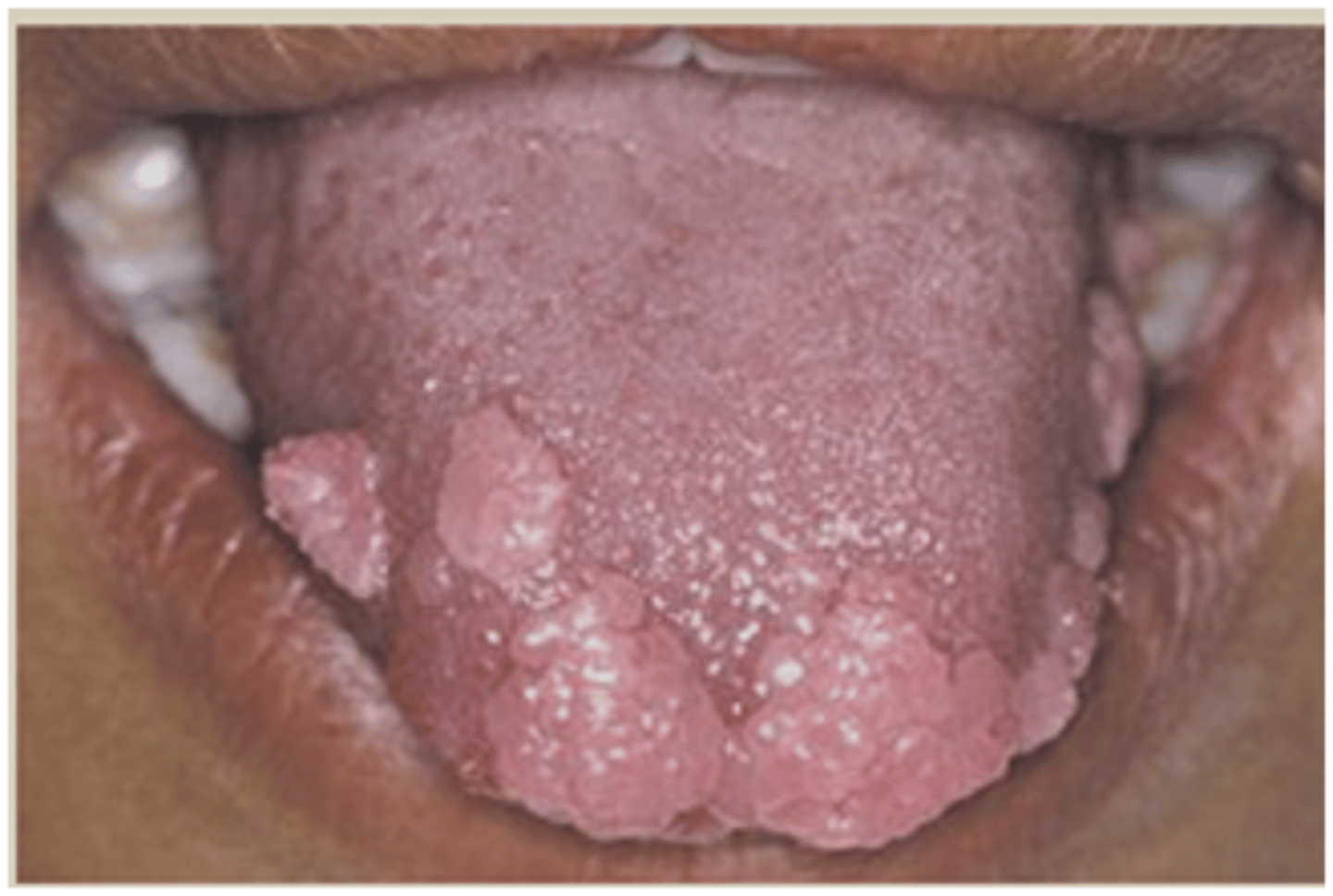
Squamous Papilloma
Hint: common, benign, HPV-induced proliferation of stratified squamous epithelium
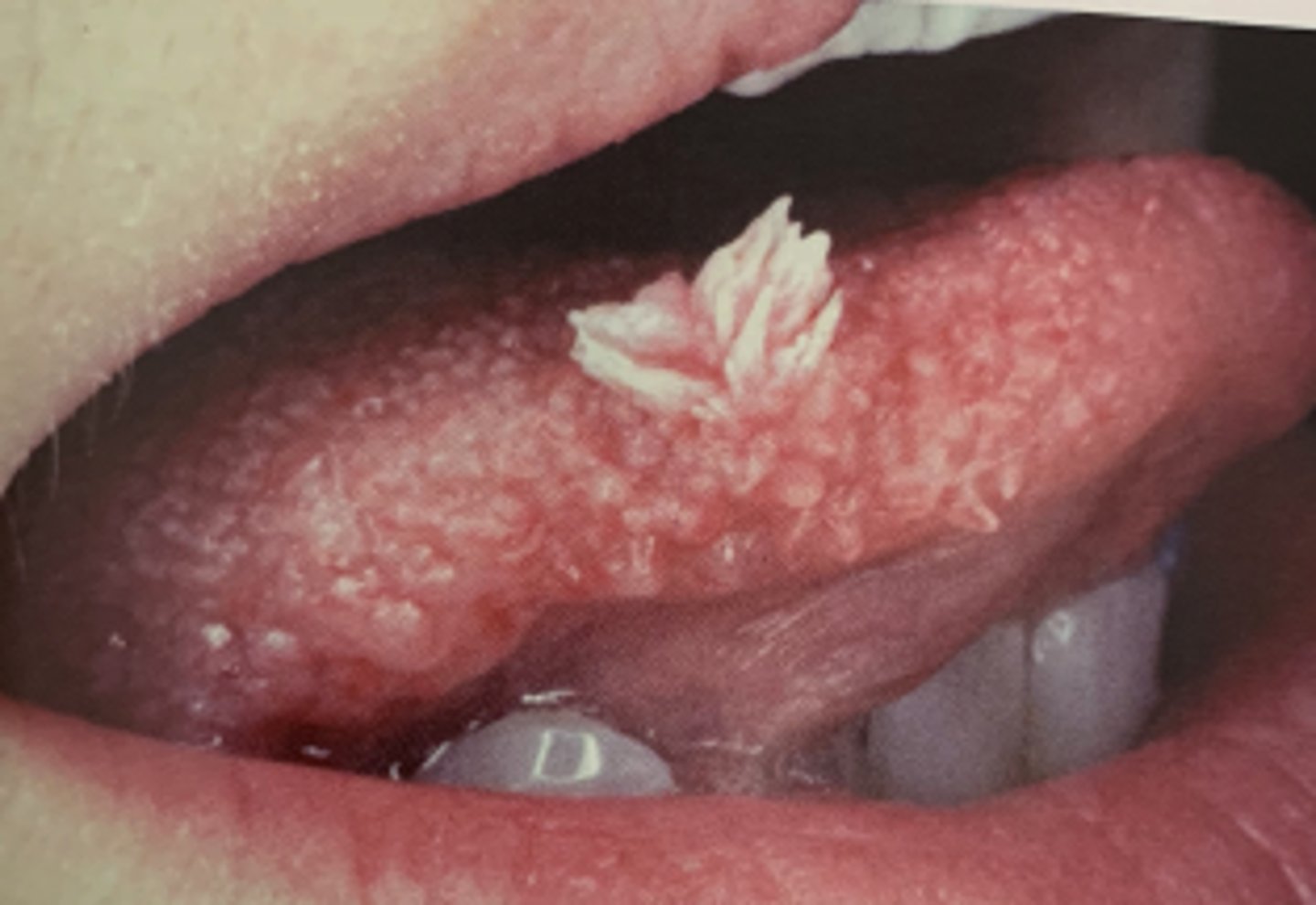
Squamous Papilloma
Hint: HPV types 6 & 11 involved
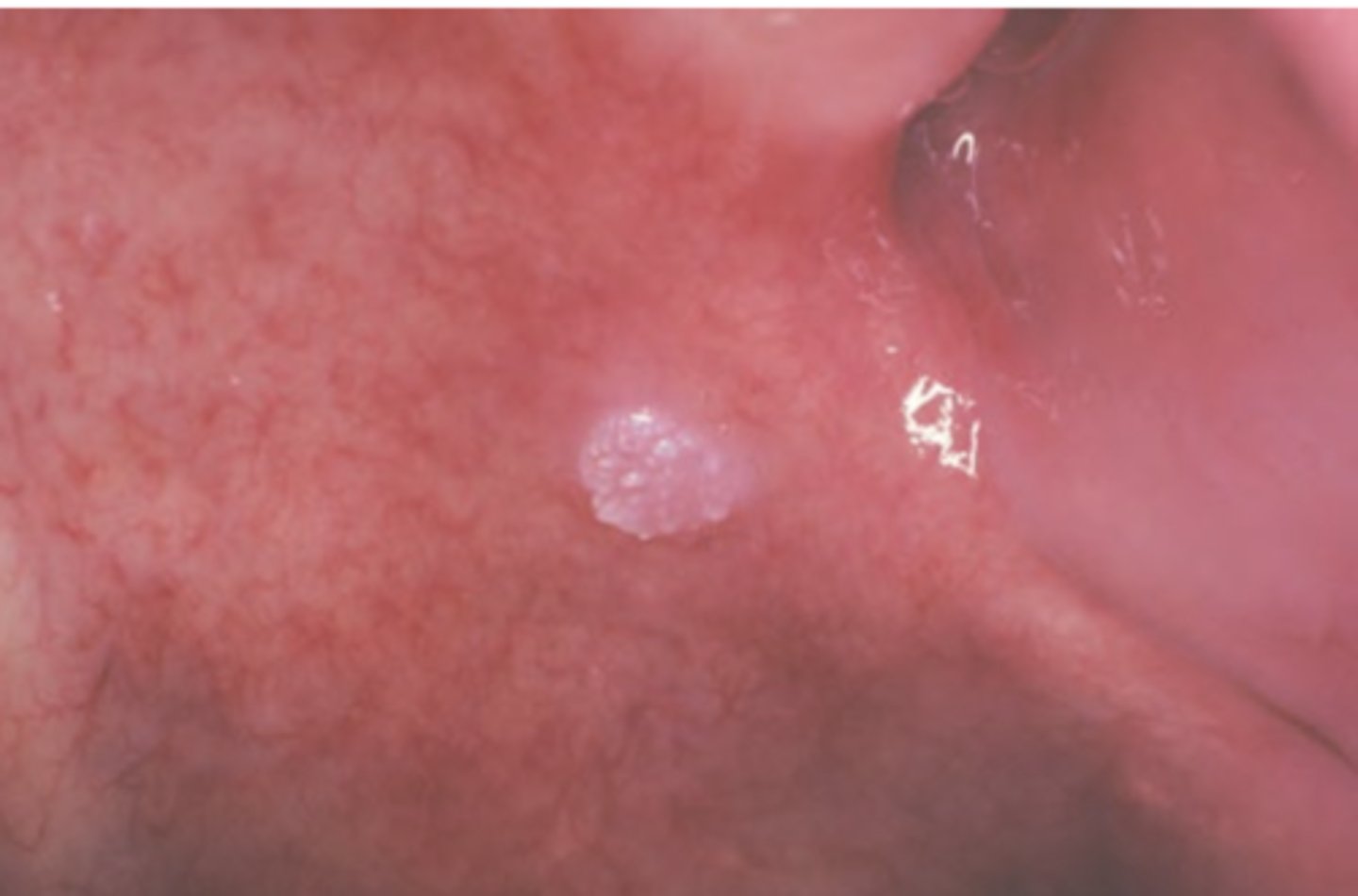
Squamous Papilloma
Hint: numerous fingerlike surface projections OR "cauliflower" appearance