Chapter 6: Vygotsky
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
3 main ideas of Vygtosky
1) children construct their knowledge (world view)
apprenticeship = chidlren’s involvement in structured activities with those who are more skilled
2) development cannot be separated from social context
Cooperative activity (specifics are culturally dependent)
guided participation through peer tutoring and group learning
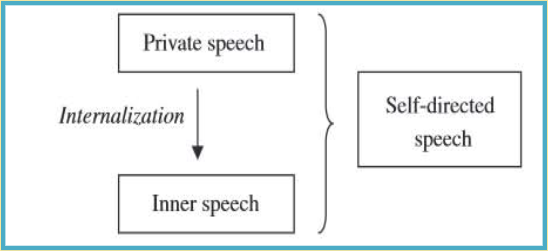
3) language plays key role in mental development => inner speech is speech for oneself while external speech is for others
inner speech is key for development (e.g. cog monitoring, self-regulation, planning)
2 key concepts associated with Vygotsky’s Theory
1) Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD): difference between what a child can accomplish alone and what can be accomplished with assistance
2) Scaffolding: support provided during learning which is tailored to the needs of the learner to help the learner achieve their goal

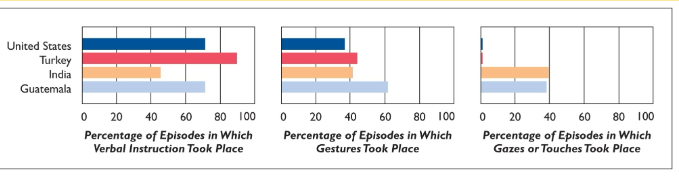
Rogoff et all (1993) => Q, S, D, M, R, C
Q: Does culture affect the way parents scaffold their children’s learning?
S: 18mo toddlers
D: cross-cultural, observational
M: parents tried to get child to operate a toy (which is a doll that dances when the strings are pulled a certain way) => no ground rules or guidelines regarding teaching
C: scaffolding was readily observed in parent's’ behavior, but cultural differences were also apparent
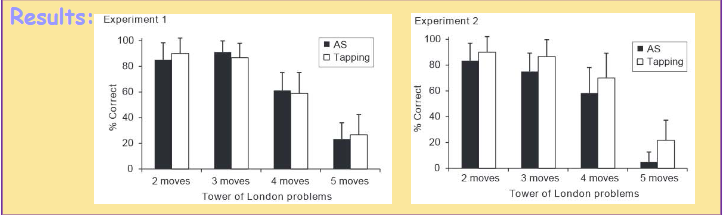
Lidstone, Meins, & Fernyhough: Q, S, D, M, R, and C
Q: does blocking private speech affect planning in school age children?
S: 30 9yo in each expt
D: experimental (within subjects)
M: Dual task version of the TOL task (E1 perform, E2 guess and perform) => Verbal articulatory secondary task: repeat monday 1 per sec =. spatial scondary task: foot tapping (repeat 1 per sec)
C: planning is reliant on self-directed speech in school age children => at least when children were required to plan ahead as in Expt 2
Clark, Menna, and Manel: Q, S, D, M, R, C
Q: does maternal scaffolding affect pre-schoolers’ social skills?
S: 30 prosocial and 30 aggressive pre-schoolers
D: Quasi IV
M: 1) measure children’s social skills via questionnaires to mothers 2) measure maternal scaffoling during joint problem-solving interactions (using multiple measures like # of times mom offers to help if child is stuck)
R: all but 1 measures of scaffolding revealed a difference in favor of mothers of prosical preschoolers, and none of the measures revealed a difference favoring the mothers of aggressive pre-schoolers
C: Mothers of aggressive pre-schoolers are less able to adequately provide scaffolding for child’s cog development. This may be a failure to help child develop better self-cotrol, BUT it may also be that the child is pre-disposed to have poor self-control (always be nervous if mom is to blame)