Bio Exam studyguide (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/121
Last updated 12:25 PM on 5/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
1
New cards
DNA stands for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
2
New cards
What does DNA coil around to make a chromosome?
Histones
3
New cards
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
5-carbon sugar ,phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
4
New cards
What are some examples of nitrogenous bases?
adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine)
5
New cards
Which two bonds are required to form DNA?
Phosphodiester bonds , Hydrogen bonds
6
New cards
What are Purines
Adenine and Guanine which consit of two rings with amine groups
7
New cards
Pyrimidines
Thymine and Cytosinem consist of one ring with amine groups. Thymine is a pyrimidine that is only found in DNA, while Uracil is only found in RNA
8
New cards
Chargaffs rule
A w/ T, G w/ C, A w/ U
9
New cards
1869, Swiss chemist identified nuclein in white blood cells?
Friedrich Miescher
10
New cards
Stole roslands franklins work, gave it to watson and kirk?
Maurice Wilkins
11
New cards
Stick and ball method
Watson and Kirk
12
New cards
supported the hypothesis that DNA replication was semiconservative meaning, one strand of DNA will be used to make another strand?
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl
13
New cards
What needs to happen before a cell can divide?
Each DNA molecule needs to be copied
14
New cards
What connects DNA strands and which way do they go?
Carbon and anitparrael from each other
15
New cards
what cells are involved in meiosis
gamete cells
16
New cards
how many daughter cells are made in meiosis
4 genetically different cells
17
New cards
how many cells do you get per parent
23 cells
18
New cards
oocytes
premature cells females are born with
19
New cards
spermatocytes
premature cells males are born with
20
New cards
homologous chromosomes
Paired chromatin that are identical
21
New cards
diploid cells
two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
22
New cards
haploid cells
half the number of chromatin than what was in the original cell
23
New cards
genes
sections of DNA that code for a trait
24
New cards
crossing over
exchange of genes during sexual reproduction between two homologous non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes
25
New cards
Prophase 1
centrioles release spindle fibers, nucleus disappears, chromatin turns into chromatid, pairs up with another sister chromatid=tetrad
26
New cards
synapsis/ crossing over
chromatid from each pair will link parts of their “arms” in order to exchange sequences of nucleotides or genes
27
New cards
synapsis
point where “arms bond”
28
New cards
Prophase I
Centrioles begin to release spindle fibers and move to opposite poles. The nucleus disappears. Chromatin condense into chromatids
29
New cards
Metaphase 1
tetrad lined up and formed, spindle fibers reach out and attach to the kinetochores of the tetrads
30
New cards
Prophase I picture
\
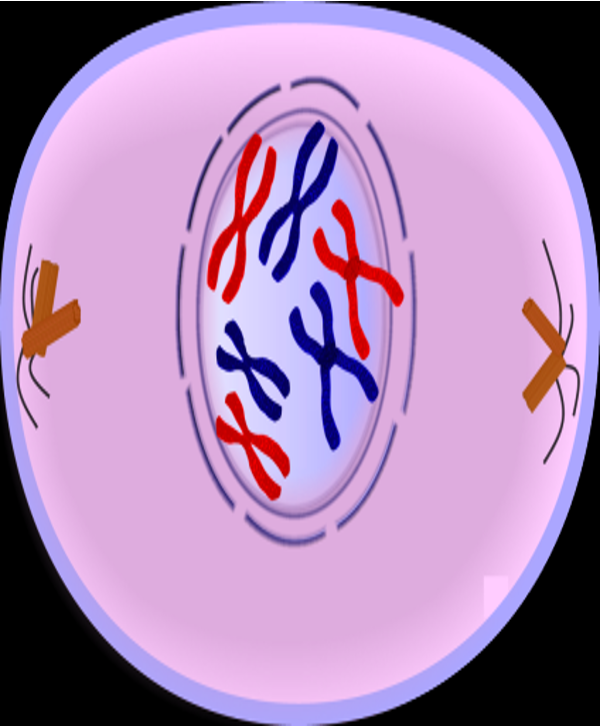
31
New cards
Metaphase 1 picture
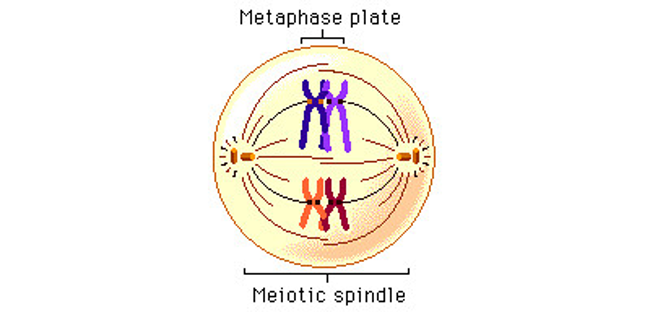
32
New cards
Anaphase I picture
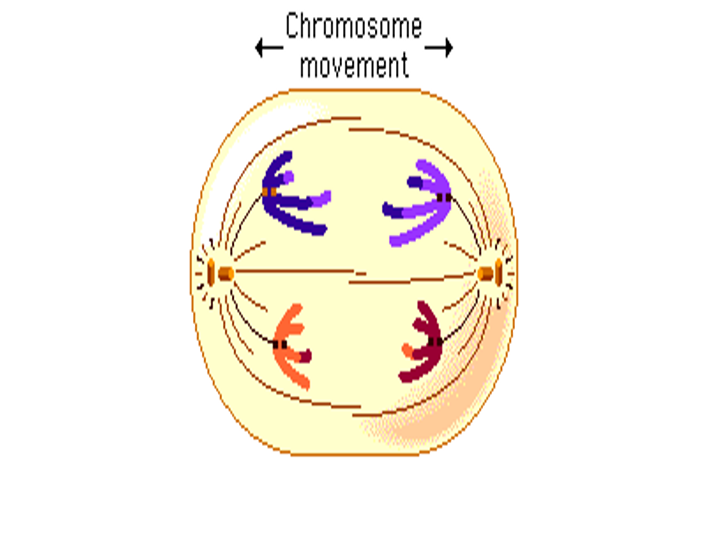
33
New cards
Telophase I picture
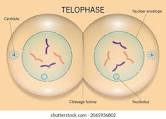
34
New cards
Cytokinesis I picture
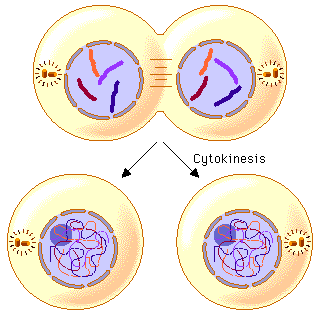
35
New cards
Prophase II picture
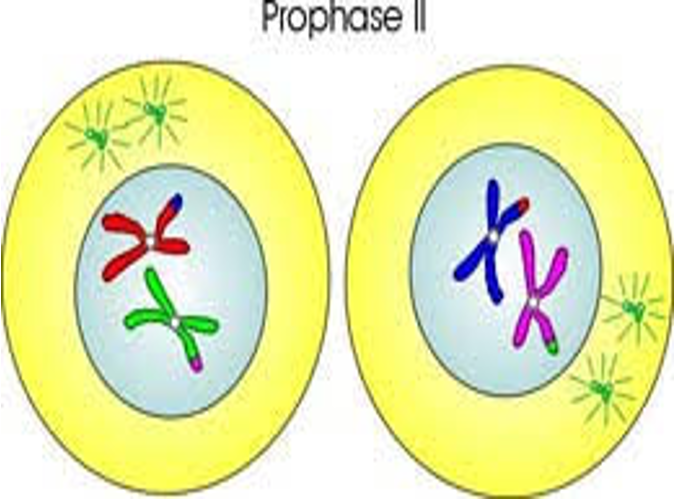
36
New cards
Metaphase II picture
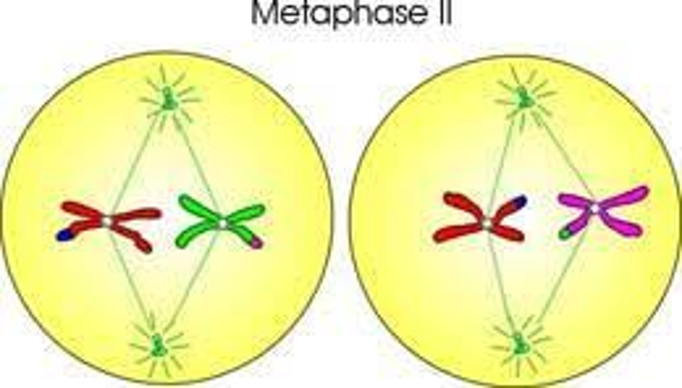
37
New cards
Anaphase II picture
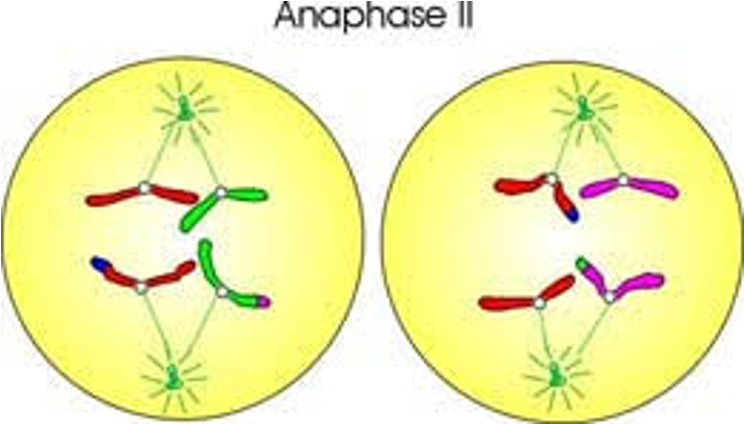
38
New cards
Telophase II picture
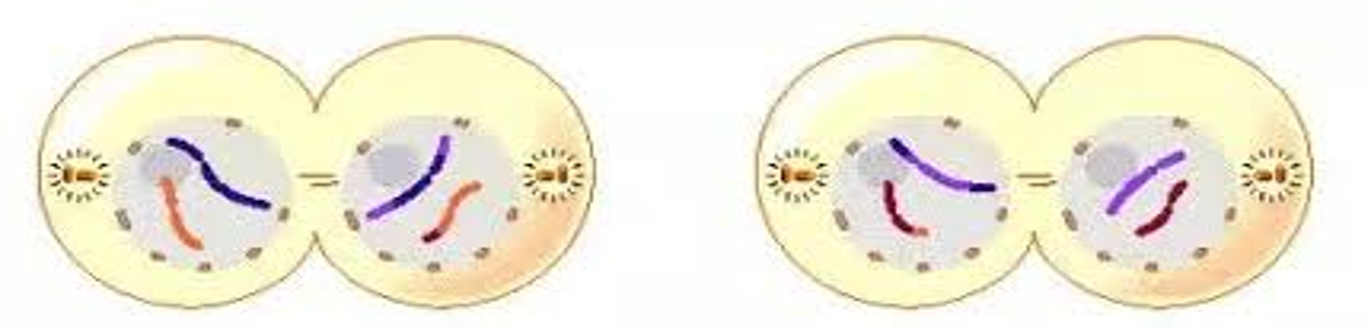
39
New cards
Cytokinesis II picture
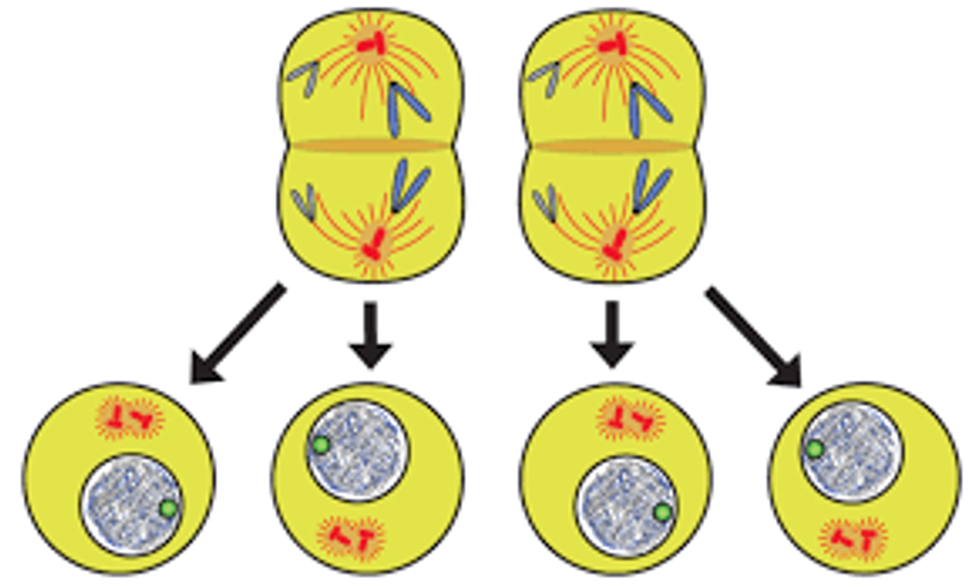
40
New cards
Anaphase I, Telophase I & Cytokinesis I
Spindle fibers will shorten, sister chromatids not identical anymore (pulled to opposite sides)
41
New cards
Prophase II
identified by the two cells, nucleus disappears and sister chromatid
42
New cards
Metaphase II
Spindle fibers connect to the kinetochores of sister chromatids
43
New cards
Anaphase II
46 chromatids were separated and pulled to opposite pole There should be 23 chromatids being pulled to each side in both cells
44
New cards
Telophase II
cleavage furrow will begin to form in both cells, 2 nuclei will reform, and chromatids will begin to de-condense into chromatin “in separate cells”
45
New cards
Cytokinesis II
4 Genetically different sperm or egg cells, with 23 chromatin each
46
New cards
Gregor Mendel
“Father of Genetics”
a priest who studied pea plants to learn about traits
he studied pea plants because they have many traits and only exist in two forms – tall or short
a priest who studied pea plants to learn about traits
he studied pea plants because they have many traits and only exist in two forms – tall or short
47
New cards
traits
a characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes
48
New cards
heredity
passing of traits from parents to an offspring
49
New cards
genetics
the study of heredity
50
New cards
gene
a segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
51
New cards
alleles
the different forms of a gene
52
New cards
recessive allele
an allele that is masked (covered up) when a dominant allele is present; represented by a lowercase letter
53
New cards
dominant allele
an allele whose trait always shows up in an organism when the allele is present; represented by an uppercase letter
54
New cards
genotype
an organism’s genetic makeup, or allele combination (ex. BB, Bb, bb)
55
New cards
homozygous/purebred
having identical alleles for a trait (ex. BB or bb)
56
New cards
heterozygous/hybrid
having different alleles for a trait (ex. Bb)
57
New cards
phenotype
the trait that is being expressed can be seen or not seen
58
New cards
incomplete dominance
Instead of looking like the dominant trait when heterozygous the offspring happen to have a third, different trait. Often it appears to be a combination or __**“blend”**__ of the dominant and recessive trait.
59
New cards
codominance
Type of inheritance that includes 2 dominant traits, no recessives. One dominant cannot “win” over the other so instead you __**“see”**__ both traits
60
New cards
insertion
adding a nucleotide
61
New cards
deletion
deleting a nucleotide=frameshift
62
New cards
subsitution
a nucleotide is swapped for a different nucleotide
63
New cards
sex linked chromosomes
Sex-linked inheritance is when the trait is carried by one of the sex chromosomes (X or Y). We will only be examining X-linked inheritance, no Y traits. This means the allele will only be present on the X.
64
New cards
silent mutation
switched for same amino acid, so no change noticed
65
New cards
missense mutation
switched for different amino acid
66
New cards
nonsense mutation
early stop
67
New cards
long arm of a chromosome
q arm
68
New cards
short arm of a chromosome
p arm
69
New cards
how is deletion caused
piece of chromosome is lost
70
New cards
how is inversion caused
Chromosome segment breaks off, Segment flips around backwards, segment reattaches
71
New cards
how is duplication caused
Occurs when a gene sequence is repeated
72
New cards
how is translocation caused
a piece breaks off and is attached to another chromosome
73
New cards
mononmy
a person is missing or has an dxtra chromosome
74
New cards
nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate during meiosis
75
New cards
Cri-Du-Chat
Deletion of part of the 5th chromosome
46, XX or XY, del(5)
46, XX or XY, del(5)
76
New cards
Mosaic Trisomy 16
47, XX or XY, +16
An extra copy of chromosome 16 is in *some* of the cells, while the other cells are normal
Typically born early and with a low birth weight, many grow to a normal weight and height by toddler age
An extra copy of chromosome 16 is in *some* of the cells, while the other cells are normal
Typically born early and with a low birth weight, many grow to a normal weight and height by toddler age
77
New cards
Patau syndrome or Trisomy 13
Extra copy of chromosome 13
47, XX or XY, +13
May also have cleft palate and weak muscle tone
47, XX or XY, +13
May also have cleft palate and weak muscle tone
78
New cards
Full Trisomy 16
47, XX or XY, +16
An extra copy of chromosome 16 in all of cells
Most common reason for miscarriage
An extra copy of chromosome 16 in all of cells
Most common reason for miscarriage
79
New cards
Trisomy 18 or Edward Syndrome
An extra copy of chromosome 18
47, XX or XY, +18
Clenched hands, rounded
feet, unusual shaped chest,
Limited Intellectual disabilities
47, XX or XY, +18
Clenched hands, rounded
feet, unusual shaped chest,
Limited Intellectual disabilities
80
New cards
Down Syndrome or Trisomy 21
An extra copy of chromosome 21
47, XX or XY, +21
47, XX or XY, +21
81
New cards
Philadelphia Chromosome
Chronic Leukemia
A translocation of part of #9 and #22
46, XX or XY, t(9,22)
uncommon type of cancer of the bone marrow where blood cells are made
A translocation of part of #9 and #22
46, XX or XY, t(9,22)
uncommon type of cancer of the bone marrow where blood cells are made
82
New cards
Klinefelter Syndrome
An extra X chromosome
47, XXY, +23
Can cause sterility, smaller testes, extra pectoral tissue (gynecomastia), can have learning and social delays
Less than average amounts of testosterone
47, XXY, +23
Can cause sterility, smaller testes, extra pectoral tissue (gynecomastia), can have learning and social delays
Less than average amounts of testosterone
83
New cards
XYY Syndrome or Jacob Syndrome
An extra Y chromosome
47, XYY, +23
Often tall and thin, with possible learning delays/disabilities
47, XYY, +23
Often tall and thin, with possible learning delays/disabilities
84
New cards
XXX (Trisomy X)
47, XXX, +23
Extra X chromosome, for a total of XXX instead of XX
Normal physically but weak muscle tone
Tall stature, learning delays, limited fertility
Extra X chromosome, for a total of XXX instead of XX
Normal physically but weak muscle tone
Tall stature, learning delays, limited fertility
85
New cards
Turner’s Syndrome (Monosomy X)
Missing an X0 chromosome
45, X0, -23
Female, sterile, short stature, webbed neck, puffiness of skin, kidney and heart defects.
45, X0, -23
Female, sterile, short stature, webbed neck, puffiness of skin, kidney and heart defects.
86
New cards
Prokaryotes
Single celled
have cell walls made of peptidoglycan
have ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane and a singular, circular DNA that floats in a nucleoid region and some can have a plasmid
have cell walls made of peptidoglycan
have ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell membrane and a singular, circular DNA that floats in a nucleoid region and some can have a plasmid
87
New cards
how do prokaryotes reproduce
asexually; by binary fission, not mitosis/meiosis
88
New cards
step one of binary fission
No interphase
89
New cards
step two of binary fission
Single circular DNA is replicated
90
New cards
step three of binary fission
Cell elongates
91
New cards
step four of binary fission
The cell membrane pinches and a septum (like a cell plate) is formed
92
New cards
step five of binary fission
The cells separate creating a single-cell with a cell wall, cell membrane, DNA
93
New cards
after a cell goes through binary fission what happens
go through gene expression/read the code of the DNA, convert into mRNA to make proteins (enzymes, protein channels, protein pumps etc.) in the cytoplasm
94
New cards
operon
group of genes that are transcribed at the same time by RNA polymerase to create a strand of mRNA that will code for a protein
95
New cards
Lac Operon
codes (has the instructions) for the lactase enzyme, needed to breakdown lactose into glucose
96
New cards
Trp Operon
codes for the amino acid tryptophan, needed by bacteria to make certain proteins
97
New cards
repressed
turned off
98
New cards
induced
turned on
99
New cards
bacterial conjugation
bacteria have the ability to “share” their genetic information
100
New cards
use of bacterial conjugation
bacterial cell has plasmid that contains a gene for antibiotic resistance, and let’s say the gene makes the bacterial cell resistant to penicillin.