Radiographic Quality pt2
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
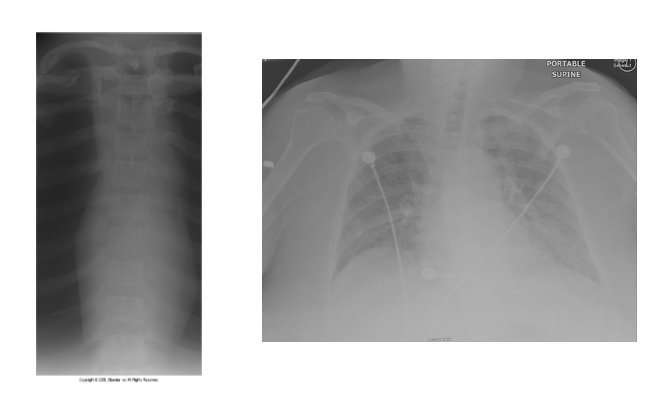
What is wrong with this xray images
This image shows scatter and fog and how little contrast there in the image
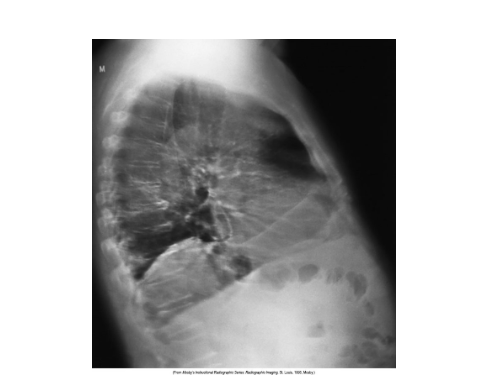
What is affecting this image
This image shows motion on sharpness The image looks out of focus not sharp and blurry
Lateral chest xray is the image
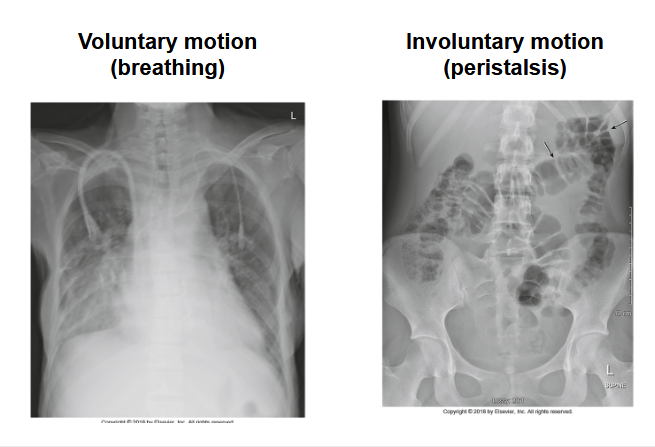
What does the left image and right image show
Voluntary and involuntary motion
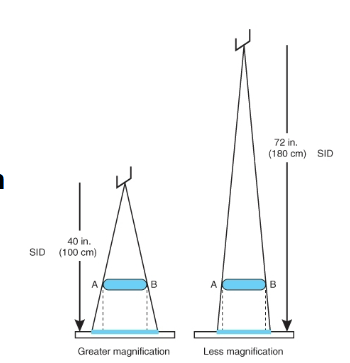
What does this image show
This image shows SID being increased reduces distortion (magnification) better spatial resolution
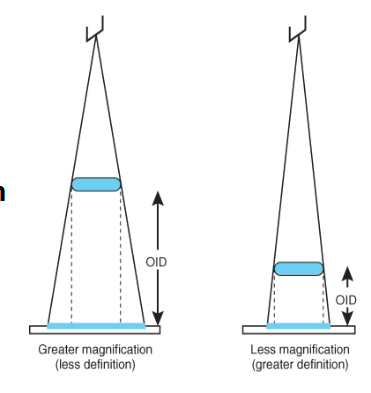
What does this image show
This image shows Decrease in OID reduces distortion (magnication) better spatial resolution
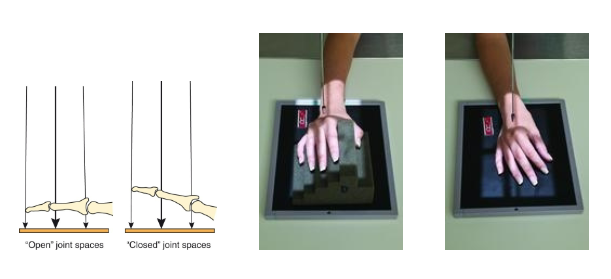
What does this iamge show
These images shows that not having the anatomy parallel will give you distortion reducing spatial resolution
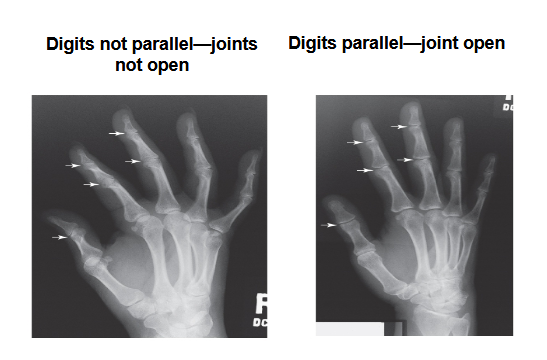
What does this image show
The left image is not parrell to IR and the right is Parallel its needs to be completely flat noo finger should be raised ]
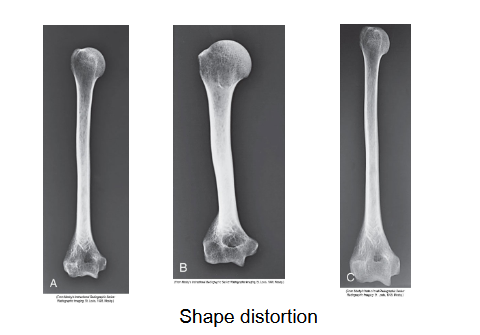
What is happening with these bones
Left is the correct
Middle is foreshortened
Right is elongated
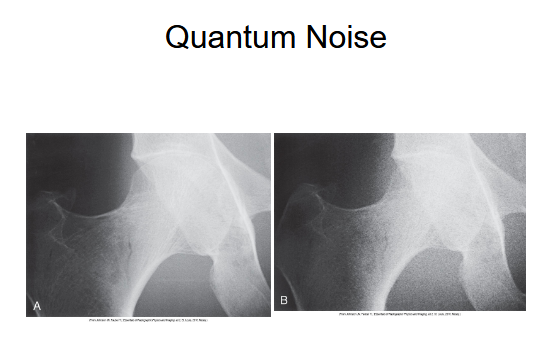
What does this image show
This image shoes quantum noise on the right image it looks very grainy like sandpaper reduces the details
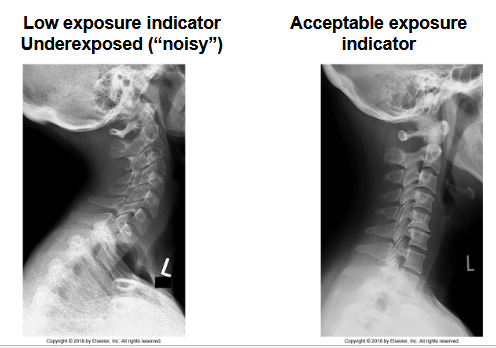
What does this image show
Quantum noise is seen more in thicker areas this image shows it on the left size
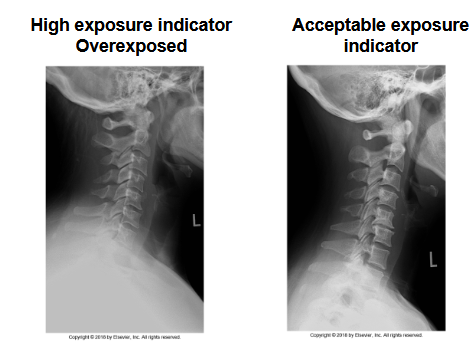
What does this image show
This image shows over exposure but can still be used because the digital imaging will adjust the brightness and contrast over saturation of contrast would mean repeat tho
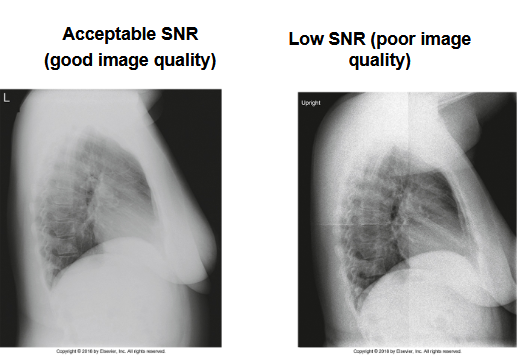
What does this image show
This shows SNR with high on left and right low SNR