Chapter 14c: Extensions and Deviations of Mendelian Genetics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
sex-linkage
-a gene located on a sex chromosome
-patterns of inheritance in males and females differ
linkage
-two or more genes are on the same chromosome
-genes do not assort independently
codominance
-heterozygotes have phenotypes of both alleles
-more than two phenotypes are seen because heterozygotes have a unique phenotype
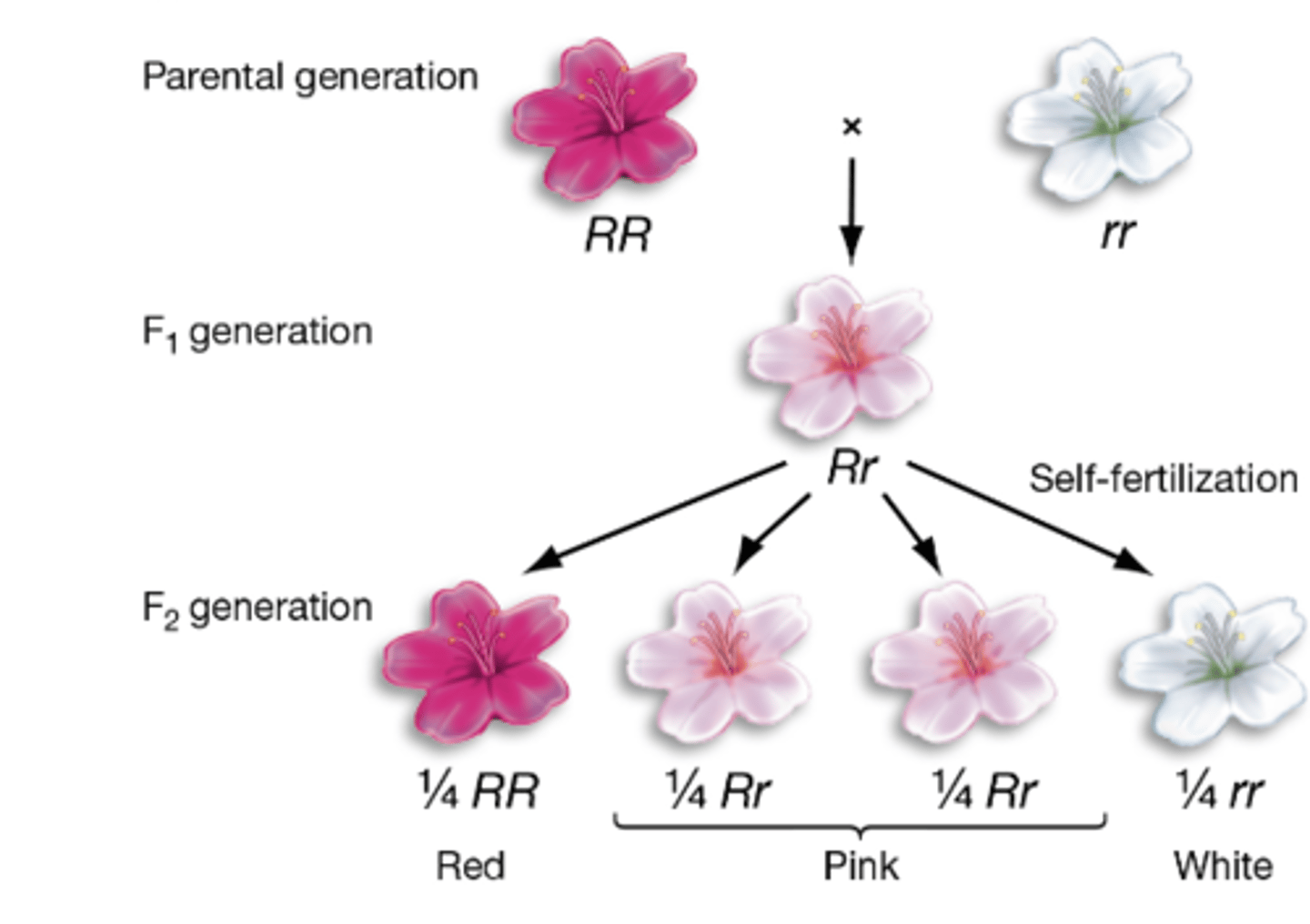
incomplete dominance
-heterozygotes have phenotypes of both alleles
-the pattern is common and more than 2 phenotypes are seen
-typically seen in pigments
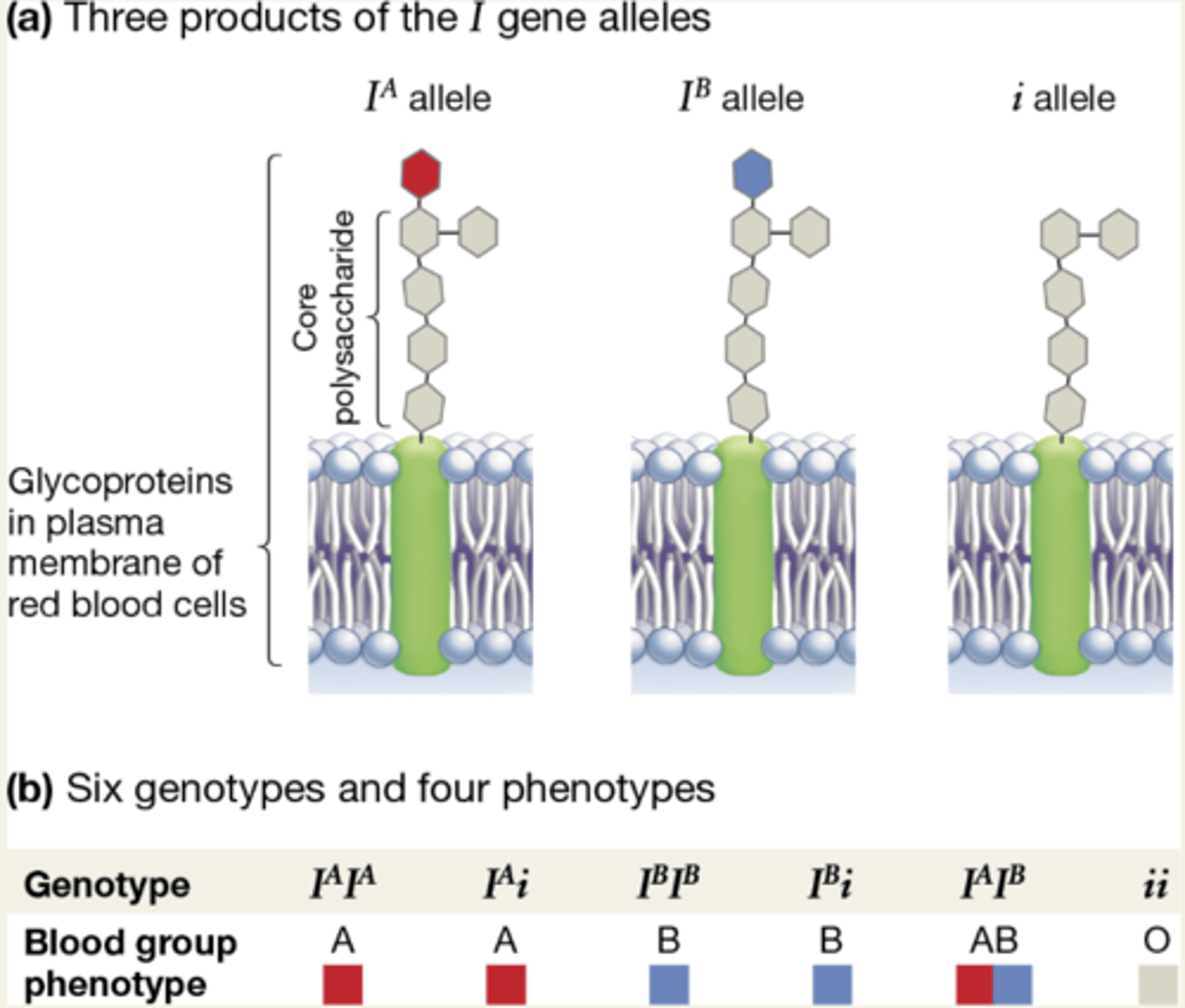
multiple allelism
-in a pop. there are more than 2 common alleles for the locus
-more than 2 phenotypes are often seen
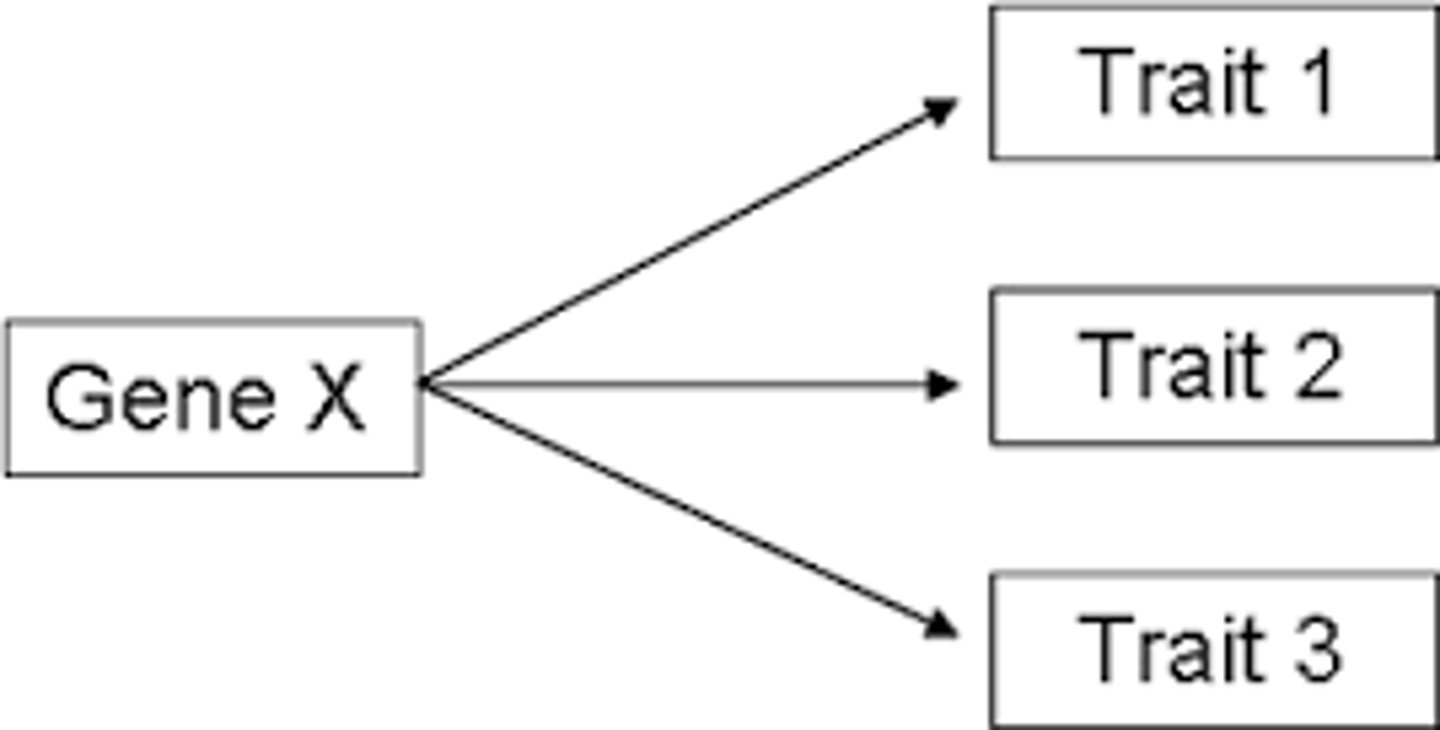
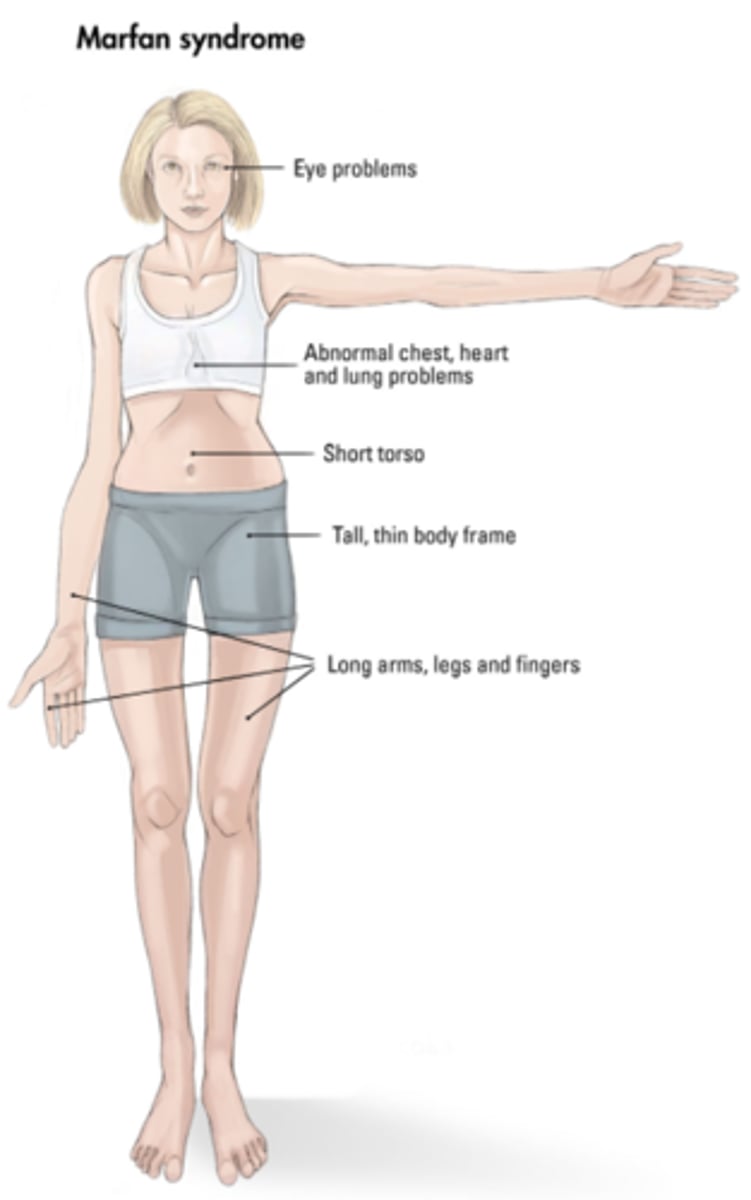
pleiotropy
-a single gene affect many traits
-Marfan Syndrome
polygenic (quantitative trait)
-a trait that is influenced by many genes and often exhibits continuous variation rather than distinct phenotypes
-each gene adds a small amount of phenotype
gene interaction
-the phenotype associated with an allele depends on which alleles of another gene are present
-leads to one allele being associated with diff phenotypes
epistasis
-a particular form of the gene interaction in which particular alleles of one gene mask the expression of the alleles of another gene
-shows that there are many forms of gene interaction and leads to surprising results in which an expected phenotype is not seen
environmental factors
-phenotype is influenced by the environment experienced by the individuals with the same genotype
-same genotypes can lead to different phenotypes

complete dominance
in the traits Mendel studied, only the phenotype associated with the dominant allele appeared in heterozygotes
Marfan syndrome
-caused by the mutation of a pleiotropic gene
-mutations in gene affect multiple traits related to connective tissue formation such as: near sightedness, scoliosis, and heart valve defects
essential gene
product necessary for life
-mutation can lead to a lethal phenotype
-can be X-linked or autosomal
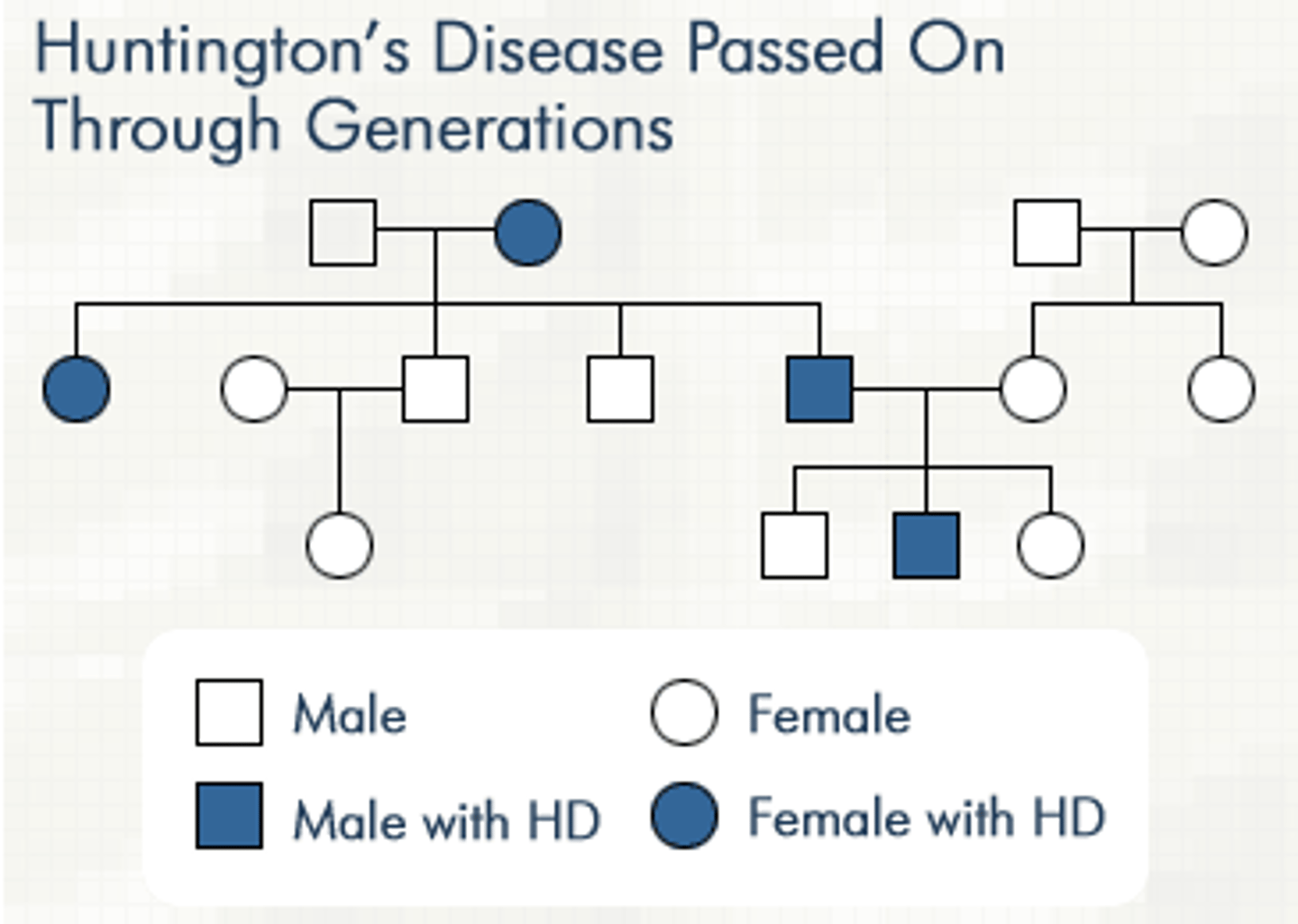
lethal allele
-an allele whose expression results in the death of the individual organism expressing it
-may be dominant(Huntington's kills you when older) or recessive (Tays-Sachs kills you young)
-if allele is dominant it will kill the homozygote and heterozygote
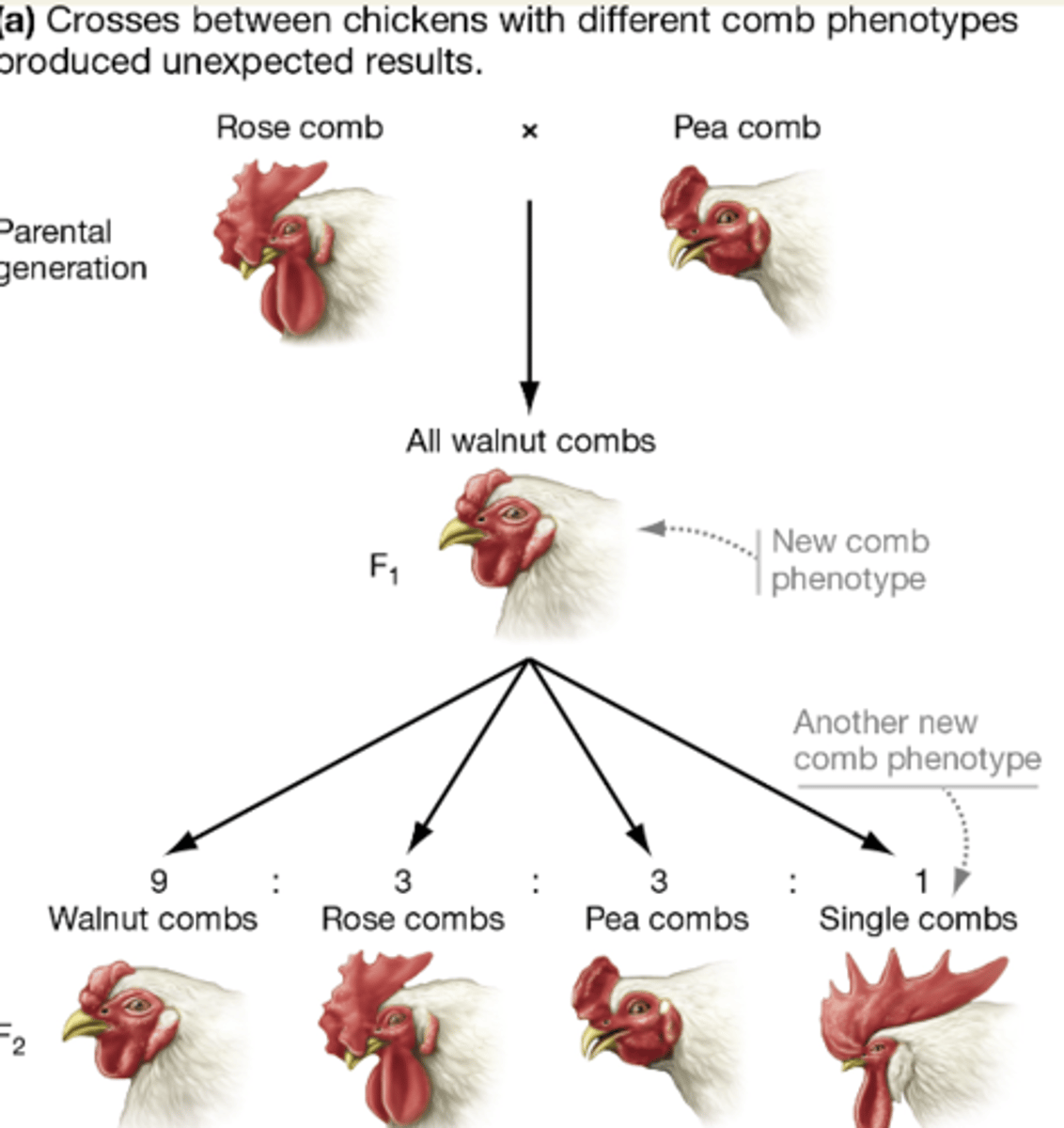
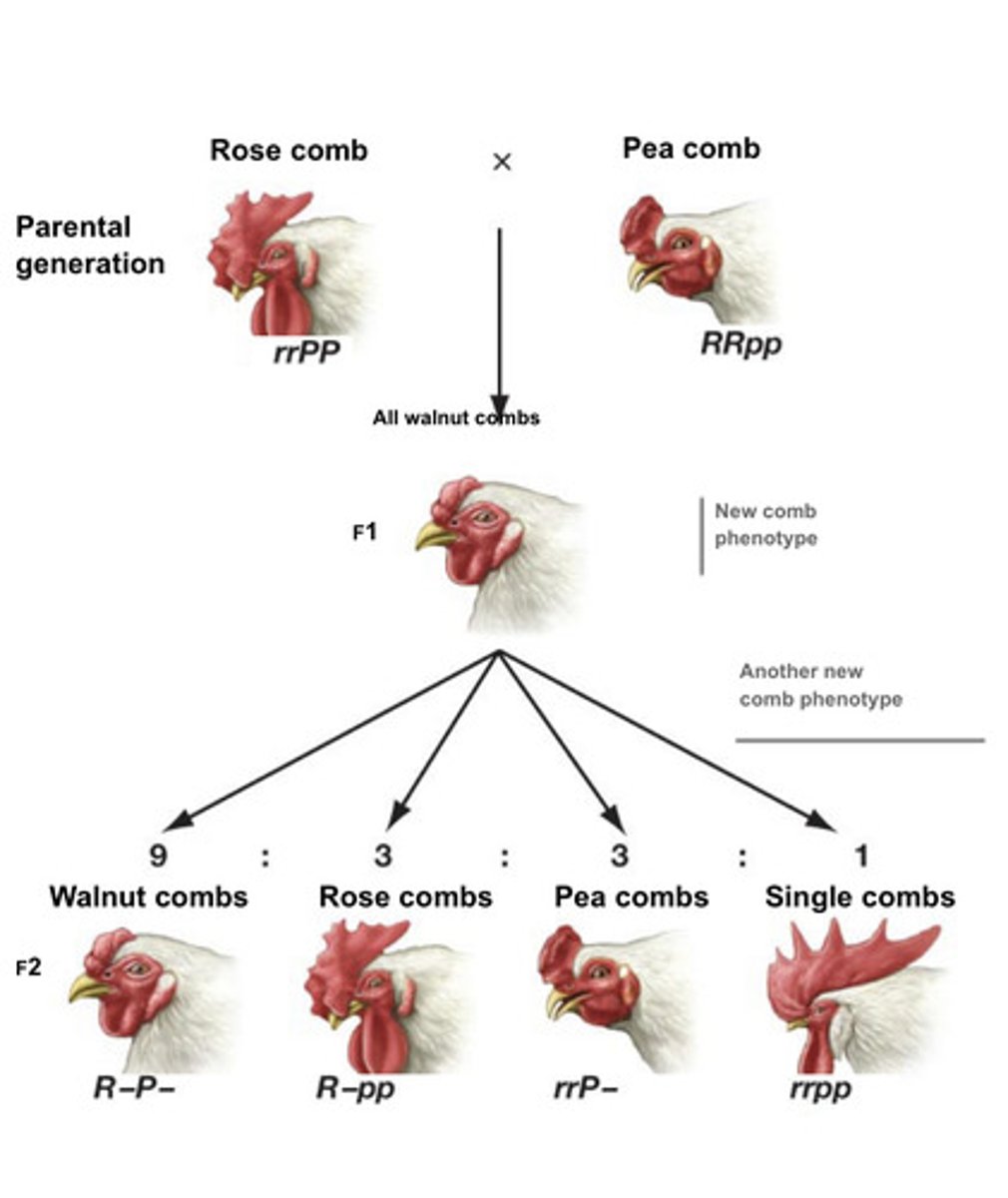
novel phenotypes
-may happen when 2 non allelic pairs (2 diff genes) affect the same trait then the gene products interact
-maintain 9:3:3:1 ratio
-in chickens the R and P genes interact to create the comb phenotype
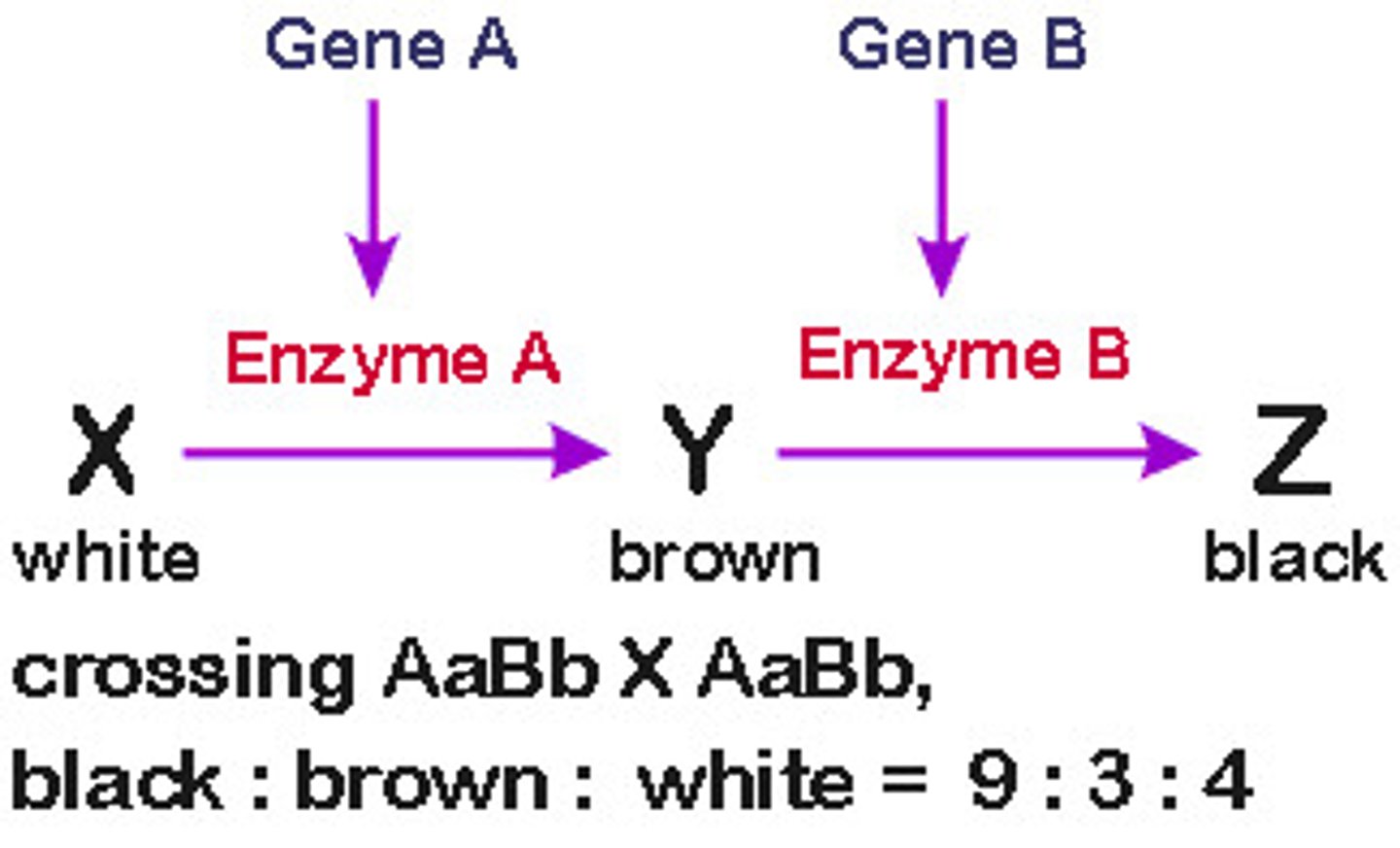
epistasis in mice
produces 9 agouti: 3 black: 4 albino
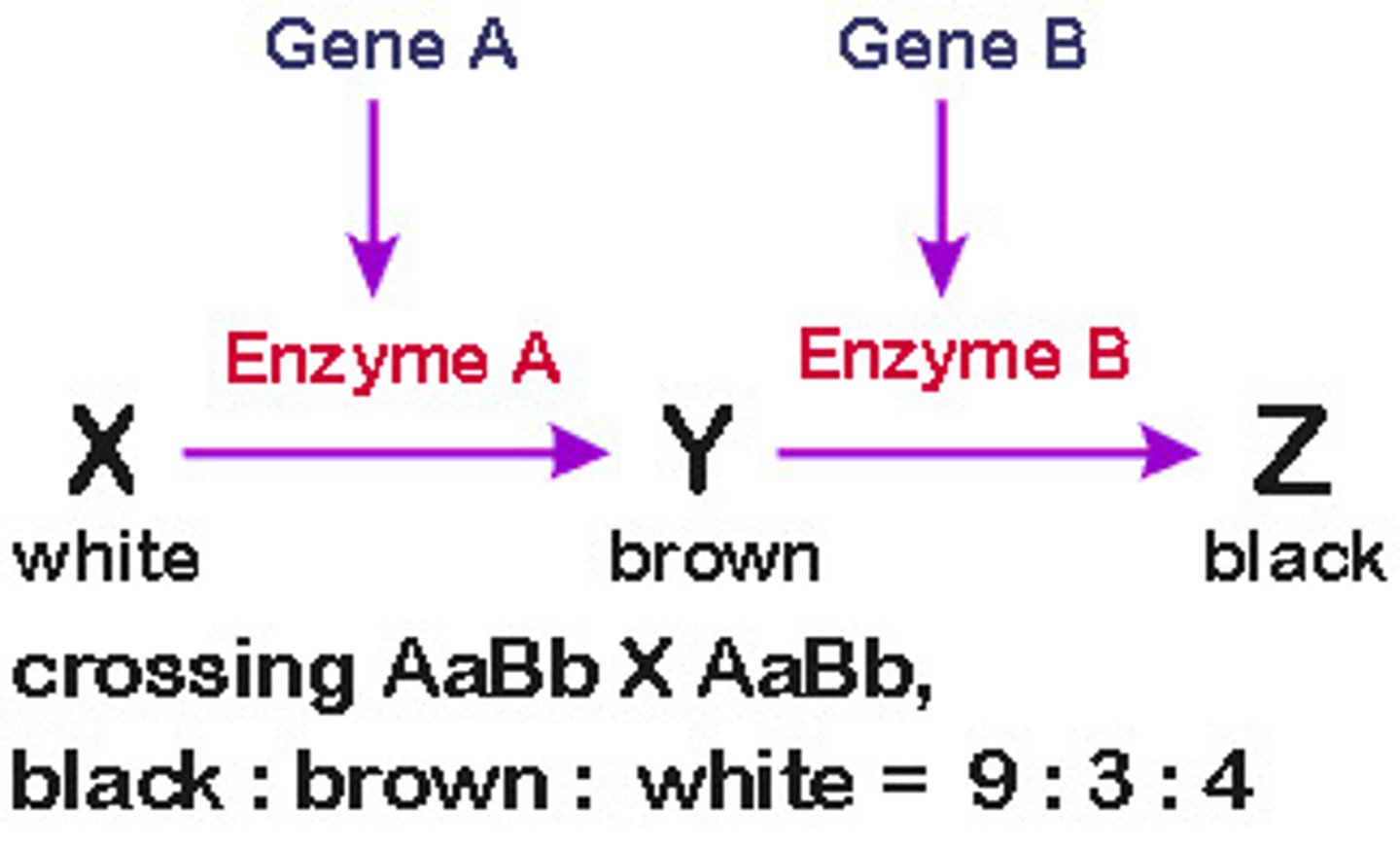
coat color of mice
-controlled by 2 genes, A and C
-A and C produce functional enzymes
-a and c do not produce functional enzymes
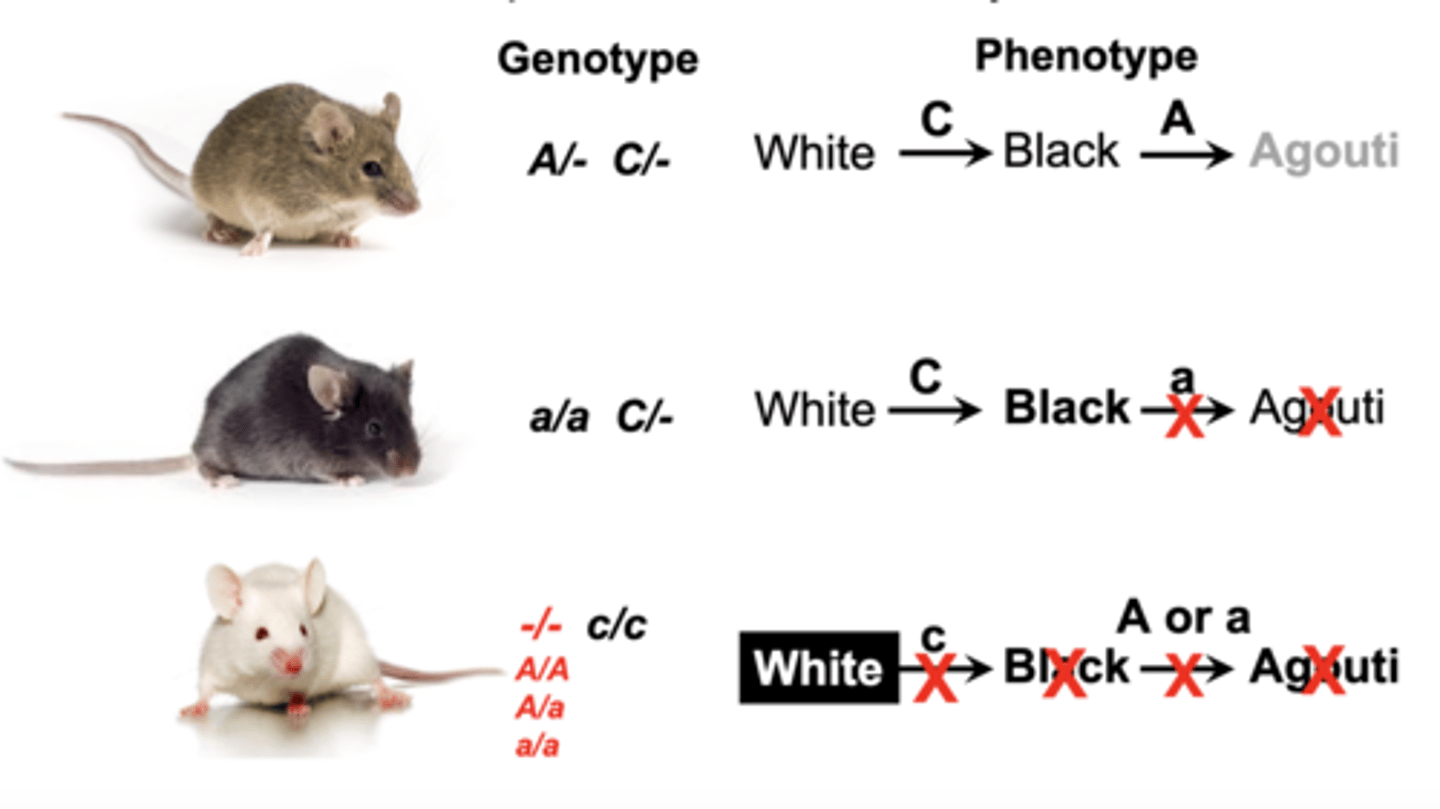
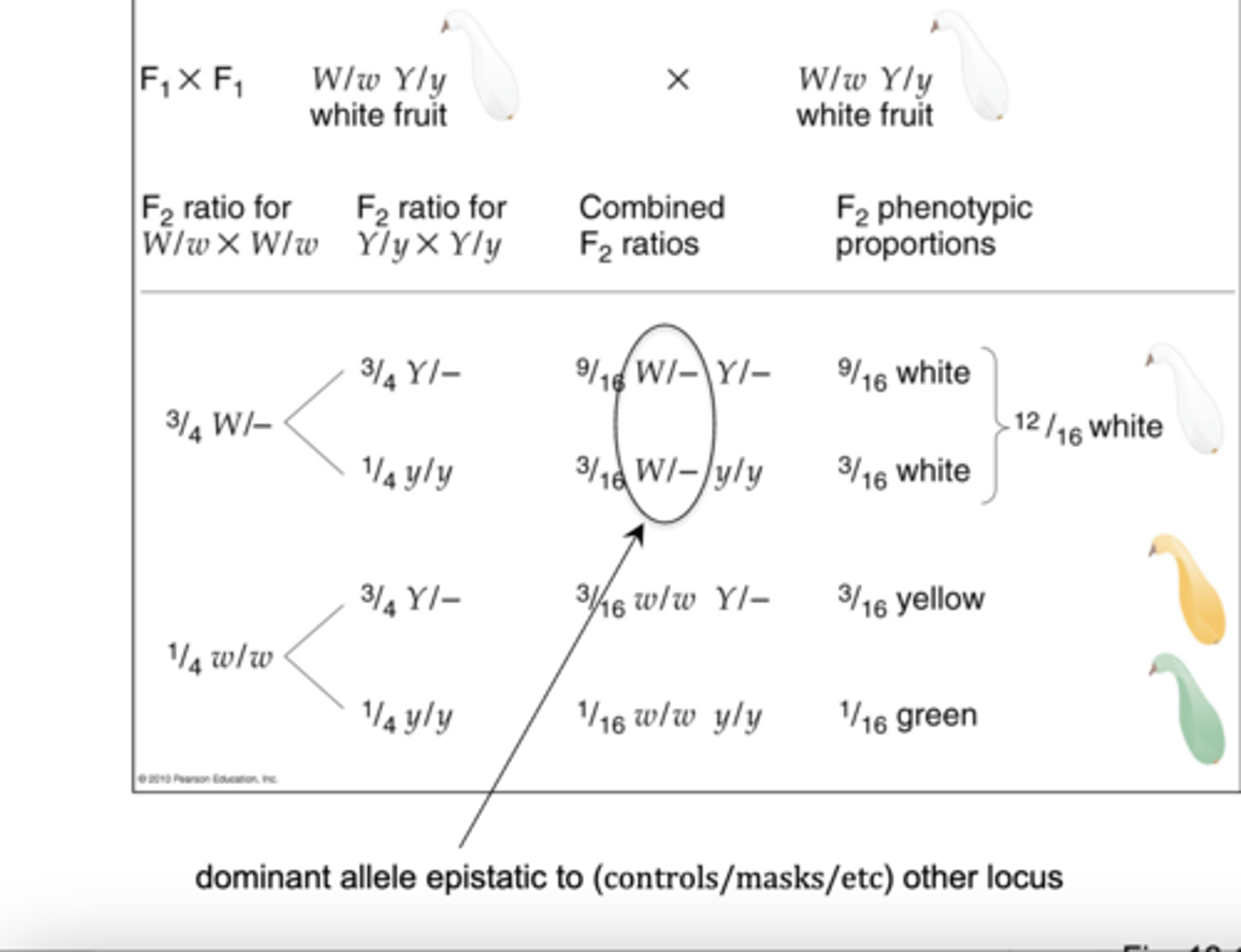
recessive epistasis
only the homozygous recessive allele at one locus masks or modifies the phenotype from another locus (A in photo)
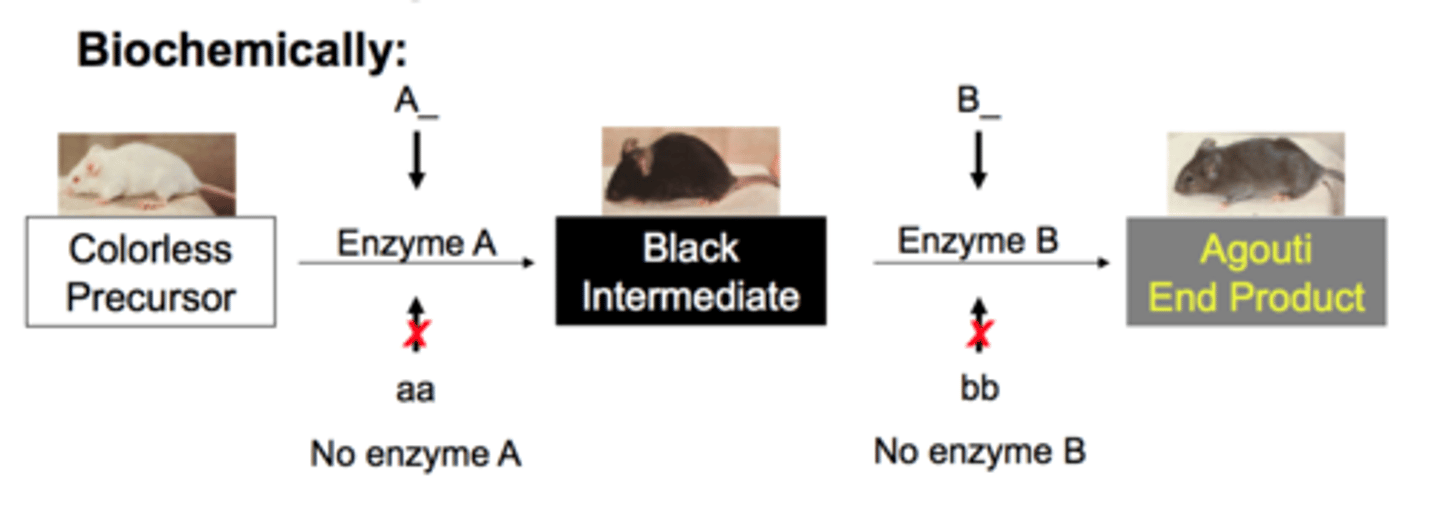
epistasis in labrador retrievers
-controlled by two genes , E and B
-E and B produce functional enzymes
-e and b do not produce functional enzyme
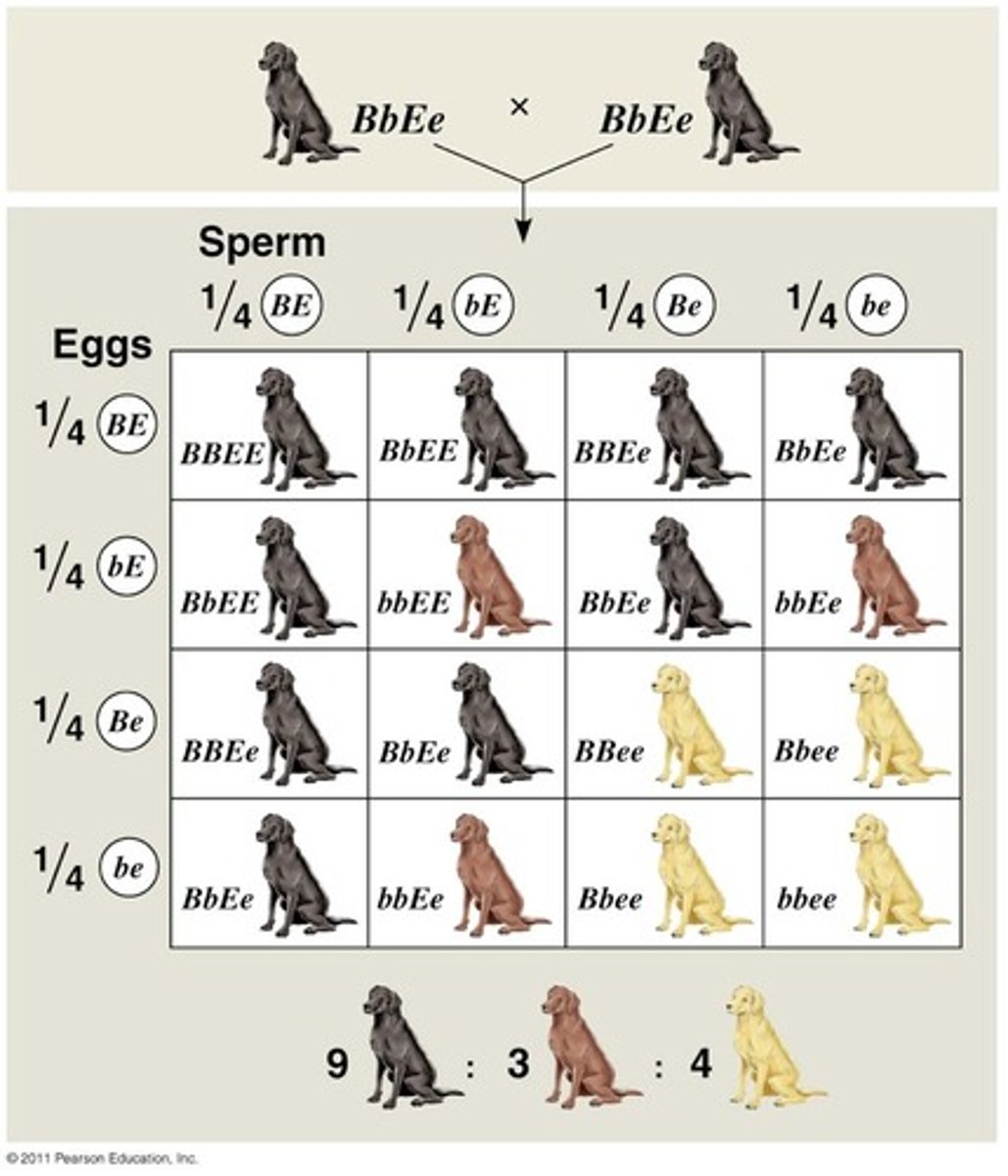
dominant epistasis
-the presence of one copy of the dominant allele completely masks the effect from the second locus
-dominant allele epistatic (masks) other locus
ratio for:
F1: A/a B/b * A/a B/b
Gene Interactions: None
A/- B/- : A/- bb : a/a B/- : a/a b/b
9 : 3 : 3 : 1

ratio for:
F1: A/a B/b * A/a B/b
Gene Interactions: a/a epistatic to B or b
A/- B/- : A/- bb : a/a B/- : a/a b/b
9 : 3 : (3+1) 4
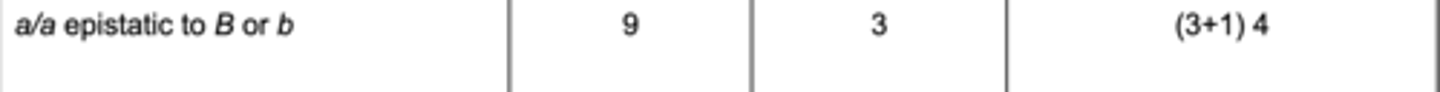
ratio for:
F1: A/a B/b * A/a B/b
Gene Interactions: A is epistatic to B or b
A/- B/- : A/- bb : a/a B/- : a/a b/b
(9+3) 12 : 3 : 1
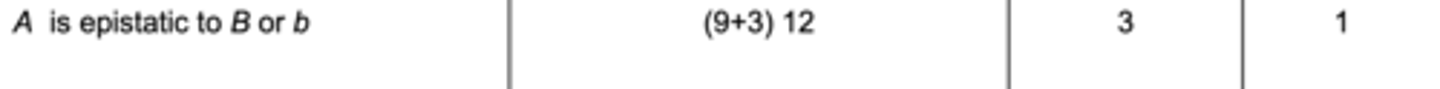
ratio for:
F1: A/a B/b * A/a B/b
Gene Interactions: a/a is epistatic to B or b
OR b/b epistatic to A and a
OR a/a = b/b = same phenotype
A/- B/- : A/- bb : a/a B/- : a/a b/b
9 : (3+3+1). 7

ratio for:
F1: A/a B/b * A/a B/b
Gene Interactions: A epistatic to B or b
OR B epistatic to A or a
OR A and B give the same phenotype
A/- B/- : A/- bb : a/a B/- : a/a b/b
(9+3+3) = 15 : 1

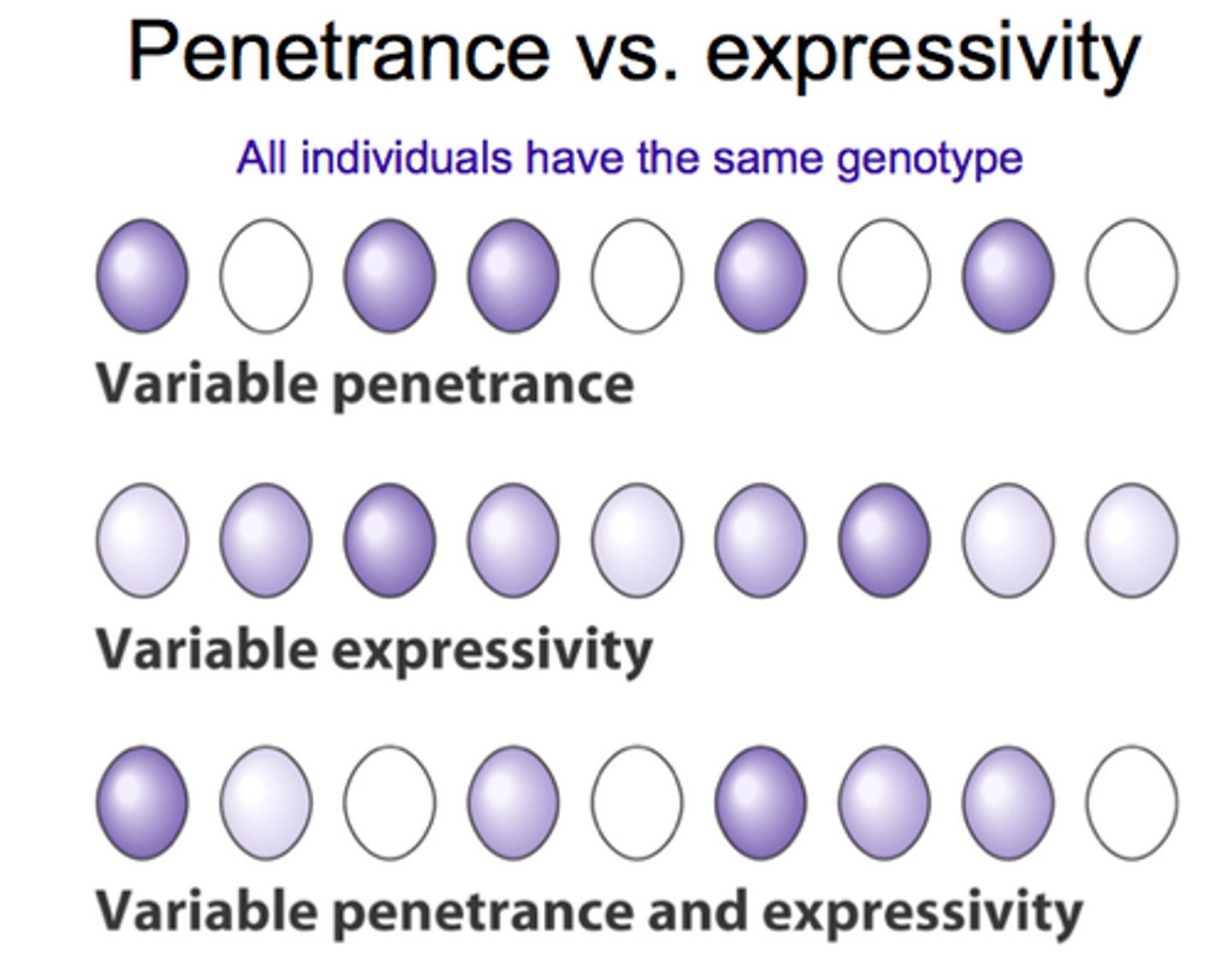
penetrance
-the percentage of individuals with the same genotype, at a specific locus, that actually exhibit the associated phenotype
-depends on both the genotype and the environment
complete pentrance
100% of individuals with the genotype all have the same phenotype
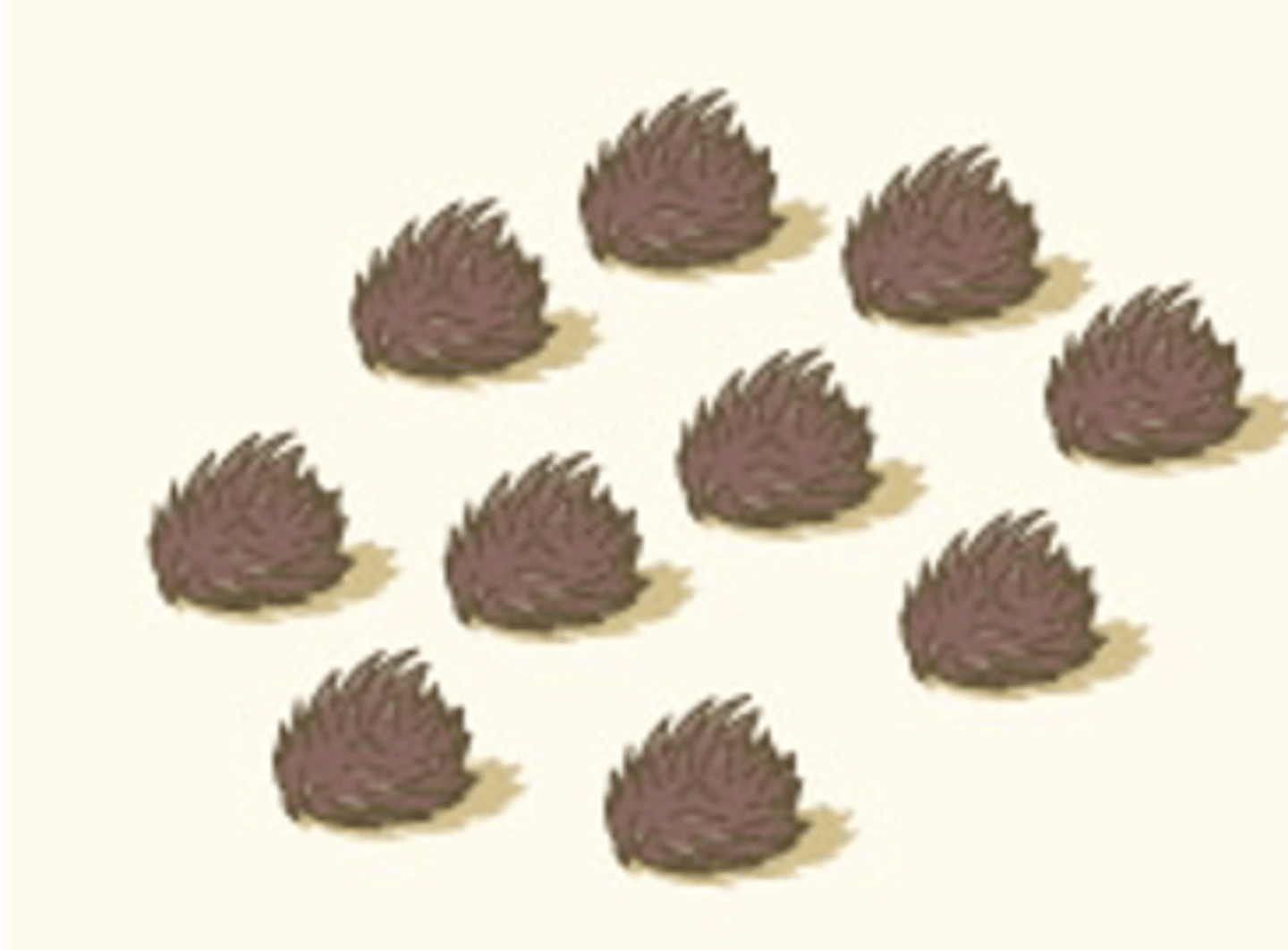

incomplete pentrance
less than 100% of individuals with the same genotype have the same phenotype
expressivity
-degree to which a penetrant gene is phenotypically expressed
-depends on genotype and the environment
-individuals show range of phenotype
constant expressivity
all individuals with a given genotype express the same phenotype
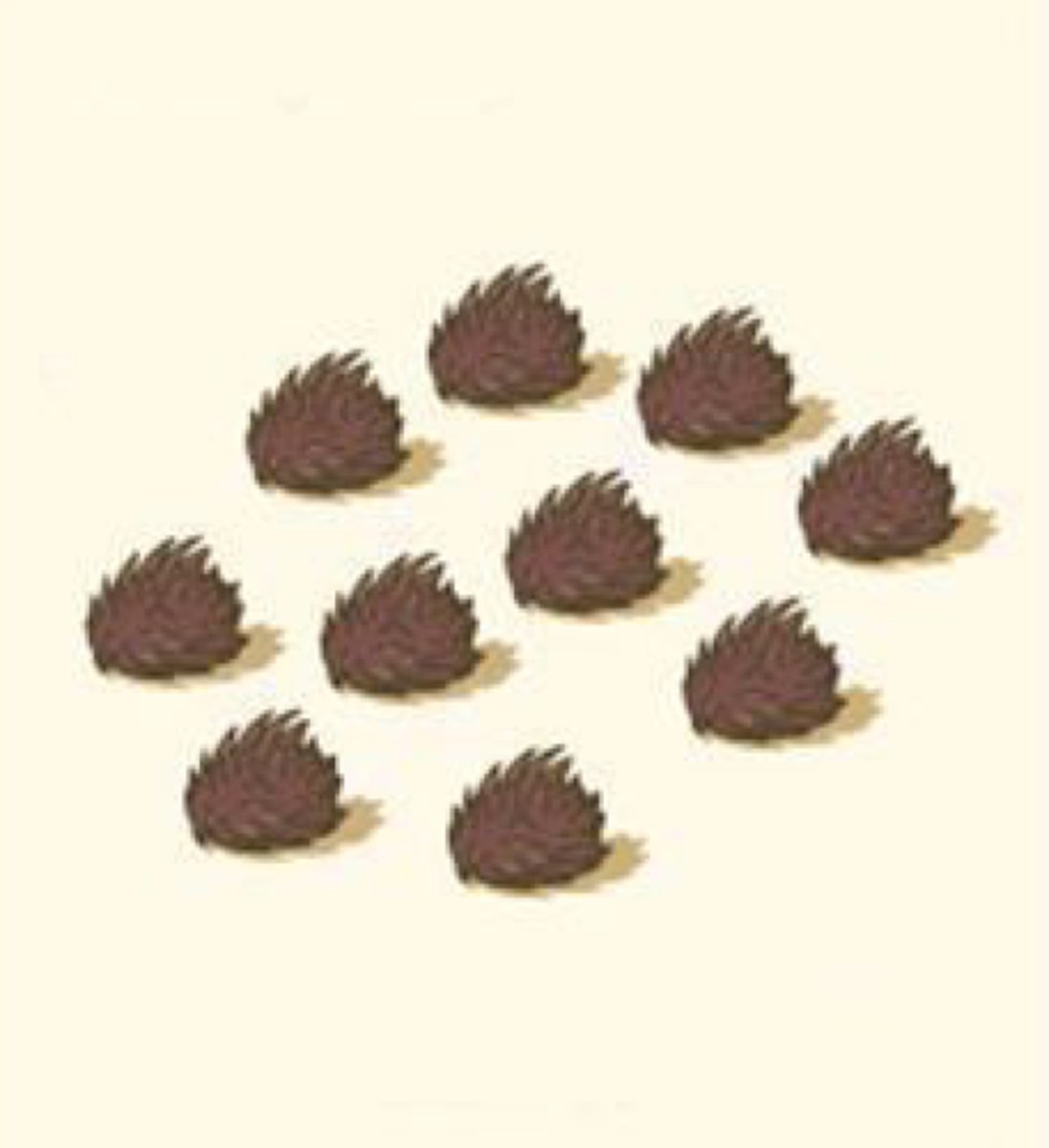

variable expressivity
individuals with the same genotype have related phenotypes that vary in intensity

incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity
identical known genotypes produce a broad range of phenotypes due to varying degrees of gene activation and expression
effect of environment on phenotype
- age of onset
- sex
- temperature
- chemicals
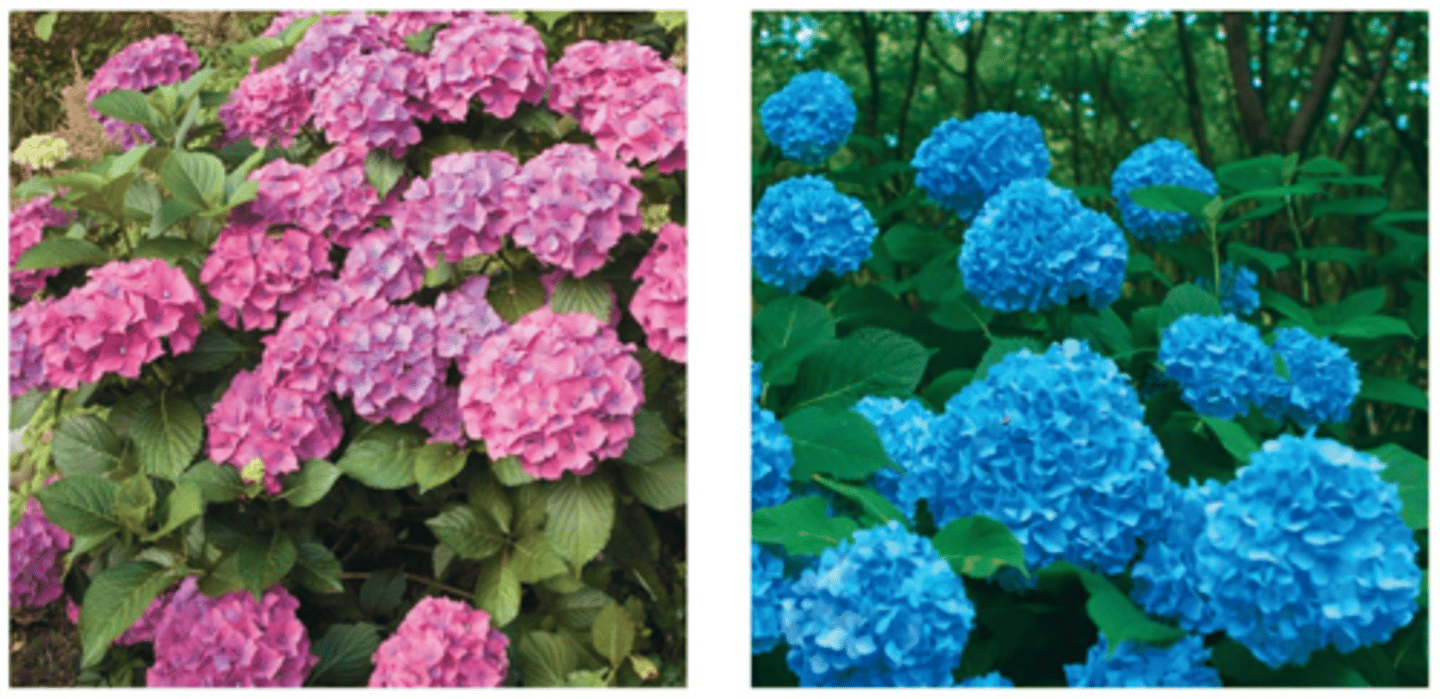

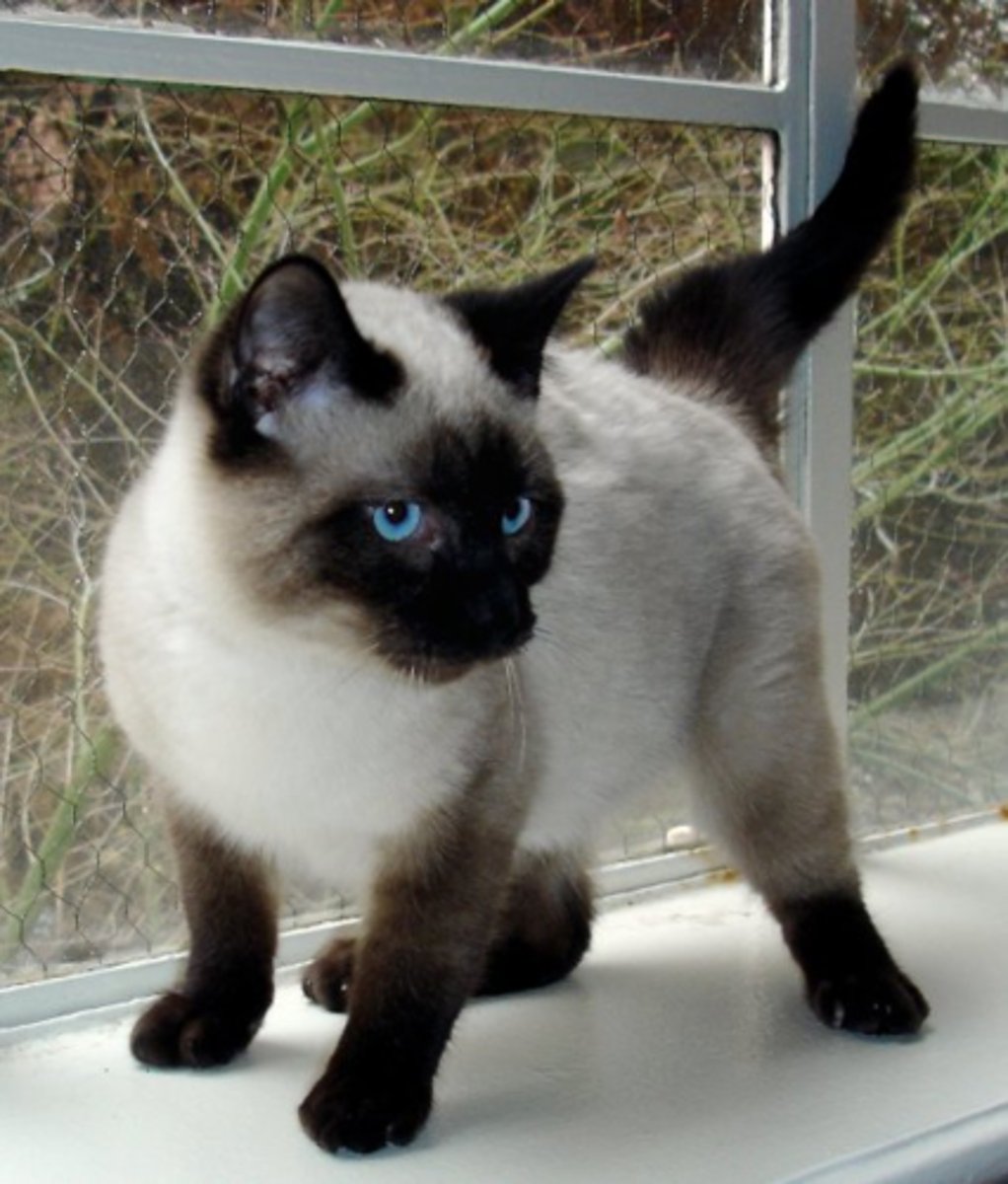
temperature sensitivity to tyrosinase
-determines coat color by converting tyrosine into black pigment
-siamese cats are homozygous recessive for siamese allele (c^s, c^s)
-c^s allele encodes for temp sensitivity so tyrosinase is only active at low temps

extranuclear inheritance
-all comes from mom (uniparental inheritance)
-mitochondrial gene (involved in TCA cycle, oxidative phosphorylation)
-chloroplast genes
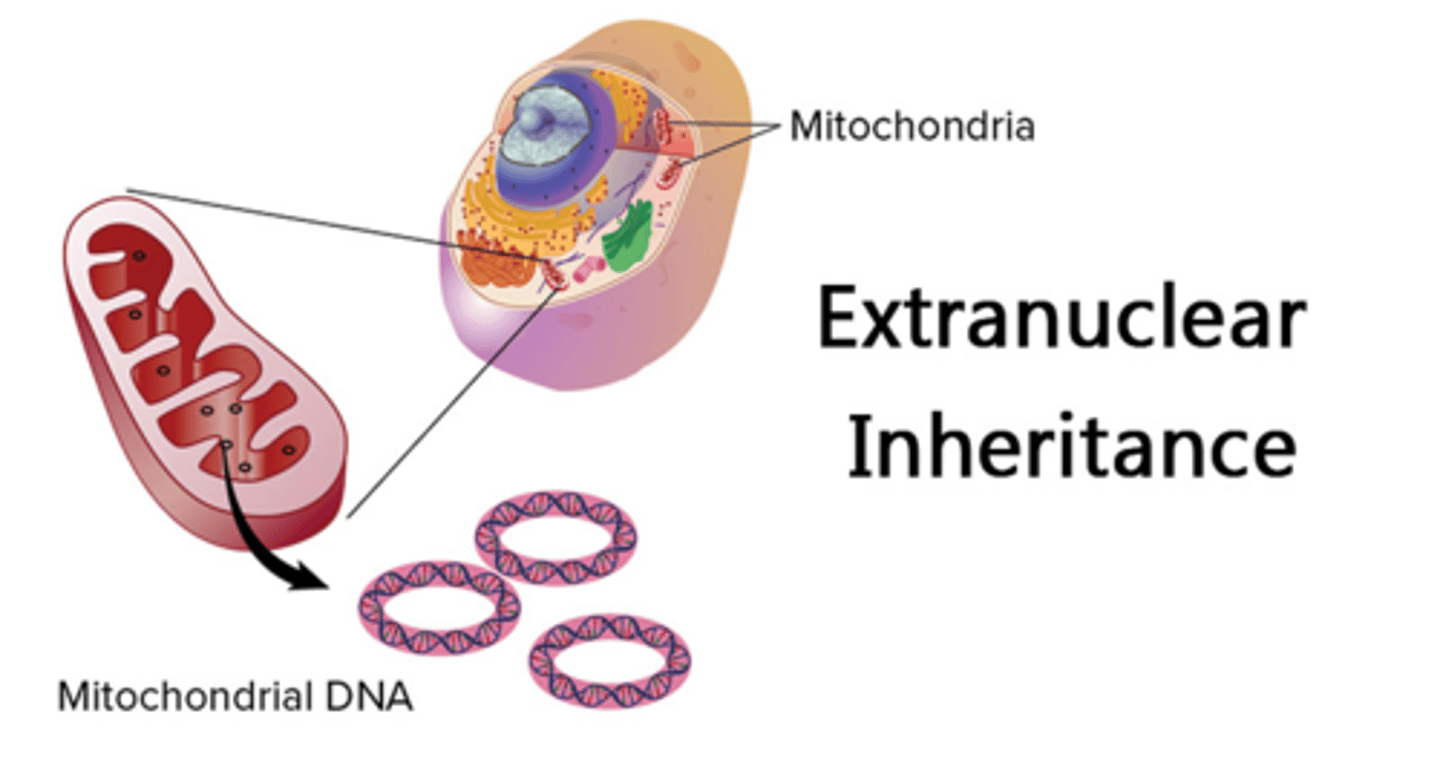
Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)
-caused by defects in ETC
-causes blindness in adults and due to maternal inheritance
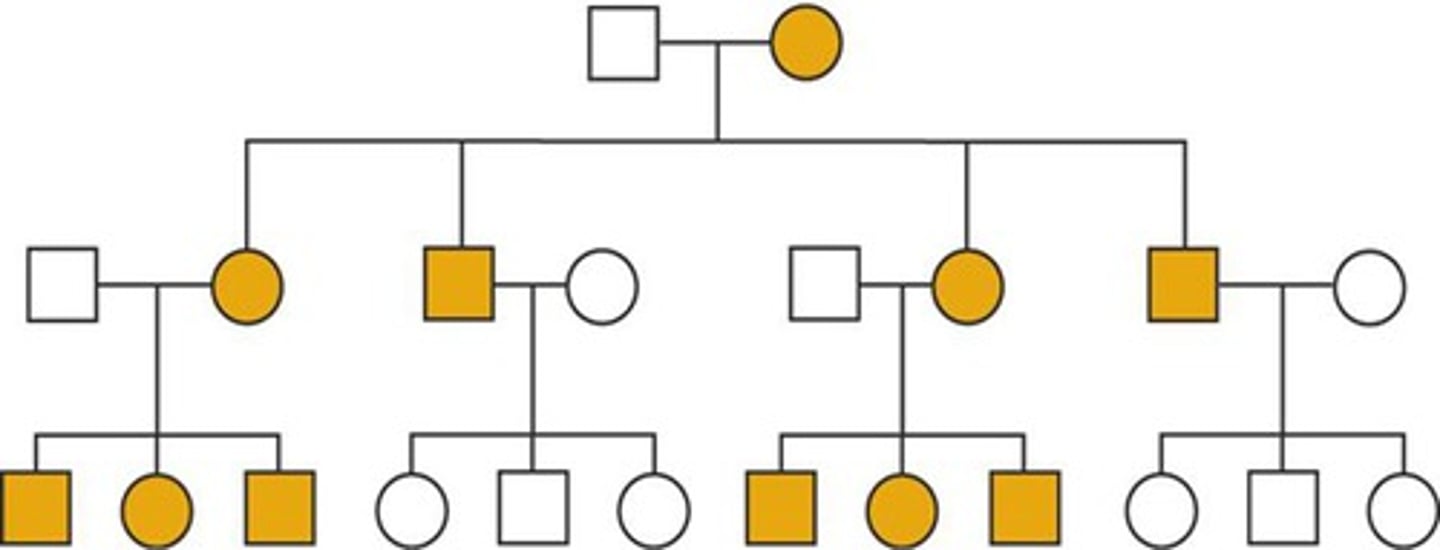
mode of transmission
describes the trait as autosomal or sex-linked and the type of dominance
pedigrees
or family trees, are used to learn the mode of transmission for the given trait
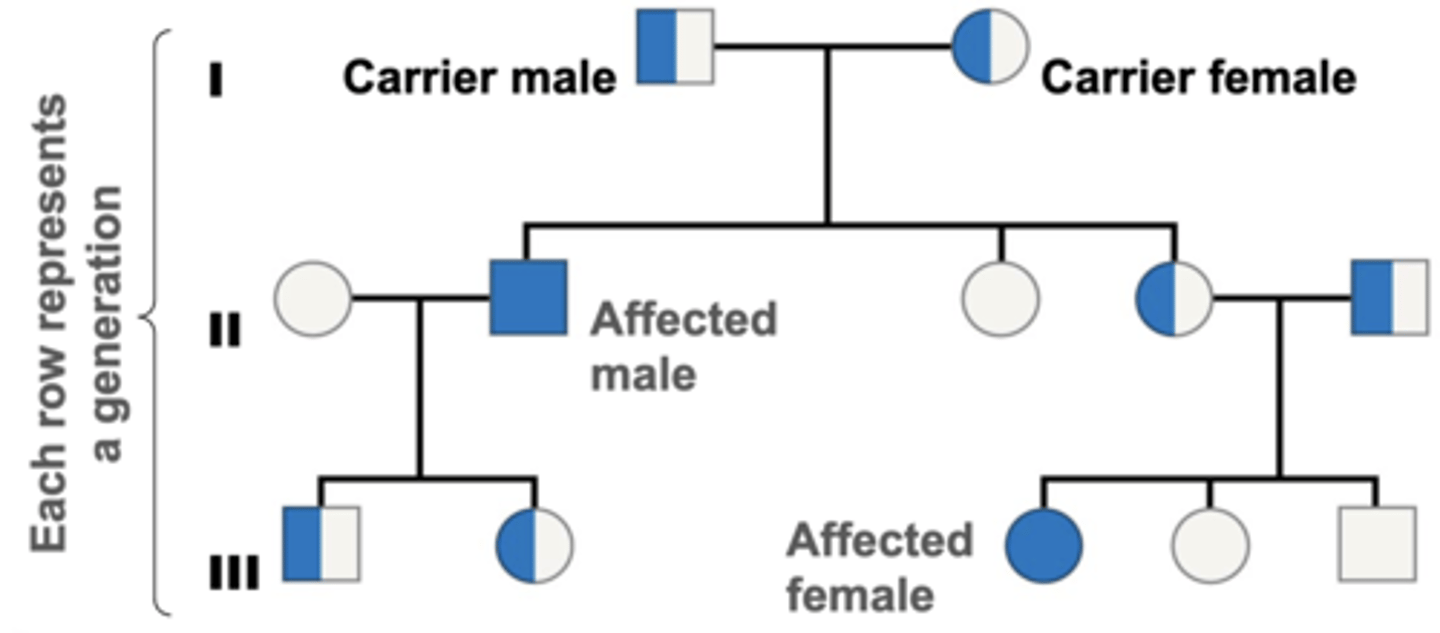
autosomal recessive traits
-Affected individuals must be homozygous for recessive allele
-Affected offspring often have unaffected parents
-Unaffected parents of affected offspring are heterozygous (carriers)
-Trait often skips generations (e.g. sickle cell anemia)
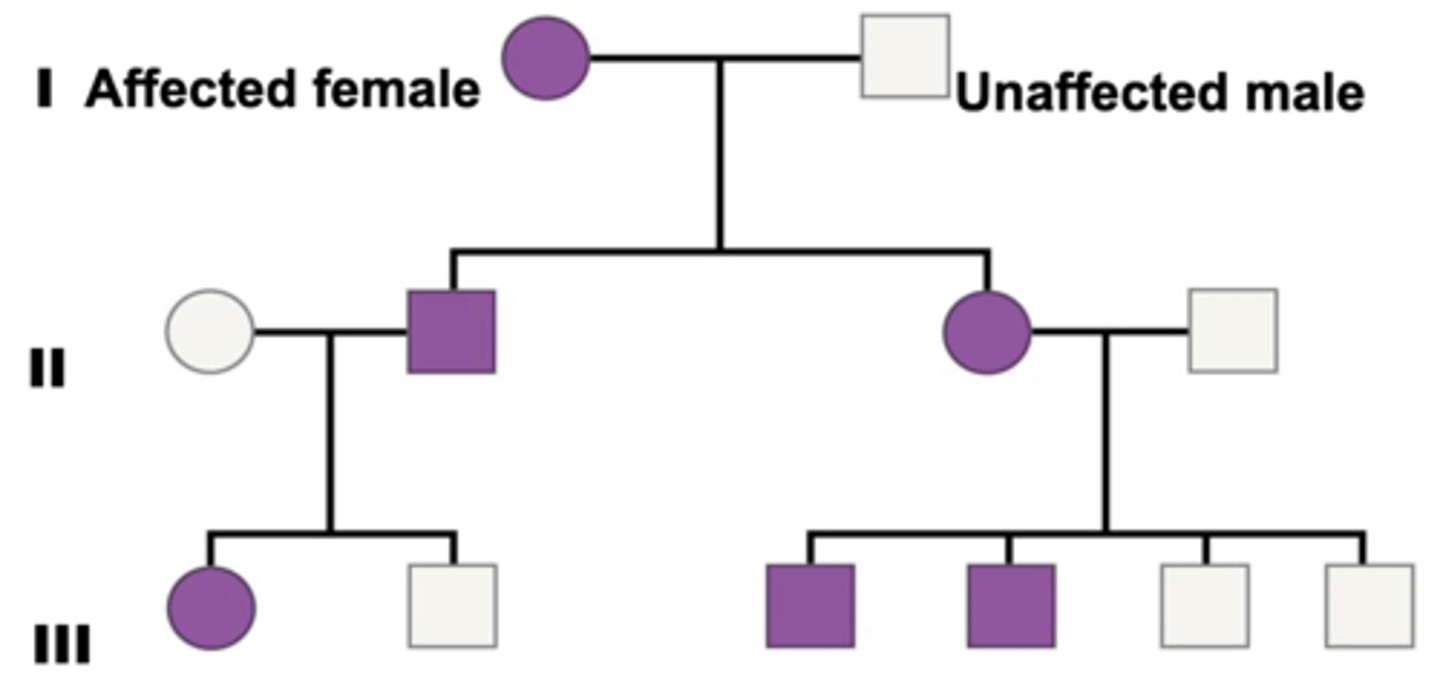
autosomal dominant traits
-Homozygous or heterozygous individuals will display the phenotype
-Affected offspring are heterozygous if only
-if one parent is heterozygous, about ½ of the offspring will be affected
-Autosomal dominant traits do not skip generations
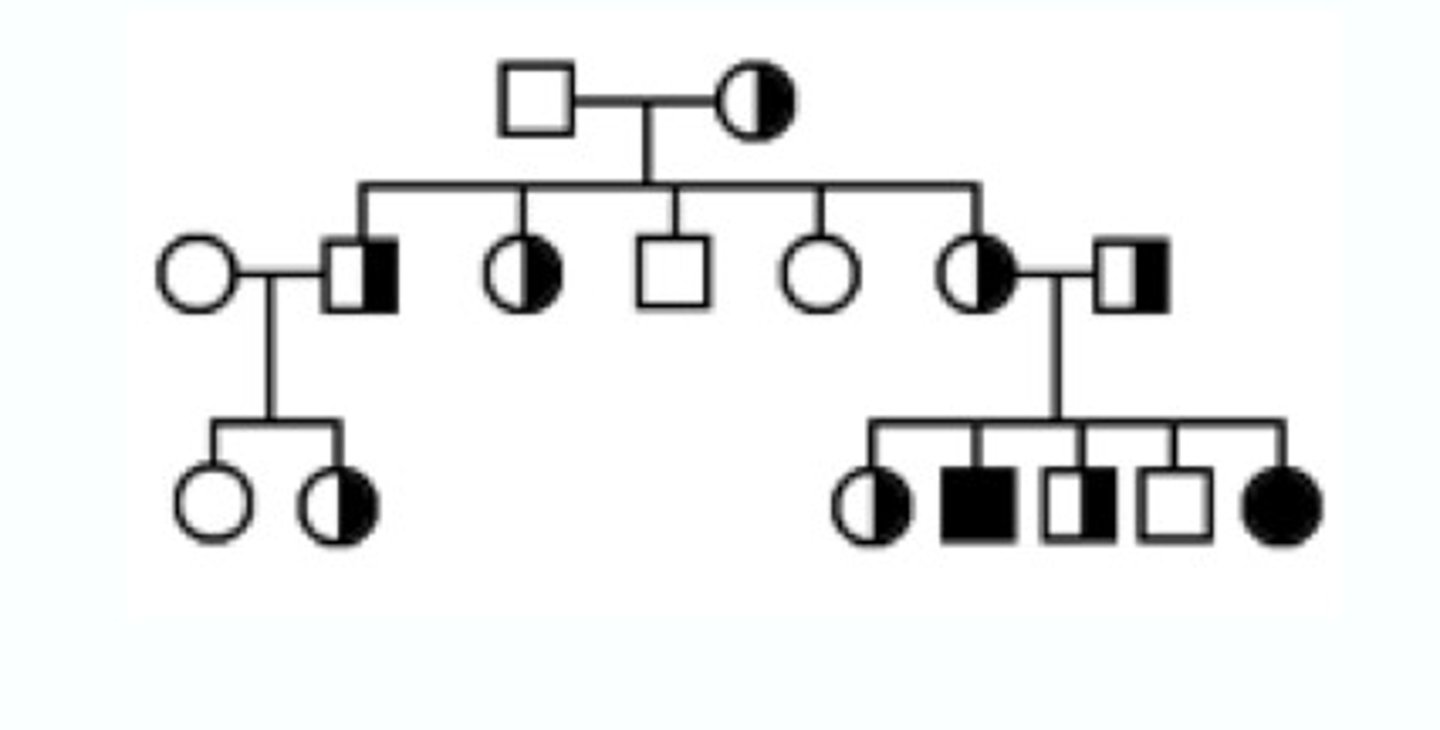
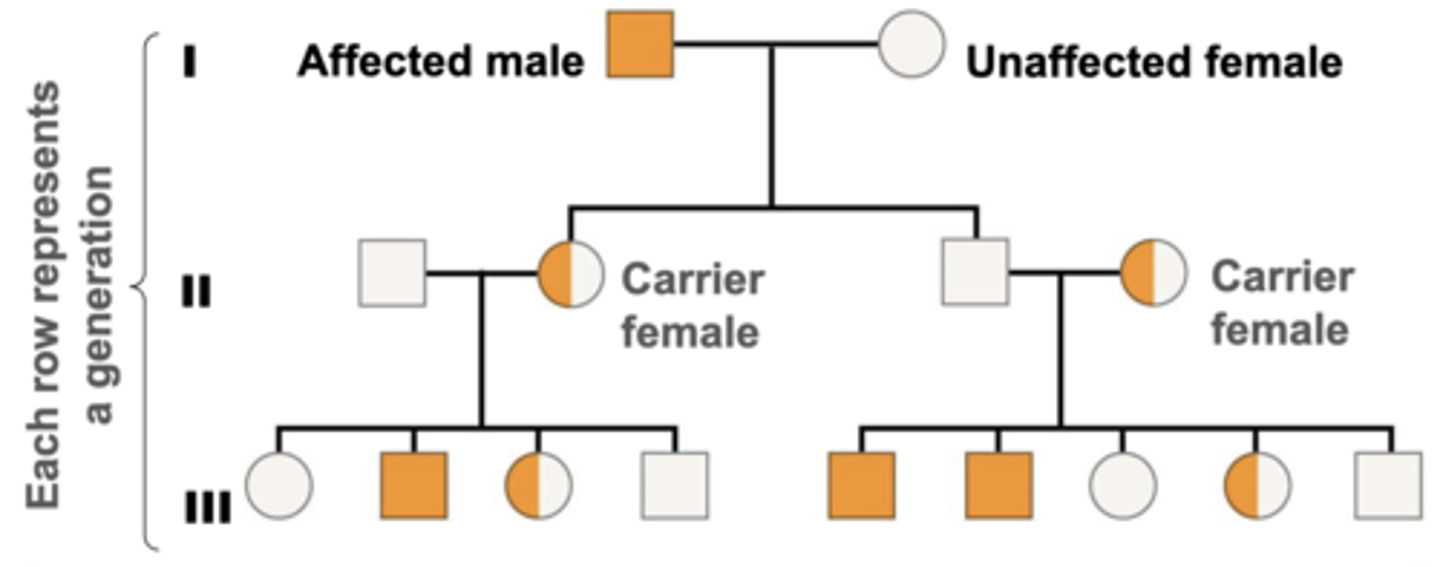
X-linked recessive traits
-Females only exhibit if they are homozygous for recessive allele
-Trait is never passed from father to son
- About ½ of the sons of a carrier mother will be affected
-All daughters of an affected male and an unaffected non-carrier female are carriers
-Trait often skips generations
X-linked dominant traits
-Males and females are equally likely to be affected
- All daughters of an affected father are affected, but no sons
- Affected sons always have affected mothers
- Trait does not skip generations
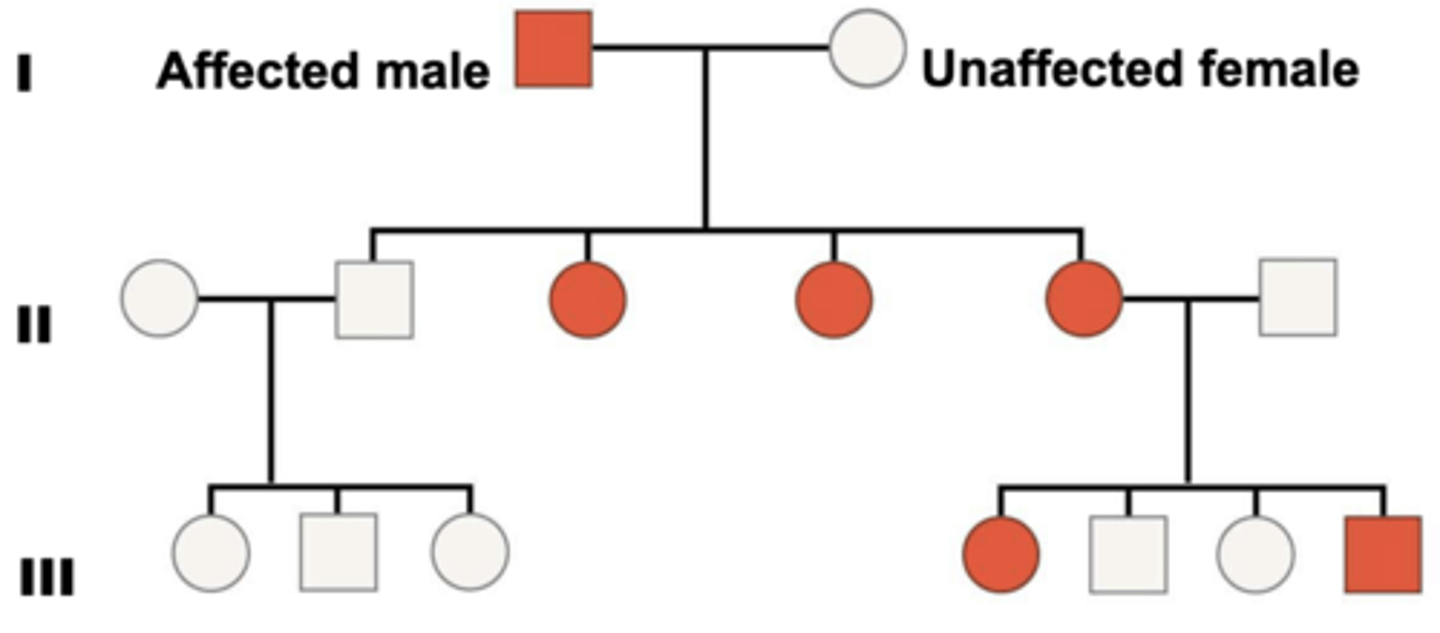
Y-linked traits
-very easily predicted since t goes straight from father to son
-few genes are on Y chromosome