Exam II: Chapter 15 and Extras
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Last updated 5:17 PM on 3/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
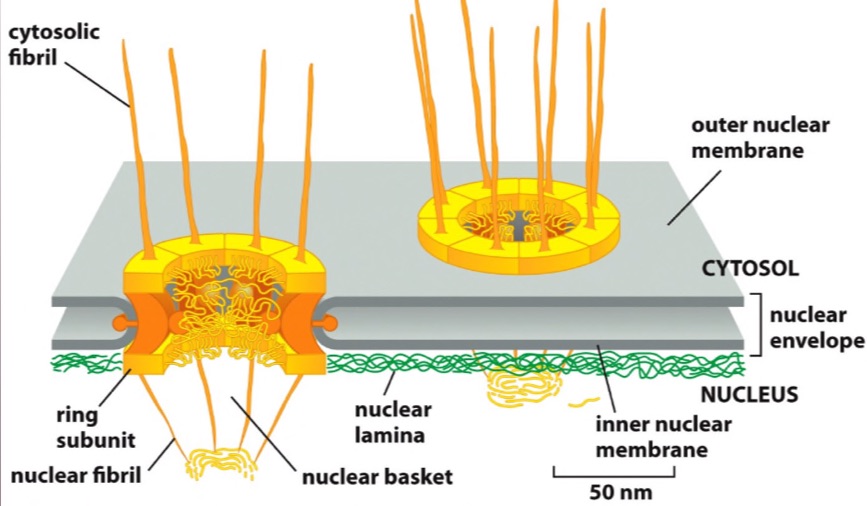
nuclear pore
bidirectional channel with meshy cage throughout hole
* passive transport
* an actual gap in the membrane
* passive transport
* an actual gap in the membrane
2
New cards
nuclear localization signal
positive string of amino acids that signal for the nucleus
* anywhere in amino acid order
* anywhere in amino acid order
3
New cards
cargo protein
the functional protein that is being moved
4
New cards
bidirectional channel
allows passive movement of solutes both ways
5
New cards
cytosolic fibril
grab protein with NLS and importin attached on cytosolic side to stuff them through nuclear pore
6
New cards
alpha importin
7
New cards
beta importin
8
New cards
importin
grab nucleus proteins based on NLS and transport to nucleus
* transport receptors
* transport receptors
9
New cards
Ran-GTP
binds to importin to release cargo
* high concentration in the nucleus
* functional protein
* high concentration in the nucleus
* functional protein
10
New cards
exportin
takes substrate out of the nucleus to cytosol
* transport receptors
* transport receptors
11
New cards
guanine exchange factor
replaces the GDP on Ran-GDP
12
New cards
Ran-GDP
non-functional importin
* high concentration in cytosol
* high concentration in cytosol
13
New cards
nuclear transport
1. proteins made on free ribosome
2. importin grabs folded protein
3. cytosolic fibril push protein through mesh
4. Ran-GTP binds
5. cargo released from importin
6. Ran-GTP (exportin) takes importin to cytosol
6a) pushed out by nuclear fibril?
7. GTP hydrolysis
8. Ran-GDP releases importin
1. GEF replaces GDP on Ran-GDP to become Ran-GTP
14
New cards
mitochondria
made of an outer membrane, inner membrane, inner membrane space, and matrix
15
New cards
CHSP70
stabilizes unwound proteins destined for mitochondria
16
New cards
mitochondrial signal sequence
positive amino acids that say “take me to the mitochondria”
* at N terminus
* at N terminus
17
New cards
receptor protein
click into mitochondrial protein from cytosolic side
18
New cards
TOM
translocator that helps push mitochondrial protein through outer membrane with chaperones
19
New cards
TIM
translator that helps push mitochondrial protein through inner membrane with chaperones
20
New cards
HSP60
prevent mitochondrial protein from folding when going through TIM and TOM
21
New cards
HSP70
help fold mitochondrial protein
22
New cards
secondary sequence
tell final destination within an organelle
23
New cards
inner membrane space
more positive region of mitochondria
24
New cards
chloroplast signal sequence
positive amino acids that say “take me to the chloroplast”
25
New cards
TOC
chloroplast outer membrane translocator
26
New cards
TIC
chloroplast inner membrane translocator
27
New cards
peroxisome
self replicating organelle
proteins delivered folded
Functions:
* oxidative reactions
* has catalase and crate oxidase
* takes protons off organics
* detoxifies ethanol
* breaks down fatty acids
proteins delivered folded
Functions:
* oxidative reactions
* has catalase and crate oxidase
* takes protons off organics
* detoxifies ethanol
* breaks down fatty acids
28
New cards
peroxisome signal sequence
string of positive amino acids that say “take me to the peroxisome”
* at **C terminus**
* at **C terminus**
29
New cards
endomembrane system
protein delivery system
1) bound ribosome
2) ER
3) Golgi apparatus
4) plasma membrane, secretion, lysosome
1) bound ribosome
2) ER
3) Golgi apparatus
4) plasma membrane, secretion, lysosome
30
New cards
co-translational transport
protein transported while it is still being made
31
New cards
signal receptor protein
grabs ER protein and pulls protein along with ribosome to touch ER
32
New cards
SRP receptor
where SRP and protein click into initially at ER
\
loads protein into translocon
\
loads protein into translocon
33
New cards
translocon
channel in the ER membrane that proteins are backed into
34
New cards
BiP
helps pull protein through translocon
35
New cards
start transfer sequence
hydrophobic sequence that says “put the amino acids after me in the ER lumen”
* can be cleaved if on N terminus
* can be cleaved if on N terminus
36
New cards
positive
charge of cytosol
37
New cards
negative
charge of ER lumen
38
New cards
stop transfer sequence
hydrophobic sequence that says “**don’t** put amino acids after me in the ER lumen”
39
New cards
multipass transmembrane protein
crosses the membrane multiple times
40
New cards
protein glycosylation
process of adding sugars to ER protein
1. Asn enters lumen through translocon
2. oligosacharotransferase adds on a 3 sugars (glucose, mannose, N-acetylglucosamine) from dolichol
3. translocation finishes
1. Asn enters lumen through translocon
2. oligosacharotransferase adds on a 3 sugars (glucose, mannose, N-acetylglucosamine) from dolichol
3. translocation finishes
41
New cards
dolichol
lipid that lives in ER membrane that holds sugars to be put on proteins
42
New cards
making sugars for protein
1. on cytosolic side add P group to dolichol using CTP
2. add P group and 2 glucosamine using UDP
3. add 5 mannose using GDP-Mannose
4. flip to ER lumen
5. add 4 mannose using GDP-Mannose
6. add 3 glucose using UDP-glucose
43
New cards
calnexin
holds protein by single glucose while other proteins check if the folding is correct
* cleaves glucose after done
* cleaves glucose after done
44
New cards
glucosidase
trims two sugars off the labeled “new protein” before loading into calnexin
45
New cards
glucose transferase
adds a single glucose onto proteins after incorrectly folded using UDP-glucose
* can be checked on calnexin again
* can be checked on calnexin again
46
New cards
ubiquitin
flags misfiled proteins for proteasome
47
New cards
proteasome
breaks bad proteins back into amino acids if tagged with ubiquitin
48
New cards
removal of bad proteins
1. checked on calnexin
2. ubiquitin attached
3. pushed out through translocon
4. proteasome eats
49
New cards
protein formation in ER
1. SRP grabs and translation paused
2. loaded onto SRP receptor
3. protein moved to translocator
4. translation finishes
1. protein inserted into ER based on start and stop sequences if transmembrane
2. phosphate group, N-acetyl glucosamine, mannose, and glucose attached at Asn
5. ribosome detaches
6. start sequence possibly cleaved
7. (2) glucose trimming
8. protein loaded onto calnexin for final checks
50
New cards
COP II
protein that helps pinch vesicles from the ER by coating the membrane
51
New cards
cargo receptor
hold onto proteins that will be inside the vesicle lumen
52
New cards
KDEL
signal for ER lumen protein retrieval
53
New cards
KKXX
signal for ER membrane protein retrieval
54
New cards
vesicle transport from ER to Golgi
1. COPII proteins including SarGTP attach to ER membrane
2. pinch
3. proteins sucked in and attached to receptors
4. pinch continues
5. SarGTP removes COPII protein coat and becomes GDP
1. vesicle closes
6. vesicle walked to Golgi
55
New cards
vesicle transport from Golgi to ER
1. COPI attaches to Golgi membrane
2. pinch part way
3. proteins attach to receptors for KDEL or KKXX
4. pinch
5. COPI falls off
1. vesicle closes
56
New cards
adaptor protein
help grab proteins into forming vesicle from ER to Golgi and back
57
New cards
clatharin
coats vesicles for secretion and endosome
58
New cards
adaptin
sits between clatharin coat and receptors in vesicle
59
New cards
kinesin
walks proteins headed towards membrane
ie ER>golgi>membrane
ie ER>golgi>membrane
60
New cards
SNAREs
labels vesicles and prevents them from fusing with each other
61
New cards
dynen
walks vesicles inwards
ie membrane>…
ie membrane>…
62
New cards
motor proteins
walk vesicles along microfilaments while using ATP
63
New cards
phosphorylation
labels lysosome with P group
64
New cards
sulfation
can help strengthen future binding
65
New cards
Golgi apparatus
main functions
* phosphorylation- like for lysosome proteins
* remove mannoses
* glycosylation
* sulfation
* phosphorylation- like for lysosome proteins
* remove mannoses
* glycosylation
* sulfation
66
New cards
cis Golgi
“beginning” of Golgi stacks
67
New cards
trans Golgi
“end” of Golgi stacks
68
New cards
complex oligosaccharide
sugar complex added to protein in Golgi with lots of other types of sugars
69
New cards
high mannose oligosaccharide
sugar complex added to protein in Golgi with lots of mannoses
70
New cards
lysosome
degrades organelles and material brought in vesicles
* acidic environment bc of protein pump
* acidic environment bc of protein pump
71
New cards
phogocytosis
taking in large substrate from outside cell
72
New cards
pinocytosis
taking in small substation from outside cell
73
New cards
early endosome
vesicles with outside material still near plasma membrane
74
New cards
protease
does protein degradation
75
New cards
nuclease
does nucleus acid degradation
76
New cards
lipase
does lipid degradation
77
New cards
mannose-6-phosphate
lysosome localization signal
* phosphates most important
* phosphates most important
78
New cards
lysosomal hydrolase
signal patch and N-linked oligosaccharide + mannose
79
New cards
GlcNAc phosphototransferase
attaches UDP-GLcNAc to signal patch
80
New cards
making M6P
1. N-linked oligosaccharide + mannose residue attach to phosphototransferase
2. UDP-GLcNAc loads onto phosphototransferase
3. bind GlCNAc-P and release UMP
4. release lysosome hydrolase with GLcNAc-P
5. remove GlcNAc
6. M6P left on signal patch
81
New cards
lysosome protein delivery
1. M6P attached to protein from ER
2. protein binds to M6P receptor
3. clatharin coats aided by adaptin
1. vesicle begins to form
4. clathrin coat releases
1. vesicle closes
5. vesicle walked to lysosome via kinesin
6. vesicle meshes to early lysosome
7. protein dissociates from receptor
1. high pH
8. P group removed to put…. in inactive state
82
New cards
endosome
organelle that becomes lysosome when more proteins are added
83
New cards
retromer
coats vesicle that will take M6P receptor back to Golgi
84
New cards
O-linked glycosylation
adding sugars to new amino acid on protein
85
New cards
N-linked glycosylation
adding sugars to Asn where sugars were added in ER
86
New cards
glycosidase I
trims first glucose off of protein tagged in ER
87
New cards
glycosidase II
trims second glucose off of protein tagged in ER
88
New cards
signal peptidase
cleaves signal off of protein in destination
89
New cards
nucleus
double membrane organelle with large pores
90
New cards
rough ER
single membrane bound with SRP receptors
91
New cards
Golgi apparatus
single membrane bounds with many stacks (cis and trans regions)
92
New cards
lysosome
single membrane bound organelles that comes from endosome and peroxisomes
93
New cards
mitochondria
double bound organelle with oxidative phosphorylation
94
New cards
chloroplast
double membrane bound organelle in plants
95
New cards
Rab protein
name tag for vesicles going to plasma membrane and anchor point
96
New cards
v-SNARE
protein that sticks off of vesicle to help bind to plasma membrane
97
New cards
tether protein
anchors onto Rab and pulls vesicle to plasma membrane
98
New cards
t-SNARE
extends from plasma membrane to attach to v-SNARE and pull vesicle in
99
New cards
unfolded protein response
ER grows and takes up more supplies when there are lots of proteins/mistakes being stored there
\
may lead to apoptosis
\
may lead to apoptosis
100
New cards
constitutive exocytosis
constant release from Golgi to extracellular via vesicle