orgo 1: functional groups
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
alkane
hydrocarbon backbone
all single bonds
“saturated”
alkene
hydrocarbon backbone
at least 1 double bond
alkyne
hydrocarbon backbone
at least 1 triple bond
aromatic
ring structure
very stable
why are functional groups important?
site of chemical reactivity, intermolecular forces
contribute to chemical and physical properties
aliphatic definition
non-ring structure (chain of carbon)
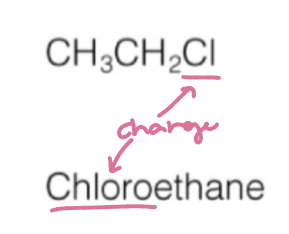
haloalkane/alkylhalide
carbon chain with any halogen
RX
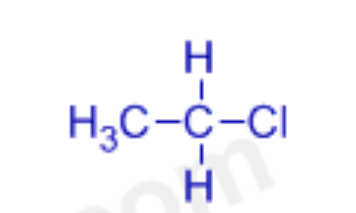
haloalkane/alkylhalide naming
halogen name + named carbon chain
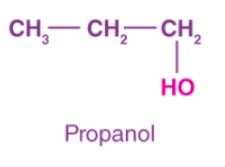
alcohol
attached hydroxyl group
ROH
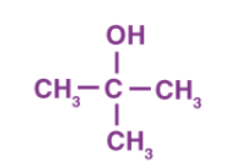
alcohol naming
carbon chain/attached name + “ol”
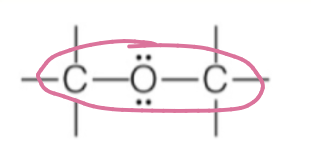
ether
oxygen within backbone
ROR
ether naming
chain before carbon name + “oxy” + chain after carbon name
or
carbon chain names + ether (dimethyl ether)
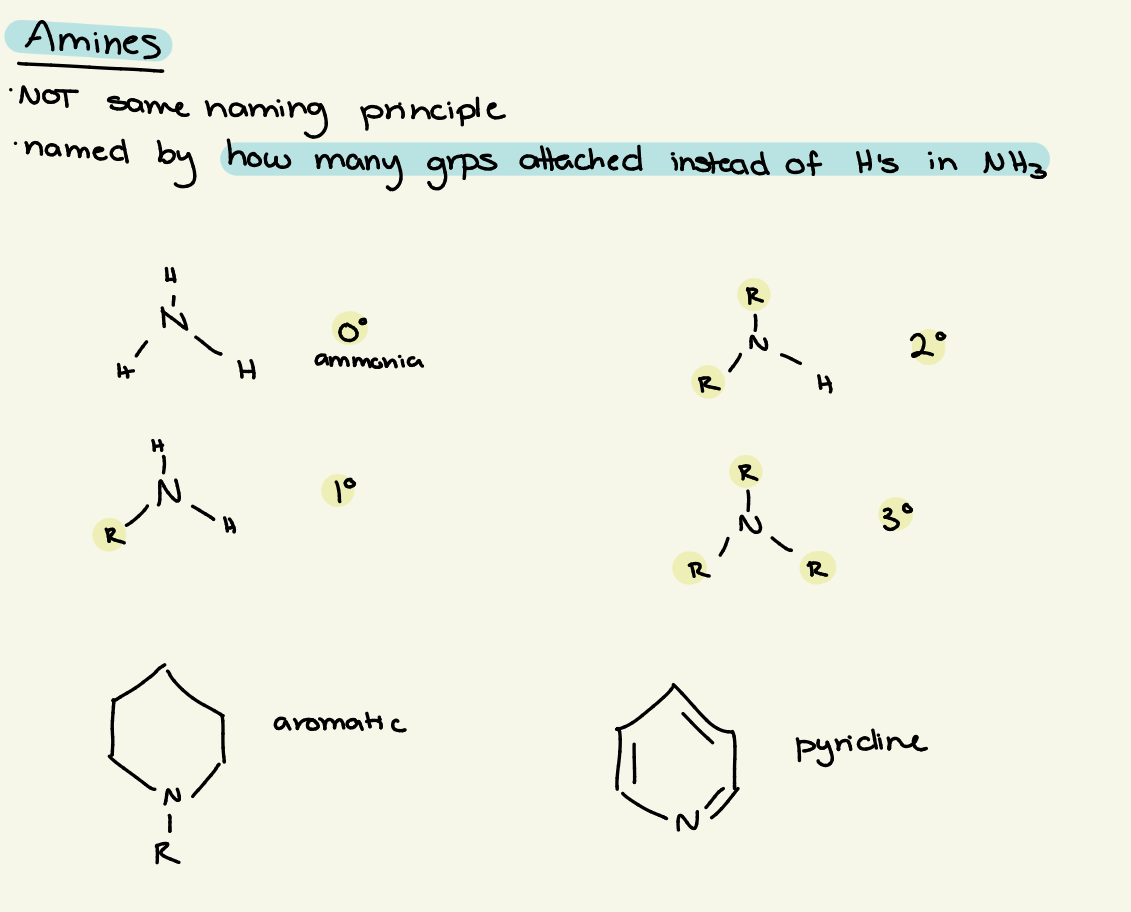
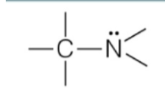
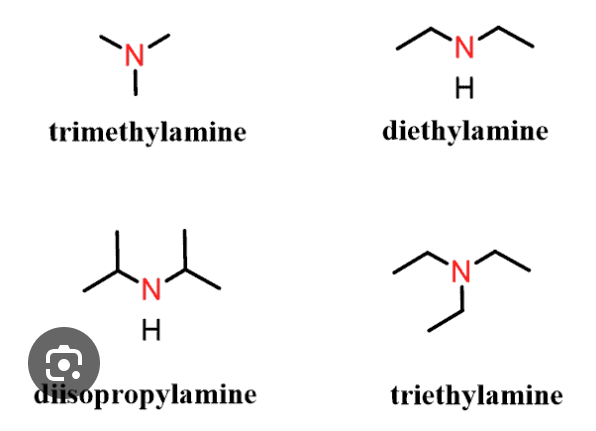
amine
nitrogen in carbon chain
RNH2, R2NH, R3N
amine naming
carbon chain name + amine
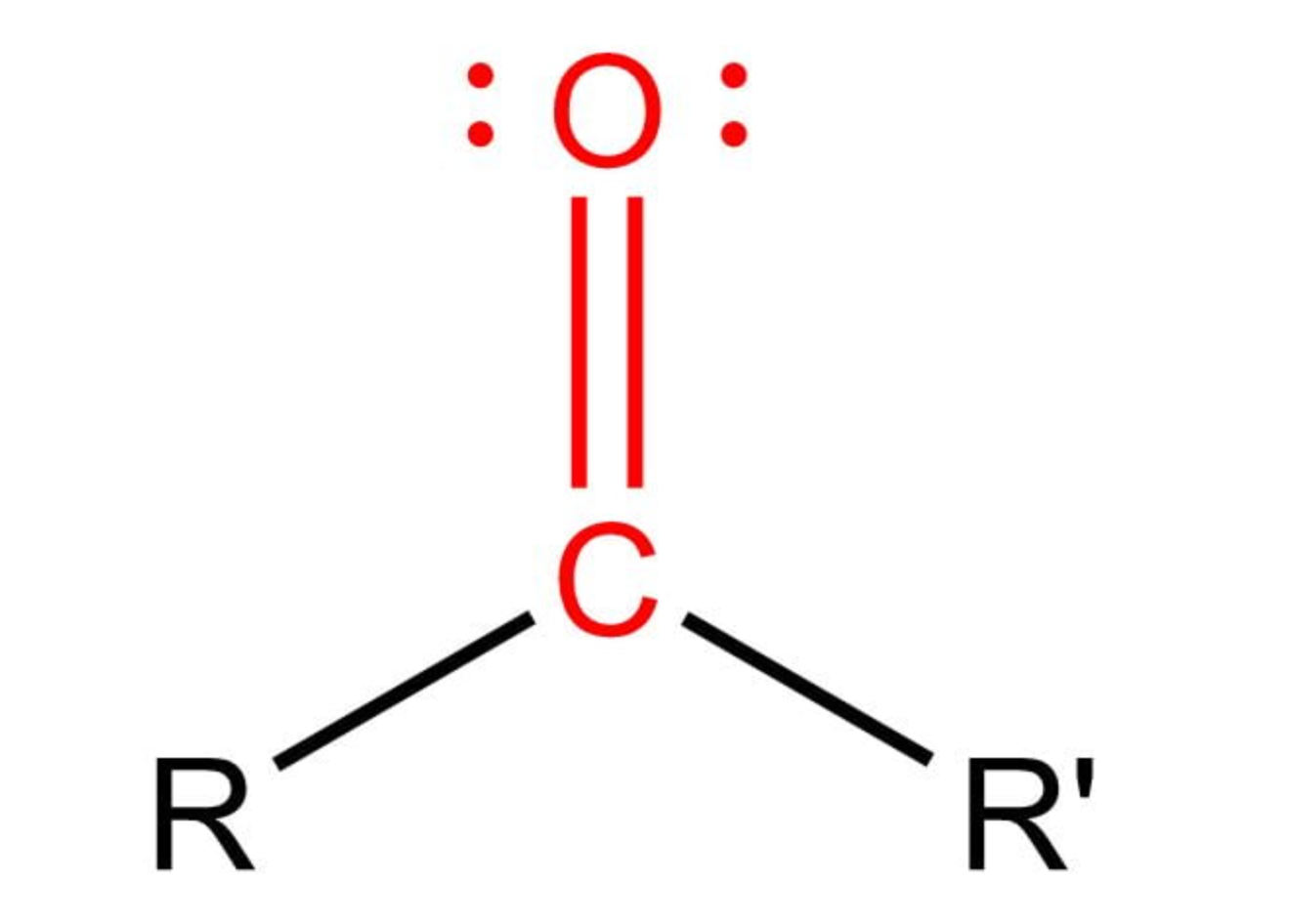
carbonyl functional group defining feature
oxygen double bonded to C of backbone
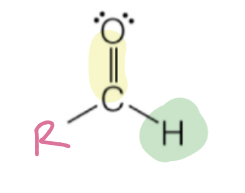
aldehyde
carbonyl with hydrogen & R group
RC(O)H
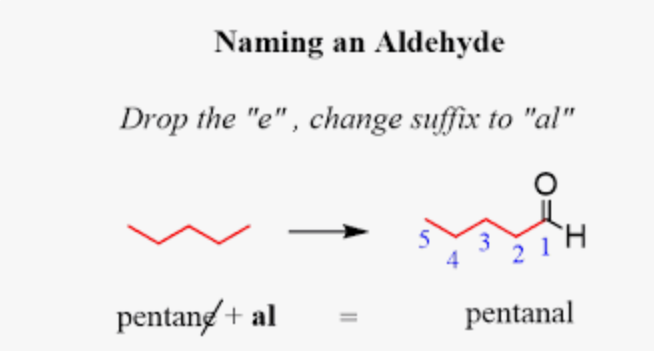
aldehyde naming
carbon chain + “al”
or
carbon chain name + “aldehyde”
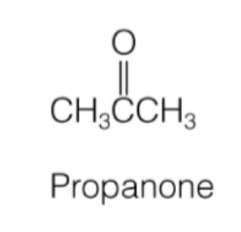
ketone
carbon chain on either side of carbonyl
RC(O)R’
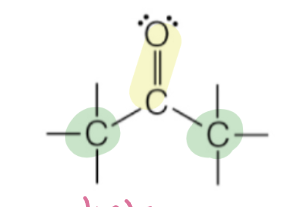
ketone naming
carbon (parent) chain name + “one”
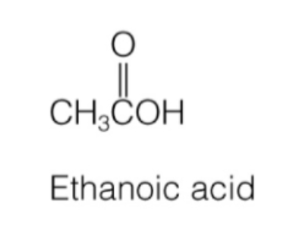
carboxylic acid
hydroxyl group attached directly to carbonyl
RC(O)OH
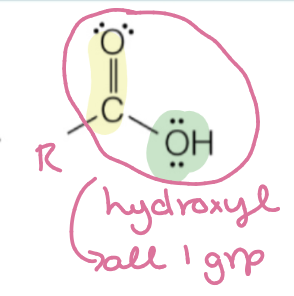
carboxylic acid naming
carbon chain name + “-ic acid”
ester
carbonyl attached to oxygen within the backbone
RC(O)OR’
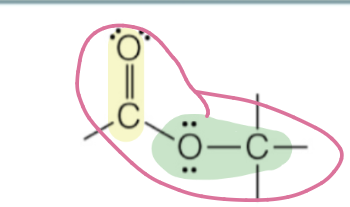
ester naming
first carbon chain name + second carbon chain name + “ate”
amide
carbonyl attached to nitrogen within backbone
RC(O)NH2, RC(O)NHR’, …
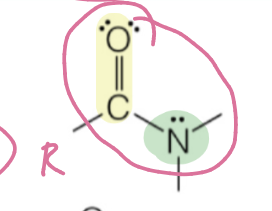
amide naming
name carbon chain + “amide”
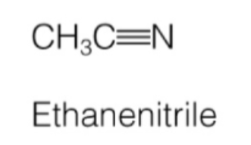
nitrile
carbon & nitrogen triple bonded
cyanide alternative name
RCN

nitrile naming
name of carbon chain + “nitrile”
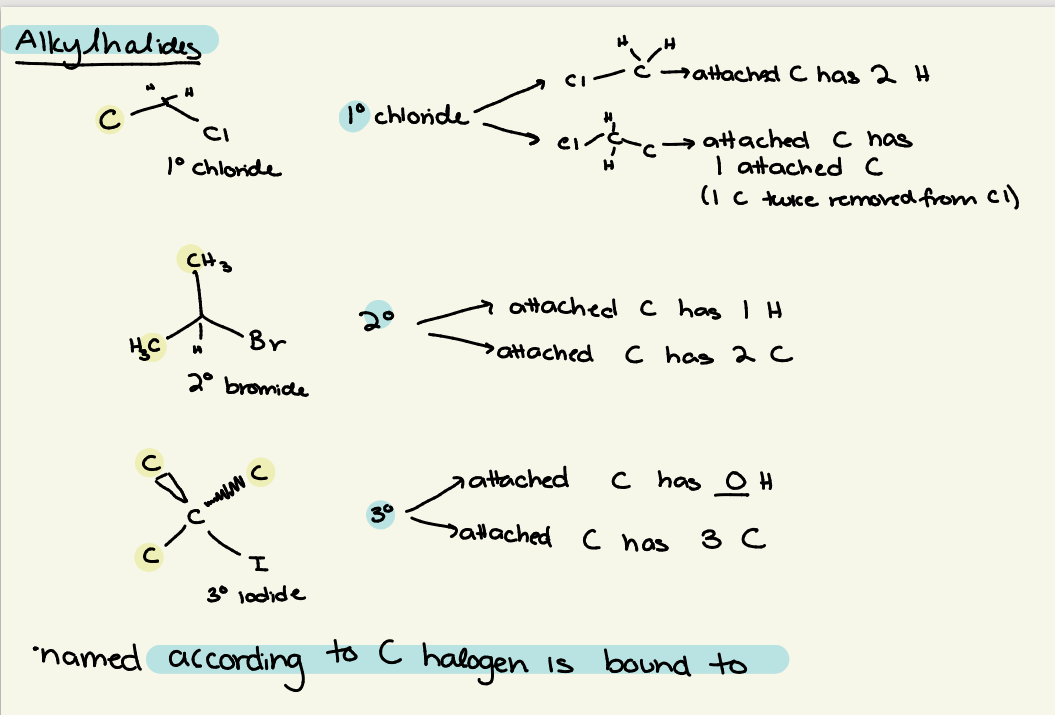
alkylhalides/haloalkynes classification
classified by how many C’s/H’s the C attached to the halogen is bound to
halogen - C - C’s & H’s classified by
1o — 2 H, 1 C
2o — 1 H, 2 C
3o — 0 H, 3 C
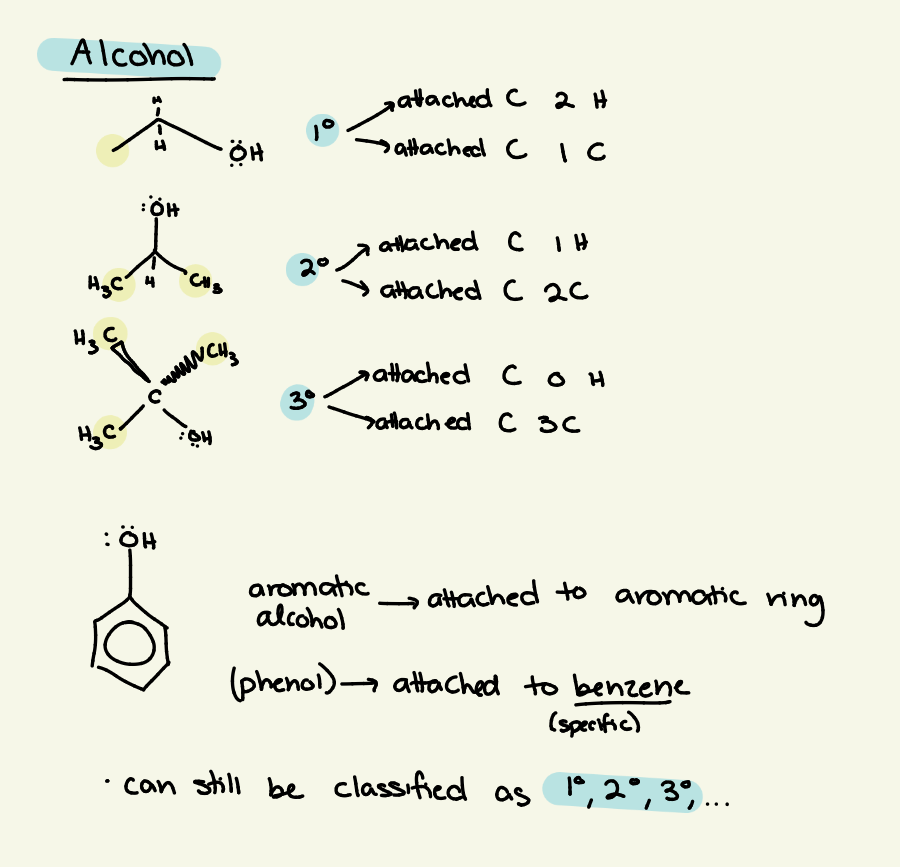
alcohol classification
classified by how many C’s/H’s the C attached to the hydroxide is bound to
hydroxide - C - C’s & H’s classified by
1o — 2 H, 1 C
2o — 1 H, 2 C
3o — 0 H, 3 C
amine classification
named by how many groups (NOT H) are attached to N
0o — NH3 (ammonia)
1o — NRH2
2o — NR2H2
3o — NR3